Kaap 309: Spinal Cord, PNS, and Synapses
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Spinal Cord Anatomy
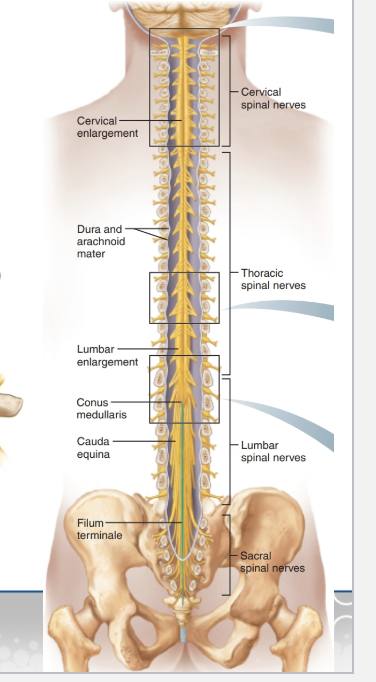
Where it runs: From foramen magnum → L1/L2.
Enlargements:
Cervical: upper limbs.
Lumbosacral: lower limbs.
End structures:
Conus medullaris: cone-shaped end.
Filum terminale: string that anchors cord to coccyx.
Cauda equina: bundle of nerves (horse’s tail).
Spinal Cord Anatomy (Internal Structure)
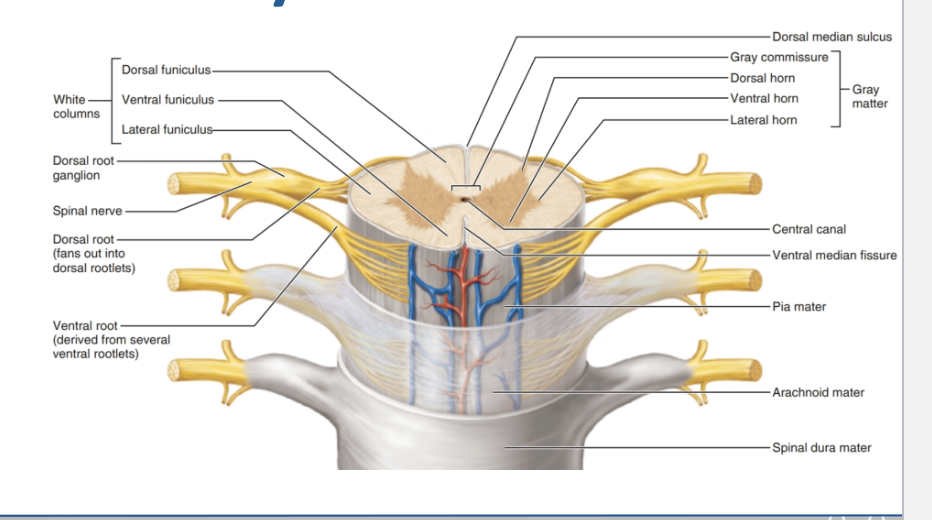
Gray Matter (H-shaped in center):
Dorsal horn → sensory input
Ventral horn → motor output
Lateral horn → autonomic (only in thoracic & upper lumbar levels)
White Matter (outer area):
Organized into funiculi (columns):
Dorsal funiculus
Lateral funiculus
Ventral funiculus
Spinal Cord Cross-Section
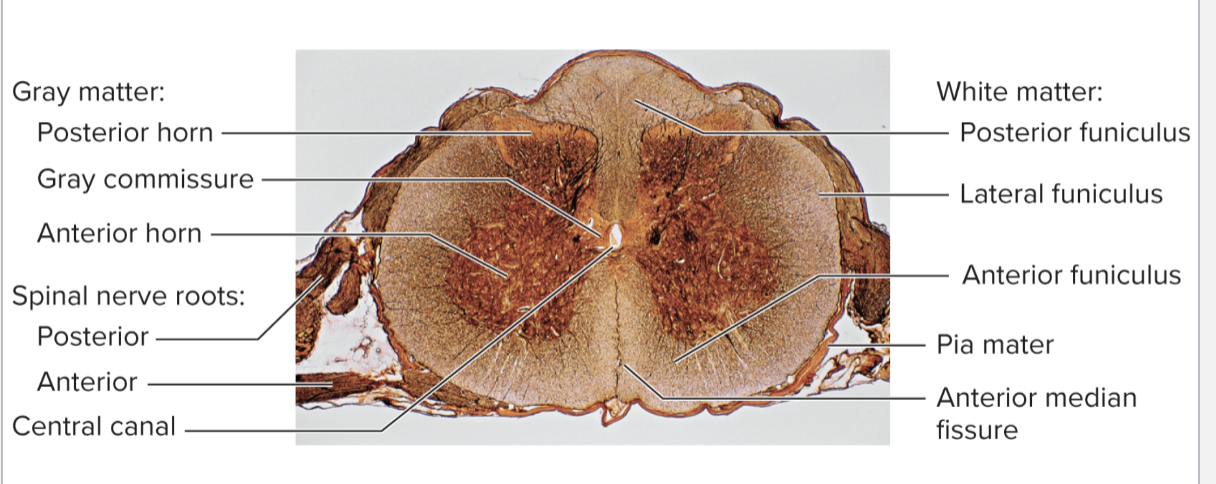
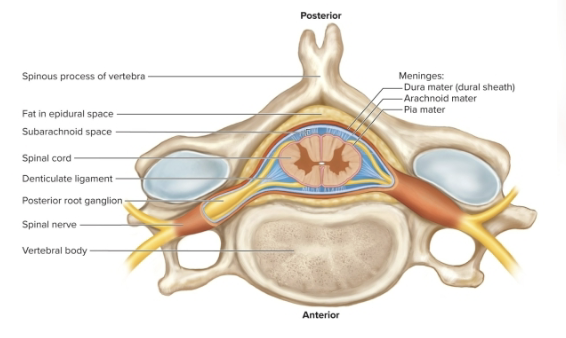
