Chapter 25: Plant Evolution
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Plant Characteristics
-Multicellular
-Photosynthetic
-Primarily live on land
-First Clade: Green Algae
Common Features Land Plants (6)
1. Photosynthesis
2. Cellulose Cell Walls
3. Chlorophyll pigments a & b
4. Common enzymes
5. Common sperm structure
6. Starch and carbon storage
Terrestrial Adaptations (Tissues)
Adapt: Water-retention and gravity
-Tissues arose from apical meristems at growing tips
-Lower S.A. / Volume ratio - dec. water loss
-Special functions
-robust against drought/stress
Land Plant Evolutionary Trends
High diversity, generally sessile, land based (exc: Sea grasses), Alternation of generations
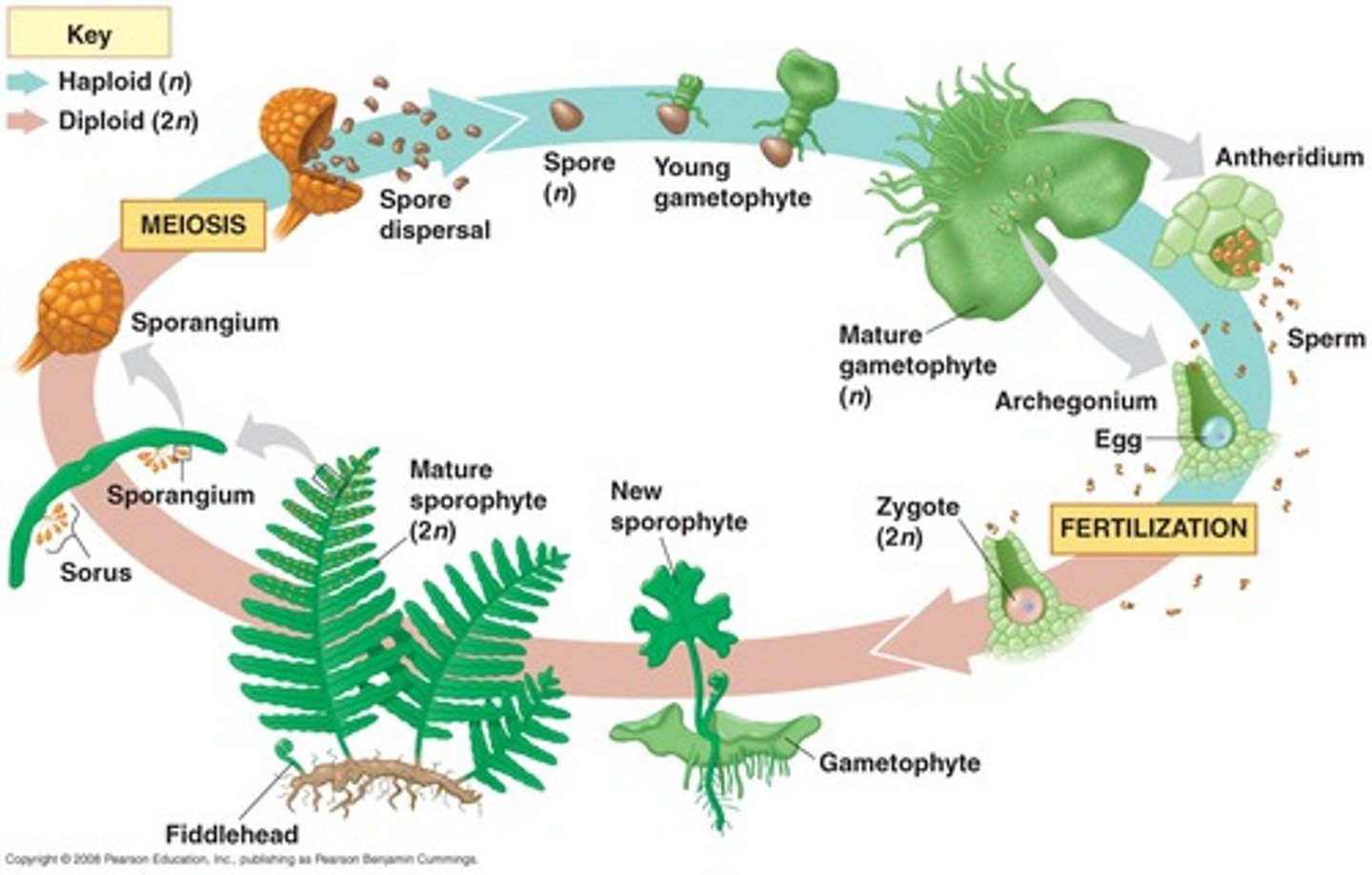
Life Cycle: Alternation of Generations
-Alternate between haploid + diploid phases
-Happens when both faces are multicellular
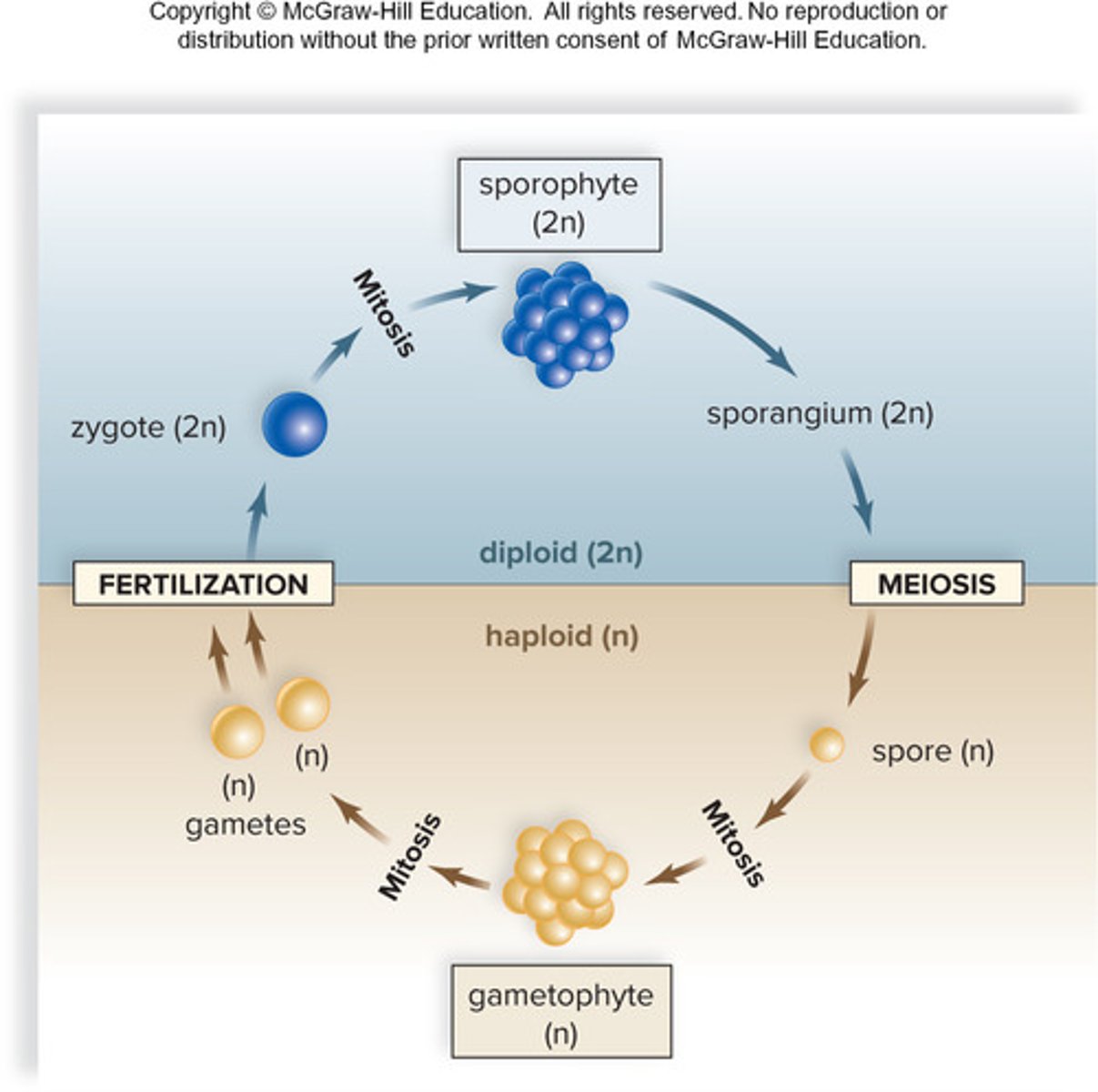
Plant Reproduction: Differences from animals
Multicellular haploid/diploid over unicellular sperm/eggs
