MedChem 310 Exam #2
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
plasma membrane
selectively permeable barrier, mechanical boundary of cell, nutrient and waste transport, location of many metabolic processes (respiration, photosynthesis), detection of environmental cues for chemotaxis
gas vacuole
an inclusion that provides buoyancy for floating in aquatic environments
ribosomes
protein synthesis
inclusions
storage of carbon, phosphate, and other substances
nuclei
localization of genetic material (DNA)
periplasmic space
in typical gram-negative bacteria, contains hydrolytic enzymes and binding proteins for nutrient processing and uptake; in typical gram-positive bacteria, may be smaller or absent
cell wall
proteciton from osmotic stress, helps maintain cell shape
capsules and slime layers
resistance to phagocytosis, adherence to surfaces
fimbriae and pili
attachment to surfaces, bacterial conjugation and transformation, twitching and gliding motility
flagella
swimming and swarming motility
endospore
survival under harsh environment conditions
what is the carbohydrate component of peptidoglycan
helical glycan chairs consisting of dissacharid subunit with N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) and N-acetylglucosamie (NAG)
what is the peptide compoent of peptidoglycan
pentapeptide chains attached to NAM-carboxyl group as amides
D/L-Ala, diamino acid, D-Glu building blocks
peptide chains involved in crosslinking glycan polymers
what are the two types of crosslinks between peptide chains
direct connection of peptide chains
connection of peptide chains via peptide inter bridges
what are the lipolysaccharide functions
negatively charged outer membrane surface
membrane stabilization
permeability barrier
host cell immune response
toxic reactions in host (lipid A)
what is the gram-positive bacteria cell wall structure
thick peptidoglycan layer
one plasma membrane
small periplasmic space with few protains (cell wall synthesis)
what is the gram-negative bacteria cell wall structure
thin peptidoglycan layer
two plasma membranes (inner and outer membrane)
outer membrane layer consisting of lipopolysaccharides
large periplasmic space with secreted proteins (eg nutrient activation and transport, cell wall synthesis)
fluid mosaic model
membranes provide an environment in which membrane proteisn “float”
what is the bacterial membrane structure
phospholipids
hopanes
glycolipid
integral protein
peripheral membrane protein
oligosaccharide
integral membrane protein
phospholipids
bacteria change the fatty acid composition of phospholipids to adapt to temperature change
hopanes
sterol analogs of bacteria
maintain membrane fluidity
integral protein
channeling or transporting membranes across the membrane
peripheral membrane protein
support, communication, enzymes and molecule transfer in the cell
oligosaccharide
cell recognition and cell adhesion
integral membrane protein
movement of molecules across them and the transduction of energy and signals
what composes of the 50S subunit
5S rRNA
LSU proteins
23S rRNA
what composes of the 30S subunit
SSU proteins
16S rRNA
