Module 2 – Foundations in Biology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
1
New cards
Which of the following statements describes an organelle which is not membrane bound?
A. contains cristae
B. modifies and packages proteins
C. contains digestive enzymes
D. is made of rRNA and protein
A. contains cristae
B. modifies and packages proteins
C. contains digestive enzymes
D. is made of rRNA and protein
D. is made of rRNA and protein
2
New cards
Which of the following structures, A to D, are found in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes?
A. a cell wall made of peptidoglycan
B. circular genomic DNA
C. a nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane
D. ribosomes
A. a cell wall made of peptidoglycan
B. circular genomic DNA
C. a nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane
D. ribosomes
D. ribosomes
3
New cards
Which of the options, A to D, occurs in the nucleus of a cell?
A synthesis of enzymes
B synthesis of RNA
C modification of polypeptides
D synthesis of carbohydrates
A synthesis of enzymes
B synthesis of RNA
C modification of polypeptides
D synthesis of carbohydrates
B. synthesis of RNA
4
New cards
State what is meant by the resolution of a microscope.
the ability to see more detail / separate two objects
5
New cards
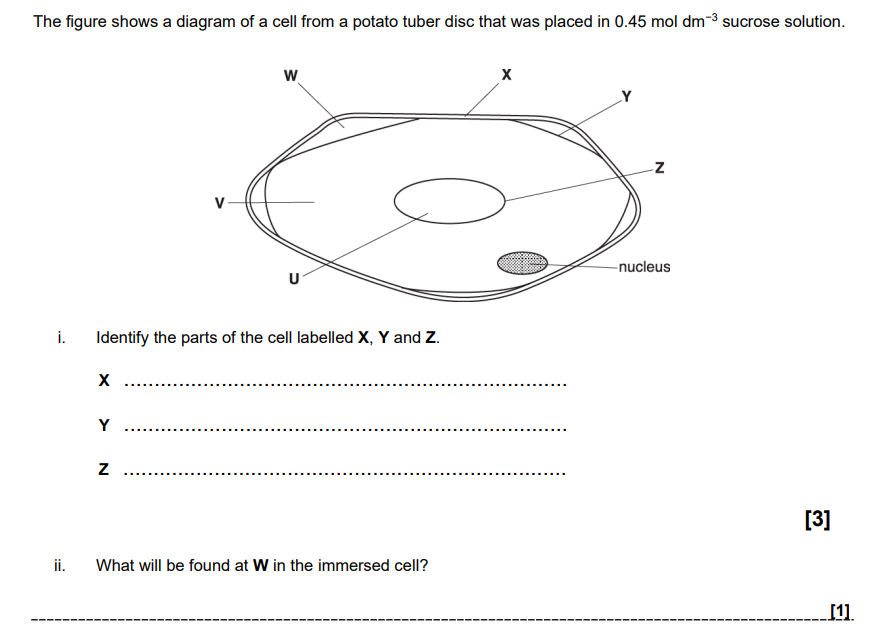
\
X (cellulose) cell wall
Y cell surface membrane / plasma membrane
Z vacuole membrane / tonoplast
ii) sucrose solution
Y cell surface membrane / plasma membrane
Z vacuole membrane / tonoplast
ii) sucrose solution
6
New cards
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is where translation of some proteins takes place in a eukaryotic cell. Explain the role of the membrane in the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
* compartmentalisation / maintain different conditions from cell cytoplasm
* separating proteins (synthesised) from cell cytoplasm
* hold, ribosomes / enzymes, in place
* separating proteins (synthesised) from cell cytoplasm
* hold, ribosomes / enzymes, in place
7
New cards
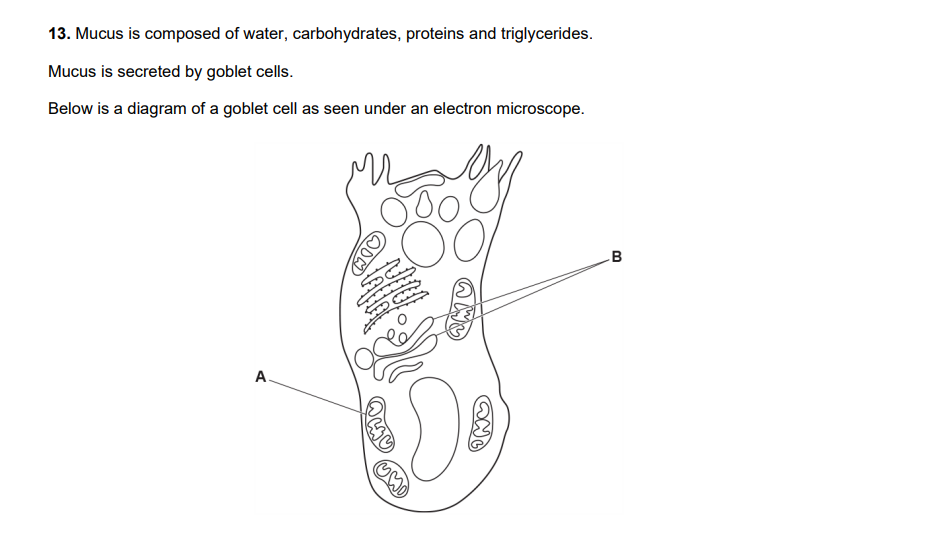
i. Suggest why goblet cells have large numbers of the cellular component labelled A.
ii. Suggest how the role of the cellular component labelled B is relevant to the function of the goblet cell
ii. Suggest how the role of the cellular component labelled B is relevant to the function of the goblet cell
i) to provide, lots of / much, energy / ATP
ii)Golgi apparatus, to, modify / process / package, protein and ref. vesicles / secretion (of mucus) / exocytosis
ii)Golgi apparatus, to, modify / process / package, protein and ref. vesicles / secretion (of mucus) / exocytosis
8
New cards
The endosymbiosis theory suggests that mitochondria may have evolved from bacteria that were taken inside other cells. These cells then evolved into eukaryotes.
i. Give two structural features of mitochondria that support this theory.
i. Give two structural features of mitochondria that support this theory.