Sporophytes = Diploid + reproduce asexually
Gametophytes: Haploid + reproduce sexually
Simplest to most complex plants:
Gametophytes has been reduced and sporophyte has become more prominent
Bryophytes -> vascular seedless plants -> angiosperms (flowering plants)
Sporopollenin: Key adaptation of land plants
Def: Highly resistant polymer that protects spores/pollen against drying/decay
-Tough spores allow plants to disperse offspring through dry air (sporangia for land plants/Gametangia for gametes)
Gametangia: Key adaptations of land plants
Def: Multicellular structures that enclose gametes + prevent them from drying out
Antheridia v. Archegonia (Gametangia)
Antheridia: Haploid sperm
Archegonia: Haploid eggs
Embryos: Key adaptations of land plants
Def: Young plants (new sporophytes) contained within a protective structure
-Not present in green algae, only land plants (embryophytes)
Nine Phyla of Land Plants
1. Liverworts
2. Mosses
3. Hornworts
4. Lycophytes
5. Pteridophytes
6. Cycands
7. Ginkgos
8. Conifers
9. Flowering plants
1-3 = Bryophytes
Bryophytes (6 facts + Who)
1-3: Mosses, liverworts, hornworts
-Damp Environments
-Earliest plant; nonvascular
-Lack roots; simple tissue transports, no structural support
-No seeds
-Gametophyte Dominant
-H20 for sexual reproduction
Lycophytes + Pteridophytes
-Oldest phyla, seedless, vascular plants
-Posses stems, roots, leaves
-Lignified cells = strength, transport H20 against gravity; tracheophytes
-Non-lig -> Lignified tracheids -> Lig. Vessels (flowering)
-Dominated by diploid sporophyte (produces many spores)
ex: Horsetails, Ferns
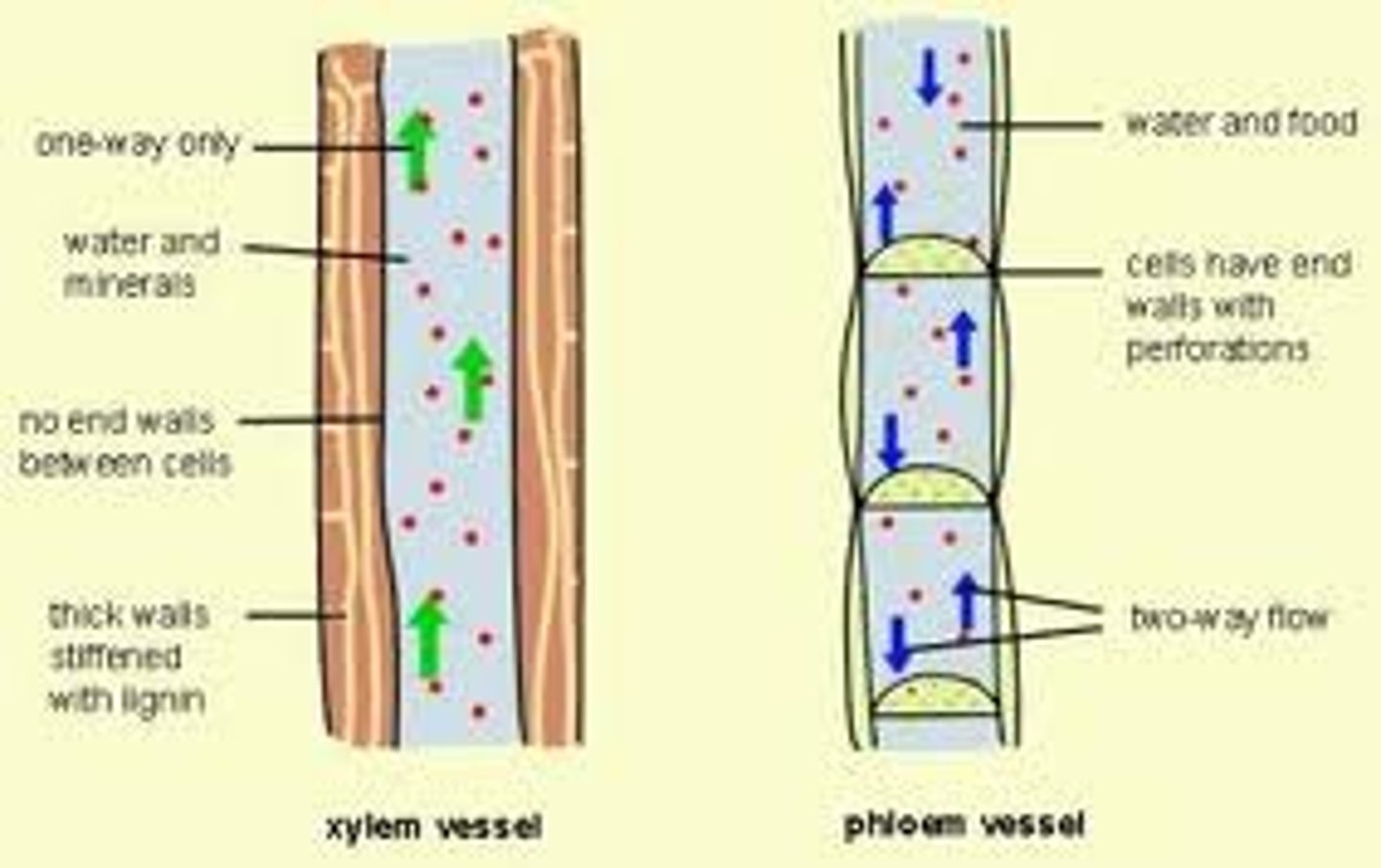
Vascular tissue system components
Xylem: Tissue carries water + minerals from roots to plant
Phloem: Alive at maturity, transports carbohydrates (sucrose)
Cuticle: Waxy coating external to cell wall; limits H20 loss
Stomata: Closable openings that regulate gas exchange + H20 loss
Lignified vascular elements
Plants can grow larger, remain metabolically active longer through internal water content in dry habitats
Lycophytes/Pteridophytes