what are the bacterial plasmids
conjugative plasmids
R plasmids
Col plasmids
virulence plasmids
metabolic plasmids
conjugative plasmids
transfer of DNA from one cell to another
R plasmids
carry antibiotic resistance genes
Col plasmids
produce bacteriocins substances that destroy closely related species
virulence plasmids
carry virulence genes
metabolic plasmids
carry genes for enzymes
what is the chain of infection
agent → virulence → exposure → dose → susceptibility
reservoir
the environment/host where an infectious agent normally resides
inanimate objects: soil
animate objects: cats
zoonosis
a disease that can be transmitted from animals to humans
direct contact with animal
animal products/waste
exposure
various forms of infection/transmission
indirect: airborne (dust), food contamination, surface contamination
direct: human/animal contact, vector (between reservoirs)
overview of infeciton process
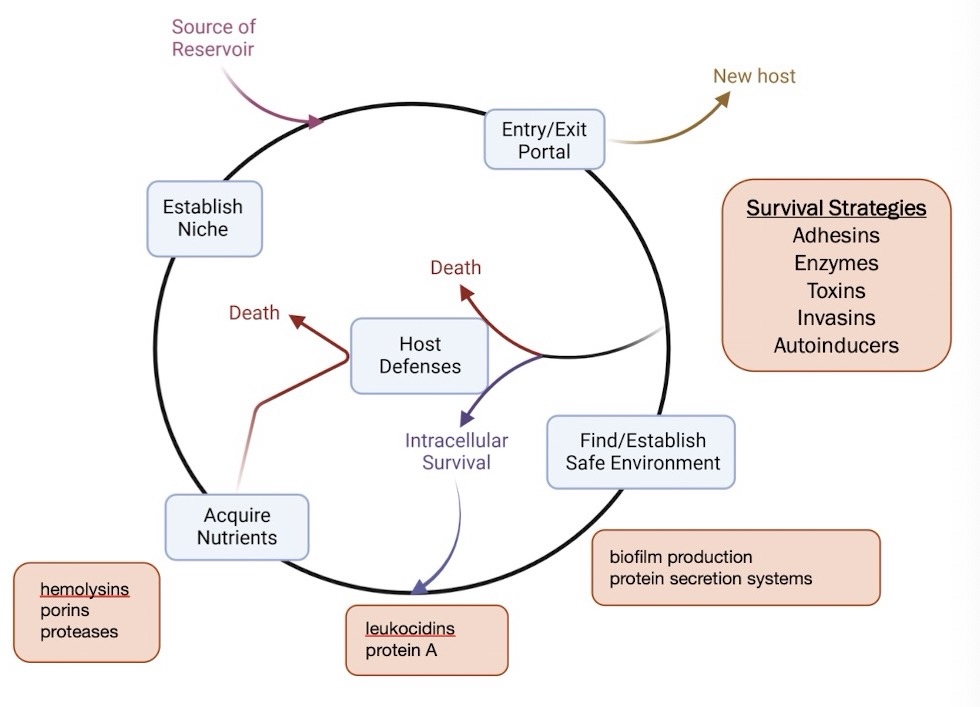
what are the conditions bacterial pathogens must survive in infected host to cause disease
suitable environment
nutrients
protection from host defense
why do bacterial pathogens employ virulence factors
find/establish environments and niches
evade host defense
acquire nutrients
what are cytosolic viruelnce factors
adaptive metabold, physiological and morpholigical shifts
response to host immune stress
waht are cell associated virulence factors
attachment and evading the host immune system
what are secreted virulence factors
attachment
damage the host
establish suitable environment
protection against host immune system
what is the objective of adherance and colonization factors
bacteria, fungi, and protozoa require a protal of entry to access nutrients
what are the 5 adherance mechanisms
pili and fimbriae
capsule
cell envelope proteins
lipopolysaccharides O-antigens
secreted polysaccharides
what is the portal of entry for adherence and colonization factors
skin
respiratory system
gastrointestinal system
urogenital system
conjunctiva of the eye
extracellular pathogens attach to intercellular spaces with intracellular pathogens invade host cells
pili and fimbriae adherence mechanism
initial host cell contact and bacteria-bacteria or interaction and movement during colonization
capsule adherence mechanism
capsular polysaccharides
cell envelope proteins adherence mechanism
often cell-type specific interaction
lipopolysaccharides O-antigens adherence mechanism
gram-negative bacteria
secreted polysaccharides adherence mechanism
attach by forming a sticky, adhesive layer on the cell surface or by being excreted into the surround environment; bacterial glycosyltransferases catalyze the transer of sugar to build complex polysaccharide chains, which are then secreted outside the bacterial cell
infectivity
ability to establich a discrete focal point of infection
invasiveness
ability to spread to adjacent or other tissues
clostridium tetani
produces toxins and enzymes eg. collagenase (protein degradation)
noninvasive because does not spread between tissue
bacillus anthracis
produces substantial virulence factors (eg. capsules and toxins)
highly invasive
streptococcus sp.
