Human Anatomy and Physiology: Nervous System Review
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms related to the nervous system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
The outer layer of the brain responsible for higher brain functions like thought and action.
Cerebral Cortex
The region of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord, controlling vital functions.
Brainstem
The part of the brain that helps coordinate voluntary movements and balance.
Cerebellum
A cylindrical structure that transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
Spinal Cord
Clear fluid that protects the brain and spinal cord by providing cushioning and nutrient transport.
Cerebrospinal Fluid
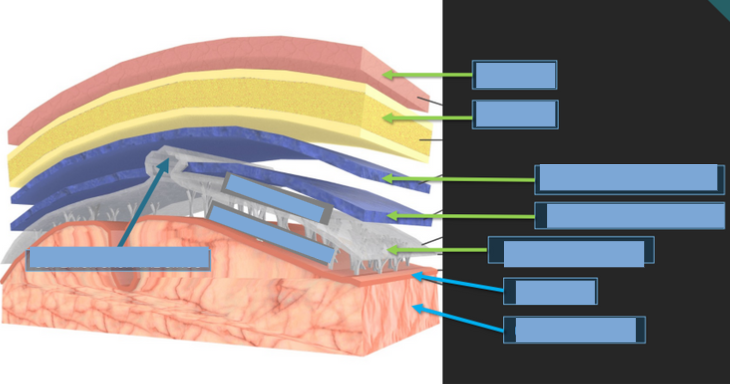
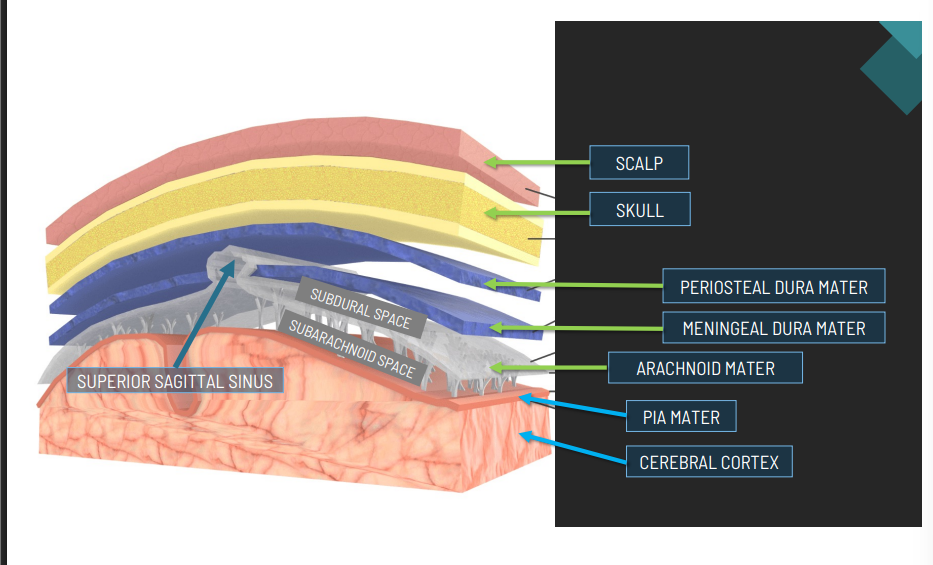
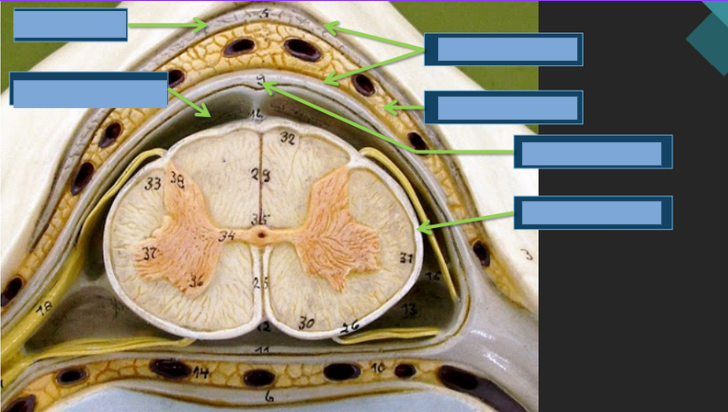
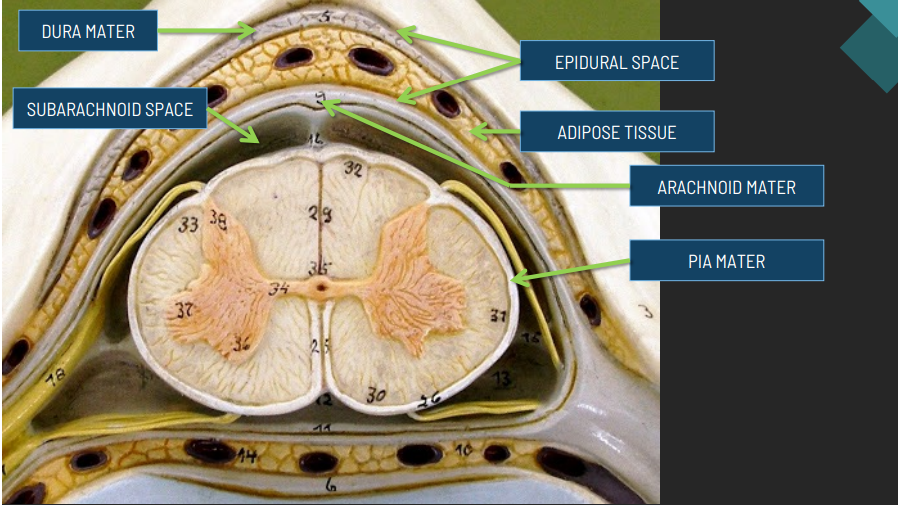
Three protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord.