Evolution of seeds
-Gymnosperms replaces seedless vascular plants
-Seeds protect embryos contain carbs, lipids, and protein that helps growth/development
-seeds produce pollen (small spores that contain male gametophytes)
Gymnosperms (6-8)
Def: Lack flowers, fruits, endosperm, egg and sperm in cones, moist environments
-Naked Seeds, pollen carried by wind, embryo encased in seed
Contain: Cycads, Ginkgos, Gnetophytes/Conifers
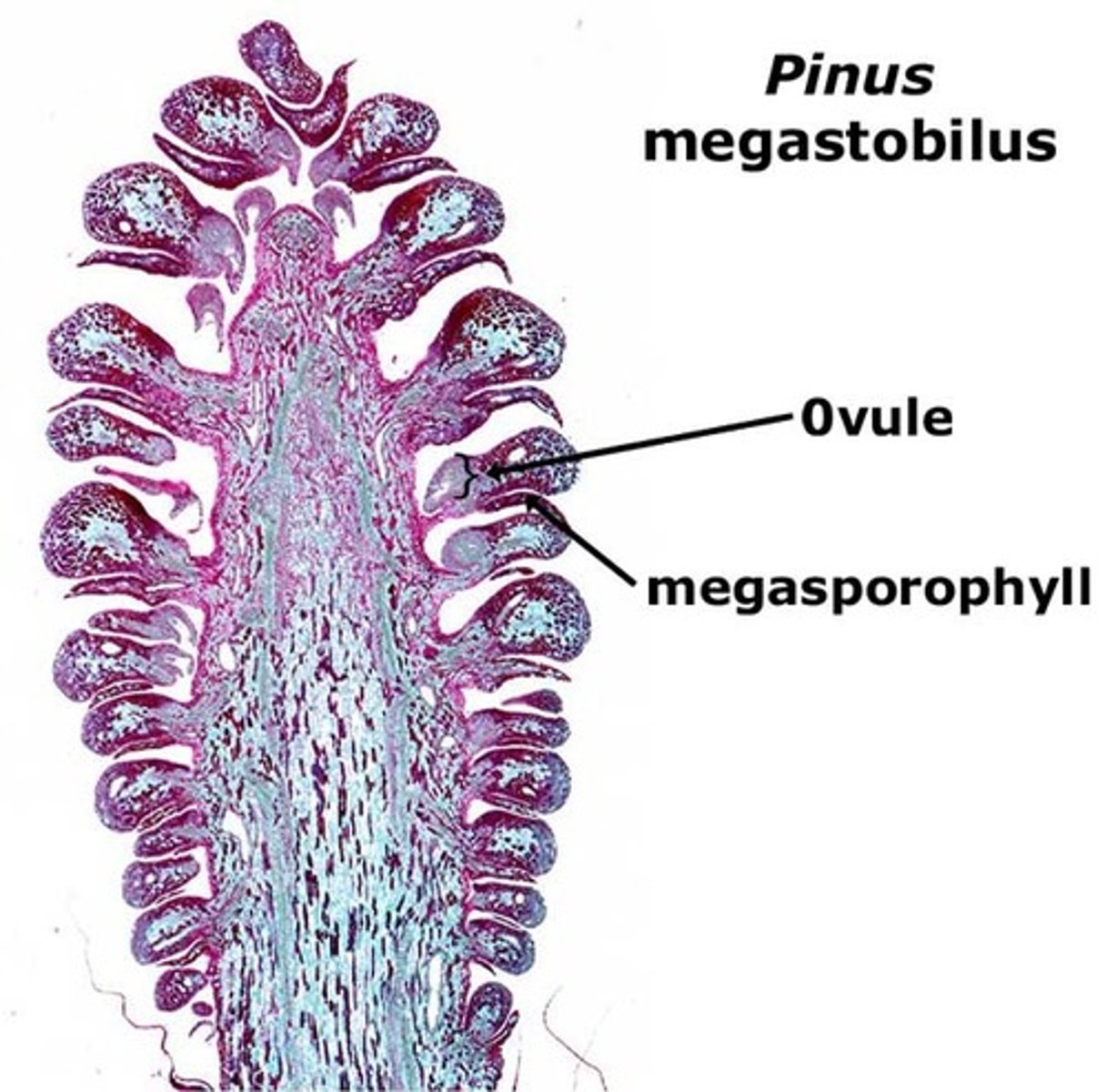
Female Cones
Seed bearing, complex, ovule
Male Cones
Pollen bearing
Angiosperms
-Flowers, Fruits, endosperm, Vessel Seeds
-Most dominant, use animals to spread pollen + fruits -> seeds
Inherited Traits from Gymnosperms: Produce wood (from xylem) and seeds

Cycads
Earliest diverging modern gymnosperm phylum, many are endangered, palm like leaves
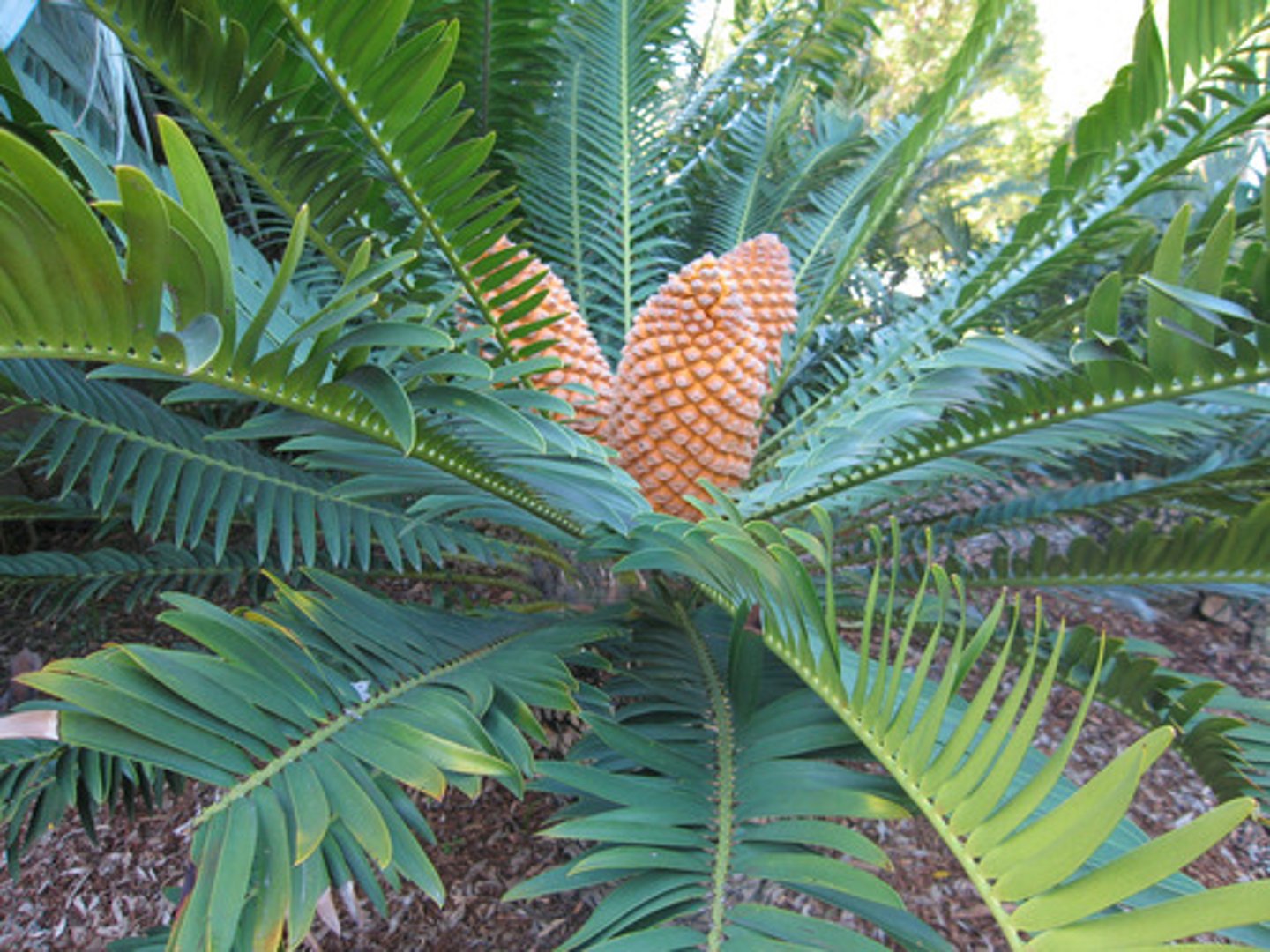

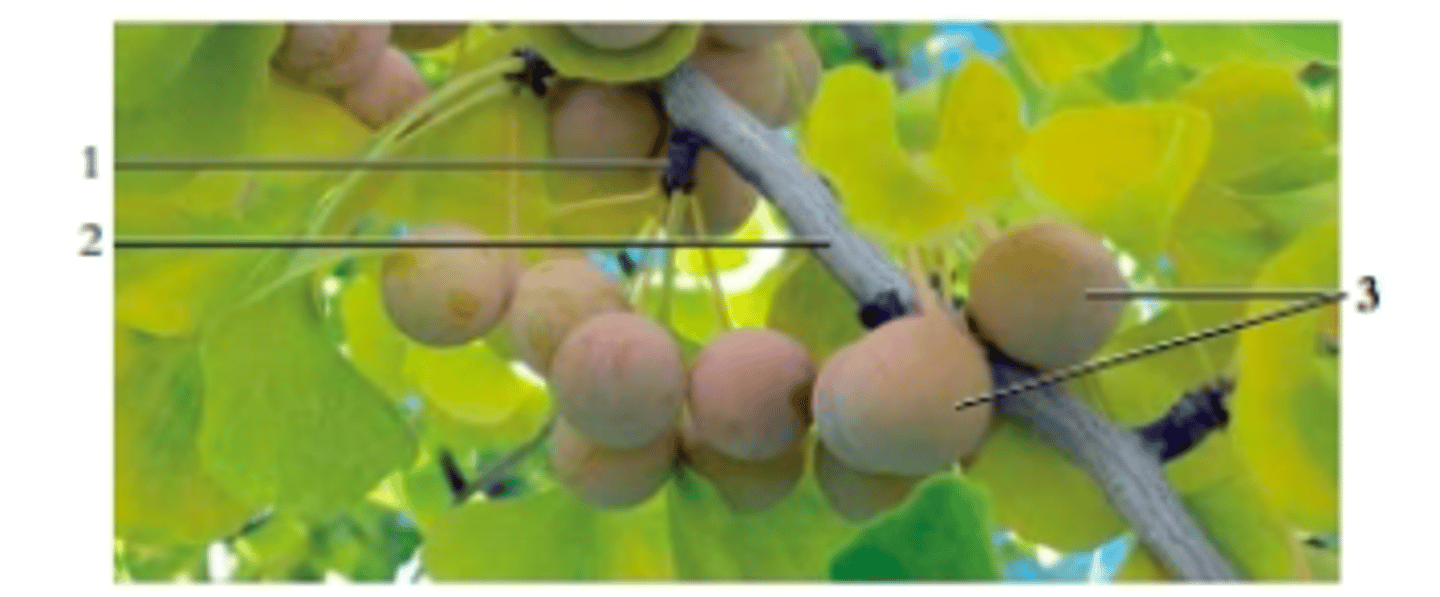
Ginko Biloba
Nearly extinct in wild, city streets -> tolerant to heat, cold, and pollution
Conifers