Spinal Nerve Roots
Anterior (ventral) root → Motor (efferent) → to skeletal muscles
Posterior (dorsal) root → Sensory (afferent) → from receptors
Ventral root + Dorsal root = Spinal nerve (mixed motor + sensory)
Ventral = Motor → Muscles
Dorsal = Sensory → Detect
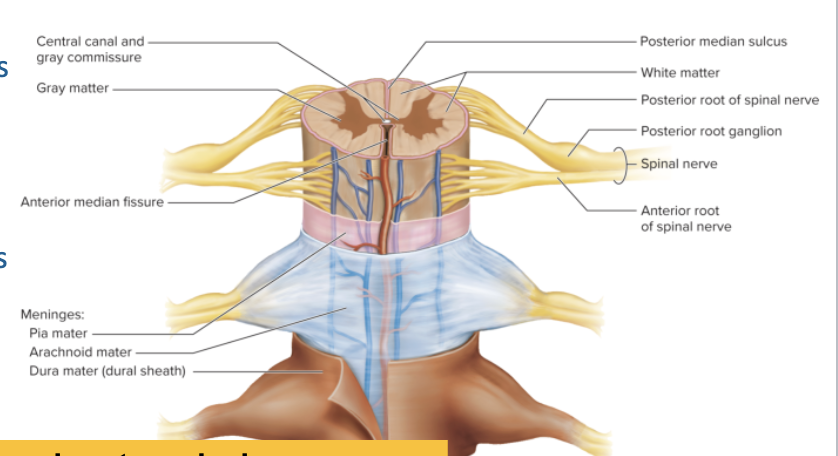
Functional Cross-Section
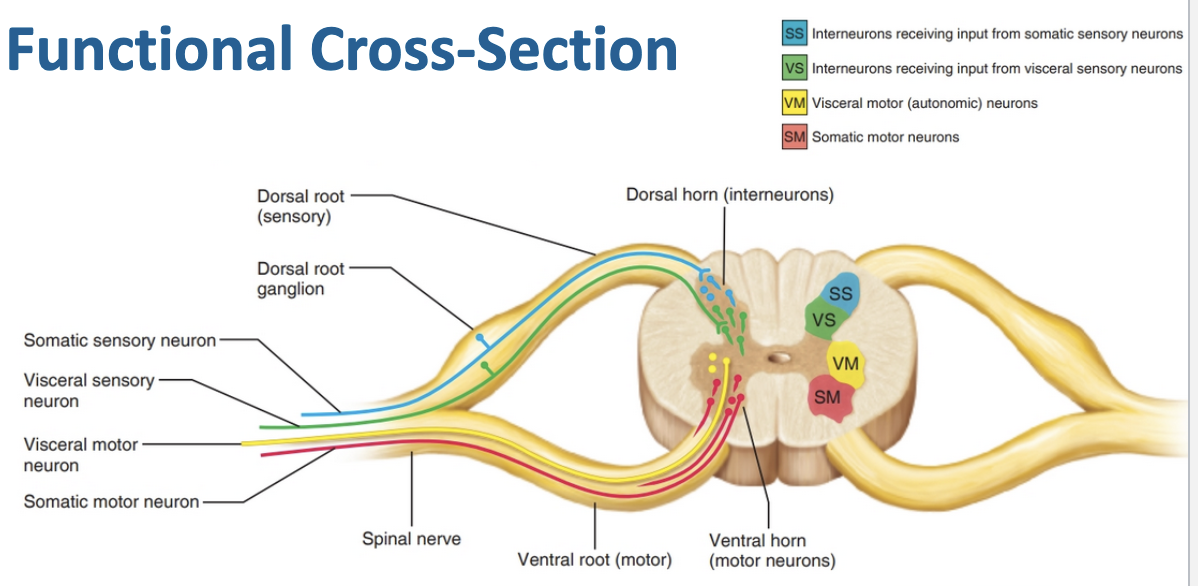
Spinal Nerve Rami
Dorsal root → sensory (afferent)
Ventral root → motor (efferent)
Dorsal root + Ventral root = Spinal nerve (mixed: sensory + motor)
After spinal nerve forms, it splits into:
Dorsal rami → supply back muscles & skin of back
Ventral rami → supply limbs & anterior/lateral trunk (form plexuses)
Naming Spinal Nerves
31 pairs total
8 Cervical (C1–C8)
12 Thoracic (T1–T12)
5 Lumbar (L1–L5)
5 Sacral (S1–S5)
1 Coccygeal (Co1)
“Breakfast at 8, Lunch at 12, Dinner at 5 + 5 + 1.”
