Pediatric Cognitive-Communication Disorders
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Pediatrics: Developmental Brain Injury
•brain injury that occurs prior to birth and can be caused by genetic, congenital or environmental factors
Pediatrics: Acquired Brain Injury
brain injury that occurs after birth but during childhood
•Trauma
•Infection
•Stroke
•Tumor
Pediatric interdisciplinary care team
•PT/OT/SP
•Physicians - Neuro, PM&R, etc.
•Psychology, Neuropsychology
•Pediatric Care Coordinator, Educational Support Team
•School, Teachers, Social Work
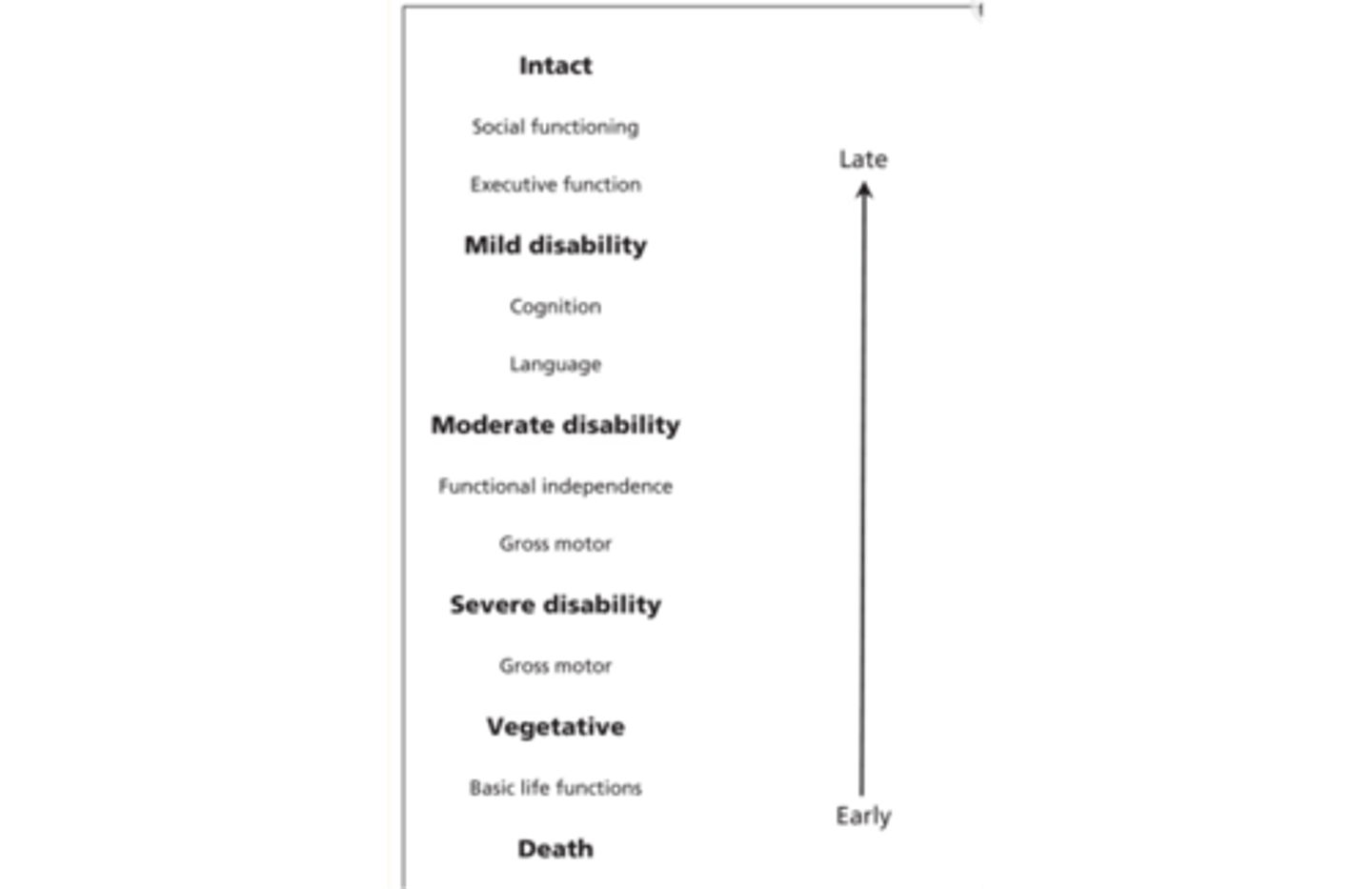
Pediatric outcomes
•Relationship of health constructs to stages of recovery and order in which abilities return after injury
Assessment - Objective Measures for pediatrics
•Pediatric Test of Brain Injury
•FAVRES - S
•RIPA - Primary
•Rivermead Behavioural Memory Test -Pediatric Edition
•Woodcock Johnson Test of Cognitive Abilities
•Behavioural Assessment of Dysexecutive Syndrome (BADS)
•*Be sure to checks norms and standardization methods*
Assessment - Case History for pedatrics
•Should always consider background and pre-injury characteristics
•Prior level of functioning
•Previous school services? or diagnoses?
•Previous grades (Favorite subject/least favorite subject)
-Core deficits inherent in executive functioning
Pediatrics: Core deficits inherent in executive functioning
establishing a framework to complete goal, starting, stopping, tracking, and switching may be circumvented by the controlled nature of standardized assessment measures
Pediatrics: Language Versus Cognition?
