BI 211 Genetics for Healthcare: Ch. 6 Autosomal Inheritance and Disorders
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Autosomal inheritance
The inheritance patterns that occur when genes are located on autosomal chromosomes, not sex chromosomes
Chromosomes
large chunks of DNA with hundreds to thousands of genes
One set of chromosomes comes from _______, the other from ______.
mom, dad
These sets of chromosomes are split during..
meiosis
Autosomal chromosomes
1-22
Meiosis
cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
Sister chromatids
Replicated forms of a chromosome joined together by the centromere
When are sister chromatids separated?
Meiosis II
How are the sister chromatids split in a normal Meiosis?
evenly between daughter cells
Homologous chromosomes vs. sister chromatids
Homologous chromosomes have have two similar chromosomes (one from mother one from father) while sister chromatids are an exact duplicate of the original chromatid
Crossing over
exchange of allele segments between non-sister homologous chromosomes
Chiasma
site of crossing over between homologous chromosomes
Recombinant DNA
DNA produced by combining DNA
When does crossing over occur?
Prophase I
Mistakes During Meiosis
Nondisjunction
Translocation
Nondisjunction
altered chromosome number in gametes or offspring due to an error in Meiosis I or II
Most nondisjunction errors are _______.
fatal
An abnormal number of chromosomes can cause what?
miscarriage
Translocation
pieces of chromosome exchanges between non-homologous chromosomes results in a free-standing chromosme being translocated onto another chromosome where it should not be
Since there are 2 cell divisions in Meiosis, how many opportunities are there for a nondisjunction event?
2
A nondisjunction event in Meiosis I will result in..
2 gametes with an extra chromosome
2 gametes with a missing chromosome
A nondisjunction event in Meiosis II will result in..
2 normal gametes
1 gamete with an extra chromosome
1 gamete missing a chromosome
Reciprocal translocation
pieces of non-homologous chromosomes switch places
Balanced translocation
when the same amount of DNA is present
Can translocations be seen in karyotypes?
YES
How do we indicate translocations?
t(first chromosome, second chromosome)
What else can be added if known?
if it occured on the p vs. q arm
Band numbers
Acrocentric chromosome
centromere is near the very top resulting in a very small p arm
Robertsonian translocation
two acrocentric chromosomes combine
Translocations are often....
balanced, meaning the total amount of genetic material is correct but it is just in a different location
Is gene expression often changed when genes move locations?
no
When do difficulties arise with translocation events?
gametogenesis
Trisomy
extra copy of a chromosome that is often fatal during fetal development
When are trisomies most common?
Advanced maternal age
Advanced maternal age
35 or older
Are any trisomy conditions survivable?
some
How do trisomies occur?
Gamete carrying translocation and the typical chromosome or nondisjunction during gametogenesis
Most common survivable trisomies
Trisomy 21
Trisomy 18
Trisomy 13
Sex chromosomes
Why are these chromosomes the most common survivable trisomies?
they are relatively small with gew genes and the X chromosome has barr bodies
Barr bodies
Inactivated X chromosomes in female cells
Extra chromosomes means..
extra genes
How is a trisomy indicated?
Number of chromosomes
Comma
Sex chromosomes
Plus sign
Trisomy chromosome number
Example of trisomy indication
47, XX, +21
Monosomy
one chromosome is lacking a pair
What is the one commonly seen survivable monosomy?
turner syndrome (1-22, X: sex-linked)
Trisomy 21
down syndrome
How rare is trisomy 21?
1:800 births with an equal race and ethnicity distribution
Common abnormalities for Trisomy 21
Single Palmar Crease
Epicanthal fold
Flat face
Wide eyes
Low ears
Short nose
Protruding tongue
Short neck
Common Phenotypes for Trisomy 21
Sleep apnea
Heart defects
Delayed intellect
Hypothyroidism
Poor muscle tone and sucking reflex
Cataracts
Low functioning immune system with increased infection risk
Intellectual delays depend heavily on?
environmental and educational stimulation
Hypothyroidism
lead to obesity and other issues
Life expectancy of Trisomy 21
increased dramatically, now 50-60 years
Reproduction for Trisomy 21
Males are sterile but puberty still occurs
Female can have normal reproduction but offspring have high likelihood of inheriting trisomy 21
Trisomy 18
Edward syndrome
Edward syndrome
Most individuals are stillborn and 90% die in the first year, females slightly more likely to survive
Common appearance of Edward syndrome
Small strawberry head with receding shin
Single palmar crease with clenched fists
Rocker bottom feet
Common Phenotypes of Trisomy 18
Seriously reduced intellectual development, heart and kidney defects, hernias, omphalocele and brain cysts
Life expectancy for trisomy 18
if not stillborn, days to months
Reproduction for trisomy 18
none
Trisomy 13
Patau Syndrome
Patau Syndrome
1:16,000 births, most stillborn but a few live to adulthood and are never independent in ADLs
Common phenotypes of trisomy 18
Most of trisomy 18 issues plus fusion of brain hemispheres, seizures, abnormal iris, close eyes, cleft palate, deafness, apnea, extra fingers and toes
What can occur if part of a chromosome is added or is missing?
Duplications or deletions
Duplications
extra copy of DNA amplifies gene expression
Deletions
missing DNA reduces gene expression
Why do duplications and deletions occur?
