Experiment B - Synthesis of Aspirin
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Acetyl Salicylic Acid Structure
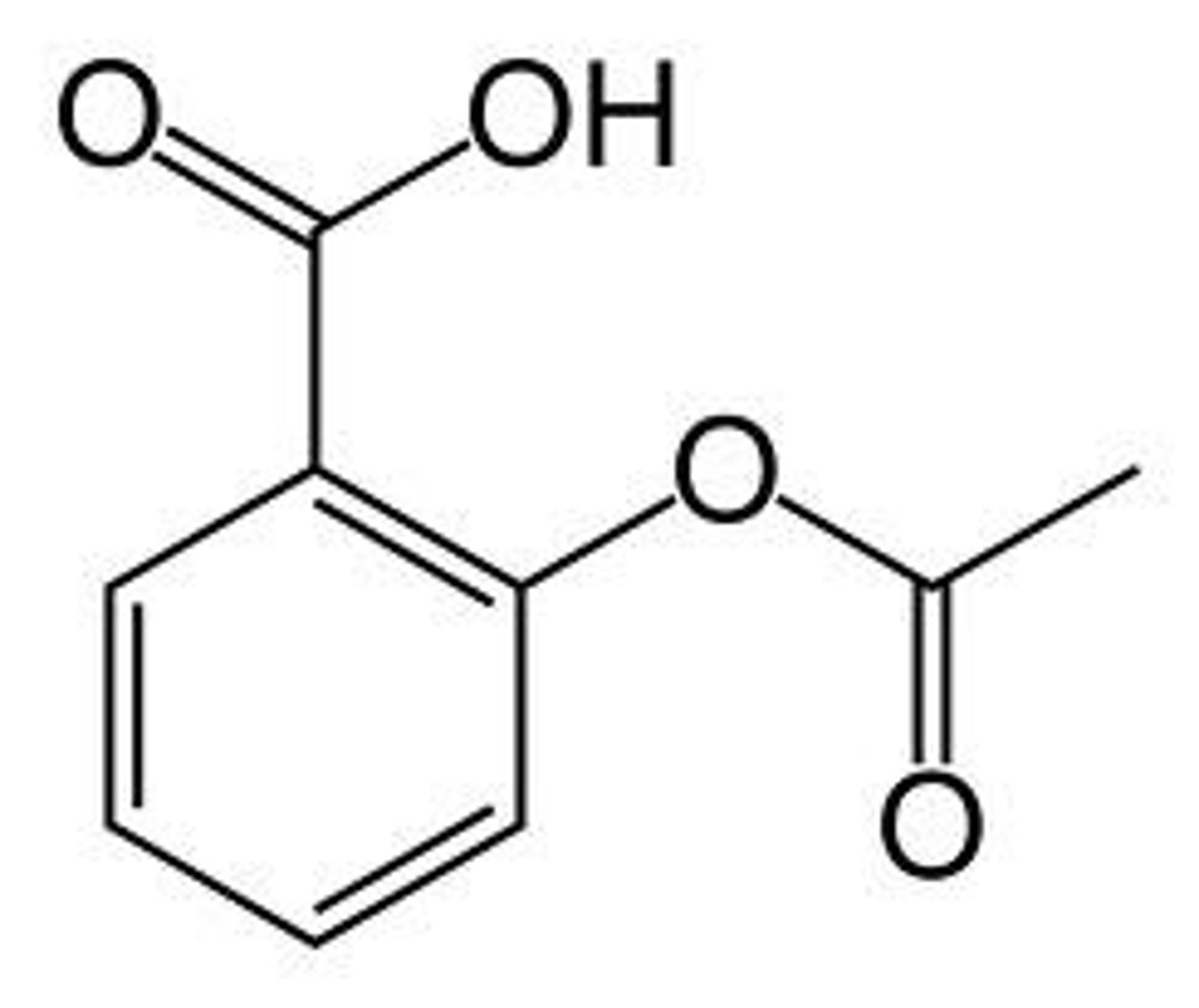
Acetyl Salicylic Acid details
ASA is known by the trade name of aspirin, because salicylic acid can also be isolated from spiraea ulmaria
Has anti-clotting activity and some evidence suggests that it can prevent additional ischemic strokes
Analgesic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory
Not only synthesized by plants; recent studies have suggested that humans synthesize salicylic acid in vivo from benzoic acid = may be endogenous regulation of synthesis