Meninges
The tough outermost layer of the meninges.
Dura Mater
The middle layer of the meninges, resembling a spider web.
Arachnoid Mater
The delicate innermost layer of the meninges that clings closely to the brain.
Pia Mater
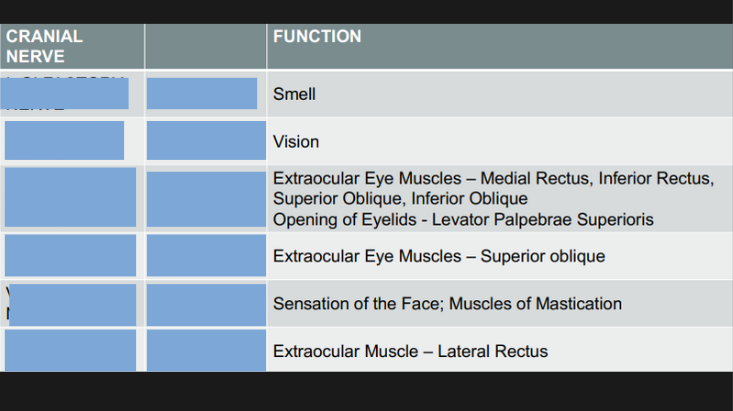
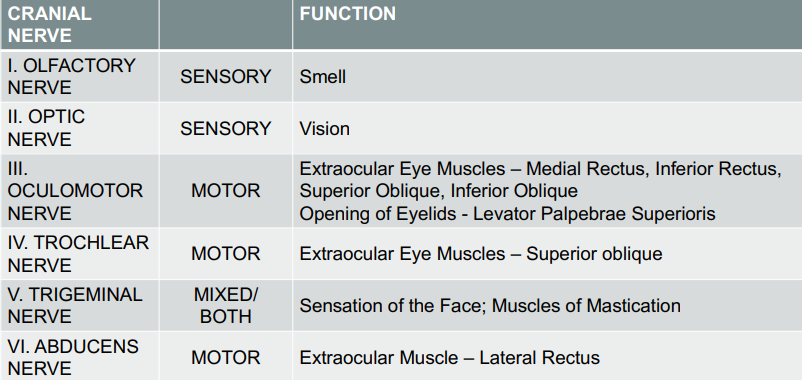
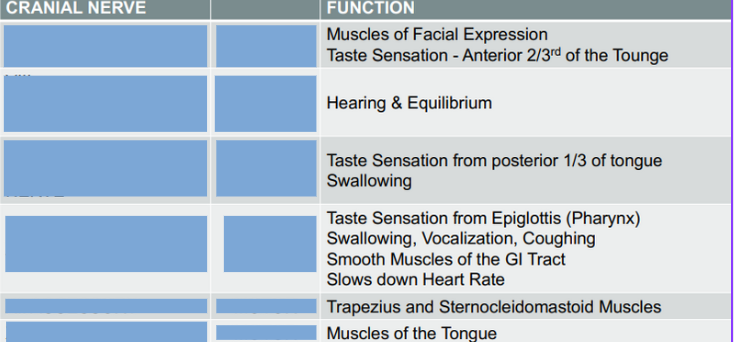
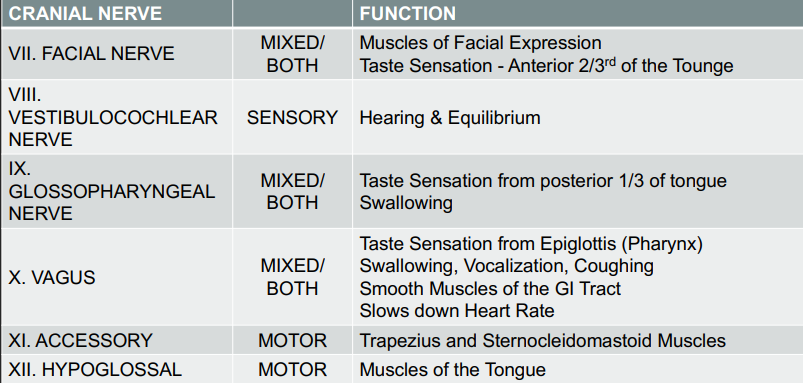
Twelve pairs of nerves that directly arise from the brain and control various functions, including sensory and motor activities.