span the spectrum of virulence factors and invasiveness
ex. hyaluronidase (carbohydrate degradation)
how does active penetration alter the host
attaching EC matrix and basement membrane of integuments/intestinal linings
degrading carbohydrate-protein complexes
disrupting host cell surface
what enzymes are associated with attaching EC matrix and basement membrane of integuments/intestinal linings
hyaluronidase
collagenase
what enzymes are associated with degrading carbohydrate-protein complexes
proteases
the glycocalyx
what enzyme is associated with disrupting host cell surface
phospholipase C in clostridum sp
what is passive mechanisms related to
lesions, ulcers, wounds, abrasions, burns
arthropod vectors
tissue damaged by other organism (animal bite)
what does the secretion of reactive oxygen species (eg. H2O2) do
damage epithelial cells
invading bacteria might reach the circulatory system (lymphatic system, blood)
toxin release → organ failure/sepsis
what are exotoxins
travel from the site of infection to other tissues or target cells
toxic in nanogram per-kilogram of body weight concentrations (eg botulinum toxin)
grouped by mechanism of action or protein structure
what are the types of exotoxins
AB toxin
channel (pore)-forming toxins
superantigens
what is an AB toxin
“B” binds to a host cell receptor determines the cell type of toxin will affect
“A” enters the cell and has enzyme activity that causes the toxicity, exerts deleterious effect
what are some examples of AB toxins
diphtheria toxin
botulinum toxin (botox)
what is diphtheria toxin
toxin uses B subunit to bind clathrin-coasted pits on cell curface
intact toxin is endocytosed and pH change from ATPase activity causes the subunits to separate
location of separation is often called a compartment of uncoupling of receptor and ligand (CURL)
B subunit is recycled
active toxin (A) exerts its effect on its target
how does the active toxin of biphtheria toxin exert its effect on its target
protein A catalyzes ADP-ribosylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2)
ADP-ribosylation prevents mRNA during translation by eEF2 in host cell ribosome
what is botulinum toxin (botox)
produced clostridium botulinum
can cause paralysis
neurotransmitter release: electrical signals travel to the neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
acetylcholine release: at the NMJ, acetylcholine binds to receptors on the muscle cells causing contraction
block the release of acetylcholine, preventing the muscles from contraction
muscle paralysis or reduced muscle contraction
among the most toxic compound known
what are channel (pore)-forming toxins
secreted protein monomers
disrupt membranes so that the cell lyses/dies
examples of channel (pore)-forming toxins
secreted protein monomers (cholesterol-dependent cytolysins from gram-positive bacteria)
secreted synergistic peptides (enterococcal cytolysis from enterococcus faecalies)
what is the mechanism for channel (pore)-forming toxins
inserts itself into the host cell membrane to form a pore
multiple membrane pores results in an osmolarity shift as water enters the cell and cytoplasmic contents move out
resulting effect of the toxin is cell lysis
what are super antigens
hyperactivates the immune system
nonspecific activation of T cells by a superantigen in the absence of antigen
crosslinking MHC-II of macrophages with T-cell receptor
stimulates release of large anounts of cytokines
what is the result of superantigens
host is overwhelmed and it results in shock/death
inflammation, toxic shock
weakens host
enables bacterial dissemination
what is Lipid A
an endotoxin
biologically active component of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) the main components of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria
highly toxic (ng/kg body weight) when released into bloodstream
bound by toll-like reseptor 4 on marcophages
innate immune response (recognition of gram-negative bacterial infection)
release of high amounts of lipid A during a servere infection
severe immune response, organ failure, sepsis
what are the bacterial strategies to evade the host immune system
prevention of detection
attack on host immune proteins
biofilms
how do bacteria use prevention of detection to evade the host immune system
mucous production on bacterial capsule to prevent binding by immune cells
surface protein production
protein M - group A streptococci (GAS), causes strep throat, binds immune system proteins and fibrinogen (clotting substrate) to evade phagocyte binding and immune response
protein A - staphylocossuc aureus, binds antibodies on the heavy-chain end which usually binds to phagocyte
O-antigen changes - gram-negative bacteria can alter the length of polysaccharide chains of LPS to evade immune detection
pill/surface protein changes
how do bacteria attack host immune proteins