* length / size , similar to that of a bacterium
* contain (circular) DNA
* contain (70S / small / 20nm) ribosomes
* (may) have plasmids
* have double membrane
* contain (circular) DNA
* contain (70S / small / 20nm) ribosomes
* (may) have plasmids
* have double membrane
9
New cards
Explain why early eukaryotes were able to grow more quickly than cells that did not possess mitochondria.
* would be able to respire aerobically
* (this) produces more ATP
* ATP needed for , active transport / cell division / protein synthesis / DNA replication
* more ATP allows faster metabolic , processes / reactions
* (this) produces more ATP
* ATP needed for , active transport / cell division / protein synthesis / DNA replication
* more ATP allows faster metabolic , processes / reactions
10
New cards
Which of the options describes the path taken by proteins, such as digestive enzymes, that are exported from a cell?
A Golgi apparatus → rough endoplasmic reticulum → secretory vesicle
B ribosome → smooth endoplasmic reticulum → Golgi apparatus
C rough endoplasmic reticulum → Golgi apparatus → secretory vesicle
D smooth endoplasmic reticulum → ribosome → Golgi apparatus
A Golgi apparatus → rough endoplasmic reticulum → secretory vesicle
B ribosome → smooth endoplasmic reticulum → Golgi apparatus
C rough endoplasmic reticulum → Golgi apparatus → secretory vesicle
D smooth endoplasmic reticulum → ribosome → Golgi apparatus
C rough endoplasmic reticulum → Golgi apparatus → secretory vesicle
11
New cards
Which organelle, A to D, is not involved in the production and secretion of enzymes in eukaryotes?
A golgi apparatus
B ribosomes
C smooth endoplasmic reticulum
D vesicle
A golgi apparatus
B ribosomes
C smooth endoplasmic reticulum
D vesicle
C smooth endoplasmic reticulum
12
New cards
Humans use the enzyme α-amylase to break down polysaccharides in food for absorption into the blood.
The gene for human α-amylase is found on chromosome 1.
The gene is transcribed in the nucleus and translation occurs on the rough endoplasmic reticulum in cells of the salivary gland.
Describe how the molecule is prepared and secreted by cells of the salivary gland after translation has taken place
The gene for human α-amylase is found on chromosome 1.
The gene is transcribed in the nucleus and translation occurs on the rough endoplasmic reticulum in cells of the salivary gland.
Describe how the molecule is prepared and secreted by cells of the salivary gland after translation has taken place
* transport vesicle from RER
* modification / processing / folding
* in / at, Golgi (body / apparatus)
* (packaged into) secretory vesicle
* vesicles move along the cytoskeleton
* (vesicle) fuses with, cell surface / plasma, membrane
* (secretion occurs by) exocytosis
* modification / processing / folding
* in / at, Golgi (body / apparatus)
* (packaged into) secretory vesicle
* vesicles move along the cytoskeleton
* (vesicle) fuses with, cell surface / plasma, membrane
* (secretion occurs by) exocytosis
13
New cards
The plasma membrane contains proteins, which are made within the cell. Outline the process and organelles involved in the translation of these proteins from RNA.
* (m)RNA transported out of nucleus
* (m)RNA transported to / associates with ribosome
* translation / protein synthesis, occurs at ribosome
* (t)RNA brings specific amino acids or (t)RNA described
* peptide bonds form between adjacent amino acids or peptide bonds described
* polypeptide / protein processed through Golgi apparatus
* (m)RNA transported to / associates with ribosome
* translation / protein synthesis, occurs at ribosome
* (t)RNA brings specific amino acids or (t)RNA described
* peptide bonds form between adjacent amino acids or peptide bonds described
* polypeptide / protein processed through Golgi apparatus
14
New cards
DNA is a polymer of nucleotides that contains the genetic code needed for a protein to be made. Tubulin is a protein that is found in all eukaryotes and some prokaryotes.
i. Explain how the genetic code in the gene for tubulin codes for the protein tubulin.
i. Explain how the genetic code in the gene for tubulin codes for the protein tubulin.
* 3 bases / triplet, code for 1 (specific) amino acid
* sequence of, bases / triplets, determines the sequence of, amino acids / primary structure
* (code) non-overlapping
* sequence of, bases / triplets, determines the sequence of, amino acids / primary structure
* (code) non-overlapping
15
New cards
Tubulin is a globular protein that can polymerise to form the cell cytoskeleton.
One example of this is the formation of microtubules, which form the spindle fibres to move chromatids during mitosis and meiosis.
Describe three other cellular functions of the cytoskeleton
One example of this is the formation of microtubules, which form the spindle fibres to move chromatids during mitosis and meiosis.
Describe three other cellular functions of the cytoskeleton
* mechanical strength (to cells)
* cell, support / stability / maintains shape
* movement of (named), molecules / vesicles / organelles within cell
* formation / movement, of, cilia / flagella
* cell, support / stability / maintains shape
* movement of (named), molecules / vesicles / organelles within cell
* formation / movement, of, cilia / flagella
16
New cards
Tubulin is a globular protein that can polymerise to form the cell cytoskeleton. One example of this is the formation of microtubules, which form the spindle fibres to move chromatids during mitosis and meiosis.
Suggest two ways tubulin is essential to protein synthesis and protein secretion in eukaryotic cells.
Suggest two ways tubulin is essential to protein synthesis and protein secretion in eukaryotic cells.