Cranial Nerves
The brain structure that acts as a relay station for sensory information.
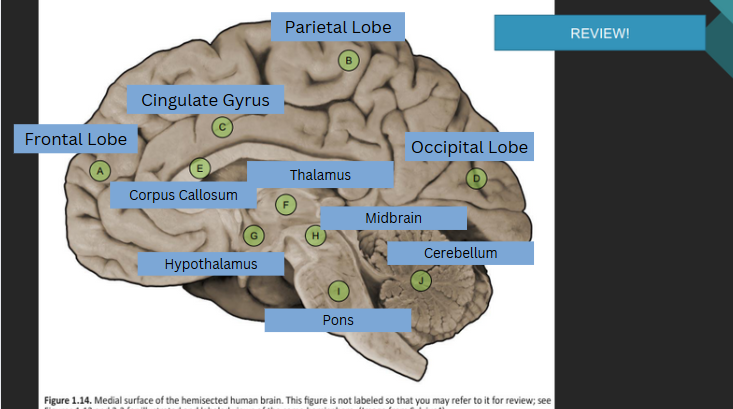
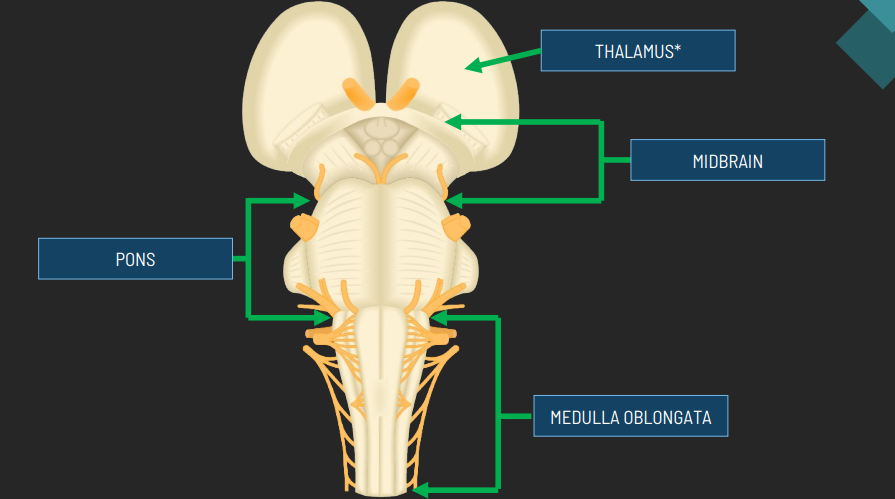
Thalamus
An area of the brain responsible for regulating many homeostatic functions, including hunger and thirst.
Hypothalamus
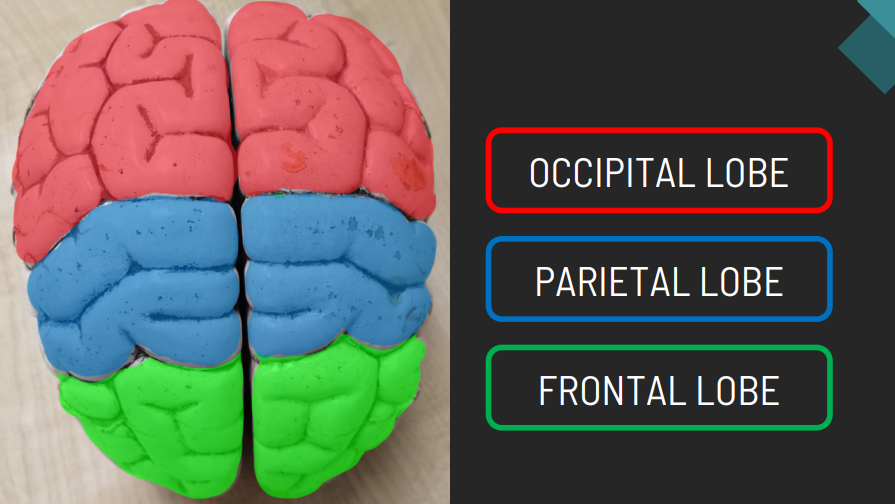
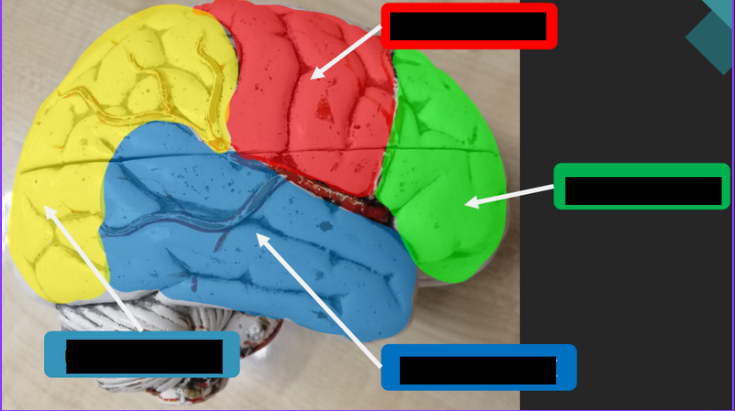
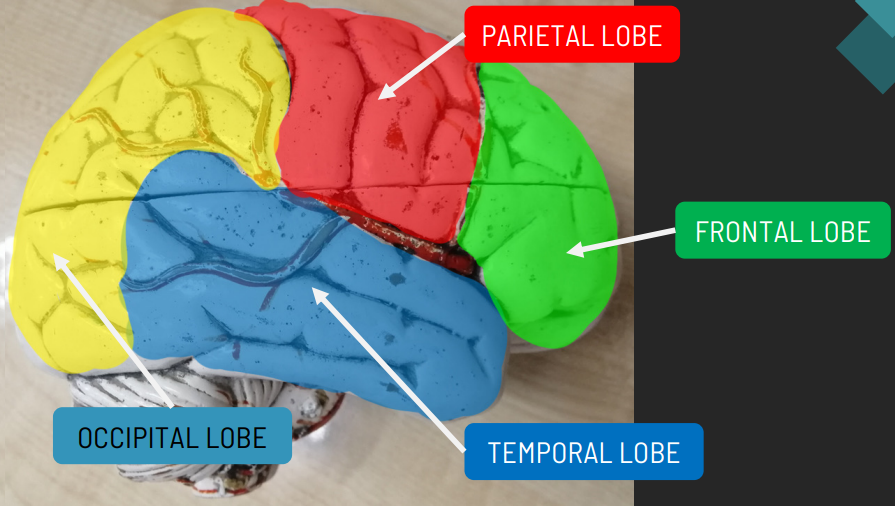
The lobe associated with reasoning, planning, movement, and problem-solving.
Frontal Lobe
The lobe responsible for processing sensory information related to touch, temperature, and pain.
Parietal Lobe