Seed cones; most diverse gymnosperm, common in cold/dry climates (many adaptations)
-Needle shaped leaves (water loss), evergreen (retain leaves in winter)
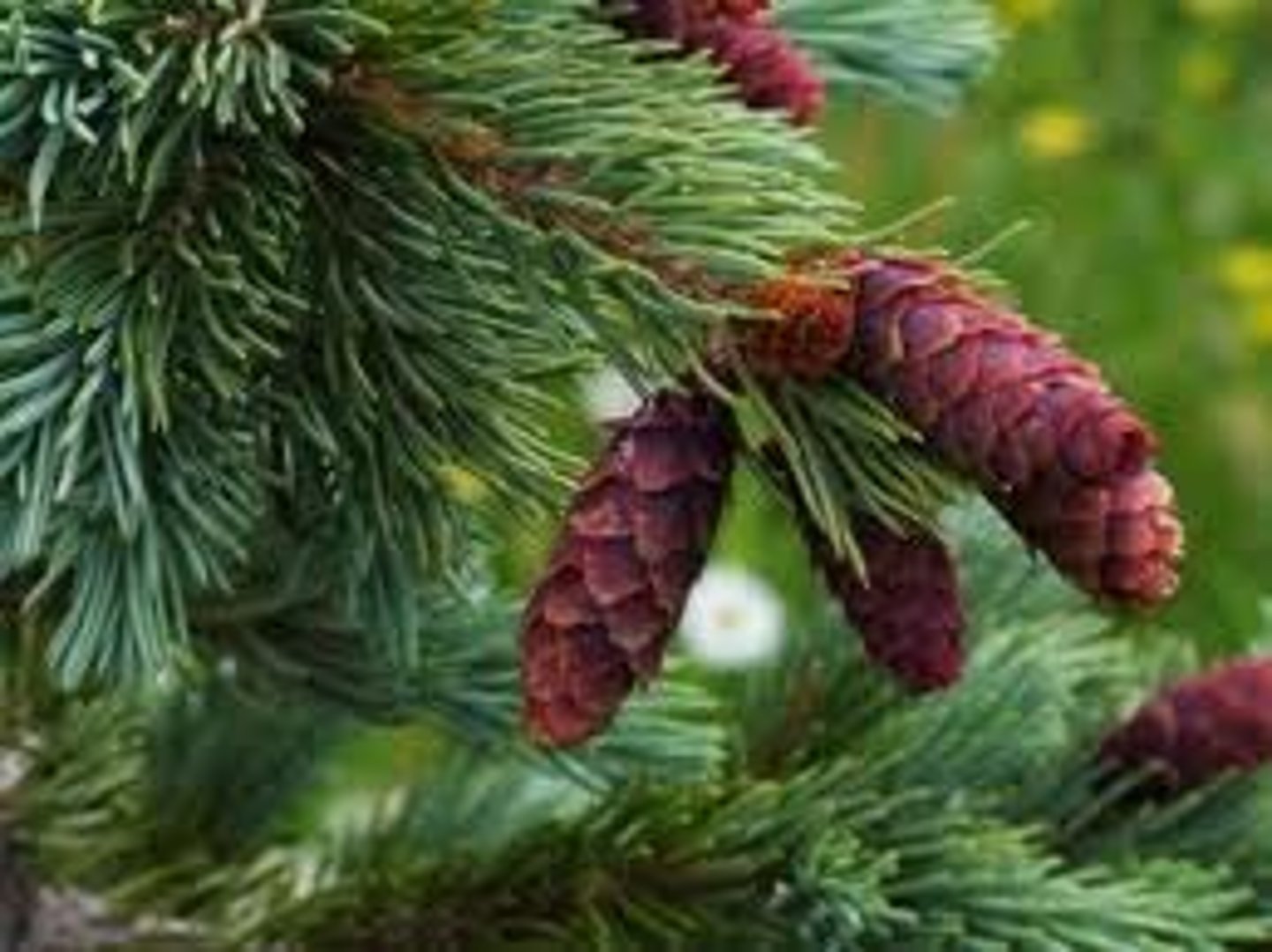

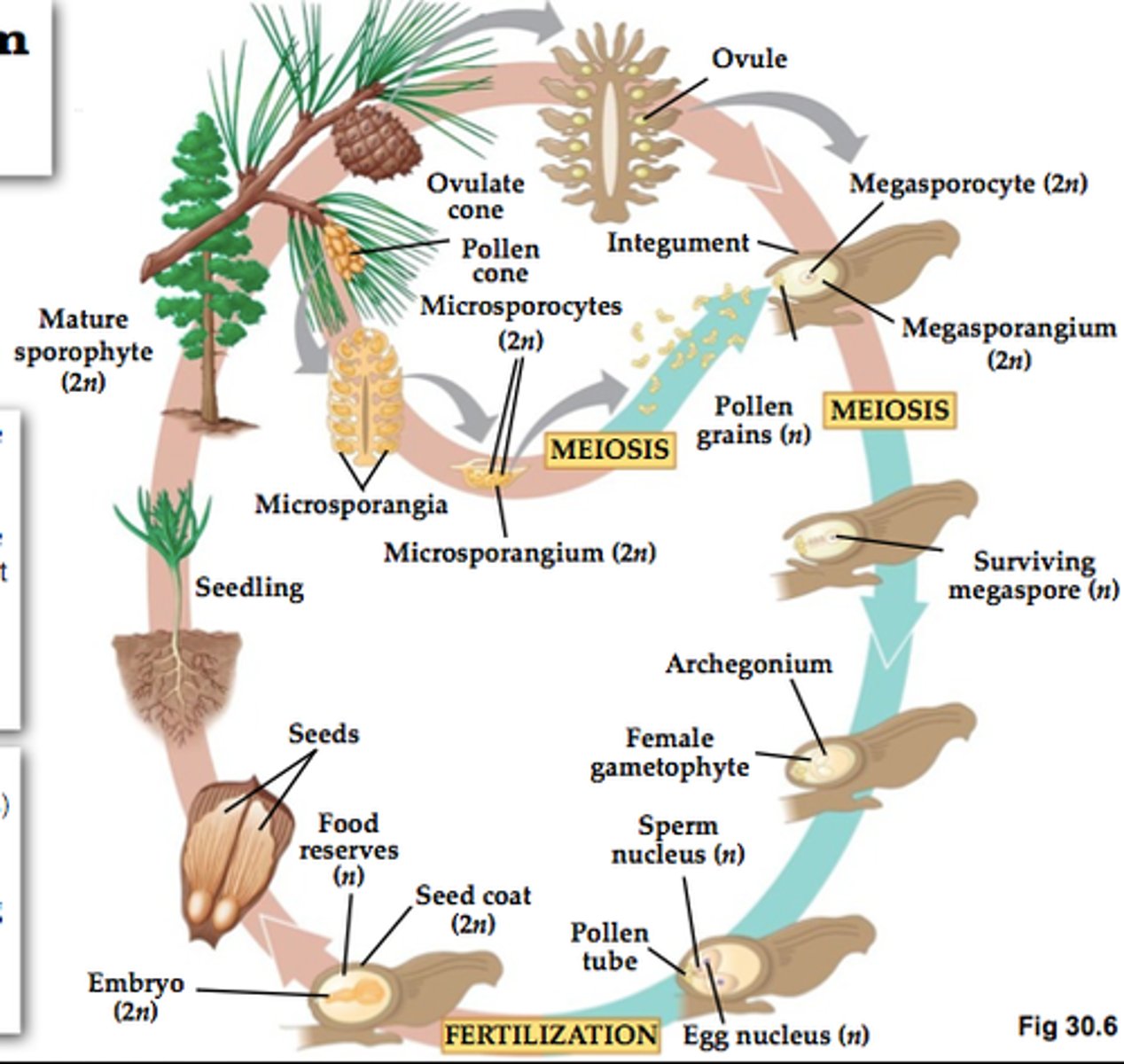
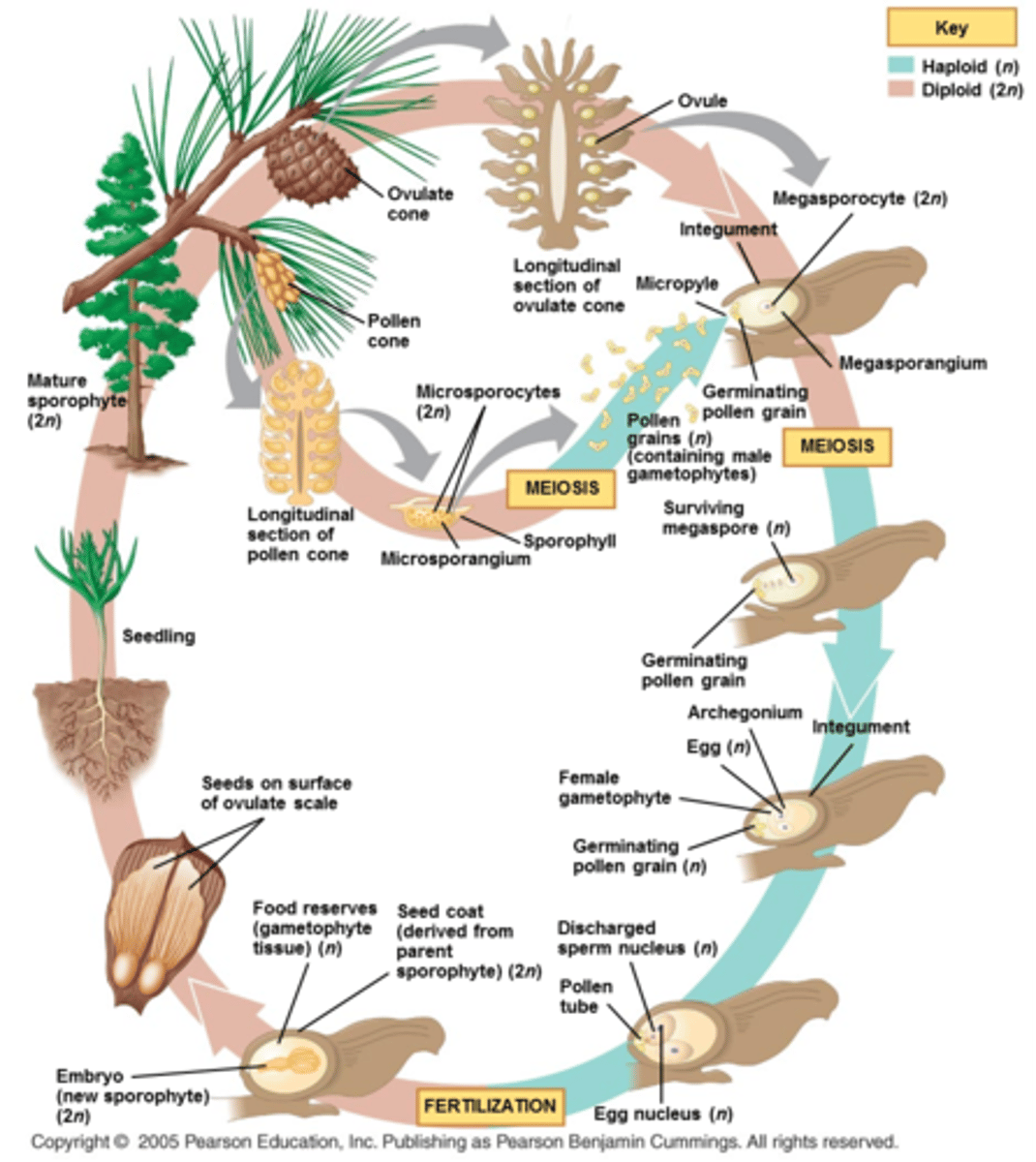
Lifecycle of conifers + Phylum (3 subgeneres)
Produce simple pollen cones + more complex ovule bearing cones
Gnetales Phylum:
1. Gnetum: unusual broad leaves, Africa or Asia
2. Ephedra: Arid regions of Southwest US, adaptations to conserve H20
3. Welwitschia: Grows in costal Namib desert of SW africa
Inflorescences
-Groups of flowers
-All parts derived from modified leaves
Perianth:
-Sepals: Often protect unopened buds
-Petals: Attract pollinators
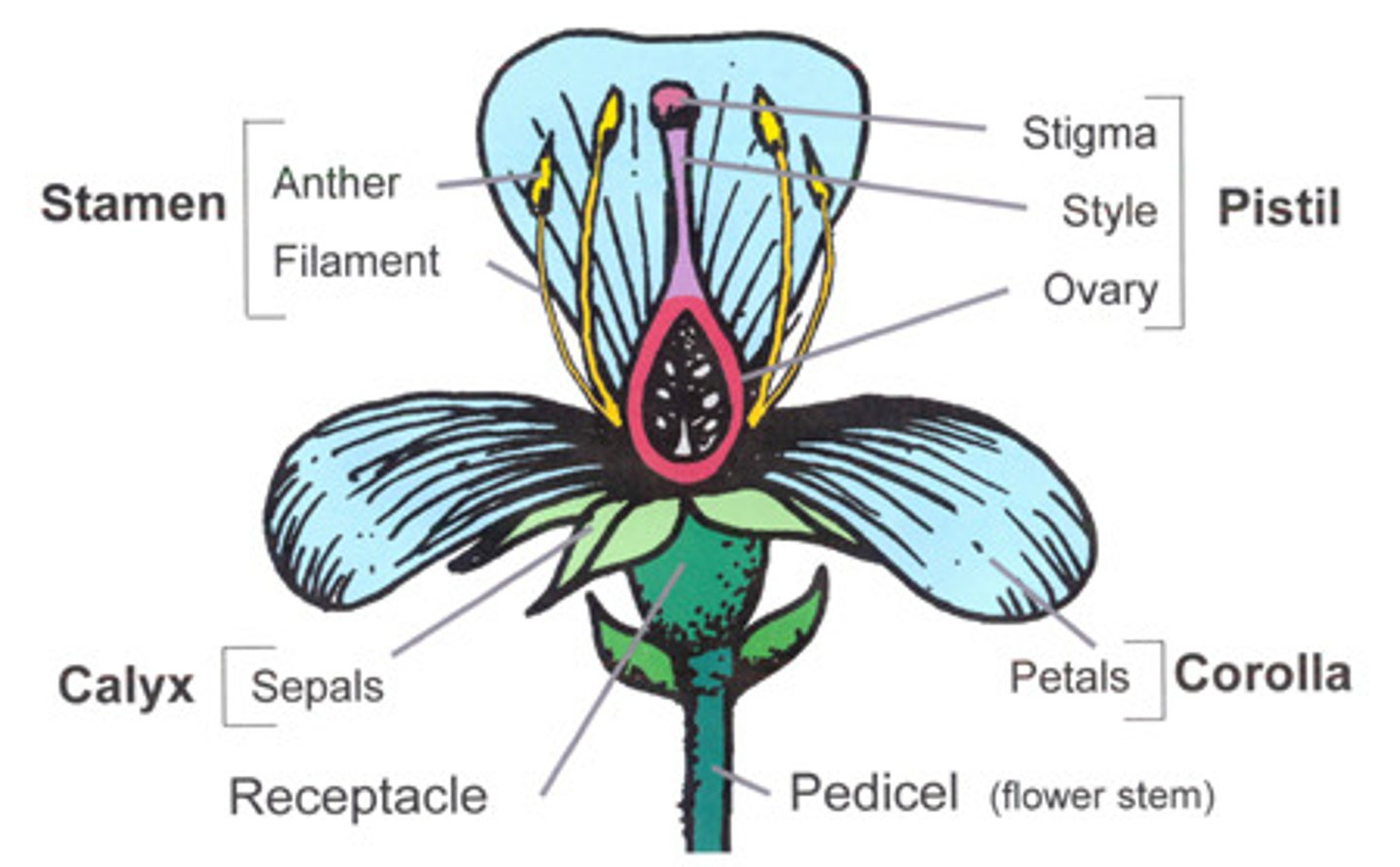
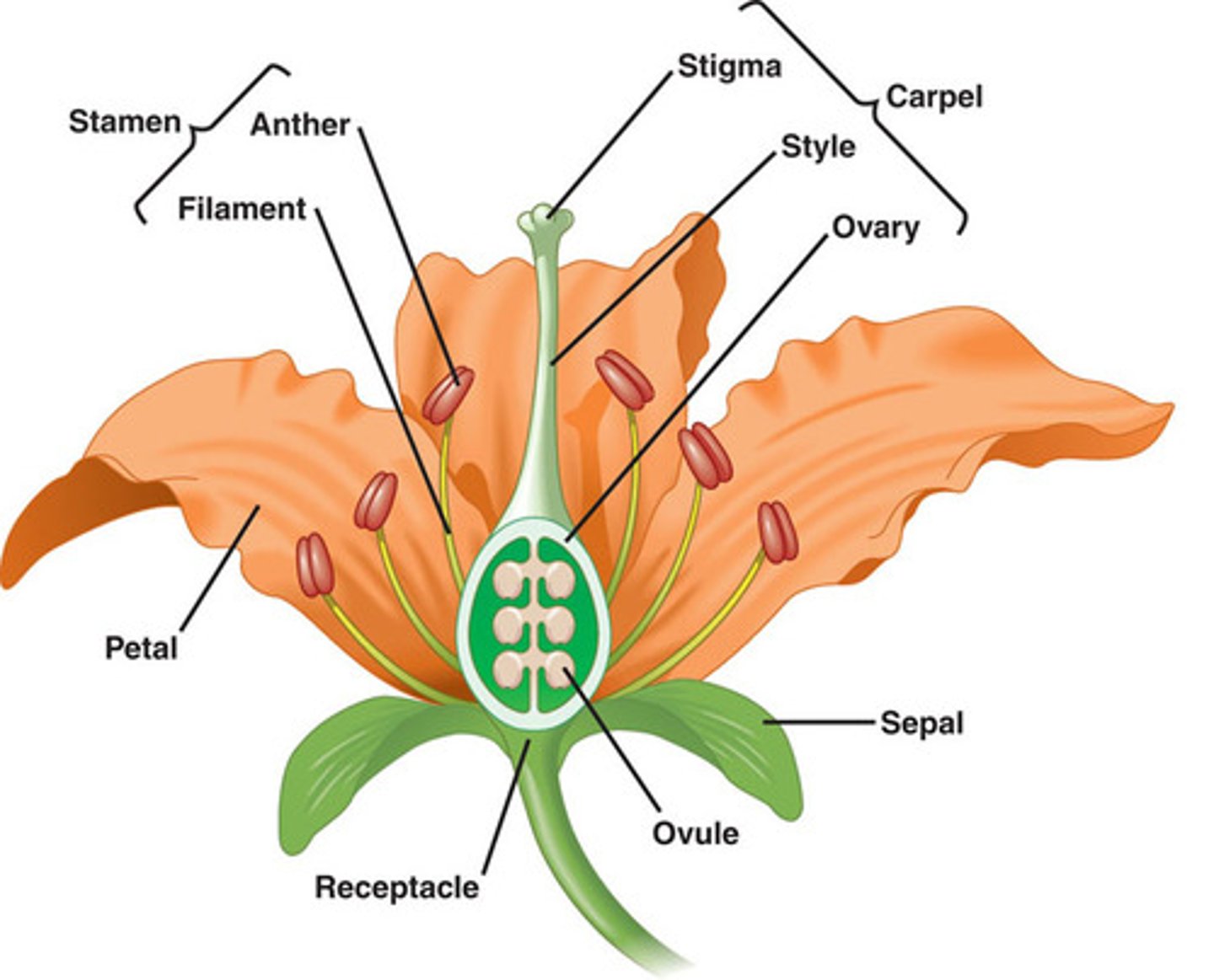
Flower Structure
Carpels: Bear female Magasporangia
Stamens: Bear male miscrosporangia (anther, filament)
Carples: Stigma, style, ovary, ovule
Pistil: May be composed of one or several fused carples
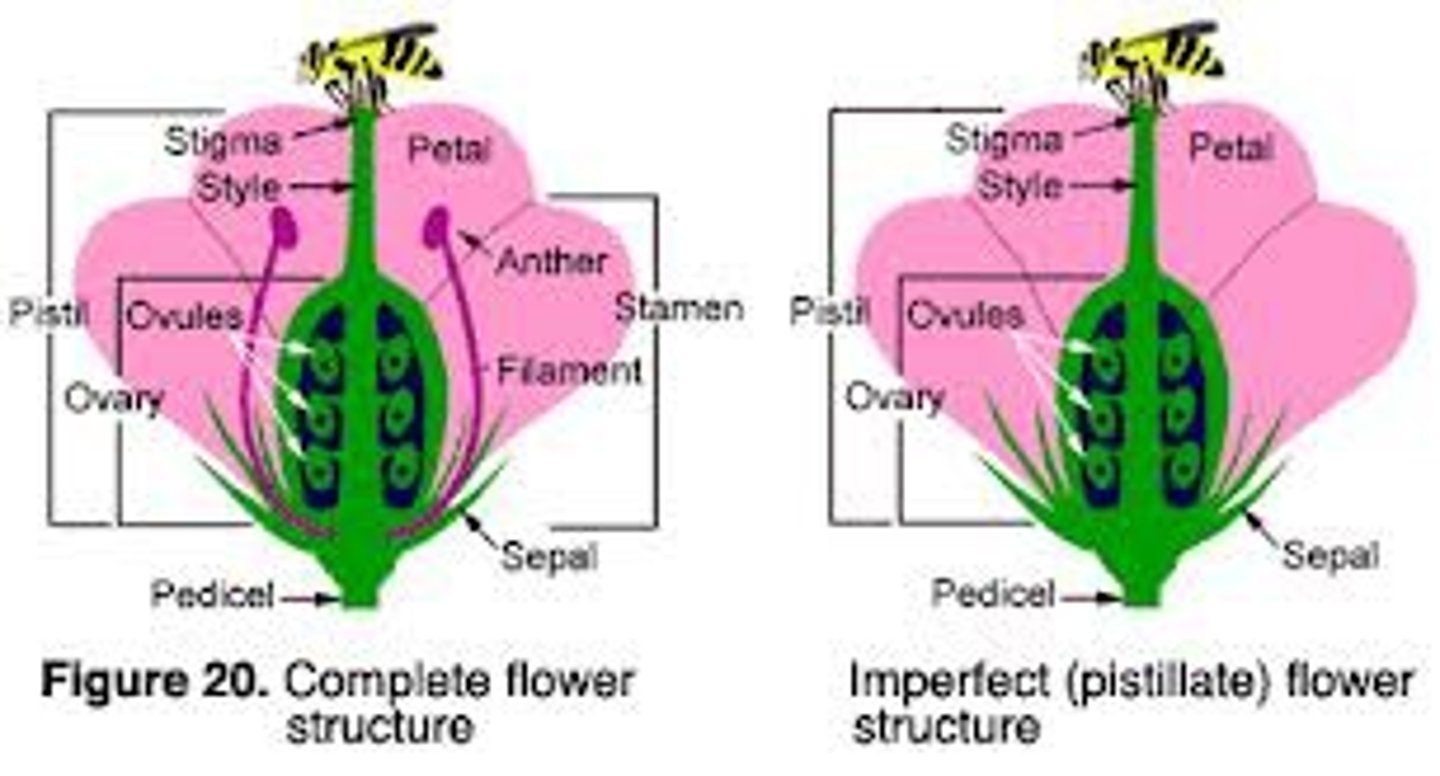
Perfect/Imperfect Flowers