Specific Spinal Nerves
C6 → 6th cervical spinal nerve
C7 → 7th cervical spinal nerve
T1 → 1st thoracic spinal nerve
T2 → 2nd thoracic spinal nerve
PNS Receptors (by Stimulus Type)
Mechanoreceptors → respond to touch, pressure, vibration, stretch
Thermoreceptors → respond to temperature
Photoreceptors → respond to light (in the eye)
Chemoreceptors → respond to chemicals (taste, smell, blood pH, O₂, CO₂)
Nociceptors → respond to pain (damage, extreme heat/cold, chemicals)
“Many Tiny People Can Nap” = Mechanoreceptors, Thermoreceptors, Photoreceptors, Chemoreceptors, Nociceptors.
PNS Receptors (by Location)
Exteroceptors → respond to stimuli outside the body
Example: skin (touch, pressure, pain, temperature), special senses (vision, hearing, smell)
Interoceptors (visceroceptors) → respond to stimuli inside the body
Example: internal organs (stretch, chemical changes, temperature, pain)
Proprioceptors → respond to body position/movement
Found in skeletal muscles, tendons, joints, ligaments, inner ear
PNS Receptors (by Structure)
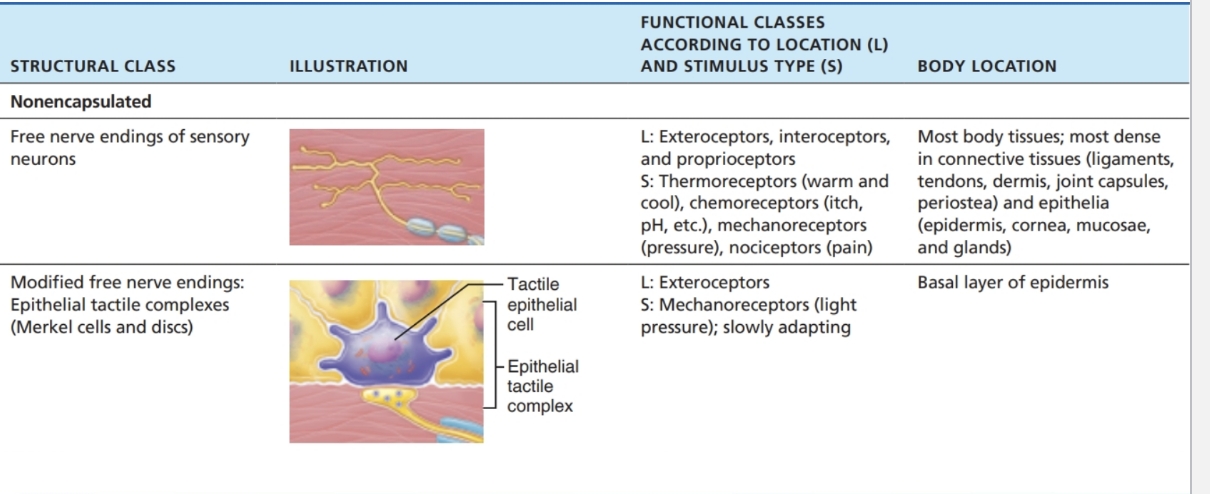
Nonencapsulated (free nerve endings):
Simple, unmyelinated endings
Found in epithelia & connective tissue
Detect pain, temperature, light touch, hair movement
Encapsulated (nerve endings wrapped in connective tissue):
More complex, specialized.
Examples:
Meissner’s corpuscles → light touch
Pacinian corpuscles → deep pressure & vibration
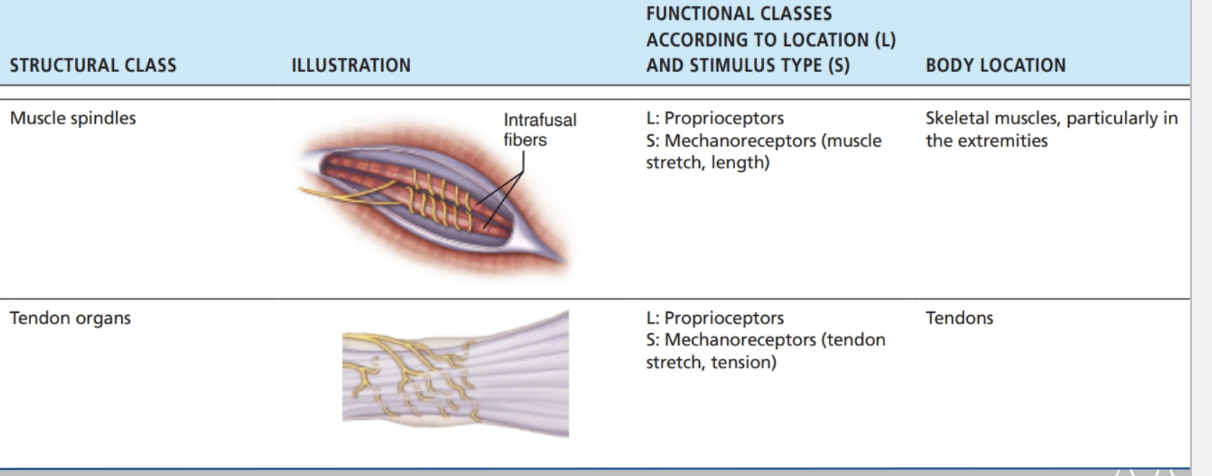
Muscle spindles, tendon organs, joint receptors → proprioception
PNS Receptors - Nonencapsulated
PNS Receptors – Encapsulated (I)
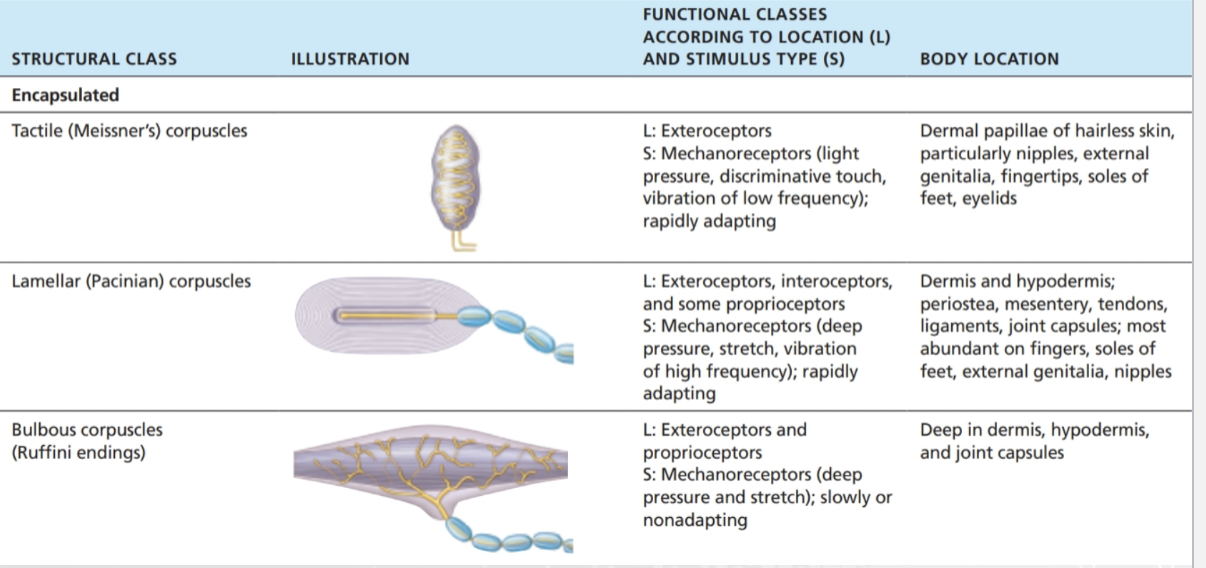
PNS Receptors – Encapsulated (II)
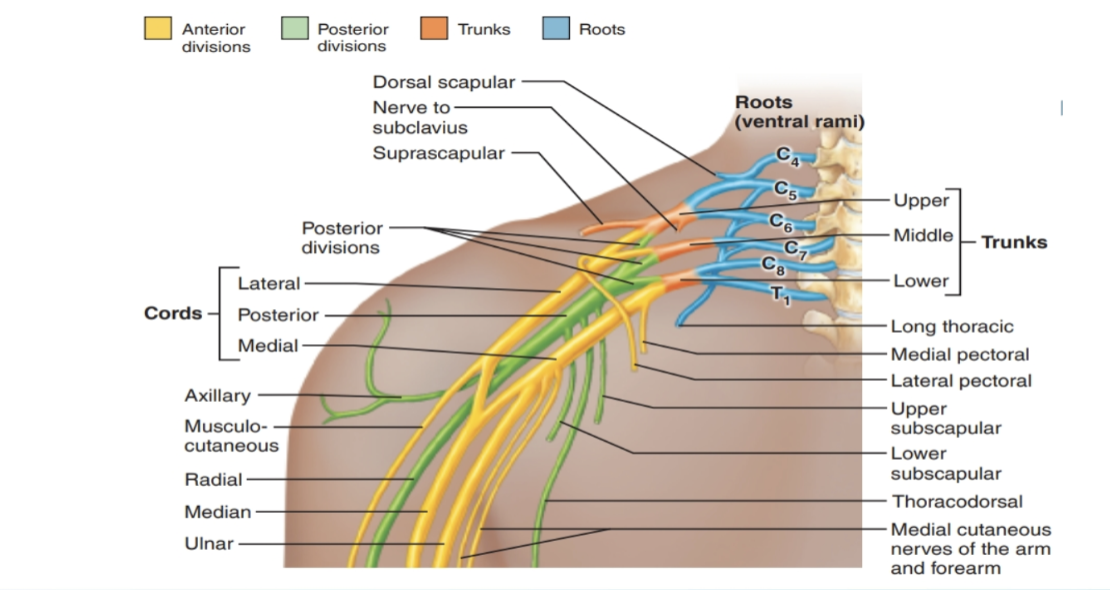
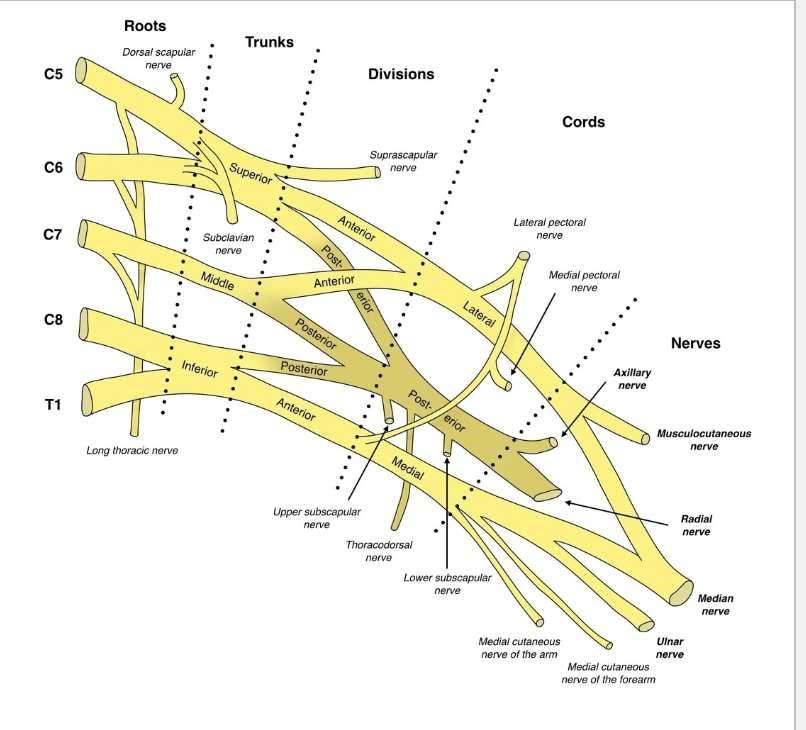
Brachial Plexus
Function: Provides almost all nerves to the upper limb
Spinal nerve contributions: (C4) C5–T1
Location: Emerges between anterior & middle scalene muscles
Organization (Remember: “Randy Travis Drinks Cold Beer”):
Roots (ventral rami C5–T1)
Trunks (upper, middle, lower)
Divisions (anterior & posterior)
Cords (lateral, posterior, medial)