The lobe that processes visual information.
Occipital Lobe
The lobe associated with hearing, taste, and memory.
Temporal Lobe
Part of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for stressful or emergency situations.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Part of the autonomic nervous system that relaxes the body and conserves energy.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The process of forming a myelin sheath around the nerves to increase the speed of neural impulses.
Myelination

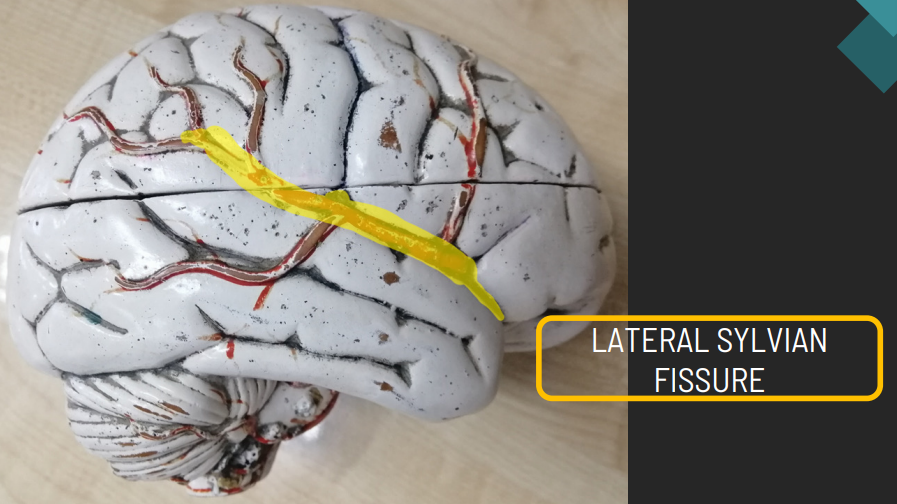
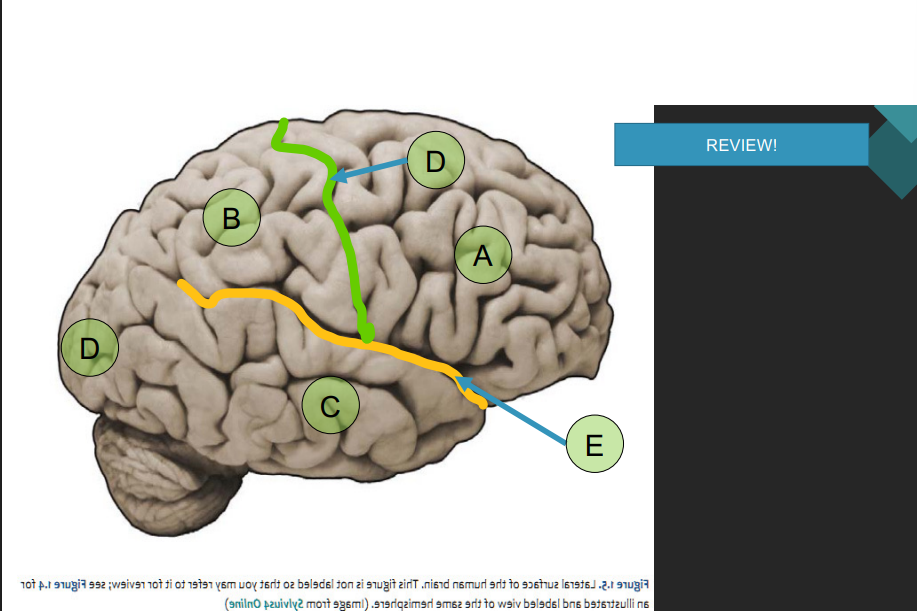
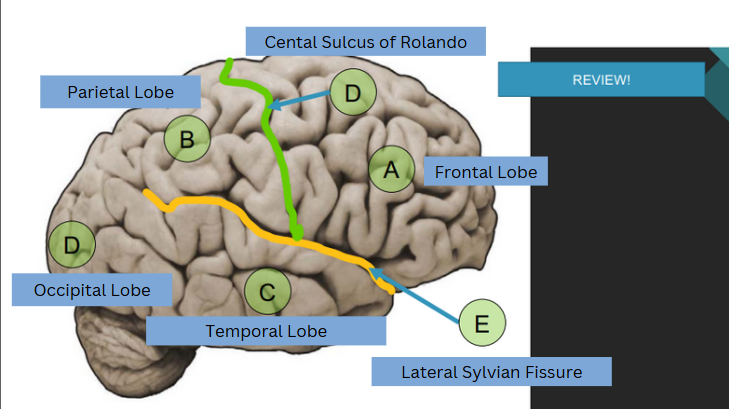