* movement of mRNA from nucleus to ribosome
* movement of polypeptides through the rER
* movement of vesicles from rER to Golgi
* movement of vesicles between cisternae of Golgi (cis to trans face)
* movement of secretory vesicles from Golgi to cell surface membrane
* movement of polypeptides through the rER
* movement of vesicles from rER to Golgi
* movement of vesicles between cisternae of Golgi (cis to trans face)
* movement of secretory vesicles from Golgi to cell surface membrane
17
New cards
Peroxisomes are vesicles that usually contain enzymes such as catalase. Explain how peroxisomes can be moved around inside the cell.
attach to cytoskeleton and moved by, protein motors / dynein
18
New cards
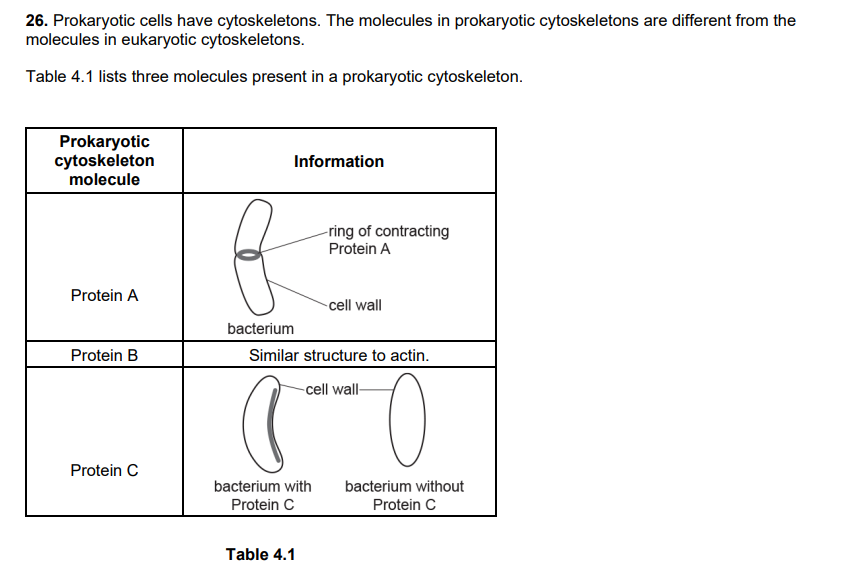
Prokaryotic cells have cytoskeletons. The molecules in prokaryotic cytoskeletons are different from the molecules in eukaryotic cytoskeletons. Table 4.1 lists three molecules present in a prokaryotic cytoskeleton.
i. Suggest the function of Protein A.
ii. Suggest the function of Protein C.
iii. An antibiotic called A22 binds irreversibly to Protein B. Despite its antibiotic properties, A22 is not used in humans. Suggest why scientists have advised that A22 should not be used in humans.
i. Suggest the function of Protein A.
ii. Suggest the function of Protein C.
iii. An antibiotic called A22 binds irreversibly to Protein B. Despite its antibiotic properties, A22 is not used in humans. Suggest why scientists have advised that A22 should not be used in humans.
i) cell division / cytokinesis or idea of cell movement
ii) idea of maintaining cell, shape / structure
iii) binds to, actin / cytoskeleton or idea that actin might not function correctly
ii) idea of maintaining cell, shape / structure
iii) binds to, actin / cytoskeleton or idea that actin might not function correctly
19
New cards
A cytoskeleton is present in all eukaryotic cells. One of its functions is to control the movement of organelles. State how the cytoskeleton moves organelles around the cell.
(using) microtubules / tubulin / motor proteins
20
New cards
Epithelial cells in the airways of mammals play an essential role in defences against pathogens. Explain the function of epithelial cells in the airways of mammals in the defence against pathogens and suggest the importance of the cytoskeleton in carrying out this function.
* goblet cells, secrete / release / make / produce / form, mucus
* mucus traps, pathogens / microorganisms
* phagocytes / neutrophils / macrophages / lysozyme
* cilia / ciliated cells / ciliated epithelium, sweep / brush / waft / move
* cytoskeleton / microtubules / tubulin, move(s) / make(s) up, the cilia
* mucus traps, pathogens / microorganisms
* phagocytes / neutrophils / macrophages / lysozyme
* cilia / ciliated cells / ciliated epithelium, sweep / brush / waft / move
* cytoskeleton / microtubules / tubulin, move(s) / make(s) up, the cilia
21
New cards
Sucrase is the enzyme that breaks down sucrose. Which of the bonds, A to D, is broken by sucrase?
A alpha glycosidic
B beta glycosidic
C ester
D peptide
A alpha glycosidic
B beta glycosidic
C ester
D peptide
A alpha glycosidic
22
New cards
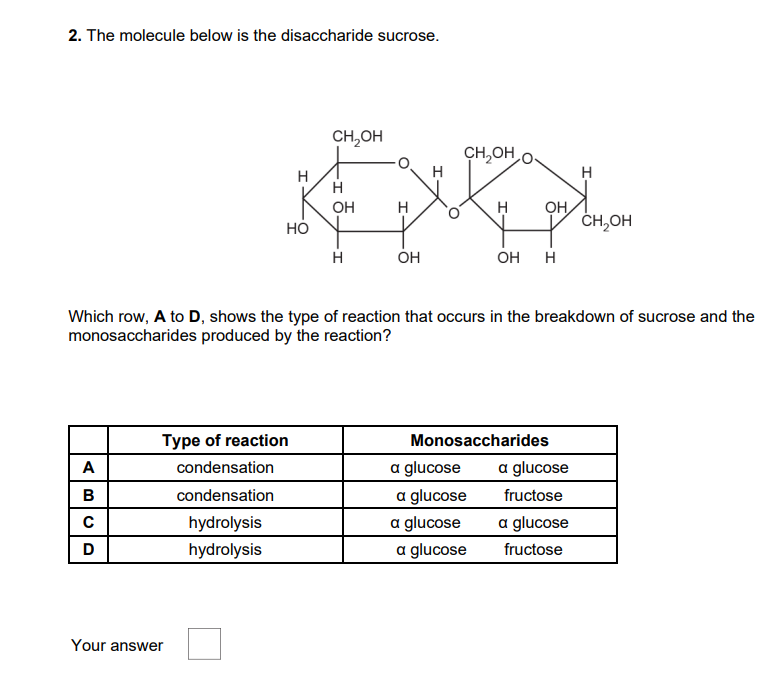
D
23
New cards
Which of the processes, A to D, describes the formation of cellulose?
