Infection Control Unit
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Pathogens
Microorganisms that cause infection and disease
Microorganisms
Organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells
Aerobic
Survive and grow in an oxygenated environment
Asepsis
No living disease-causing microorganisms are present
Disinfectant
Chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces
Sterilization
Chemical that is applied to inanimate objects to kill all microorganisms as well as spores
Anaerobic
Germs that can survive and grow where there is no oxygen
Antiseptic
Reduce or stop the growth of potentially harmful microorganisms on the skin and mucous membranes
Contaminated
Impurity, or some other undesirable element that renders something unsuitable, unfit or harmful for both physical body or nature
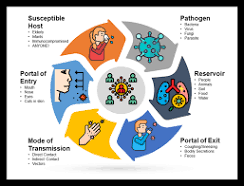
Chain of Infection
Infective agent
Reservoir
Portal of Exit
Mode of Transmission
Portal of Entry
Susceptible host
Bacteria
Antibiotics are usually effective
Protozoans
Some antibiotics may be effective
Fungi
Antibiotics are not effective; need antifungals
Rickettsiae
Antibiotics are effective
Viruses
Antibiotics are NOT effective
Two Viral Disease of Major Concern to Healthcare Workers
Hepatitis B/C and AIDs
Endogenous
Infection or disease originates
within the body.
Exogenous
Infection or disease originates
outside the body
Nosocomial
Infection acquired by a patient
while inside a healthcare facility
Opportunistic
Infection or disease that occur when the immune system weakened.
Localized
Infection is restricted to a specific area
Sepsis
An infection has spread throughout the whole body
Common Aseptic Techniques
1. Handwashing
2. Good personal hygiene
3. Use of gloves when handling contaminated
materials
4. Proper cleaning of instruments and equipment
5. Cleaning of the environment
Antiseptics
Prevent or inhibit growth of most pathogens.Can be used on the skin
Disinfection
Chemicals that kill pathogens, but not all viruses,
spores, or prions. Used mainly on objects – can damage skin
Sterilization
Destroys all pathogens except prions. Uses
steam under pressure, gas, radiation, or chemicals. Used ONLY on objects, never people
When to wash hands
Upon arrival and before leaving medical facility
Before and after every patient contact
If hands become contaminated during a procedure
After removing gloves
After handling any specimen
After contact with any contaminated item
After picking up item off floor
After use of bathroom
After coughing, sneezing, or using tissue
Before eating
Before inserting or removing contact lenses
Order of Handwashing
Turn on the water
Verbalize temperature (lukewarm)
Do NOT lean against sink/counter- Wash for at least 20 seconds.
Wet hands: wrist-hands-fingers pointed down
Lather with soap (enough to cover hands/wrists with visible lather)
Surfaces->wrist-hands(front/back)->fingers
Interlace fingers with the opposite hand
Cleans fingernails circular motion on the opposite palm
Rinses hands/wrists pointing down (lower than elbow)
Dries using a paper towel in correct order (wrists->hands->fingers)
Turns off sink/water with a paper towel
Donning PPE
Gown
Mask
Goggles
Gloves
Doffing PPE
Gloves
Goggles
Gown
Mask
Rules developed by the CDC to protect workers and
patients.(Standard Precautions)
Every body fluid must be considered a potentially
infectious material, and all patients must be considered potential sources of infection, regardless of their diagnosis or disease