Perfect: Both megasporangia + Microsporangia
Imperfect: Male/Female distinctions
-Monoecious: M and F flowers occur on same plant
-Dioecious: M/F Flowers produced on diff plants
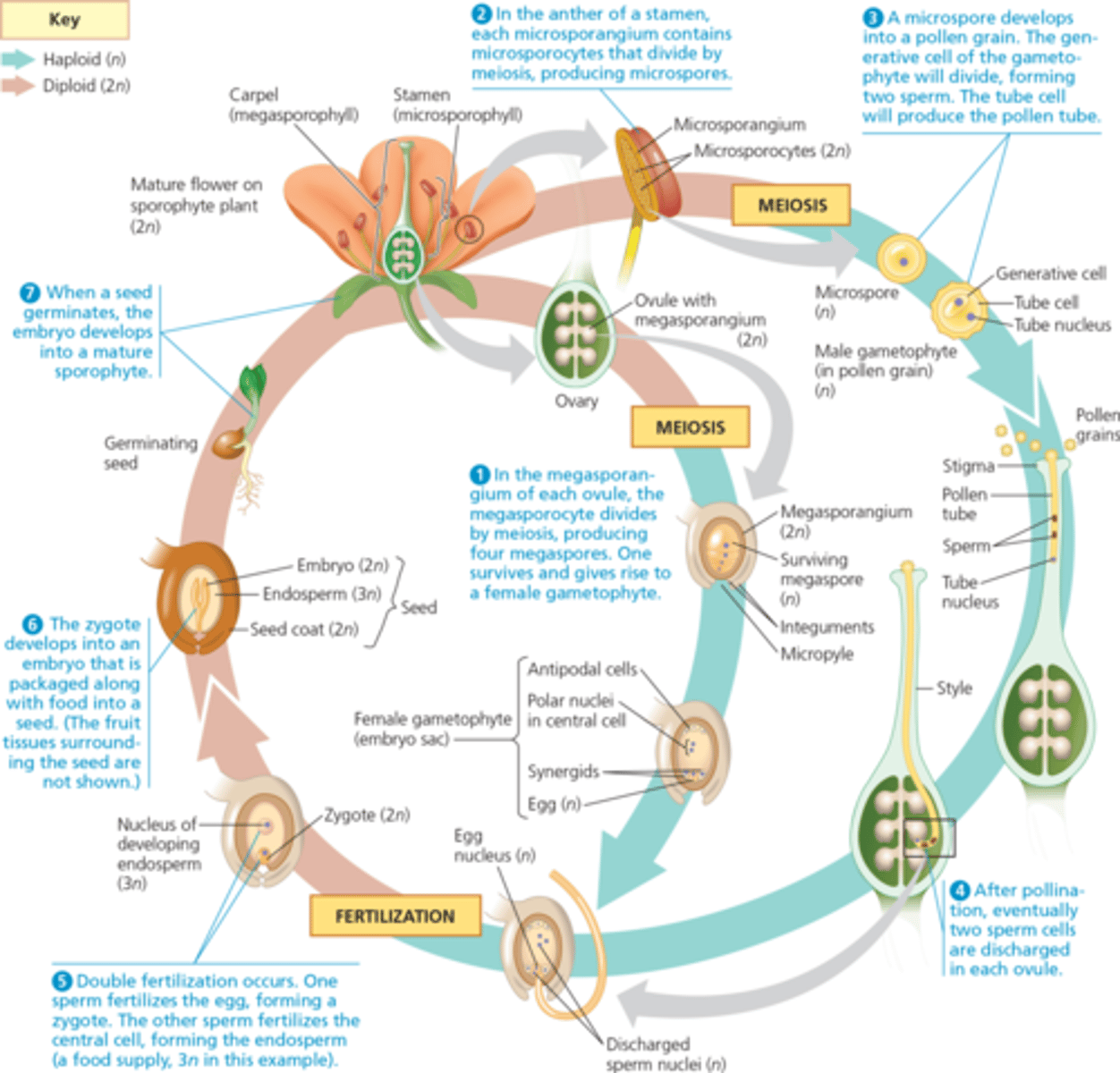
Double Fertilization
Angiosperms reproductive process
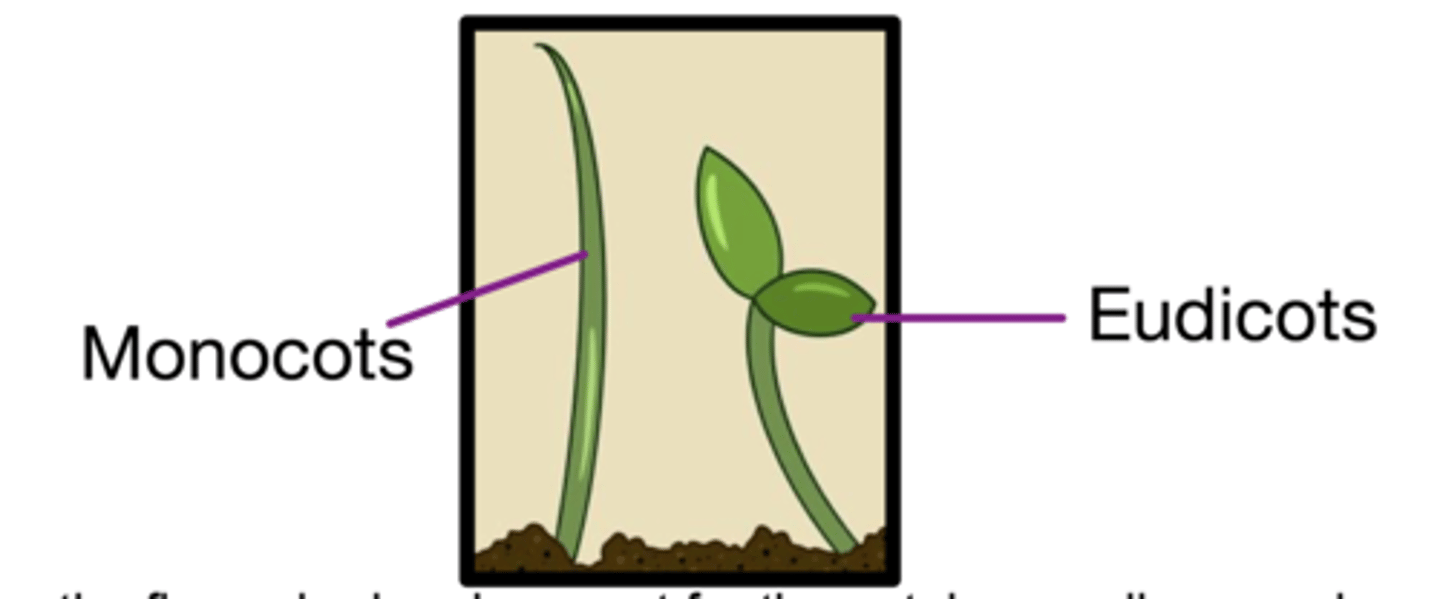
Monocots / Eudicots
Two large / diverse angiosperm lineages
Monocots: 1 Cotyledon
Ex: Grasses, cattailes, lilies, orchids, palms
Eudicots (2 Cotyledons): most familiar seed plants
Wind to Animal Pollination
Animal costs the plant more but it is more targeted and leads to symbiotic relationship
No perianths -> Complex perianths
Conifers -> Angiosperms (Seed Components)
Naked seeds -> Seeds inside fruits
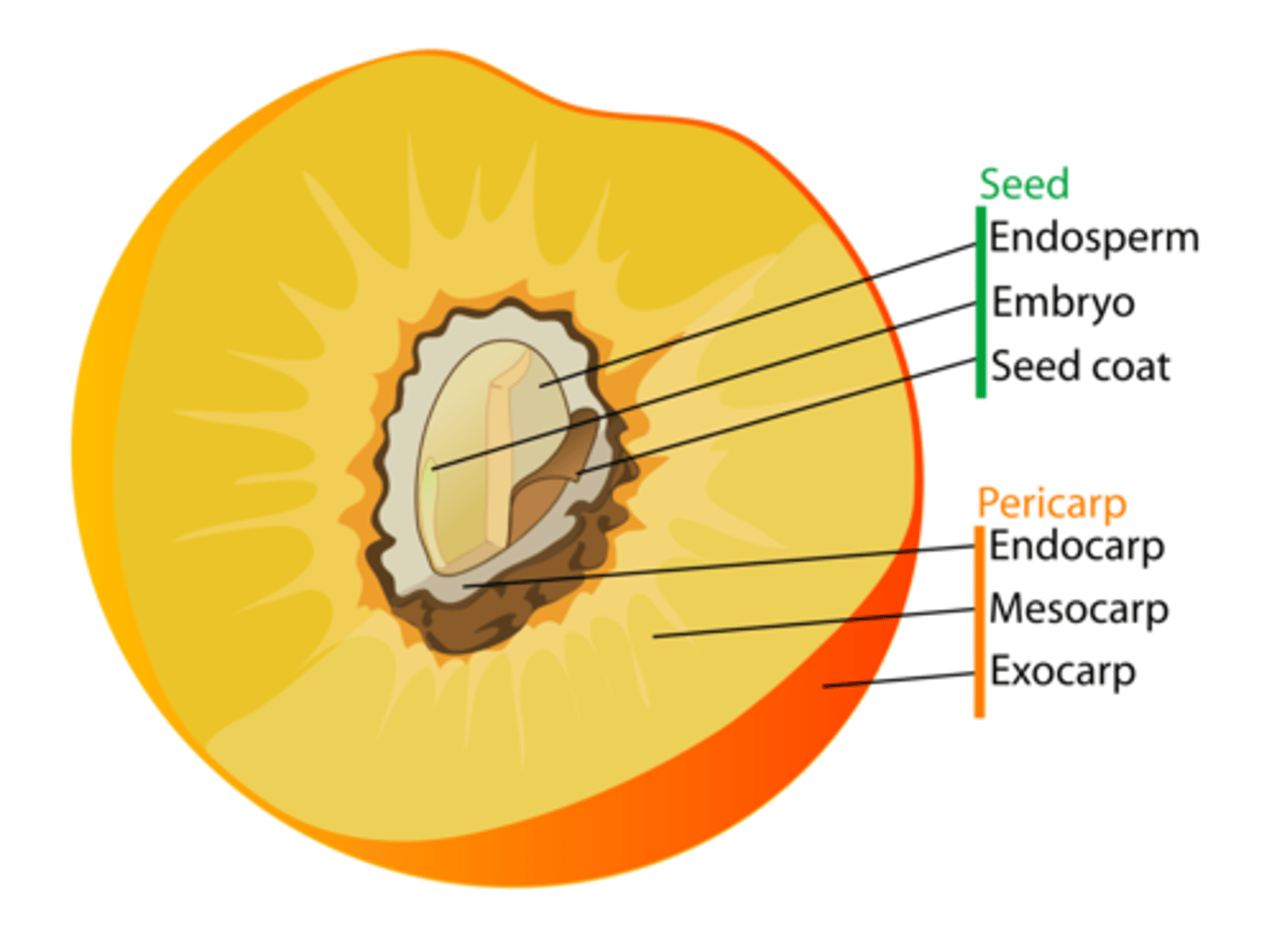
Cereal Grains (wheat): Endosperm, embryo, seed coat (bran, inner, dry fruit ovule outer wall)
Refined Foods: lack embryo/bran
Coevolution
Between animals and flowering plants
-Fused petals form tube flowers that grant access to certain species
-Timing of flowering targets other species
Fruits (development? Job? Vegetables?)
-Develop from ovaries after fertilization
-Protect seeds + aid in dispersal (fruit consumed by animal, excrete the seeds)
-Vegetables: everything else, leaves, roots
Fruit Types (5 + examples)
1. Simple: 1 carpel or fused carpels (peach, dandelions, seed + husk)
2. Multiple Inflorescence: Multiple flowers (Pinneapple)
3. Aggregate: Several fused carpels (raspberries, blueberries)
4. Accessory: 1 carpel + other parts (pears)
5. Aggregate Accessory: Ovary on outside of fruit (strawberries)

Secondary Metabolites
Organic compounds not essential for basic cell structure + growth but aid in survival, structure, and reproduction
3 Major Classes in Plants (secondary metabolites)
1. Terpenes/Terpenoids: citronella, rubber, turpentine, amber
2. Phenolics: Responsible for colors/distinctive flavors (cinnamon, ginger, vanilla) - some antioxidants or absorb UV
3. Alkaloids: Affect nervous system (Caffeine, nicotine, morphine, cocaine)
Domestication (Def, Corn?, Loss of...)