Random events, not linked to parental age
Retinoblastoma
tumors in retina due to deletion of RB gene on 13qdel(q12.2-q14.3)
RB gene
a tumor suppressor gene, therefore lacking a copy of this gene increased cell division resulting in tumors
Cri du Chat
deletion on chromosome 5 (5p) that results in microcephaly, cleft palate, heart defects, severe intellectual deficiencies, and a cry that sounds like a cat
The larger deletion, the more..
severe the disorder
Angelman Syndrome
deletion of maternal chromosome 15 that results in developmental delays, reduced cognition, clumsy gait, hand flapping, enlarged face and broad chin
Prader-Willi Syndrome
deletion of paternal chromosome 15 resulting in short, small hands and feet, reduced cognition, scoliosis, micropenis, insatiable appetite, delayed or incomplete puberty
Angelman and Prader-Willi Syndrome are..
deletion of the SAME part of chromosome but different syndromes due to parent is was deleted from
Why does chromosome 15 matter so much?
Unknown, but something is different for Chromosome 15 between men and women
Genetic imprinting
maternal and paternal DNA is marked slightly differently to allow for better regulation through histone methylation
Mosaicism
2 or more karyotypes are consistently present in 1 person, with some normal and abnormal cells
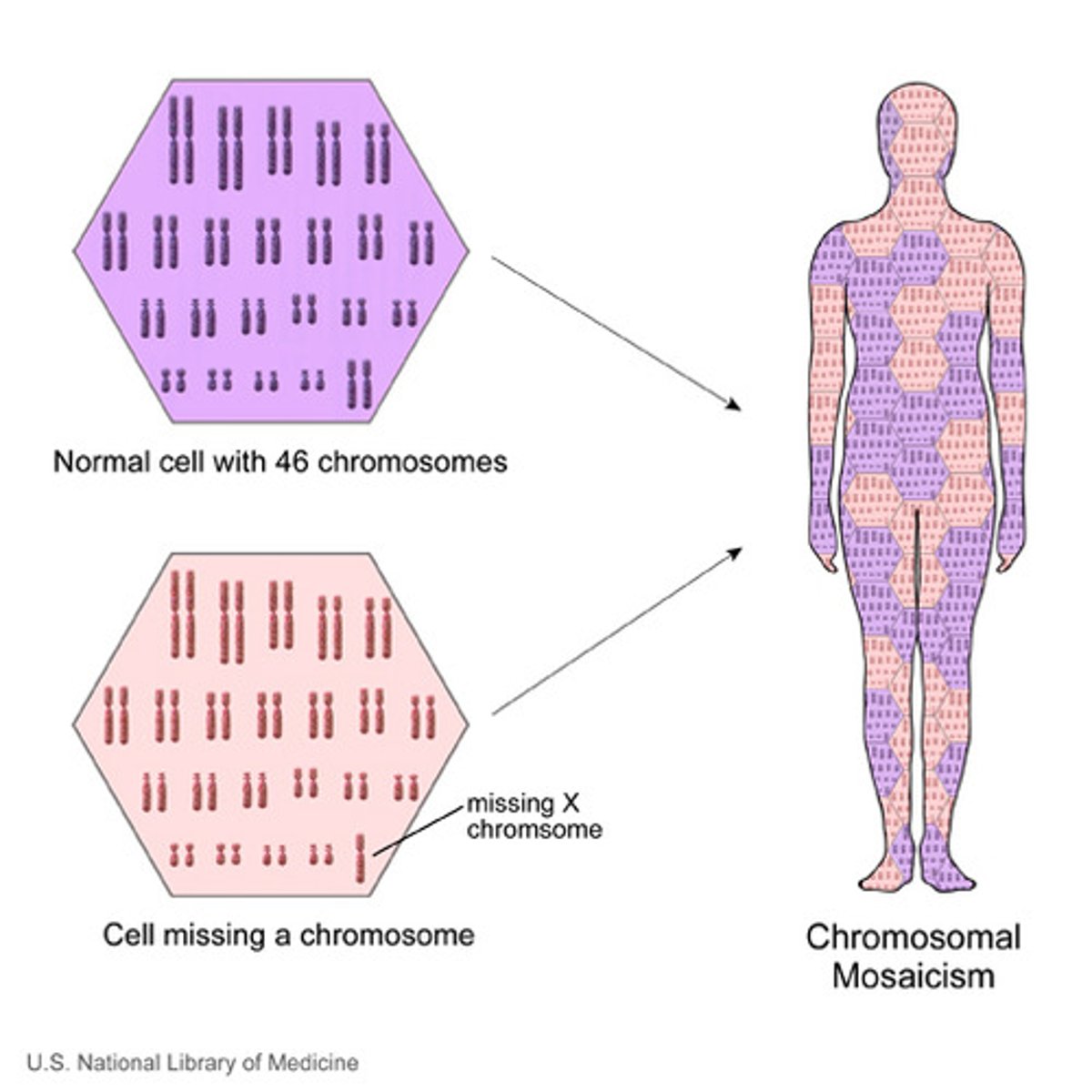
With mosaicisim, distribution in tissues is _____, therefore?
uneven; phenotypes are highly variable
How might mosaicism occur?
due to errors in cell division that happen after fertilization, leading to an individual having two or more genetically different sets of cells
How does mosaicism affect the severity of a syndrome with a genetic origin?
can cause a spectrum of symptoms, ranging from none to severe, depending on the number and location of affected cells
What is a phenotype common in both Trisomy 18 and 13?
rocker bottom feet