Branches (terminal nerves: musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, median, ulnar)
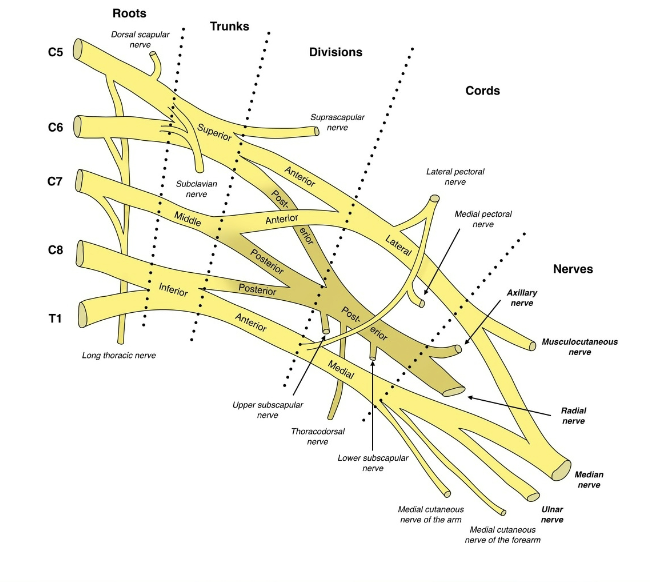
Terminal Branches of the Brachial Plexus
Musculocutaneous nerve → anterior arm (flexors, skin of lateral forearm)
Axillary nerve → deltoid & teres minor, skin of shoulder
Radial nerve → posterior arm & forearm (extensors, back of hand)
Median nerve → anterior forearm (flexors), most hand lateral palm & fingers
Ulnar nerve → forearm & most hand medial side (funny bone nerve)
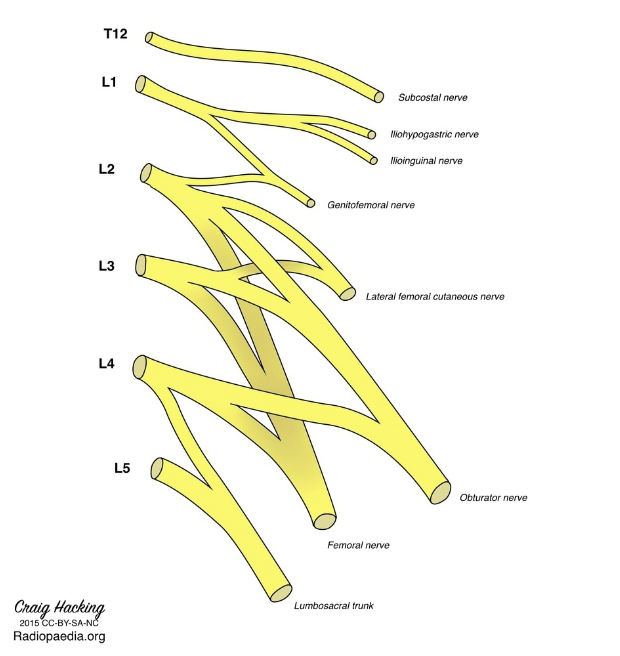
Lumbar Plexus
Function: Provides nerves to the lower abdomen, anterior & medial thigh
Spinal nerve contributions: L1–L4
Major Terminal Branches:
Femoral nerve → anterior thigh muscles, skin of anterior thigh & medial leg
Obturator nerve → medial thigh muscles, skin of medial thigh
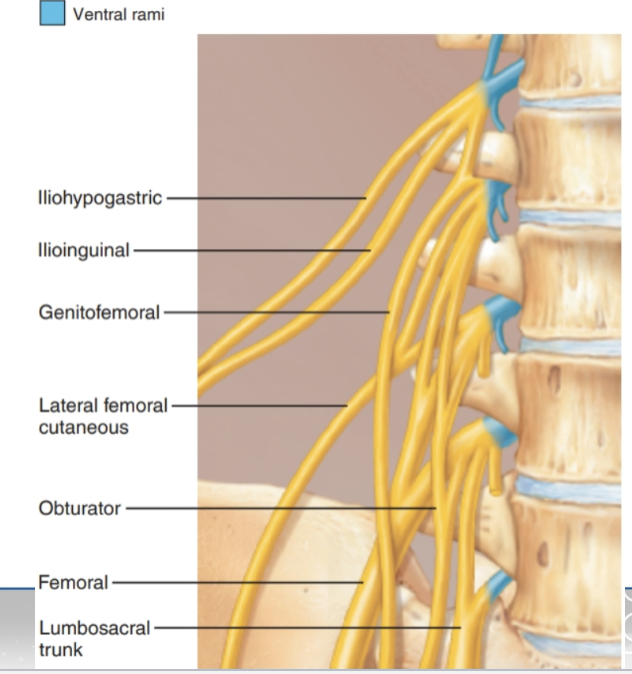
Lumbar Plexus
Sacral Plexus
Function: Provides nerves to the pelvis, posterior thigh, and most of the leg & foot
Spinal nerve contributions: L4–S5