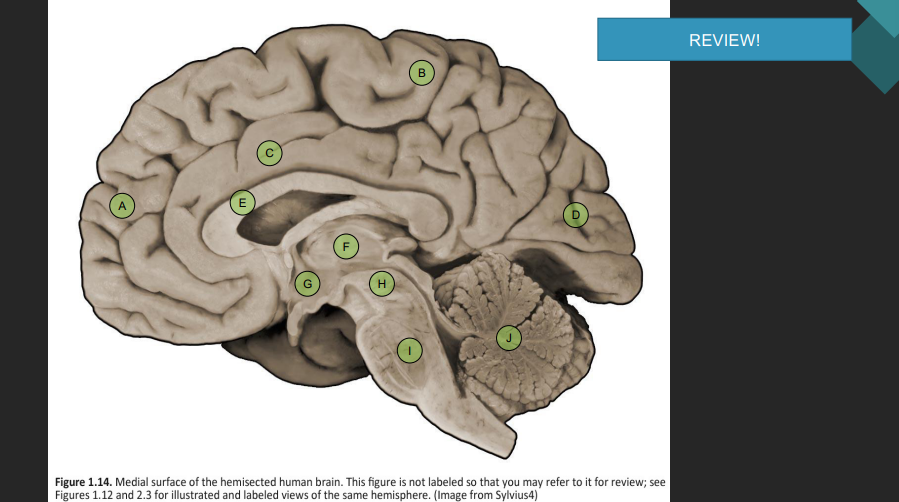
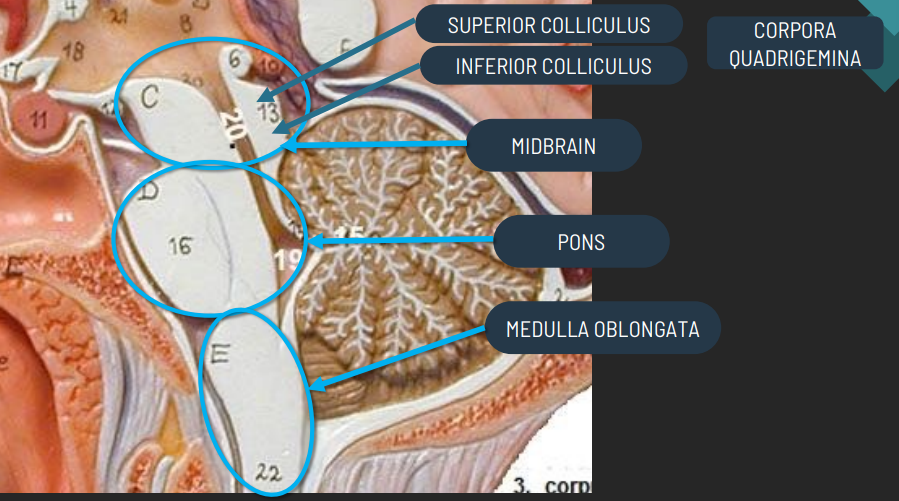
function of midbrain
Coordinates movement of head, eyes, & trunk in response to visual & hearing stimuli
Contribute to control of movement
Functions of Pons
Relays nerve impulses from motor areas of cerebrum to cerebellum
Control of breathing
Function of medulla oblangata
Control of heart beat and blood pressure
Control of breathing
Vomiting, swallowing, sneezing, coughing, & hiccups
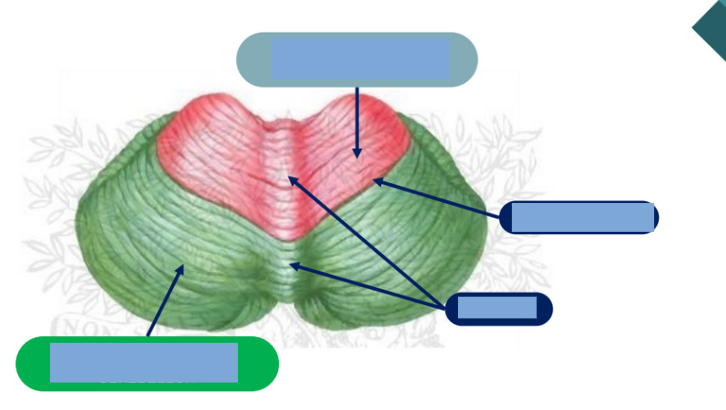
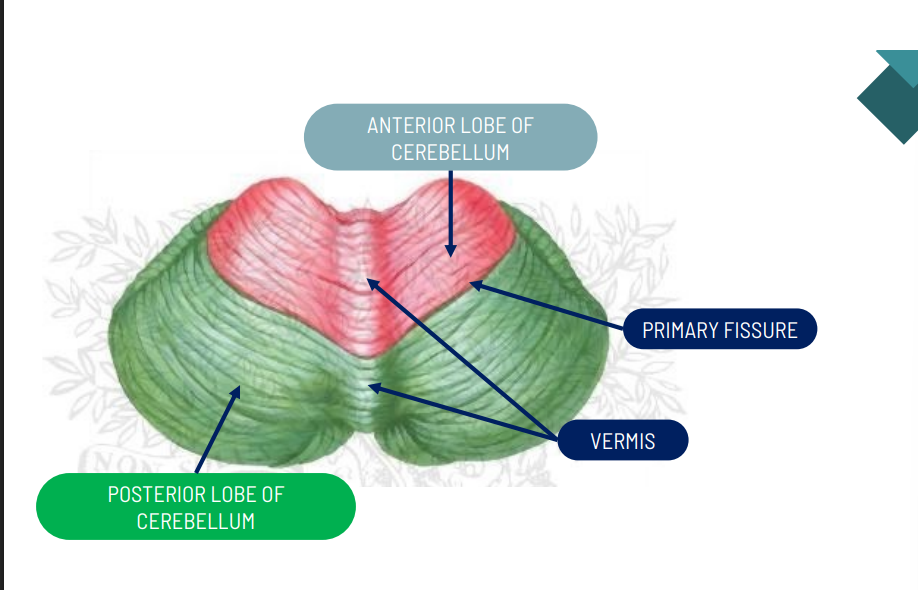
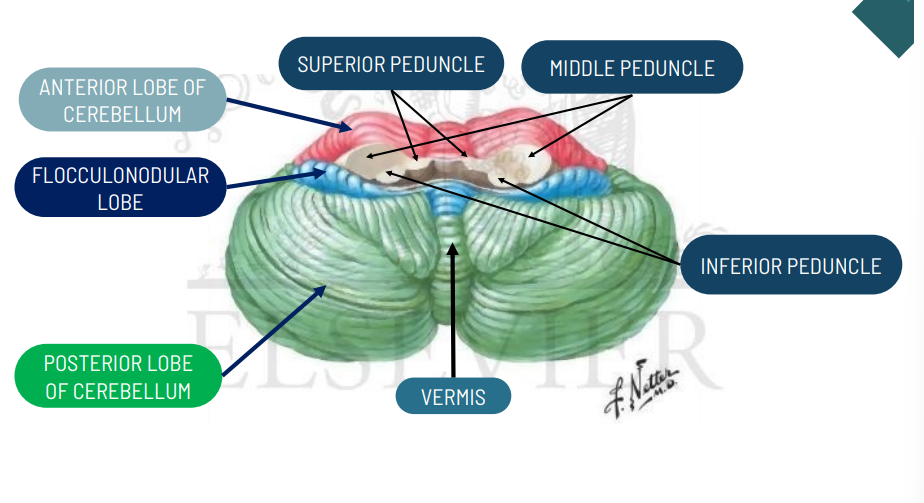
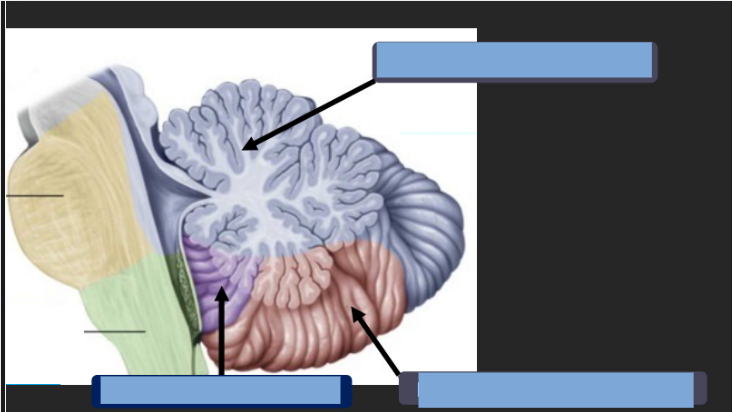
