Chapter 17 -> Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What do you need to make an acid buffer solution?
significant amounts of both a weak acid and it's conjugate base
How do buffers work?
Help keep pH from drastically changing
Describe common ion effect.
Adding salt contain the anion NaA, which is the conjugate base of the acid shifts equilibrium to the left; this causes the pH to be higher than the pH of the acid solution lowering [H3O]
What does Henderson-Hasselbalch equation allow us to do?
calculate pH of a buffer solution
what is the henderson-hasselbalch equation?
pH = pKa +log(base/acid)
What does adding H+ do to a buffer?
increases acid
What does adding OH- do to a buffer?
increases base
What is buffer capacity?
amount of acid or base that can be added to buffer without causing a large pH change
A concentrated buffer can neutralize ______ added acid or base than a dilute buffer.
more
A buffer will be effective when _____________
0.1 < [base]:[acid] < 10
What is buffer range?
the maximum and minimum pH at which the buffer will be effective
What is the effective buffer range?
pKa +_ 1
Describe an acid-base titration.
a solution of known concentration (titrant) is slowly added to a solution of unknown concentration (analyte)
When is equivalence point reached?
When moles of acid are stoichiometrically equal to moles of base
What is an indicator?
A chemical that changes color when pH changes
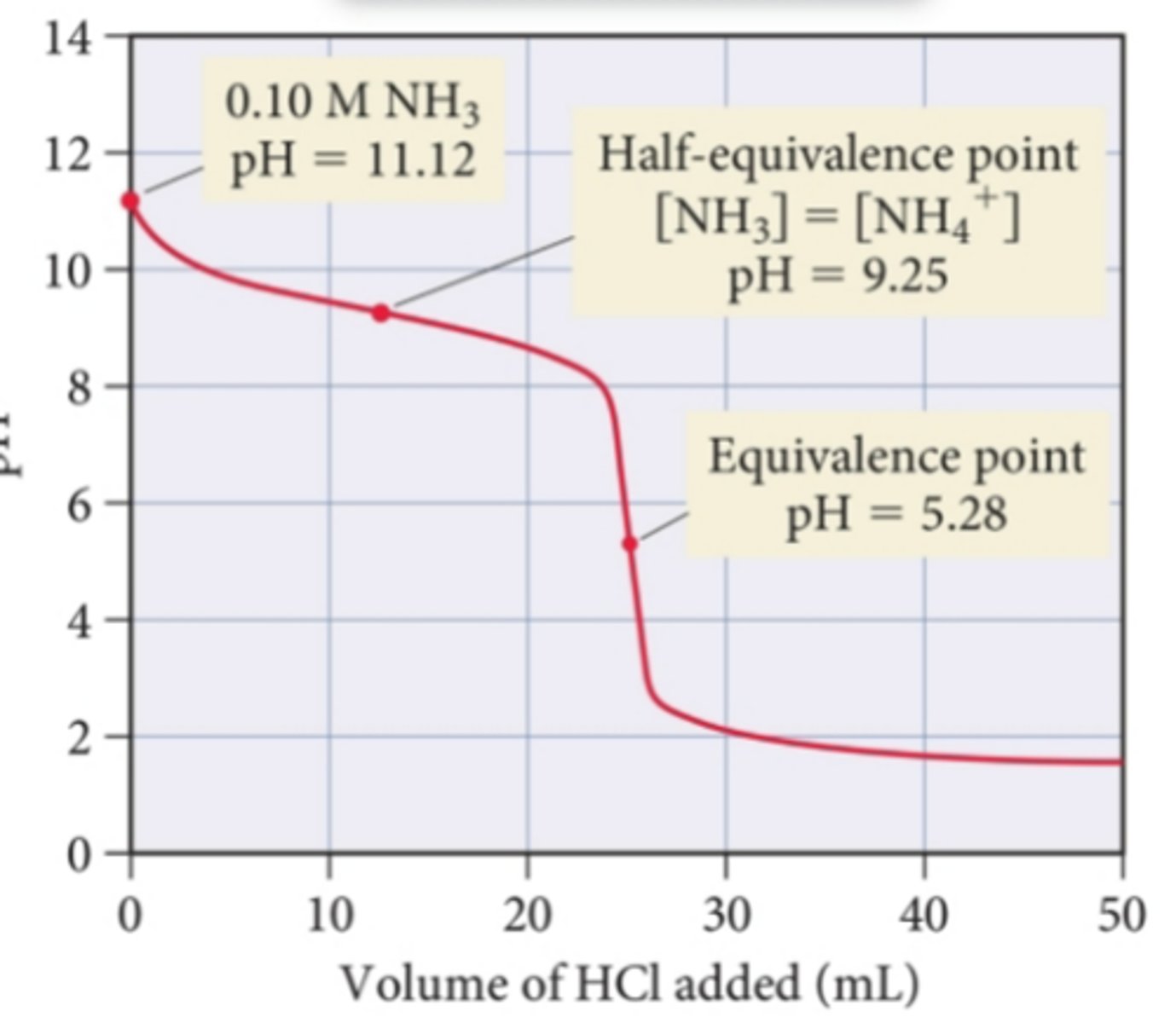
What type of titration curve goes in the negative direction with equivalence at 5?
weak base strong acid
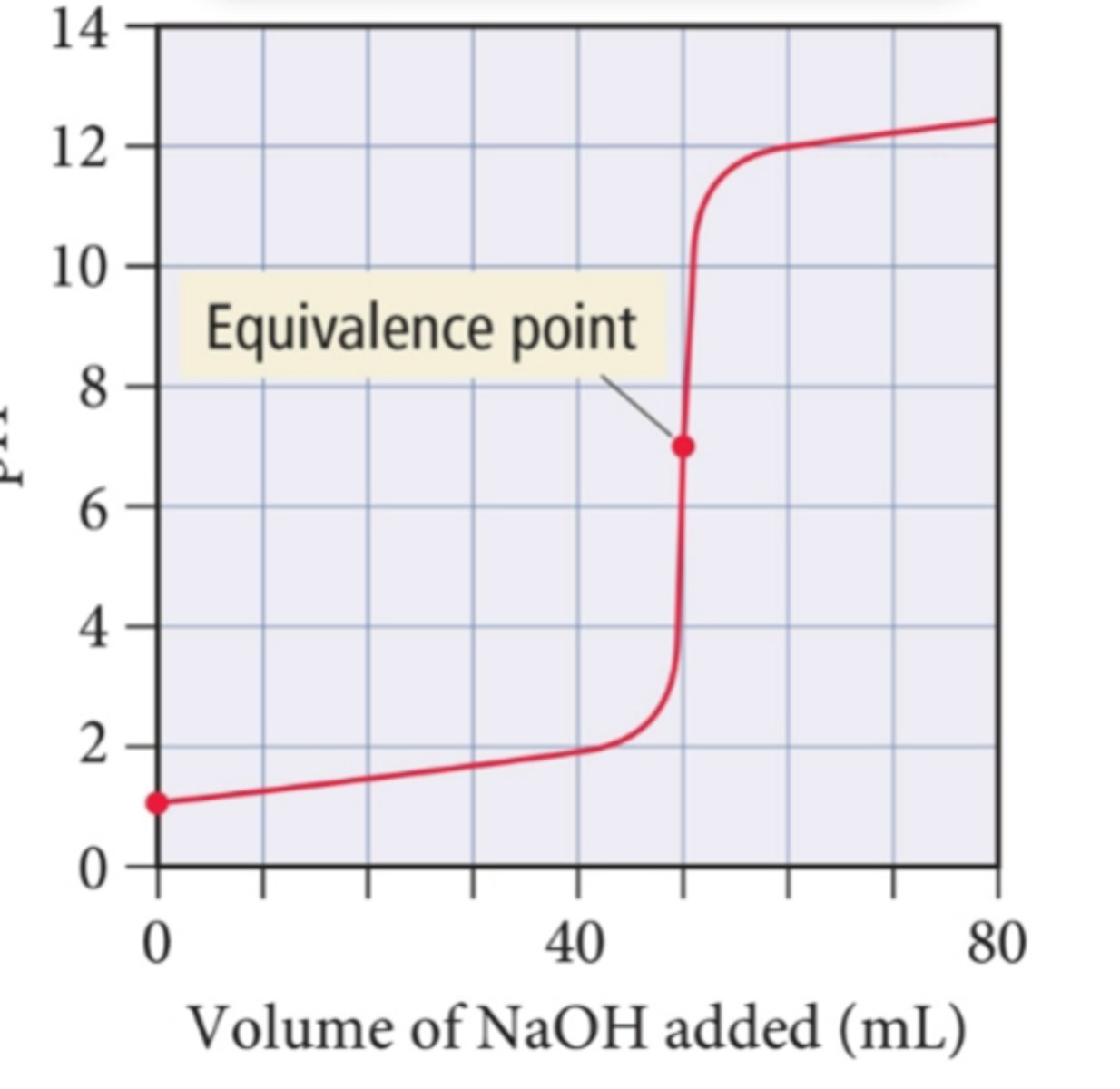
what titration curve goes in the positive direction with equivalence at 7?
strong acid strong base
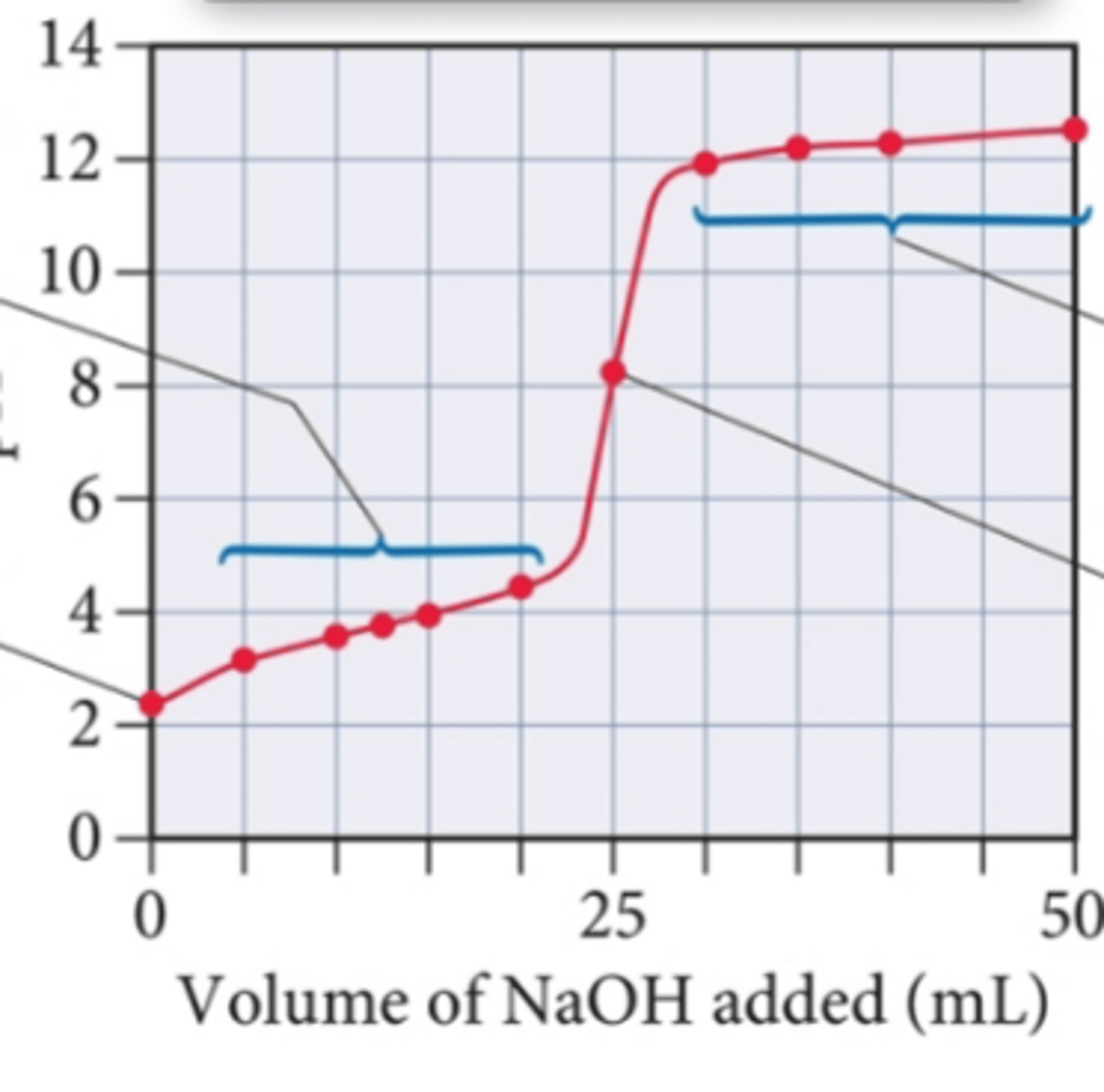
what type of titration curve goes in the positive direction with a pH above 7?
weak acid strong base
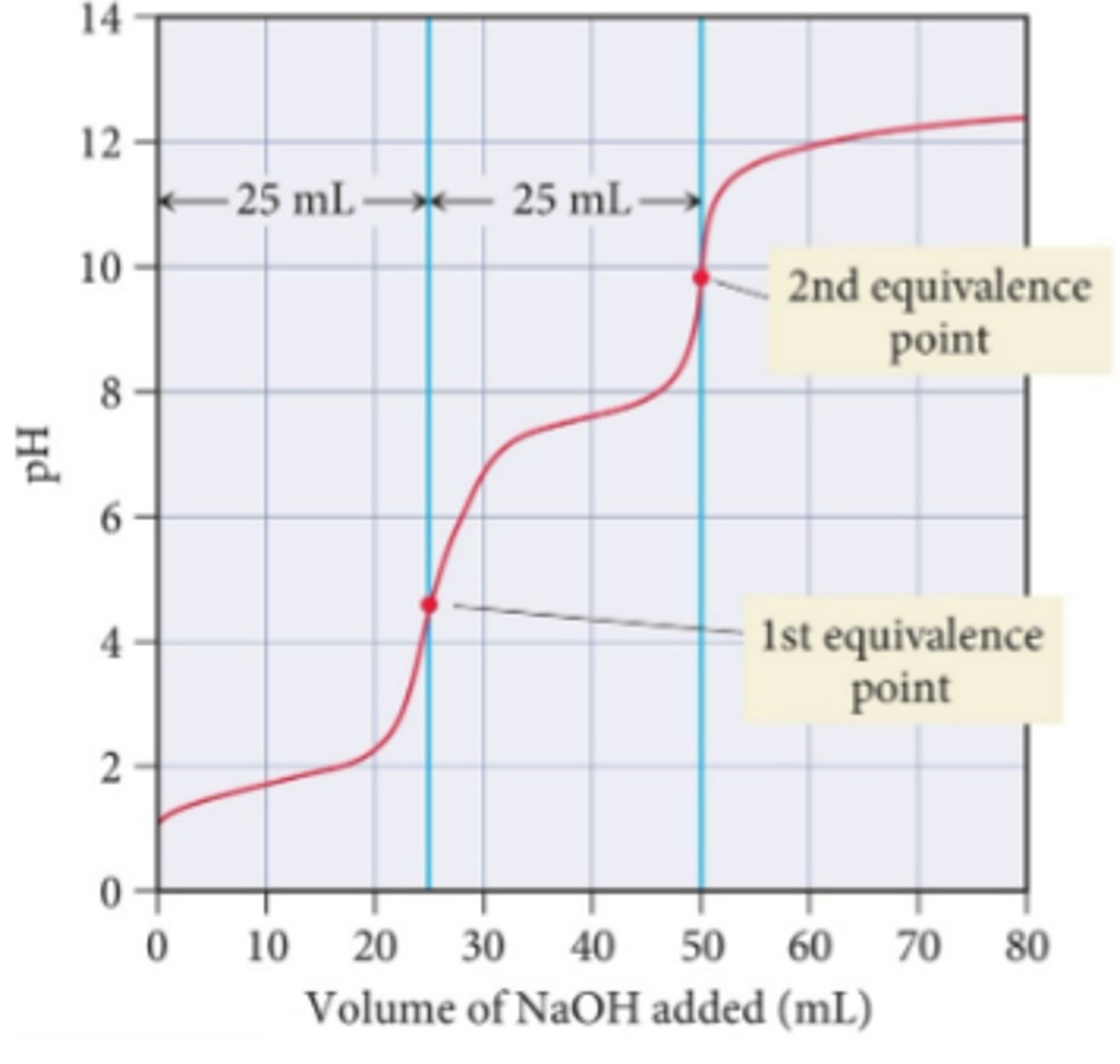