Location: Emerges through the pelvis inferior to the piriformis muscle
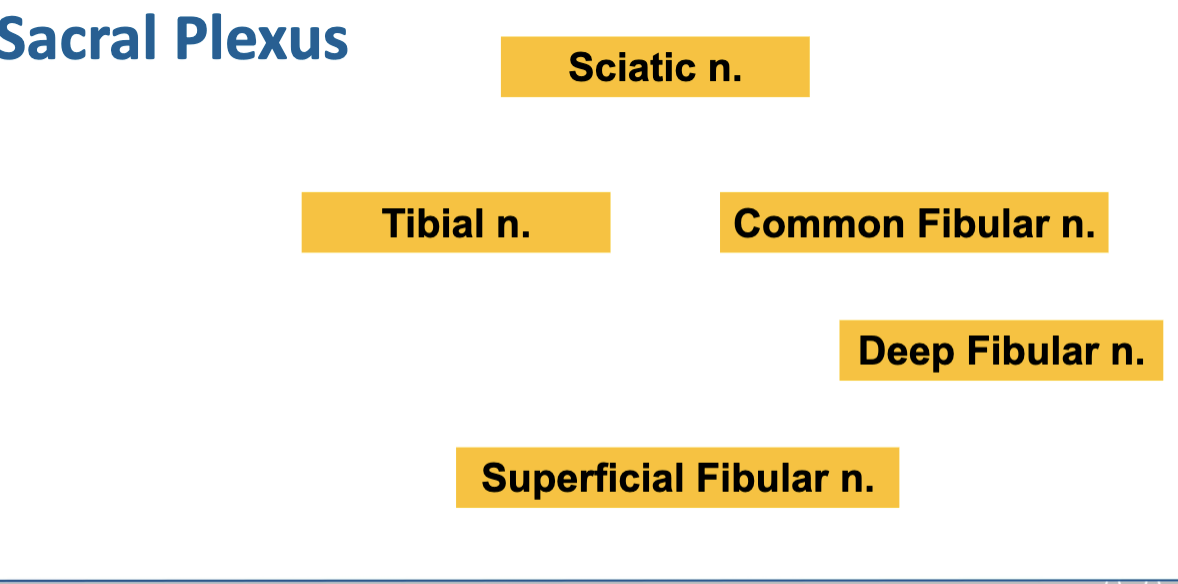
Major terminal branch: Sciatic nerve (splits into tibial & common fibular nerves)
Sacral Plexus
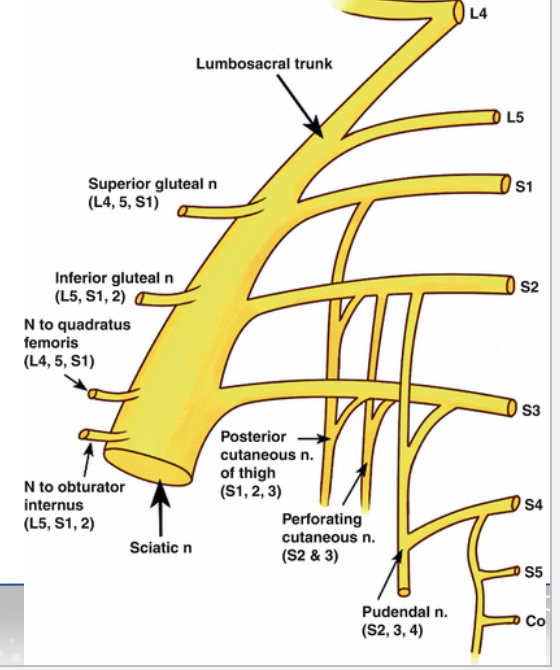
Sacral Plexus – Sciatic Nerve Branches
Sciatic nerve → largest nerve in the body, posterior thigh & leg
Tibial nerve → posterior leg & plantar foot
Common fibular (peroneal) nerve → lateral & anterior leg
Superficial fibular nerve → lateral leg muscles, dorsum of foot
Deep fibular nerve → anterior leg muscles, skin between first two toes
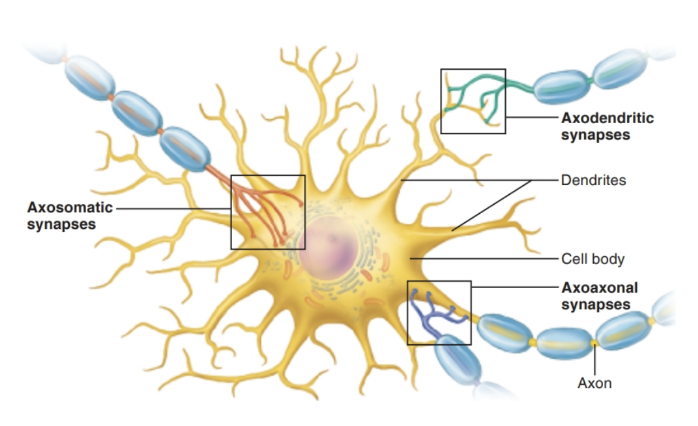
Synapses
Definition: Junction that transmits information from one neuron to another
1. Location (where the synapse occurs):
Axosomatic → axon → cell body
Axodendritic → axon → dendrite
Axoaxonal → axon → axon
2. Type (how the signal is transmitted):
Electrical → direct current flow through gap junctions
Chemical → via neurotransmitters across a synaptic cleft
Key Terms:
Presynaptic neuron → sends the signal
Postsynaptic neuron → receives the signal