A condensation polymerisation of amino acid molecules
B condensation polymerisation of β-glucose molecules
C hydrolysis polymerisation of α-glucose molecules
D hydrolysis polymerisation of deoxyribose molecules
A condensation polymerisation of amino acid molecules
B condensation polymerisation of β-glucose molecules
C hydrolysis polymerisation of α-glucose molecules
D hydrolysis polymerisation of deoxyribose molecules
B
24
New cards
Which of the statements, A to D, about amylopectin is correct?
A it contains 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds between α-glucose monomers
B it is an unbranched chain of α-glucose monomers
C it contains α 1-4 and β 1-6 glycosidic bonds
D it is made up of β-glucose monomers and is uncoiled
A it contains 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds between α-glucose monomers
B it is an unbranched chain of α-glucose monomers
C it contains α 1-4 and β 1-6 glycosidic bonds
D it is made up of β-glucose monomers and is uncoiled
A it contains 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds between α-glucose monomers
25
New cards
Name the bond that holds the α-glucose and the fructose together A 1,6-glycosidic bond
B phosphodiester bond
C ester bond
D 1,4-glycosidic bond
B phosphodiester bond
C ester bond
D 1,4-glycosidic bond
A 1-6 glycosidic bond
26
New cards
Which of the options, A to D, is a correct statement about polysaccharides of glucose?
A Cellulose microfibrils are formed by hydrogen bonding between adjacent chains of α-glucose molecules bonded with 1,4-glycosidic bonds.
B Amylose is a straight chain of α-glucose monomers bound by 1,6-glycosidic bonds to allow for dense packing.
C Glycogen has a high proportion of 1,6-glycosidic bonds to produce a highly branched molecule for rapid release of α-glucose.
D Amylopectin has a mixture of 1,4-glycosidic and 1,6-glycosidic bonds between β-glucose molecules for rapid release of energy
A Cellulose microfibrils are formed by hydrogen bonding between adjacent chains of α-glucose molecules bonded with 1,4-glycosidic bonds.
B Amylose is a straight chain of α-glucose monomers bound by 1,6-glycosidic bonds to allow for dense packing.
C Glycogen has a high proportion of 1,6-glycosidic bonds to produce a highly branched molecule for rapid release of α-glucose.
D Amylopectin has a mixture of 1,4-glycosidic and 1,6-glycosidic bonds between β-glucose molecules for rapid release of energy
C Glycogen has a high proportion of 1,6-glycosidic bonds to produce a highly branched molecule for rapid release of α-glucose.
27
New cards
Most termites eat only dead vegetable material, so their principle food source is cellulose. Cellulose is a polymer. State the name of the monomer in cellulose.
beta glucose
28
New cards
Carbohydrates, such as starch, are made from monosaccharides joined together. Which of the bonds, A to D, joins monosaccharides together?
A. ester
B. glycosidic
C. peptide
D. phosphodiester
A. ester
B. glycosidic
C. peptide
D. phosphodiester
B. glycosidic
29
New cards
Energy can be stored in living organisms in the form of carbohydrates or lipids. Name the carbohydrate molecules used to store energy in plants and animals.
starch AND glycogen (ALLOW amylose , amylopectin**)**
30
New cards
Many multicellular organisms need to be able to convert monosaccharides into polysaccharides and back again. Mammals convert the monosaccharide glucose into a highly branched polysaccharide called glycogen, which gets stored in liver cells. Explain why mammals store glycogen instead of glucose.
* insoluble, so has no effect on, water potential / Ψ (of cell)
* metabolically inactive
* compact / lots can be stored in a small space
* able to store, large amounts / lots, of energy
* (highly branched so) has lots of ends for, adding / removing, glucose (when needed) or can be broken down, fast / quickly / rapidly, to release glucose
* metabolically inactive
* compact / lots can be stored in a small space
* able to store, large amounts / lots, of energy
* (highly branched so) has lots of ends for, adding / removing, glucose (when needed) or can be broken down, fast / quickly / rapidly, to release glucose
31
New cards
Another disaccharide is maltose. Maltose and lactose both contain the same number of atoms of each element, C, H and O.
i. State two other structural similarities between lactose and maltose.
i. State two other structural similarities between lactose and maltose.
two, 6-membered rings / hexoses
(1-4) glycosidic bond
two CH2OH (groups)
rings contain one, oxygen atom
(1-4) glycosidic bond
two CH2OH (groups)
rings contain one, oxygen atom
32
New cards
Identify differences between the structures of lactose and maltose
* lactose
* (contains) beta / β-glucose
* β-glycosidic bond
* sugars in opposing orientation
* maltose
* (contains) alpha / α-glucose
* α-glycosidic bond
* both (monomers) in same direction
* (contains) beta / β-glucose
* β-glycosidic bond
* sugars in opposing orientation
* maltose
* (contains) alpha / α-glucose
* α-glycosidic bond
* both (monomers) in same direction
33
New cards
One of the monomers of lactose is galactose. The bacterium E. coli usually uses glucose as a respiratory substrate. Under certain circumstances, E. coli is able to use galactose as a respiratory substrate by breaking down lactose into glucose and galactose and then using both glucose and galactose as respiratory substrates. i. Explain how the structure of galactose allows it to be used as a respiratory substrate.
* bonds contain energy
* (bonds) can be broken by (respiratory) enzymes
* soluble so, can move (within cell)
* H / OH, (groups) can form H bonds with water / allow solubility
* (bonds) can be broken by (respiratory) enzymes
* soluble so, can move (within cell)
* H / OH, (groups) can form H bonds with water / allow solubility
34
New cards
E. coli usually grows in conditions where the extracellular concentration of lactose is low. In such conditions lactose does not easily cross the bacterial cell surface membrane. Suggest and explain why lactose is unable to cross membranes.
* too big to pass between phospholipids
* no / small, concentration gradient
* needs, carrier protein / pump
* no / small, concentration gradient
* needs, carrier protein / pump
35
New cards
In order for lactose to enter the cytoplasm of E. coli a protein is required. The E. coli living in the digestive system of young mammals are more likely to contain this protein than E. coli living in the digestive system of old mammals. Suggest an explanation for this observation.