What type of titration curve has multiple equivalence points?
polyprotic acid
When titrating a weak acid with a strong base... the initial pH is that of the ______________; before the equivalence point the solution _________________; half neutralization pH = _______; at equivalence point mol HA = ________; resulting solution has only _________________________ before equilibrium is established; beyond equivalence point _______ is in excess
weak acid solution; becomes a buffer; pKa; mol base; conjugate base; OH-
What happens if Ka1 >> Ka2?
there will be two equivalence points
when is the endpoint of a titration reached?
the indicator changes color
what type of solutions are indicators?
weak acids
What does the color of solution depend on?
Concentrations of In:HIn
When In:HIn = 1
mix of colors
When In:HIn > 10
colors of In
When In:HIn < 0.1
colors of HIn
An indicator changes color within the same range as the _____________
rapid change in pH (endpoint)
pKa of HIn =
pH at equivalence point
What is Ksp?
solubility product
Describe Ksp.
equilibrium constant for dissociation of a solid salt into its aqueous ions
Describe solubility.
amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solution at a particular temperature
Define molar solubility.
Number of moles solute that will dissolve in a liter of solution; molarity of dissolved in a liter of solution
molar solubility is related to _______
Ksp
What must you have in order to compare Ksp values?
have the same dissociation stoichiometry
Describe the effect of common ion on solubility.
adding a soluble salt that contains one of the ions the "insoluble" salt decreases the solubility of the "insoluble" salt
How does pH effect solubility?
for insoluble ionic compounds that contain ions of weak acids; lower pH = higher solubility; for insoluble ionic hydroxides; higher pH = lower solubility
When will precipitation occur?
when the concentrations of ions exceed solubility of the ionic compound
Q = Ksp
saturate; no precipitation
Q < Ksp
unsaturated; no precipitation
Q > Ksp
above saturation; salt will precipitate
When Q > Ksp what can happen?
some will not precipitate unless disturbed
How is a hydrated ion formed?
transition metals bonding to one of more H2O molecules
Define complex ion.
ions formed by combining a cation with several anions or neutral molecules
Define a ligand.
ions or molecules that act as lewis bases
Define a complex ion formation reaction.
reaction between an ion and ligands to form a complex ion
What is kf?
formation constant
Describe Kf.
equilibrium constant for the formation reaction
Describe the effect of complex ion formation on solutiliby.
Solubility of an ionic compound that contains a metal cation that form a complex ion increase in the presence of aqueous ligands
The closer Ka values are...
the less distinguishable equivalence points are
how is pH monitored during a titration?
a probe that measures [H3O]