Chemical Synapses
Definition: Use neurotransmitters to transmit signals between neurons
Components:
Axon terminal (presynaptic) → releases neurotransmitters
Receptor region (postsynaptic) → usually on dendrite or cell body
Synaptic cleft → small gap between presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons
Synaptic delay: Time it takes for signal to cross the synapse (0.3–5.0 ms) → rate-limiting step in transmission
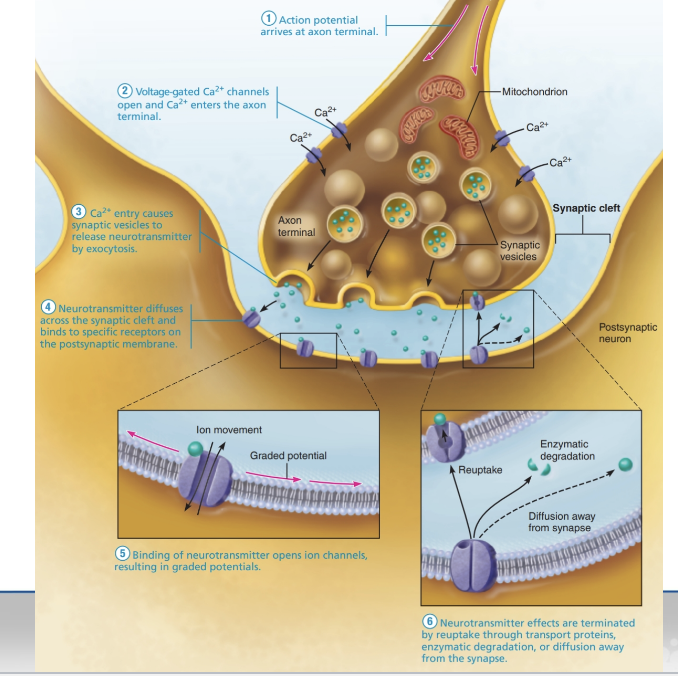
Chemical Synapse Transmission
Action potential arrives at the axon terminal.
Voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels open, allowing Ca²⁺ to enter the terminal.
Ca²⁺ triggers synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters via exocytosis into the synaptic cleft.
More frequent impulses → more vesicles released.
Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to postsynaptic receptors.
Ion channels open on the postsynaptic neuron → graded potentials form → neuron may be excited or inhibited depending on the neurotransmitter.