* (mammal diet high in milk, so) high lactose concentration
* (structural) gene for protein channel / lactose permease gene / lac Y, is, transcribed / expressed switched on
* (protein is) lactose permease
* (structural) gene for protein channel / lactose permease gene / lac Y, is, transcribed / expressed switched on
* (protein is) lactose permease
36
New cards
Plant cell walls are made of cellulose. Cellulose is a polymer of β-glucose. Give three properties of cellulose that make it suitable as the basis of plant cell walls.
* insoluble
* unreactive / inert
* high tensile strength
* flexible
* can form hydrogen bonds with neighbouring chains
* unreactive / inert
* high tensile strength
* flexible
* can form hydrogen bonds with neighbouring chains
37
New cards
State one property of glucose that allows it to be easily transported in animals.
soluble/polar
38
New cards
Explain how the structure of glycogen differs from that of amylopectin to make it better suited as an energy store in animals.
* glycogen (compared to amylopectin) more branched
* more coiled
* (so is) more compact / less space needed (for storage)
* (branching gives) many / more, free ends
* where glucose can be added or removed
* (so) speeds up glucose, release / hydrolysis
* more coiled
* (so is) more compact / less space needed (for storage)
* (branching gives) many / more, free ends
* where glucose can be added or removed
* (so) speeds up glucose, release / hydrolysis
39
New cards
Human pancreatic lipase breaks the bonds between fatty acids and glycerol. What name is given to this reaction?
A condensation B esterification C hydration D hydrolysis
A condensation B esterification C hydration D hydrolysis
D hydrolysis
40
New cards
Phospholipid molecules are similar to triglycerides but they also contain the element phosphorus as part of a phosphate group. Explain how the structure of phospholipids allows them to form the bilayer of a plasma membrane
* hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails
* hydrophobic part / tails, repelled / AW, by water
* head / hydrophilic part, forms H bonds with water
* idea that medium outside / inside plasma membrane is aqueous
* idea that hydrophobic nature of tails results in their facing towards each other
* hydrophobic part / tails, repelled / AW, by water
* head / hydrophilic part, forms H bonds with water
* idea that medium outside / inside plasma membrane is aqueous
* idea that hydrophobic nature of tails results in their facing towards each other
41
New cards
Living organisms have many uses for triglycerides, one of which is the production of phospholipids.
i. Name three other functions of triglycerides in living organisms.
i. Name three other functions of triglycerides in living organisms.
* energy source for respiration / respiratory substrate
* energy storage
* thermal insulation
* electrical insulation
* buoyancy
* idea of: (physical) protection
* energy storage
* thermal insulation
* electrical insulation
* buoyancy
* idea of: (physical) protection
42
New cards
Phospholipid molecules also contain fatty acids. Explain how the fatty acids in phospholipids allow the formation of membranes
* they / fatty acids, hydrophobic / described ✓ phospholipid bilayer (formed)
* fatty acids / tails, on the inside / pointing inward
* fatty acids / tails, on the inside / pointing inward
43
New cards
Triglycerides are a type of lipid molecule that can be broken down during hydrolysis reactions. Using the structure of triglyceride molecules as an example, explain what is meant by hydrolysis.
uses / AW, water
(to) break 3 ester bonds
lysis means splitting and fatty acids are, split
(to) break 3 ester bonds
lysis means splitting and fatty acids are, split
44
New cards
A vet is concerned that a llama is unwell. The vet suspects there may be haemoglobin in the urine of the llama. Explain how the vet could confirm this suspicion
* add biuret / NaOH and CuSO4, solution / reagent to urine
* observe colour change (from blue to purple)
* compare with, control / blank (urine containing no protein
* observe colour change (from blue to purple)
* compare with, control / blank (urine containing no protein
45
New cards
Lactose is a reducing sugar. Benedict’s reagent can be used to detect the presence of lactose in a solution. A colorimeter can be used to measure the concentration of lactose. The colorimeter first needs to be calibrated.
Describe how a method that uses Benedict’s reagent and a colorimeter could be calibrated to measure the concentration of lactose in an unknown sample.
Describe how a method that uses Benedict’s reagent and a colorimeter could be calibrated to measure the concentration of lactose in an unknown sample.
* zero the colorimeter / set to zero
* using blank
* use red filter
* use known concentrations (of lactose)
* (produce) serial / series, dilutions
* construct calibration curve
* test unknown sample (using the same method)
* use / read from, graph / calibration curve, to determine (unknown) concentration
* using blank
* use red filter
* use known concentrations (of lactose)
* (produce) serial / series, dilutions
* construct calibration curve
* test unknown sample (using the same method)
* use / read from, graph / calibration curve, to determine (unknown) concentration
46
New cards
Some organisms use a disaccharide called trehalose as a respiratory substrate. Trehalose has a similar structure and very similar chemical properties to sucrose. Suggest how you could test for the presence of trehalose.
* (carry out) Benedict’s test / described
* (if test for reducing sugar negative) boil with (dilute) HCl and (re)test (with Benedict’s)
* (if test for reducing sugar negative) boil with (dilute) HCl and (re)test (with Benedict’s)
47
New cards
A conjugated protein is held together by many different types of bond. Which bond is not formed when a conjugated protein folds into its quaternary structure?
A disulphide B hydrogen C ionic D peptide
A disulphide B hydrogen C ionic D peptide
D peptide
48
New cards
Which of the options is a function of fibrous proteins?
A aids rigidity of membranes
B involved in cell signalling
C provides elasticity in alveoli
D speeds up reactions
A aids rigidity of membranes
B involved in cell signalling
C provides elasticity in alveoli
D speeds up reactions
C provides elasticity in alveoli
49
New cards
Root vegetables require sulfate ions (SO4 2-) in order to grow to a normal size. The plant uses the sulfur atoms to synthesise biological molecules during growth. Sulfur atoms are required for the synthesis of which type of biological molecule?
protein / polypeptide
50
New cards
Explain what is meant by the term conjugated protein.
* contains non-protein groups
* has prosthetic group
* (prosthetic group) is attached by , covalent bonds / ionic interactions / hydrogen bonds
* has prosthetic group
* (prosthetic group) is attached by , covalent bonds / ionic interactions / hydrogen bonds
51
New cards
Collagen is a fibrous protein. State three properties of a fibrous protein that are different from those of a globular protein.