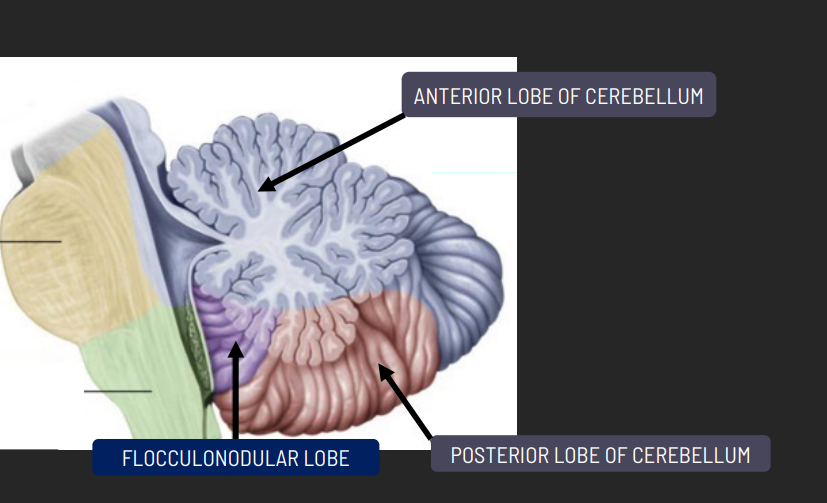
What are the parts of the cerebellum?
Anteriori Lobe: Spinocerebellum and Paleocerebellum
Posterior Lobe: Cerebrocerebellum and neocerebellum
Flocculonodular Lobe: Vestibulocerebellum and Archicerebellum
function of the Spinocerebellum and Paleocerebellum?
Trunk Control
function of the Cerebrocerebellum and neocerebellum?
Coordination
function of the Vestibulocerebellum and Archicerebellum?
Balance and Equilibrium
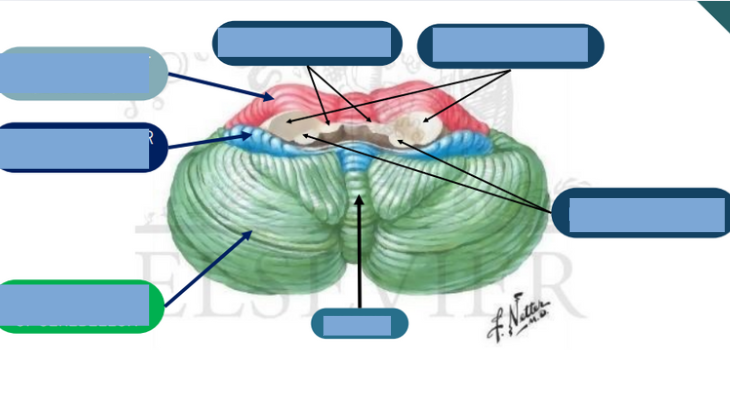
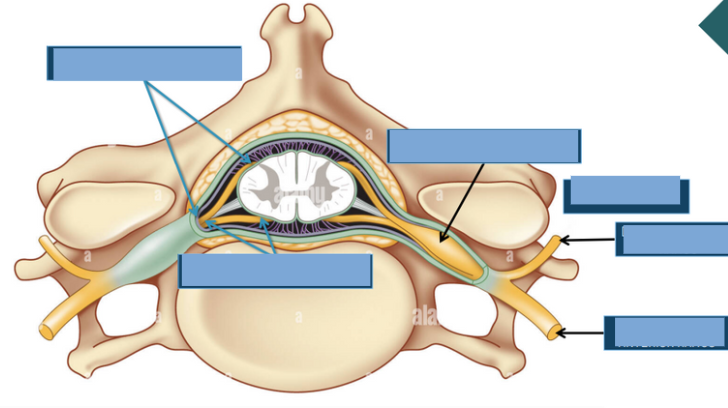
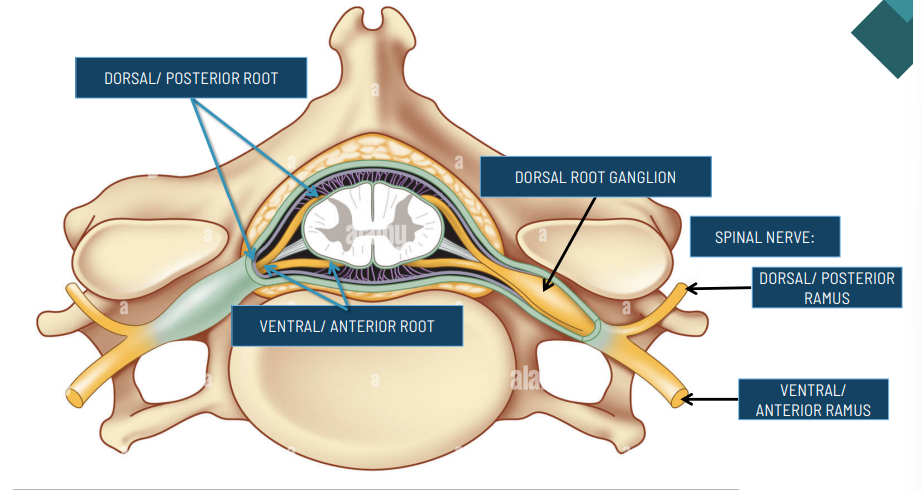
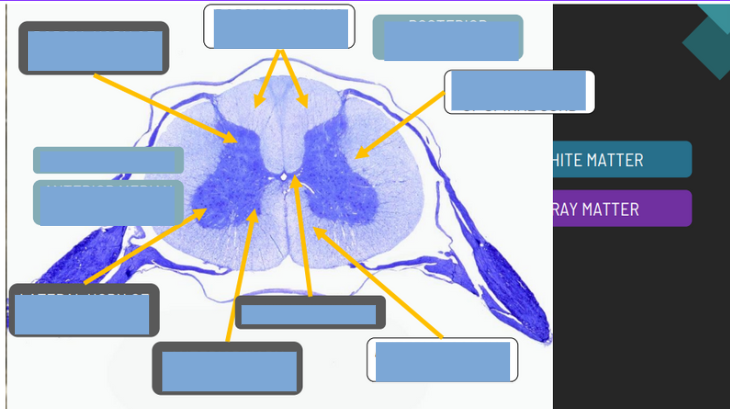
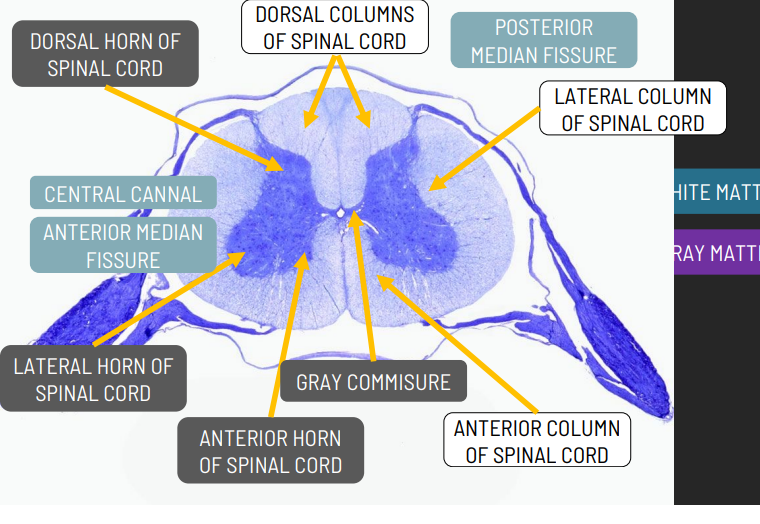
functioon of Dorsal/posterior Horn
receives sensory input
function of the ventral/anterior horn
sends motor impulses
function of the lateral horn
sympathetic nervous system
function of the dorsal columns
sensory input about proprioception
function the anterior columns
Sensory input about tactile sensations
function of the lateral columns
Sensory input about tactitle sensations
Characteristic and function of the parts of the cerebrospinal fluuid
• Clear, color less liquid composed primarily of water, small amounts of O2, glucose and other needed chemicals from blood ton neurons & neuroglia
• Total volume Is 80-150mL or 3-5oz
for mechanical protection, chemical protection, and circulation.
how is the flow of the cerebrospinal fluid?
CSF is produced by the choroid plexus in three main ventricles:
Lateral Ventricle → Flows through Foramen of Monroe
Third Ventricle → Flows through Aqueduct of Sylvius
Fourth Ventricle → Exits via Foramen of Luschka & Foramen of Magendie
CSF enters the subarachnoid space, where it circulates the brain and spinal cord.
CSF is drained into the arachnoid villi of the dural venous sinuses and reabsorbed into the bloodstream.
Arterial blood (from the heart and lungs) supplies oxygen and nutrients to maintain CSF production.