Artificial selection, where traits that are desirable to humans are selected
-Over 8000 yrs, corn was domesticated from wild grass. teosinte (mexico) - many vegetables from one species
-Led to loss of shattering: ears of wild grain break apart + shatter their grains
Diversity of Modern Gymnosperms (5 categories)
1. Streptophyte Algae
2. Land Plants (Embryophytes), Nonvascular Plants (Bryophytes: Liverworts, mosses, hornworts)
3. Vascular Plants (Tracheophytes: Lycophytes, pteridophytes, spermatophytes)
4. Seed Plants (Spermatophytes)
5. Gymnosperms (Cycads, ginkgos, conifers), Angiosperms (flowering plants)
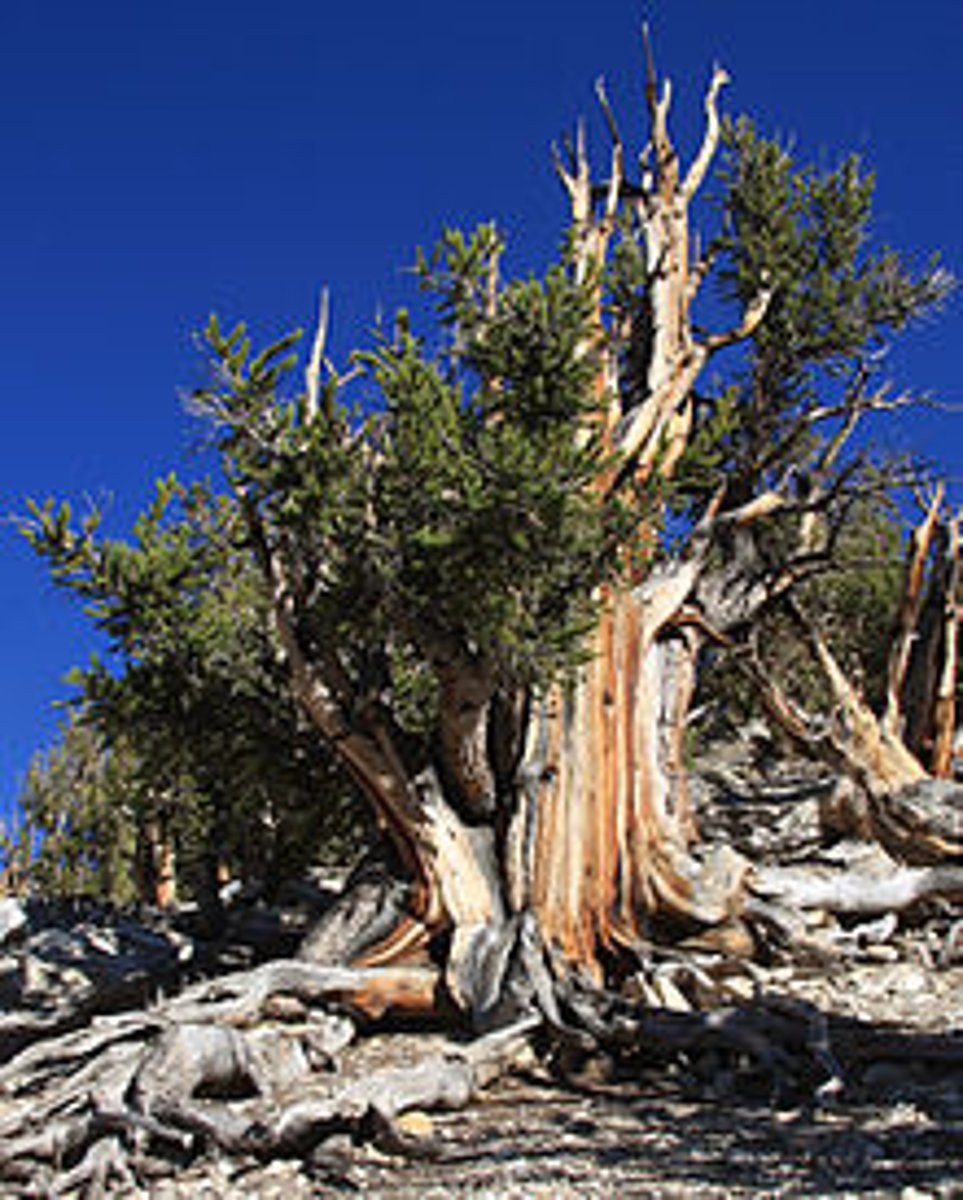
Plant Superlatives
Tallest: Coast Redwood
Oldest: Bristlecone Pine
Heaviest: Giant Sequoia

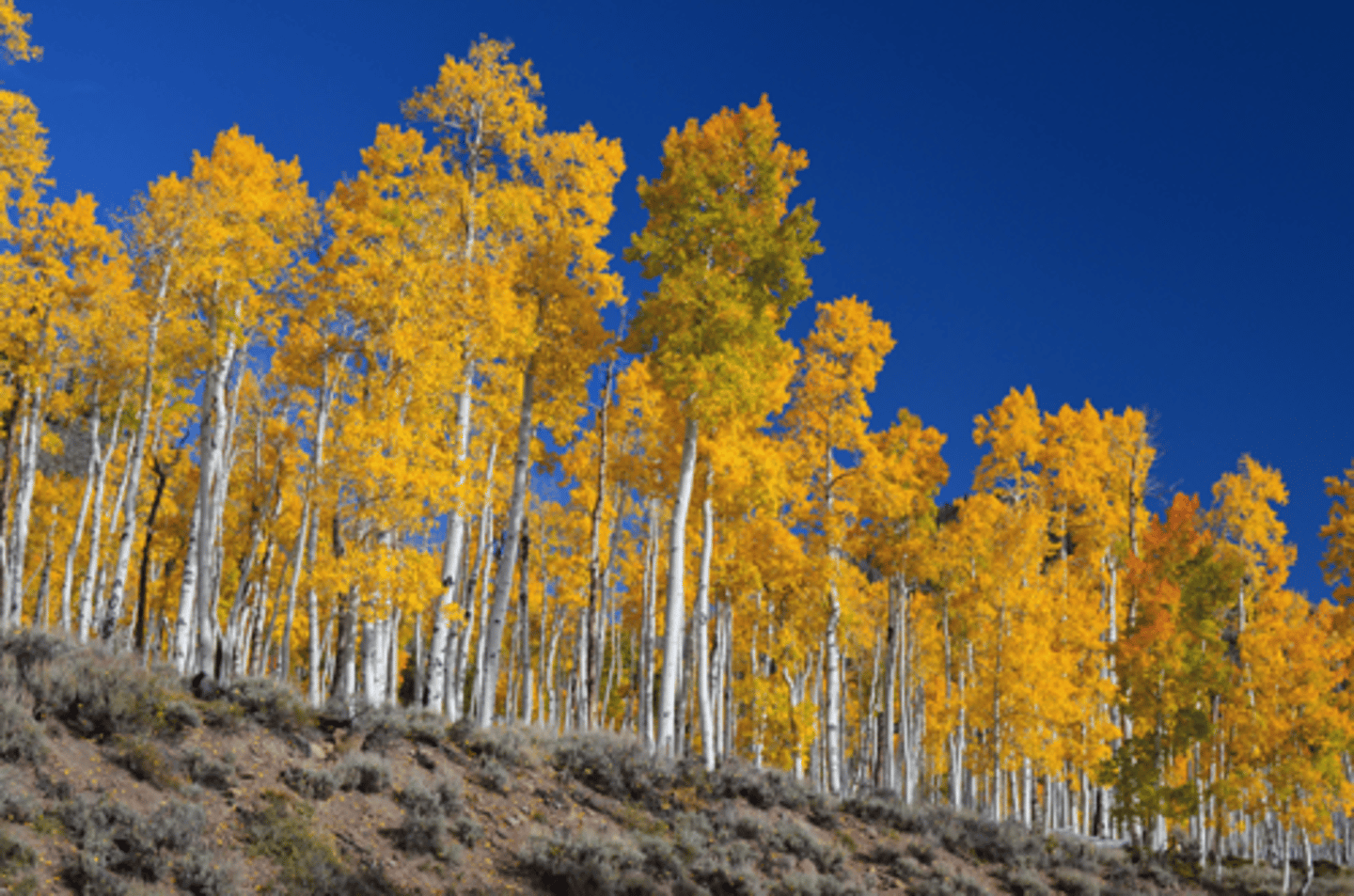
Colonial Organisms
Aspen Grove: This is the
single, largest land organism, whose 47,000 stems are connected by the same root
system and are all genetically
identical (clones)

Possible Written Portion Topic:
Alternation of generations or flower structure + function
-25.1 (Ancestry + Diversity of Land Plants), 25.3 (Diversity of modern gymnosperms), 25.4 (Diversity of modern angiosperms)