human bio
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
DNA- deoxyribonucleic acid
contains genetic information about organisms within nucleus of our cells. capable of self- replication
Purpose of DNA
for organism survive, develop and reproduce → production of proteins, regulation, metabolism + reproduction of cell
Structure of DNA
shaped like double-stranded helix (like a corkscrew)
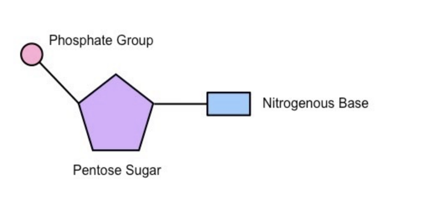
Nucleotide: (building blocks)
make up backbone of DNA
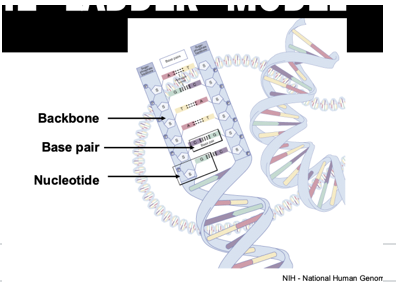
DNA model (ladder)
Twisted ladder
label sugar, hydrogen, phosphate, nitrogenous
sides= sugar phosphate backbone
Rung: bases: AT, GC
4 different Nitrogenous base
Thymine (T):
Adenine (A):
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G):
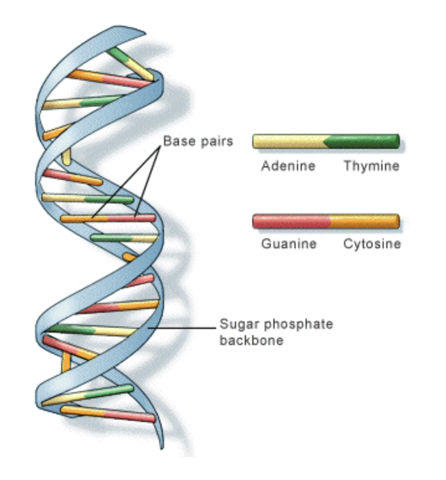
Within a DNA chain
- Adenine - Thymine (u) : AT
Guanine - Cytosine: GC
Genes + chromosomes
Each cell contains approx. 1.8m of DNA
Coils around histones (proteins) to allow it to condense
• Chromosomes only present when cell replication is occurring.
• DNA is usually found as chromatin
• 23 pairs or 46 chromosomes in each cell
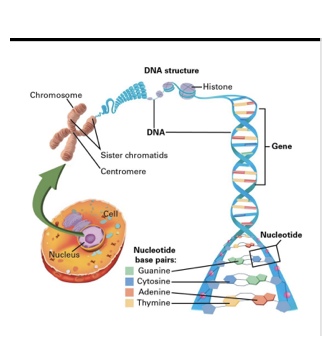
Function of DNA genes
1. chromosome consists of segments of DNA (genes)
2. Genes contain the instructions for the construction of a particular protein, or RNA.
3. estimated about 20,000–25,000 genes in human genome ( 3 b base pairs).
Purpose of proteins:
important role in many bodily functions
Humans use 1 billion proteins every day to function
• Build and repair tissues
• Enzymes to break down substances
• Hemoglobin in blood carries oxygen
• Hormones regulate development
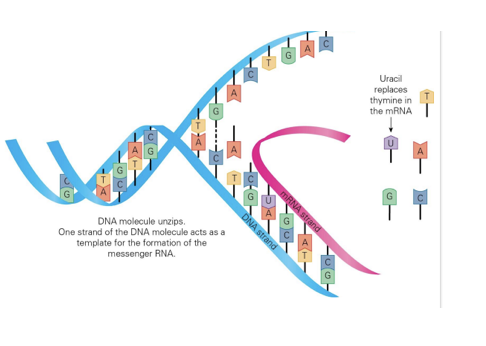
Protein synthesis transcription:
Happens in the nucleus of the cell
DNA → messenger RNA (mRNA)
An enzyme binds to the DNA at the gene being copied
The DNA strand unwinds
One side of the strand is read
A complementary copy of the strand is made - mRNA
The only difference is Uracil (U) replaces Thymine (T)
The mRNA moves away from the DNA and the DNA strand is zipped back up
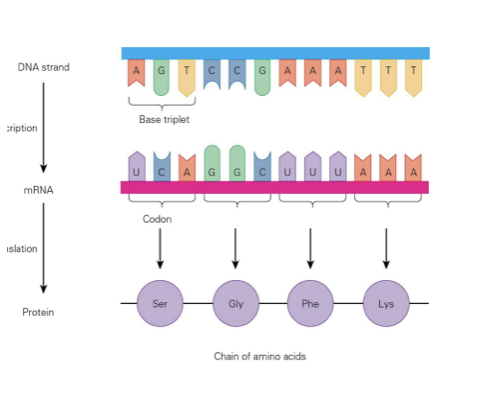
Translation:
mRNA moves into the cytoplasm and binds to a ribosome
The ribosome reads the mRNA one codon at a time (3 bases)
Each codon is code for a specific amino acid
The amino acids are joined together to form a protein
DNA mutations:
changes in nucleotide sequence of DNA
> somatic cells/mutation
- in normal body cells
- not passed on to offspring
Mutations
hange in nucleotide sequence of DNA
Somatic mutation:
not passed on + occurs in body cells
Gremlin mutation:
- in gametes (sex cells)
- can be passed on, cause inherited disease
Helpful or harmful?