Neurotransmitter effects end via:
Reuptake by cells (e.g., astrocytes)
Enzymatic degradation
Diffusion away from the synapse
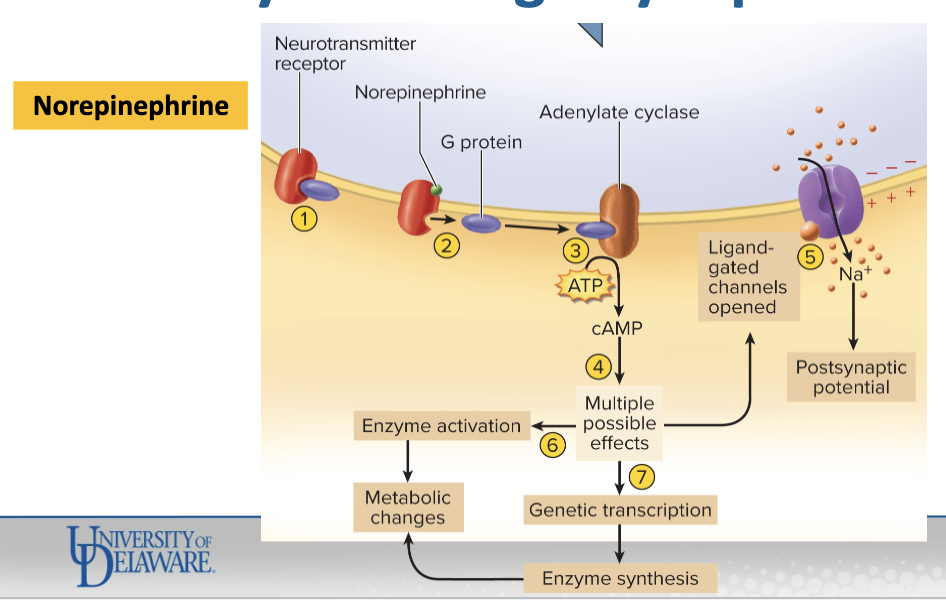
Specific chemical synapses
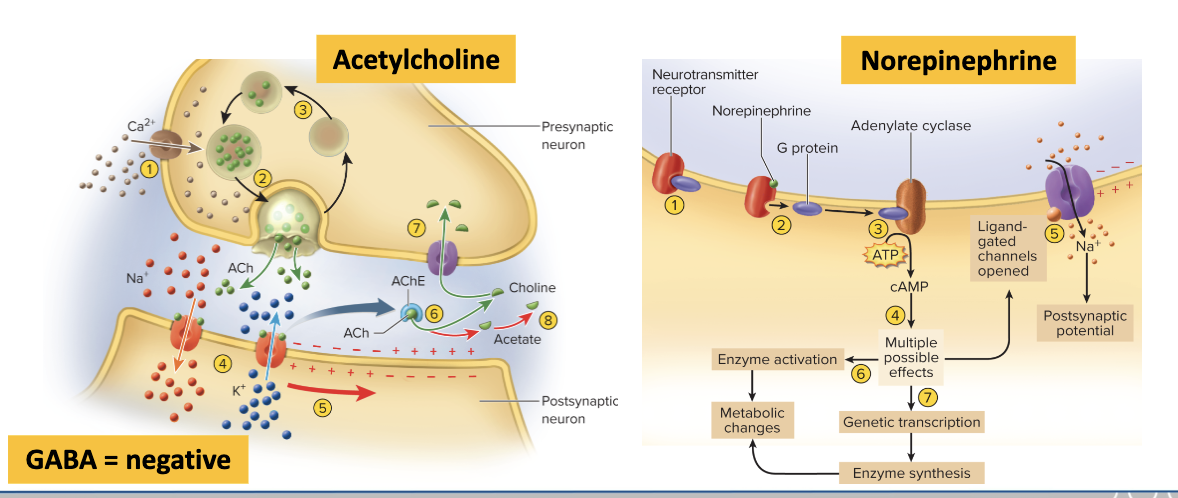
Excitatory adrenergic synapse (Norepinephrine, NE)
Resting state: NE receptor is bound to a G protein.
NE binds to the receptor → G protein dissociates.
G protein activates adenylate cyclase, which converts ATP → cAMP.
cAMP effects in the postsynaptic cell:
Opens ligand-gated ion channels → depolarizes cell
Activates cytoplasmic enzymes → metabolic changes
Induces gene transcription → produces new enzymes → metabolic effects
Excitatory adrenergic synapse
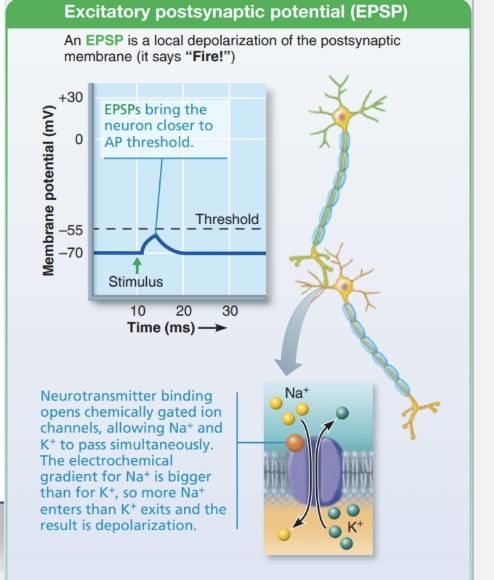
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP)
Definition: Neurotransmitter binding depolarizes the postsynaptic membrane
Key point: Produces EPSPs, not action potentials
Goal: Bring the axon hillock closer to threshold so an AP can be triggered
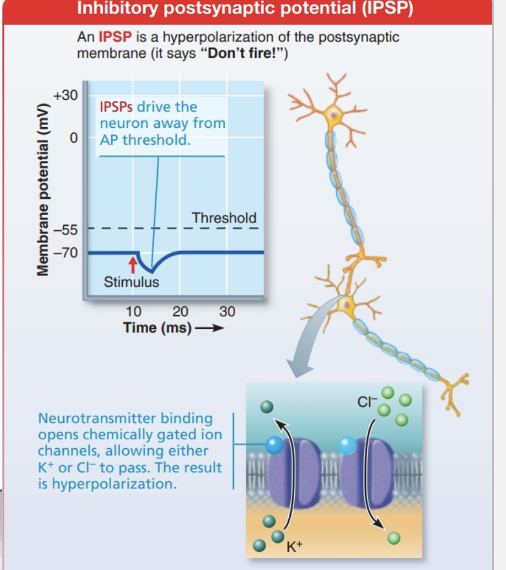
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP)
Definition: Neurotransmitter binding hyperpolarizes the postsynaptic membrane
Key point: Produces IPSPs, not action potentials
Goal: Make the membrane more negative, moving it away from threshold