"Aspirin"
Patented by Bayer in 1893 (oldest and most consumed drugs)
American consumption = 16,000 tons/year = 80 million pills/ year
Ester group
Other medicinal compounds contain this functional group
Demerol
Narcotic analgesic
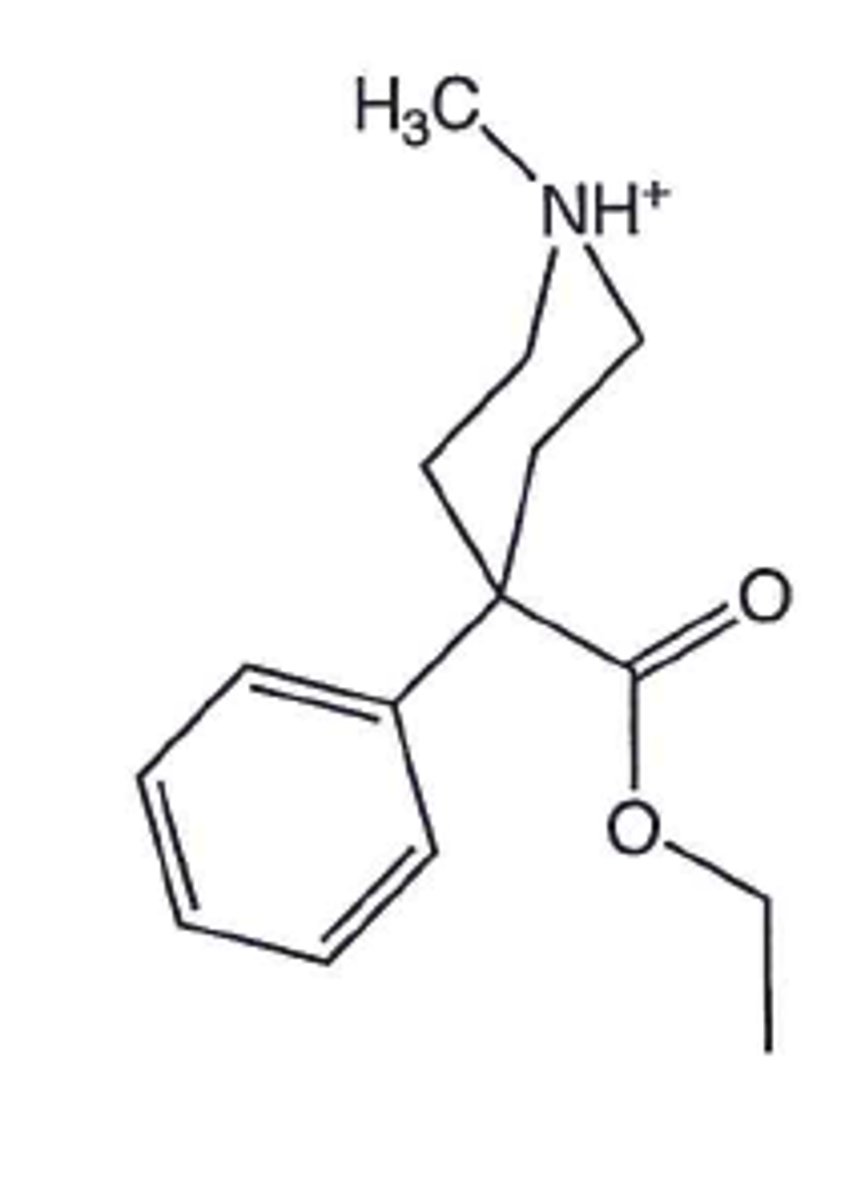
Benzocaine
Topical anesthetic
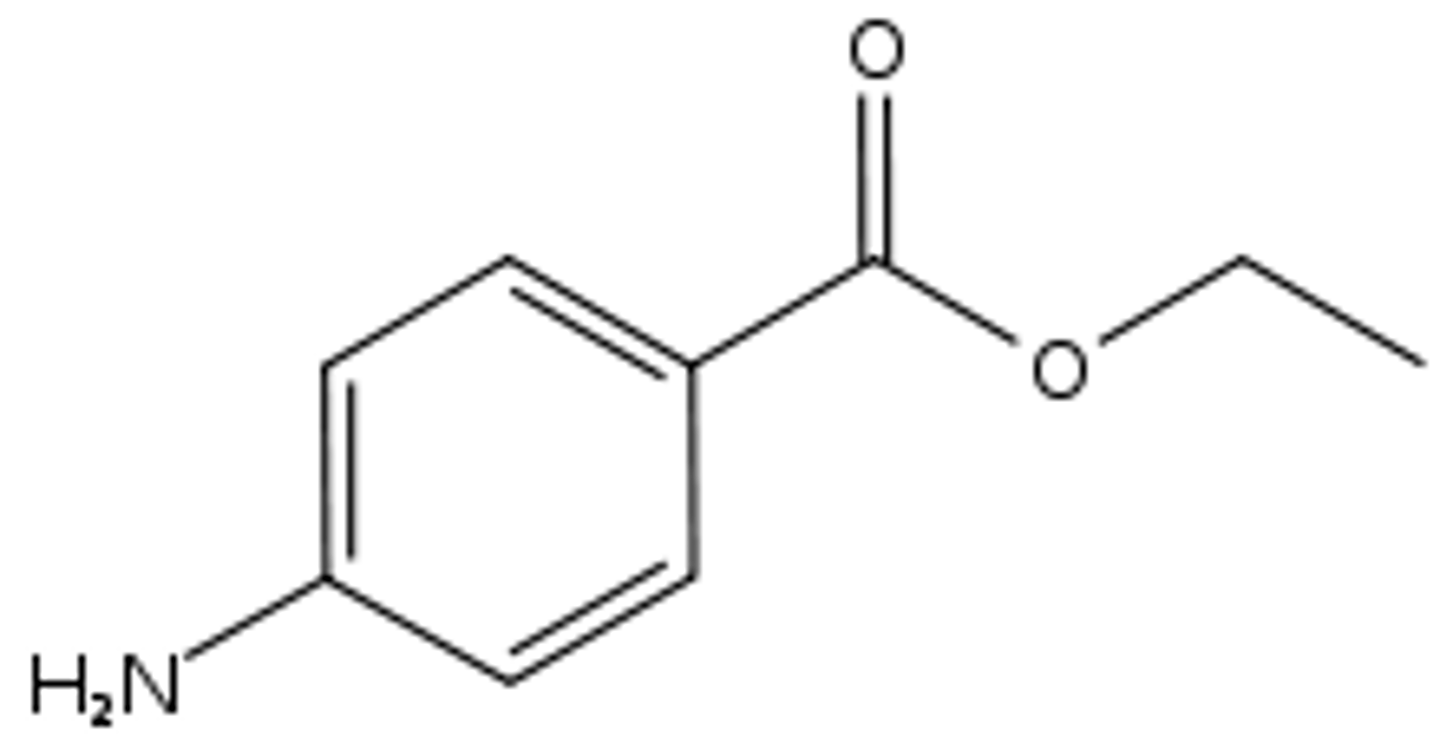
Maxicaine
Maxicaine - local anesthetic
Acetic anhydride
Two molecules of acetic acid (one of the components of vinegar) with a molecule of water removed
Need an excess of this reactant to drive the reaction - also serves as the solvent
Irritating to the nose - keep in hood
Phosphoric acid
Acid catalyst - corrosive
Equivalent
The experimental ratio in which reactants are added to the reaction
Equivalent ratio
3:1 for AA to SA (stoichiometrically they are 1:1)
Overall reaction
Salicylic Acid + Acetic Anhydride + H3PO4 catalyst --> Acetylsalicylic acid (aspiring) + acetic acid
This also includes the hydrolysis of excess acetic anhydride:
acetic anhydride + H2O --> 2 acetic acid
What is thermometer lag? How will this affect your melting points? How can you avoid thermometer lag? What is another problem with determining your melting point too
quickly?