* haemoglobin , is a larger molecule / has greater molecular mass / has more amino acids
* haemoglobin has , quaternary structure / more than one polypeptide chain
* haemoglobin has , more than one / four , prosthetic groups / iron ions
* haemoglobin contains haem (groups)
* haemoglobin has , quaternary structure / more than one polypeptide chain
* haemoglobin has , more than one / four , prosthetic groups / iron ions
* haemoglobin contains haem (groups)
52
New cards
DNA sequences in genes code for polypeptide molecules such as pepsin and titin. Explain why a process known as transcription is necessary for polypeptide synthesis.
* gene / DNA, copied/ transcribed, to (m)RNA
* (idea that RNA goes to / translation is at) ribosome(s) / RER
* DNA, is too large to / cannot / is not able to, leave nucleus / cross nuclear envelope / fit through nuclear pores
* (idea that RNA goes to / translation is at) ribosome(s) / RER
* DNA, is too large to / cannot / is not able to, leave nucleus / cross nuclear envelope / fit through nuclear pores
53
New cards
Describe and explain why collagen is a fibrous protein
* is long chain (of amino acids)
* little / no, tertiary structure
* insoluble / has many non-polar amino acids
* has, only two different amino acids / only glycine and proline / a small range of amino acids
* has a structural function / provides strength (to the artery wall
* little / no, tertiary structure
* insoluble / has many non-polar amino acids
* has, only two different amino acids / only glycine and proline / a small range of amino acids
* has a structural function / provides strength (to the artery wall
54
New cards
Suggest why collagen is such a strong molecule.
* many, hydrogen bonds (between polypeptides)
* many, covalent bonds / crosslinks (between collagen molecules)
* polypeptides overlap / polypeptides have staggered end
* many, covalent bonds / crosslinks (between collagen molecules)
* polypeptides overlap / polypeptides have staggered end
55
New cards
State the name of the bond that holds water molecules together.
hydrogen
56
New cards
DNA is one of many substances which will dissolve in water. Explain why water is a good solvent.
molecules are polar
(polarity) enables (water) molecules to, attract / bind to, solute molecules
(polarity) enables (water) molecules to, attract / bind to, solute molecules
57
New cards
A student studied the pack of ‘plant food’ supplied with some cut flowers. The list of ions included hydrogen and sodium. Suggest what roles these may play in helping the cut flowers to last longer.
hydrogen ions used to affect / regulate pH
sodium ions used to regulate water potential
sodium ions used to regulate water potential
58
New cards
Outline the properties of water which make it an ideal habitat for an amphibian.
(good) solvent, high specific heat (capacity) / temperature stability
(high) density (so frog floats / buoyant)
ice is less dense than water
(high) density (so frog floats / buoyant)
ice is less dense than water
59
New cards
Which of the stains, A to D, would be chosen to bind to the phosphate group of DNA to make chromosomes more visible when using a light microscope?
A carbolfuchsin – a non-polar dye
B nigrosin – a negatively charged dye
C methylene blue – a positively charged dye
D Sudan 111 – a lipid-soluble dye
A carbolfuchsin – a non-polar dye
B nigrosin – a negatively charged dye
C methylene blue – a positively charged dye
D Sudan 111 – a lipid-soluble dye
C methylene blue – a positively charged dye
60
New cards
Which of the statements, A to D, shows that the genetic code is degenerate?
A CCA and CCT code for proline
B rRNA is manufactured in the nucleolus
C tRNA is not complementary to DNA
D uracil is not found in DNA
A CCA and CCT code for proline
B rRNA is manufactured in the nucleolus
C tRNA is not complementary to DNA
D uracil is not found in DNA
A CCA and CCT code for proline
61
New cards
Which of the following statements, A to D, about DNA replication is correct?
A RNA will bind to DNA through complementary base-pairing.
B The distance between the strands in the double helix will always be the same.
C The proportion of adenine in a nucleic acid will always equal the proportion of guanine.
D The formation of phosphodiester bonds will occur in the same direction on each strand during DNA replication
A RNA will bind to DNA through complementary base-pairing.
B The distance between the strands in the double helix will always be the same.
C The proportion of adenine in a nucleic acid will always equal the proportion of guanine.
D The formation of phosphodiester bonds will occur in the same direction on each strand during DNA replication
D The formation of phosphodiester bonds will occur in the same direction on each strand during DNA replication
OR
A RNA will bind to DNA through complementary base-pairing.
OR
A RNA will bind to DNA through complementary base-pairing.
62
New cards
DNA is made up of two polynucleotide chains. Which of the bonds, A to D, forms between two nitrogenous bases holding the two polynucleotide chains together?
A phosphodiester B ionic C covalent D hydrogen
A phosphodiester B ionic C covalent D hydrogen
D hydrogen
63
New cards
Which statement, A to D, describes the function of DNA polymerase?
A break the hydrogen bonds between complementary bases
B make phosphodiester bonds between adjacent nucleotides
C make phosphodiester bonds between polynucleotides
D make the hydrogen bonds between complementary bases
A break the hydrogen bonds between complementary bases
B make phosphodiester bonds between adjacent nucleotides
C make phosphodiester bonds between polynucleotides
D make the hydrogen bonds between complementary bases
B make phosphodiester bonds between adjacent nucleotide
64
New cards
A group of students attempted to extract and purify DNA from a plant in Upper End Meadow. The students used the following steps:
1\. Mix the plant sample with detergent.
2\. Add salt.
3\. Add protease enzyme.
4\. Spool the DNA precipitate onto a glass rod.
Suggest whether this method would successfully extract and purify DNA. Justify your conclusion.
1\. Mix the plant sample with detergent.
2\. Add salt.
3\. Add protease enzyme.
4\. Spool the DNA precipitate onto a glass rod.
Suggest whether this method would successfully extract and purify DNA. Justify your conclusion.