secretion of proteases to degrade immune proteins
what are biofilms and how do they work
provide a unique environment for bacteria to exchange genetic information and collectively resist antimicrobial agents and host defense mechanisms
bacterial pathogens form biofilms for improved resistance to antibiotics and host immune system during host colonization - chronic infectious diseases
clusters of bacteria that are attached to a surface and/or each other and embedded in a self-produced matrix (proteins, polysaccharides, environmental DNA) - protection from host immune cells and proteins
biofilms offer advantage of protection, shared nutrients and rapid exchange of plasmid DNA - slower metabolism makes bacterial pathogens more persistent
biofilm attack by phagocytes can cause tissue damage
how de we classify antibiotics
broad spectrum
narrow spectrum
minimum inhibitory concentration
minimum bactericidal concentration
bacteriostatic
bactericidal
broad spectrum antibiotics
inhibition of both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
narrow spectrum antibiotics
inhibition of only a few genera of either gram-negative or gram-positive bacteria
minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
prevents visible growth of a bacterium (in virtro culture with drug)
minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC)
lowest concentration of an antibiotic agent that kills a bacterium (in vitro subculture without drug)
bacteriostatic antibiotic
MBC/MIC > 4, MBC concentration too high for safe in vivo dosage
bactericidal antibiotic
MBC/MIC < 4, MBC concentration can be safely administered in vivo
what drugs inhibit cell wall synthesis
beta-lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, monobactams)
vancomycin
bacitracin
cell membrane (polymyxins)
what drugs inhibit nucleic acid synthesis
folate synthesis → sulfonamides, trimethoprim
DNA gyrase → quiolones
RNA polymerase → rifampin
what drugs inhibit protein synthesis
50S subunit → macrolides, clindamycin, linezolid, chloramphenicol, streptogramins
30S subunit → tetracyclines, aminoglycosides
what is the structure of beta-lactams
feature of beta-lactam (=4 membered cyclic amide, aka azetidinone)
beta-lactam antibiotics are classified by the ring fused to the beta-lactam
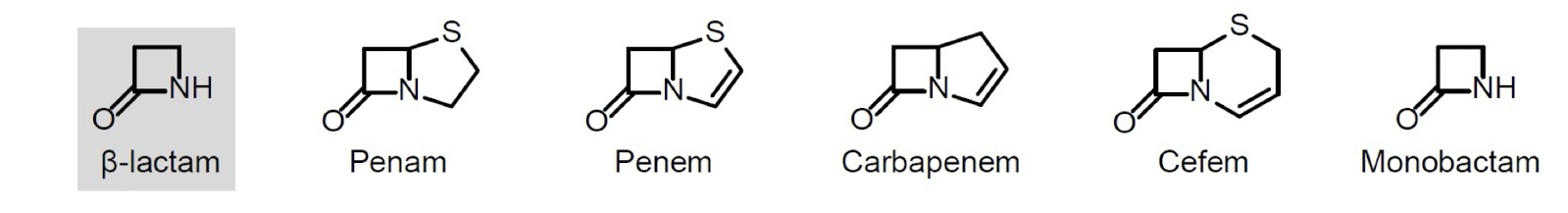
what is the reactivity of beta-lactams
amide has no planar bond character due to the fused ring and beta-lactam stereochemistry creating a V-shaped ring system
strained ring system
more reactive than peptide bond amides eg. to nucleophilic attack to the lactam carbonyl group
what is the mechanism of action for beta-lactams
inhibit transpeptidase domains of penicillin-binding proteins (PBP), which catalyze the crosslinking of peptide chains of peptidoglycan during cell wall biosynthesis
role of PBP transpeptidases in the formation fo 4→ 3 peptidoglycan cross-links
mimic D-Ala-D-Ala substrate of penicillin-binding proteins
irreversible inhibition
what is the structure of penicillin
penam core structure (=beta-lactam + fused thiazolidine)
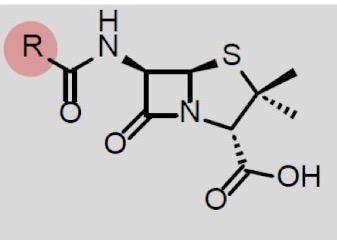
what does the R group on beta-lactam ring substituent have no effect on in penicillin
acid stability and intact drug absorption in GI tract
stability against bacterial beta-lactamase (resistance mechanism)
blood concetrations
antibacterial activity
more info on acid stability and intact drug absorption in GI tract for penicillin
acid stable penicillin are oral drugs
under acidic conditions (eg. at stomach pH) the carbonyl of the R-acyl substituent can attack the beta-lactam intramolecularly as a mucleophile, open the ring and inactivate the drug
an electron-withdrawing R-group reduces nucleophilicity of the R-acyl carbonyl and therefore increases acid stability of the drug
more info on stability against bacterial beta-lactamase (resistance mechanism) for penicillin
beta-lactamases (aka penicillinase) - serine proteases can catylze hydrolysis of beta-lactams
can be regenerated from covalently bound beta-lactam adduct → inactivation of many beta-lactams
secreted into medium (gram-positive bactera) or into periplasmic space (gram-negative bacteria)
large R group incrases resistance to beta-lactamases
more info on blood concentrations for penicillin
less hydrophobic R decreases binding of penicillin to plasma proteins and thus, increases blood plasma drug concentration
more info on antibacterial activity for penicillin
R group can change the antibacterial spectrum of penicillin eg. more hydrophilic R enables transport through gram-negative outer membrane porins (hydrophilic pore)
ampicillin = broad spectrum antibiotic
what are cephalosporins
cefem core structure
broad spectrum including many very dangerous bacteria
often lack oral activity
z-oxime on R1-group increases stability against beta-lactamase
bactericidal
what are carbapenems
potent broad-spectrum activity