Language is embedded in cognition
•Consider naming tests - most brain injury assessments will have language components/subtests
•Consider age-appropriate convergent and divergent naming tasks
•Language sample
•Consider age-appropriate phonological awareness tasks and premorbid levels
•Parent report
Pediatrics and attention
•Consider all types of attention and how they relate to school/premorbid activities- try to simulate all in order to determine deficits and effectiveness in different environments
•Breakdowns may depend on the complexity of the task
Expected attention spans by age
•2 year old: 4-6 min
•4 year old: 8-12 min
•6 year old: 12-18 min
•8 year old: 16-24 min
•10 year old: 20-30 min
•12 year old: 24- 36 min
•14 year old: 28-42 min
•16 year old: 32-48 min
•These are just averages to consider
Pediatrics and memory
•Be able to discern if the breakdown is occurring at the attention, encoding, storage or retrieval process level
•Determine appropriate compensatory strategies
•Internal strategies
•External strategies and aids
•Consider the complexity of working memory tasks
•Be aware of the high demand of new learning for students – usually assessment and treatment sessions only span the course of ~30 min – 1 hour
What Do Executive Functioning Deficits Look Like in Peds?

Peds treatment
•Balancing motivating activities and those that address cognitive functions necessary for successful return to school
•Types of activities and how you address deficits will be dependent on age of the child
•For younger children important to be aware of developmental norms
Treatment - Metacognition and Strategy Training for Peds
•Planning, monitoring and adapting/modifying plans
•Think Aloud Tasks
•Consider all tasks that might be required in school
•Ask questions like how can we prepare for this task? How ill I know when I need to take a break? What are the steps to complete this? Why did you make that decision? Would you do anything differently next time?
•Don't fall into the TUTOR TRAP - teach skills that generalize across contexts
Peds education
•Educate family, caregivers of recommended strategies
•Family/caregivers should be a part of sessions
•Educate teachers, paraprofessionals, etc. on brain injury and deficits
•Family empowerment - connecting with resources, advocacy tools, etc.
•Family involvement is a key prognostic indicator of recovery and return to functional independence
•Consider the psychological impact of injury to all involved and especially the patient
Peds: return to school
•School integration should be gradual with close monitoring of successes and challenges
•Homebound tutoring is available for students who are not medically appropriate to return to school yet
•Communication between rehab team and school is essential for successful return
•Patient can still continue to receive OP SP services as needed when returning to school
Recommendations and Accommodations for Peds
•Consider what a child's deficits are - there are NOT universal recommendations - recommendations should be individualized
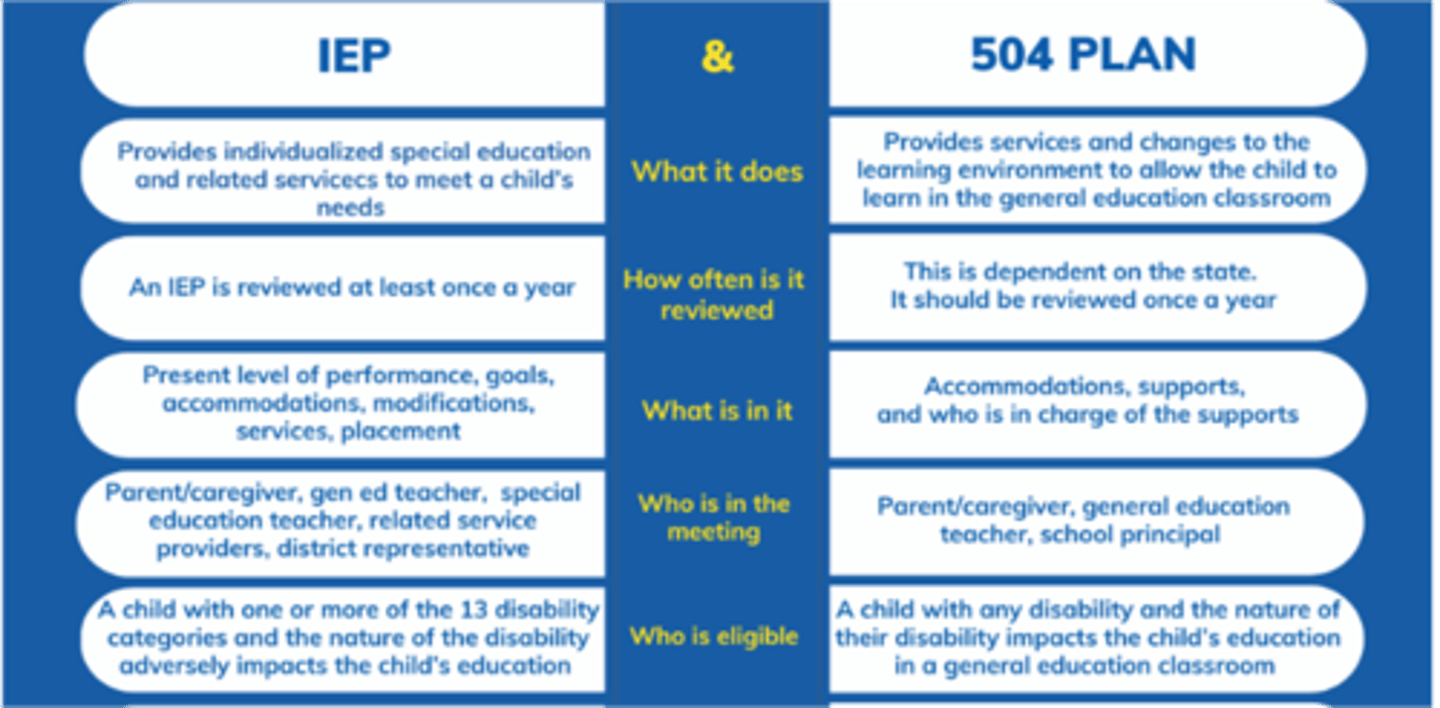
504 VS. IEP