Yes because
* detergent, breaks / disrupts, (cell) membrane(s) / nuclear envelope
* salt, helps DNA, shed water / precipitate
* protease breaks down, histones / proteins around DNA / proteins attached to DNA
* detergent, breaks / disrupts, (cell) membrane(s) / nuclear envelope
* salt, helps DNA, shed water / precipitate
* protease breaks down, histones / proteins around DNA / proteins attached to DNA
65
New cards
A student tried to extract some DNA from a crushed banana at home. DNA dissolves in water but the student realised that they needed to add something to break open the nuclear envelope to release the DNA. Suggest a suitable substance the student could use to release the DNA, and explain why it should work.
detergent works as an emulsifier / attracts phospholipid molecules and water molecules. It will break up the plasma / nuclear membranes
66
New cards
Name the chemical released when the bond is formed between the two nucleotides.
water
67
New cards
What type of chemical reaction takes place when two nucleotides in a single polynucleotide strand are joined together?
condensation
68
New cards
A DNA molecule contains two polynucleotide chains. Describe how these two chains are held together.
* phosphodiester bonds in, backbone / described
* hydrogen / H, bonds / bonding (between chains / bases)
* purine to pyrimidine / A to T and C to G
* hydrogen / H, bonds / bonding (between chains / bases)
* purine to pyrimidine / A to T and C to G
69
New cards
Explain how the nucleotides in a DNA molecule are arranged as two polynucleotide strands
* nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds
* hydrogen bonds between, complementary / named bases
* (polynucleotides) are anti parallel / described
* hydrogen bonds between, complementary / named bases
* (polynucleotides) are anti parallel / described
70
New cards
DNA is arguably the most important molecule in the whole of biology. When a cell divides an identical copy of its DNA is made in a process called DNA replication. Explain how pairing of nitrogenous bases allows identical copies of DNA to be made.
* adenine / A pairs with thymine / T and cytosine / C pairs with guanine / G
* (because of) hydrogen bonding
* idea that purine can only bind with pyrimidine because they are different sizes
* idea that if one base is known it can pair with only one other base
* (because of) hydrogen bonding
* idea that purine can only bind with pyrimidine because they are different sizes
* idea that if one base is known it can pair with only one other base
71
New cards
Name two enzymes involved in DNA replication.
helicase
DNA polymerase
ligase/ gyrase
DNA polymerase
ligase/ gyrase
72
New cards
Explain why enzymes are essential to all organisms.
enzymes , are (biological) catalysts / speed up reactions
they lower the activation energy (so reactions can take place at, low / body, temperatures)
high temperatures (in living organisms), would denature, enzymes / proteins
they lower the activation energy (so reactions can take place at, low / body, temperatures)
high temperatures (in living organisms), would denature, enzymes / proteins
73
New cards
Explain the meaning of the phrase semi-conservative replication
(new DNA molecule comprises) one, original / old / parent, strand and one new strand
OR
each strand (of DNA molecule) acts as a template strand (for a new double helix
OR
each strand (of DNA molecule) acts as a template strand (for a new double helix
74
New cards
DNA ligase is one enzyme involved in the replication of DNA. State two other enzymes involved and describe their functions.
* DNA helicase
* unzips the DNA molecule / breaks hydrogen bonds (between complementary bases) / separates the (2) strands
* DNA polymerase
* forms phosphodiester bonds / joins (adjacent) nucleotides / forms sugar-phosphate backbone
* DNA gyrase
* unwinds/uncoils the DNA
* unzips the DNA molecule / breaks hydrogen bonds (between complementary bases) / separates the (2) strands
* DNA polymerase
* forms phosphodiester bonds / joins (adjacent) nucleotides / forms sugar-phosphate backbone
* DNA gyrase
* unwinds/uncoils the DNA
75
New cards
Outline how the process of DNA replication is completed, following the pairing of nitrogenous bases.
* (involves) DNA polymerase
* sugar-phosphate backbone (re)forms / condensation reaction between phosphate and sugar
* DNA winds into double helix
\
* sugar-phosphate backbone (re)forms / condensation reaction between phosphate and sugar
* DNA winds into double helix
\
76
New cards
Why is DNA replication described as semi-conservative?
(new molecule consists of) one old strand and one new strand
77
New cards
Suggest two ways tubulin is essential to protein synthesis and protein secretion in eukaryotic cells.
* movement of mRNA from nucleus to ribosome
* movement of polypeptides through the rER
* movement of vesicles from rER to Golgi
* movement of vesicles between cisternae of Golgi (cis to trans face)
* movement of secretory vesicles from Golgi to cell surface membrane
* movement of polypeptides through the rER
* movement of vesicles from rER to Golgi
* movement of vesicles between cisternae of Golgi (cis to trans face)
* movement of secretory vesicles from Golgi to cell surface membrane
78
New cards
Which of the following statements, A to D, about the nature of the genetic code is incorrect?
A. It is a degenerate code.
B. It is a triplet code.
C. It is overlapping.
D. It is universal.
A. It is a degenerate code.
B. It is a triplet code.
C. It is overlapping.
D. It is universal.
C. It is overlapping
79
New cards
A student investigated the effect of pH on the rate at which an enzyme breaks down a substrate. What would be a suitable control for this investigation? An identical tube set up with:
A. no buffer
B. no buffer and no enzyme
C. no enzyme
D. no substrate
A. no buffer
B. no buffer and no enzyme
C. no enzyme
D. no substrate
C. no enzyme
80
New cards
Which of the following, A to D, is an incorrect statement about enzymes?
A. amylase and trypsin catalyse extracellular reactions
B. catalase catalyses intracellular reactions
C. extracellular enzymes are produced outside the cell
D. intracellular enzymes work inside the cell
A. amylase and trypsin catalyse extracellular reactions
B. catalase catalyses intracellular reactions
C. extracellular enzymes are produced outside the cell
D. intracellular enzymes work inside the cell
C. extracellular enzymes are produced outside the cell
81
New cards
Which of the following, A to D, is true of a competitive enzyme inhibitor?