happen regularly
Usually neutral
Caused by mutagens (chemicals, UV)
Many mutations healed by enzymes
Some are benefits
Point mutation: (one base changes)
Change in ONE nucleotide
point mutation:
Intersection: extra base added
Deletion: base is removed
Substitution: one base is swapped (A->G)
Sickle cell disease
result of one nucleotide substation (in haemoglobin gene)
Frame shift mutation
inserting or deleting one or more nucleotides
Changes reading frame like changing a sentence
Proteins built incorrectly
DNA fingerprinting
tracing ancestry
Forensic science e.g
Identification of carriers of hereditary disease
Early detection of inherited disease e.g certain cancers
Risk of passing on disease
Parentage e.g who did is for child
Research e.g species of fossils
forensics:
all bands are the same= same person
*parentage:
about half of bands from each parent
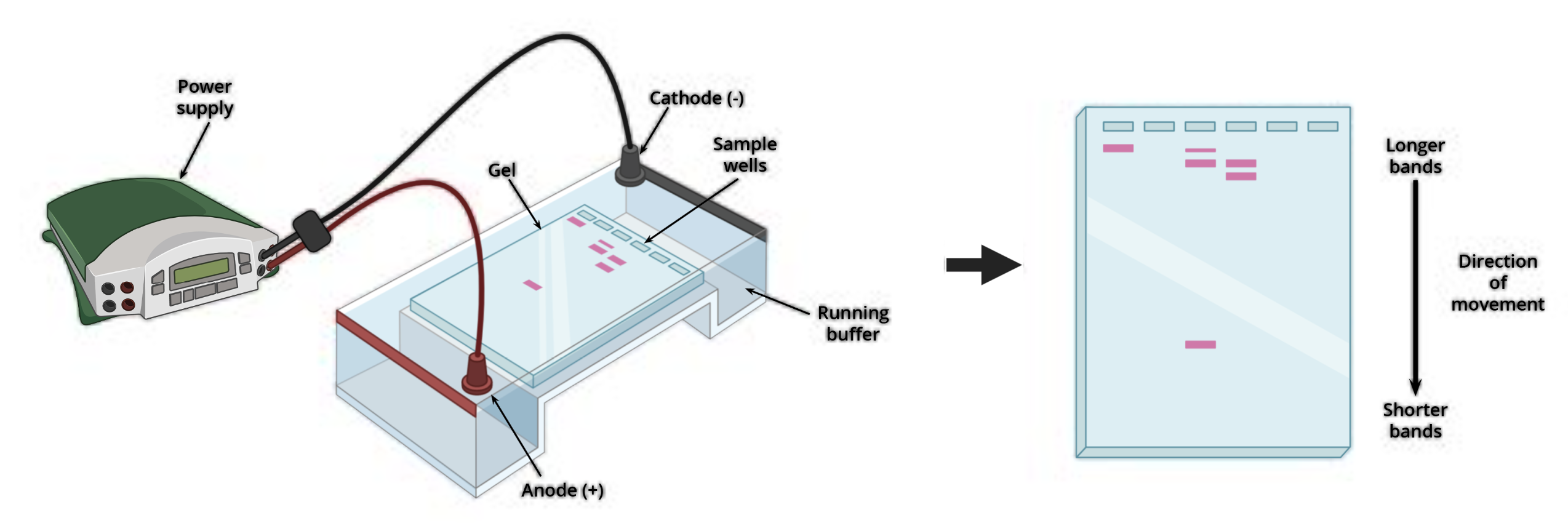
Gel electrophoresis: 1984 profiling techniques
DNA cut by enzymes then placed on semi solid gel bed
Electric current passed through plate
DNA negatively charged- moves towards positive electrode
Smaller piece's= faster + further, lager pieces= slower
PRC: polymerase chain reaction
fast + inexpensive technique used to ‘amplify’ (copy) small segments of DNA
Need a significant amount of DNA to perform molecular and genetic analyses
Studies of isolated DNA are nearly impossible without PCR amplification
Once amplified the DNA can be used in many procedures including DNA fingerprinting and diagnosis of genetic disorders
steps of PCR
Denaturing - 94-95ºC: Heat DNA to break hydrogen bonds between bases – 2 single strands
Annealing – 50-56ºC: Primers bind to complementary strand on target sequence
Extending – 72ºC: Starting at the primer, the DNA polymerase reads the DNA code and builds a complementary strand of DNA – each strand can then be used to create 2 new copies and so on
Can be repeated as many as 30-40 times leading to the creation of more than 1 billion exact copies of the original strand
Ethical issues:
Do benefits outweigh risks?
What will happen if info is stolen?
Cases (parentage) where DNA was obtained without consent