seedless vascular plants
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
until vascular tissue evolved…
all land plants were short, ground cover plants
when do the oldest seedless vascular plants fossil?
425 MYA
what are example of SVPs?
ferns and club moss
what are branched sporophytes independent of?
gametophyte for nutrition
what is the dominant form of the life cycle in SVPs?
diploid sporophyte dominant
what do SVPs have that NVPs don’t?
transport through a xylem and phloem which is a vascular system
xylem
made of lignified cells specialized to move water and minerals
phloem
cells specialized to move sugars, amino acids, and other organic products
what true evolution occurred is SVPs ?
evolution of true roots and true leaves
microphyll leaves
small, spine shaped leaves supported by a single stab of vascular tissue; unbranched vascular tissue
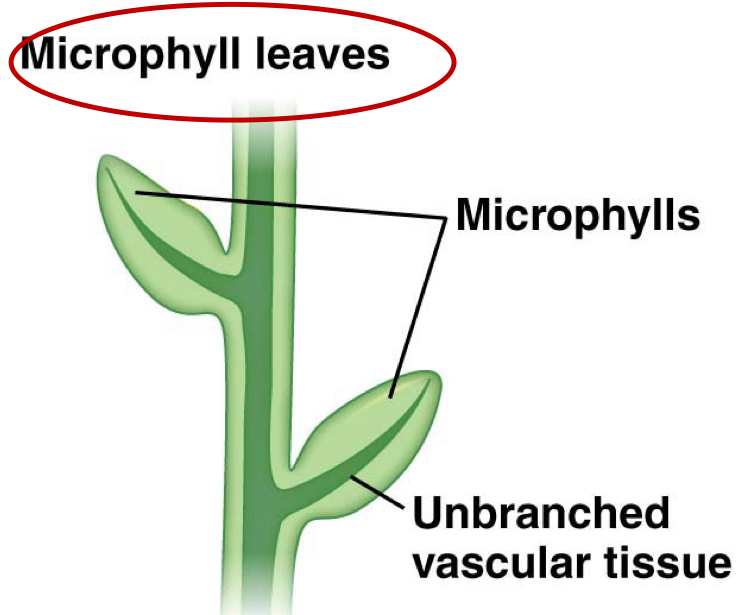
what’s an example of a lycophyte with microphylls?
spike moss
what are the only SVP that have microphylls?
lycophytes
what do almost all other SVPs have?
megaphylls
megaphyll leaves
leaves with a highly branched vascular system
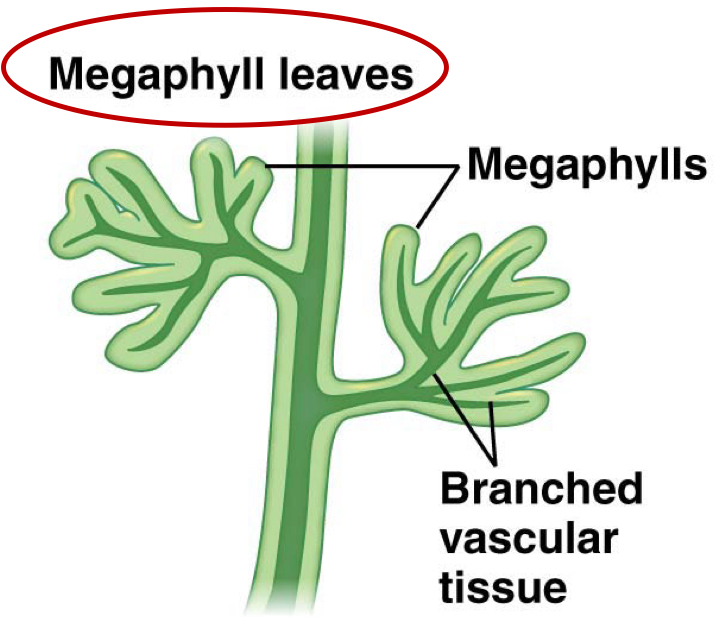
what is an example of a SVP that has megaphylls?
tunbridge filmy fern
what’s an advantage of megaphylls?
they have greater photosynthetic productivity
sporophyll
leave that do photosynthesis that were modified to bear sporangia
fern sporophyll
normal leaves that have sori
sori
generate spores on underside of fern leaves
lycophyte sporophyll
cone-like structure called strobilus
strobilus
cone-like structure containing sporangia
what are the types of spore production?
homosporous and heterosporous
how is sperm production for most SVPs?
homosporous
explain homosporous spore production
sporangium on sporophyll produce one type of spore that is a bisexual gametophyte including eggs and sperm
how is sperm production for all seed plants and few SVPs ?
heterosporous
explain heterosporous spore production for megasporangium
megasporangium on the megasporophyll produce megaspores that form the female gametophyte including eggs
explain heterosporous spore production for microporangium
microsporangium on the microsporophyll produce micropores that form the male gametophyte including sperm
what are the first type of SVPs?
lycophytes
what are the 3 lycophytes?
spike moss, quilwort, and club moss
out of the 3 lycophytes which is homosporous?
club moss
out of the 3 lycophytes which are heterosporous?
spike moss and quilworts
what’s the current species that are all small tropical and temperate of lycophytes?
1200
what are the second type of SVPs?
pterophytes
what are the 3 pterophytes?
horestails, whisk ferns, and ferns
what branching do whisk ferns have?
dichotomous branching
do whisk ferns have true leaves or roots?
no
are whisk ferns heterosporous or homosporous ?
homosporous
where does photosynthesis occur in whisk ferns?
the stem
how are the stems of horsetails?
jointed with tiny leaves
what sporophyll do horestails have?
strobili
are horsetails homosporous or heterosporous?
homosporous
where does photosynthesis occur in horsetails?
the stem
what are the most widespread and diverse monilophytes?
ferns
are ferns homosporous or heterosporous?
homosporous
do ferns have megaphyll leaves or microphyll leaves?
large megaphylls
how do large megaphylls develop on ferns?
frond develops as the fiddlehead unfolds
what’s on the underside of sporophyll of fern?
sori
where do ferns live?
many in understory or as epiphytes
epiphyte
grows on the surface of a plant; not parasites
what is the importance of seedless plants?
mosses biologically indicate environmental pollution, ferns are used as food & form topsoil, peat moss is a soil conditioner & used as fuel , and extinct SVPs were an energy source