A binds to a site other than the active site
B can bind irreversibly to the active site
C changes the shape of the active site
D effects can be overcome by adding more substrate
A binds to a site other than the active site
B can bind irreversibly to the active site
C changes the shape of the active site
D effects can be overcome by adding more substrate
D effects can be overcome by adding more substrate
82
New cards
What is the correct definition of the term coenzyme?
A An inorganic ion that forms the centre of a globular protein.
B A molecule that binds to the enzyme, changing the shape of the active site, preventing an enzyme substrate complex from forming.
C A non-protein organic molecule, not permanently attached to an enzyme, but needed to allow the enzyme to function.
D A metal ion that attaches to the enzyme, changing the shape of the active site, increasing the likelihood of a reaction.
A An inorganic ion that forms the centre of a globular protein.
B A molecule that binds to the enzyme, changing the shape of the active site, preventing an enzyme substrate complex from forming.
C A non-protein organic molecule, not permanently attached to an enzyme, but needed to allow the enzyme to function.
D A metal ion that attaches to the enzyme, changing the shape of the active site, increasing the likelihood of a reaction.
C A non-protein organic molecule, not permanently attached to an enzyme, but needed to allow the enzyme to function.
83
New cards
Which of the following factors does not affect the shape of the active site of an enzyme?
A a drop in temperature
B non-competitive inhibitor
C a change in pH
D binding of substrate
A a drop in temperature
B non-competitive inhibitor
C a change in pH
D binding of substrate
A a drop in temperature
84
New cards
Amylase activity is increased in the presence of chloride ions. State the name given to any inorganic ion that increases the activity of an enzyme.
cofactor
85
New cards
Describe how a non-competitive inhibitor works to inhibit the activity of an enzyme
* inhibitor binds to, allosteric site / enzyme away from active site
* changes, tertiary / 3D, structure of, enzyme / active site / protein OR active site no longer complementary to substrate OR substrate and, enzyme / active site, cannot, bind / fit (together) OR E-S compex cannot form
* changes, tertiary / 3D, structure of, enzyme / active site / protein OR active site no longer complementary to substrate OR substrate and, enzyme / active site, cannot, bind / fit (together) OR E-S compex cannot form
86
New cards
Membranes are found within and surrounding cells. Which of the statements, A to D, is not a role of membranes in cells?
A acts as a barrier between areas
B cell signalling
C provides support for cell
D site of chemical reactions
A acts as a barrier between areas
B cell signalling
C provides support for cell
D site of chemical reactions
C provides support for cell
87
New cards
Which of the following is not a role of an intracellular membrane? A cell to cell signalling
B partially permeable barrier
C site of chemical reactions
D transport of substances across the membrane
B partially permeable barrier
C site of chemical reactions
D transport of substances across the membrane
A cell to cell signalling
88
New cards
Explain why glucose cannot pass through a cell membrane by simple diffusion.
phospholipids act as a barrier and (glucose) molecules too large
89
New cards
There are differences between the plasma membrane and membranes within cells. Outline the role of membranes within cells.
* compartmentalisation OR form / surround , (named) organelles
* purpose of / need for , compartments / separation
* sites of chemical reactions
* provide attachment sites for , enzymes / pigment
* purpose of / need for , compartments / separation
* sites of chemical reactions
* provide attachment sites for , enzymes / pigment
90
New cards
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is where translation of some proteins takes place in a eukaryotic cell. Explain the role of the membrane in the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
* compartmentalisation / maintain different conditions from cell cytoplasm
* separating proteins (synthesised) from cell cytoplasm
* hold, ribosomes / enzymes, in place
* separating proteins (synthesised) from cell cytoplasm
* hold, ribosomes / enzymes, in place
91
New cards
Name one other molecule that can cross plasma membranes.
water / H2O/ oxygen/ carbon dioxide
92
New cards
State how the structure of the cell surface membrane allows potassium ions to enter or leave a cell.
channel / carrier / transport / cotransporter, proteins
93
New cards
ATP is made up of phosphate groups and two other molecules. Name the two other molecules.
adenine and ribose
94
New cards
How does the fluid mosaic model describe the structure of plasma membranes?
* phospholipid bilayer
* hydrophilic / phosphate (containing), heads facing, outwards / towards external environment AND hydrophobic / fatty acid, tails facing, inwards / away from external environment
* proteins / phospholipids, free to move (in membrane)
* proteins, scattered / randomly arranged / spread throughout / here and there (between the phospholipids)
* hydrophilic / phosphate (containing), heads facing, outwards / towards external environment AND hydrophobic / fatty acid, tails facing, inwards / away from external environment
* proteins / phospholipids, free to move (in membrane)
* proteins, scattered / randomly arranged / spread throughout / here and there (between the phospholipids)
95
New cards
Explain how the structure of phospholipid molecules allows for the formation of plasma membranes.
* phosphate (on head), is hydrophilic / bonds with water (molecules)
* (two) fatty acid tails are hydrophobic
* heads orientate towards water / tails orientate towards other fatty acids / tails orientate away from water , (so a bilayer forms
* (two) fatty acid tails are hydrophobic
* heads orientate towards water / tails orientate towards other fatty acids / tails orientate away from water , (so a bilayer forms
96
New cards
Describe the structural difference between alpha and beta glucose molecules
alpha glucose H above ring / OH below ring, on, carbon 1
97
New cards
Salts that a plant needs, such as nitrates and phosphates, are taken into root hair cells by active transport. For which macromolecule does a plant need both nitrogen and phosphorus?
DNA / RNA / nucleic acid
98
New cards
Flooding of fields by seawater can damage crops. Seawater contains dissolved salts, including sodium chloride. How would flooding affect soil water potential?
lower / reduce / make more negative
99
New cards
Explain how the Casparian strip prevents these ions from reaching the xylem of the plant by the apoplast pathway
* strip is impervious to, water / solutions
* forces water / solutions, to pass through, plasma / cell surface, membrane
* phospholipid (bilayer), repels / AW, ions / charged particles
* forces water / solutions, to pass through, plasma / cell surface, membrane
* phospholipid (bilayer), repels / AW, ions / charged particles
100
New cards
Define osmosis.
diffusion of water across a partially permeable membrane down a, water potential gradient