Why do you do this reaction in an Erlenmeyer flask rather than a beaker?
What are the characteristics of a good recrystallization solvent?
Thermometer lag is when the solution reaches a certain temperature, but the thermometer takes a second or two to calibrate to that temperature. This will affect m.p. by giving inaccurate data. You can avoid this, as well as a broad range of temperatures, by heating the solution slowly
Erlenmeyer Flasks help to avoid lose of product by splashing and evaporation.
A good recrystallization solvent is insoluble when cool and soluble when heated.
General procedure for past week
1. Obtain mass of dry salicylic acid crystals, use 90% of this for this week's experiment (calculate amount of acetic anhydride you will need)
2. Determine M.P. of salicylic acid
General procedure for this week
1. Transfer salicylic acid into 50 mL flask
2 . Obtain acetic anhydride that YOU need for YOUR reaction (dispensed for you), add it to flask (cloudy white solution forms)
3. Have TA give 4-5 drops of 85% phosphoric acid - loosely stopper the flask
4. Let stand for 10 minutes, heat in warm water bath for 10 minutes (homogenous mixture, slightly yellow tint)
5. Chill in an ice water bath while scratching the inside of the flask with a glass rod (paste forms), add 10 mL of cold water and ice respectively, stir
6. Vacuum filtration: wash crystals (white) twice w/ 2 mL of ice cold water, empty filtrate and draw air
over crystals.
7. Find which solvent to use: put a small spatula
full of aspirin into two test tubes - fill 1/3 with water and 1/3 ethanol respectively. If material doesn't dissolve, gently heat the tube, if it now dissolves this is your solvent.
8. Add 10 mL of water to aspiring, boil on hot plate, remove, let cool on bench top, until crystal formation has occurred.
9. Vacuum filtration: rinse crystals (white, flaky, shiny) once with max. 2 mL of water to recover crystals on walls of flask.
10. Aq. FeCl3 test: Put the two compounds into two test tubes, add 1 mL of ethanol, and make sure the compounds are dissolved - dispense 3 drops of 0.02 M aq. FeCl3, make note of any color changes you observe (this test indicates the presence of unreacted starting material in your final product)
Following week: Determine the dry mass/m.p. of aspirin - transfer remaining aspirin to a vial
Waste disposal
1. Filtrate (step 6) must be neutralized using NaHCO3
2. Solvent tests: water test tube can go down the drain, ethanol test tube must be emptied out into the C,H,O Non-Halogenated Container.
3. Aq. FeCl3 test): All must be poured
out into container "Aq. FeCl3 waste".
4. Used glass pipettes disposed of into red sharps container
Theoretical yield of salicylic acid:
mol methyl salicylate x mol ratio (SA/MS) x molecular weight of SA = g of SA
Calculation of acetic anhydride
0.9 x obtained dry mass (SA) x 3/1 (mol ratio of AA/SA) x MW AA/Density AA = mL of AA
Overall yield for aspirin
yield of SA x yield of Aspirin x 100
Salicylate poisoning
Determined by use of iron trichloride (FeCl3) - in vivo methyl salicylate/acetyl salicylic acid --> salicylic acid --> salicylate.
Test is sensitive enough that it can detect salicylate, but a positive result can be caused by the presence of interfering compounds (any containing phenol groups)