macro global context (chap 34-36)
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
international trade, globalisation, trade policies and negotiations
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
open economy
one nation is free to trade openly with another
what process has allowed for easier and increased international trade
globalisation
what does successful international trade provide an economy with
source of foreign exchange and more GDP, more capital equipment and technology, injection of demand into CFI, increased employment due to new industries surrounding exports, increased consumer choice, more availability for goods and services
how can international trade benefit emerging economies
raise their GDP as there is a larger market for their export of goods, provision of capital goods, more information and expertise, economies of scale
how can international trade benefit developing countries
foreign markets provide ability to exploit economies of scale (higher production leads to less cost per unit), usually very high demand due to lower prices, capital goods and machinery to boost production, fair trade agreements increasing income for primary sector workers
how do developing and emerging countries suffer when it comes to international trade
limited spending power as home incomes are small, unable to exploit economies of scale, lack of expertise to build capital goods, primary production domination (low productivity and volatile)
what are the issues with high exports in international trade
reliance on exports is not sustainable in the long run as financial crashes (e.g 2000s financial crisis) could lead to less trade
how does international trade link to poverty
trade can reduce extreme poverty as more exports raises the income for countries, provides jobs too
terms of trade
ratio of export prices too import prices
how are the terms of trade measured
index of export prices/ index of import prices x100
how does a change in the terms of trade index describe an economy
index goes up then terms of trade have improved, index goes down them terms of trade have deteriorated
comparative advantage
an economy can produce a good or service more efficiently and economically competitive than peers due to there being a lower opportunity cost
what is the law of comparative advantage
there will be gains in terms of trade when countries choose to specialise in production
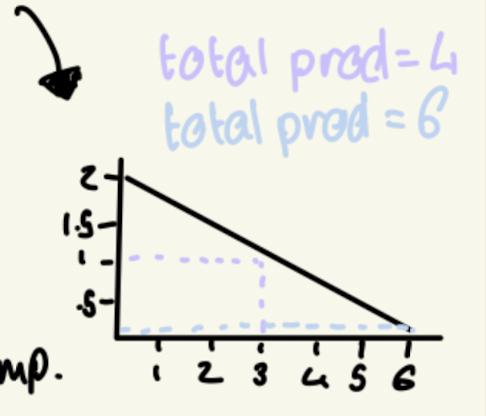
absolute advantage
economies have more technology or better conditions that means the goods they produce use less resources
how does the exchange rate affect terms of trade
appreciated rate means more imports and depreciated rate means more exports and tourism
globalisation
closer integration of global economies
what are the four main causes of globalisation
transport and communication improvements, reduction in trade barriers, deregulation of financial markets, migration
what are some consequences of globalisation
standard of living can vary as some lower income countries don’t have the income to access imported goods, structural. economic changes such as deindustrialization, emerging economies can move intoxicated production sectors to generate income
what are the three types of motives for FDI from MNCs
market seeking (selling), resource seeking (natural and labour), efficiency seeking (procurement, distribution etc)
what are the benefits from MNC FDI
provides countries with technology and infrastructure, employment, tax revenue
what are the drawbacks of MNC FDI
profits go overseas so cant enter the domestic economy, technology may not the relevant and not be used
what are some issues with global economic interdependency
oil prices cause a lot of volatility for global economies, spread of financial crisis such as the 2008 financial crisis, can jeopardise environmental progress
outline the economic activities that lead to the China and US trade war
China had rapid economic growth and US had a BOP deficit due to less exports, china had a fixed pegged exchange rate to the USD and bough government securities to maintain exchange rate, purchase of securities meant US interest rates were low and people could continue borrowing and spending, lead to an increase in the BOP deficit leading to Trump tariffs
trump tariffs
tariffs imposed on chinese imports to the US by donald trump due to the current account deficit their cheap imports fuelled
how did china respond to trump tariffs
imposed their own tariffs for US exports which reduced US demand
protectionism
measures taken by a country to reduce and restrict international trade
tariff
tax imposed on imported goods
why are tariffs important for productivity
they cant reduce demand internationally and encourage domestic producers to increase productive capacity
what is a government benefit from a tariff and how is this shown on a graph
tax revenue and increased productive potential, shown between q3 and q4
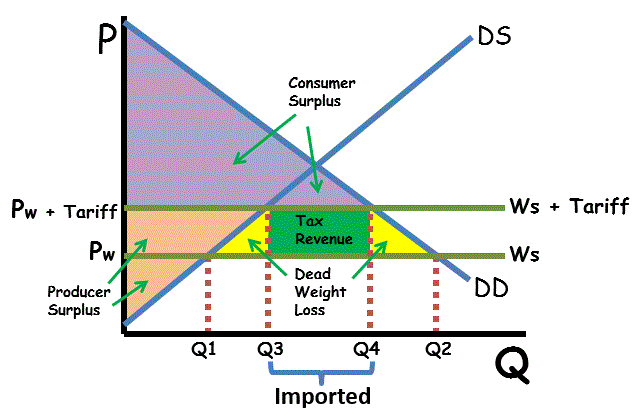
what happens to consumer surplus when tariffs are imposed
reduced consumer surplus as they are charged more as a result of higher import costs
how do tariffs affect a countries incentive to specialise
reduces the incentive as its likely to mean countries cant export to as many regions and generate more revenue therefore they may resort to diversifying their product portfolio
how can specialisation affect trade policies
as countries create surplus through specialisation and have comparatively cheaper exports, they may be able to reach trade negotiations and deals to benefit them and trading partners
who are the GATT
general agreements on tariffs and trade, organisation that promoted free trade, predecessors to the WTO
who are the WTO
world trade organisation, formally oversee international trade activities and govern them, enforce short term costs for long term gains
what is a trade war
when countries put tariffs up in response to other high tariffs, thus reducing the access to trade and spiking prices which can lead to a spike in inflation
what is a VER
voluntary export restraint- signed by countries and not enforced
quota
agreement between two countries to limit the quantity of exports to each other
what does a quota diagram look like and what does it show
demand shifts outwards slightly but not too much that domestic demand is reduced, producer gain is represented by the green rectangle and the welfare loss is the triangles on the sides as the country must import
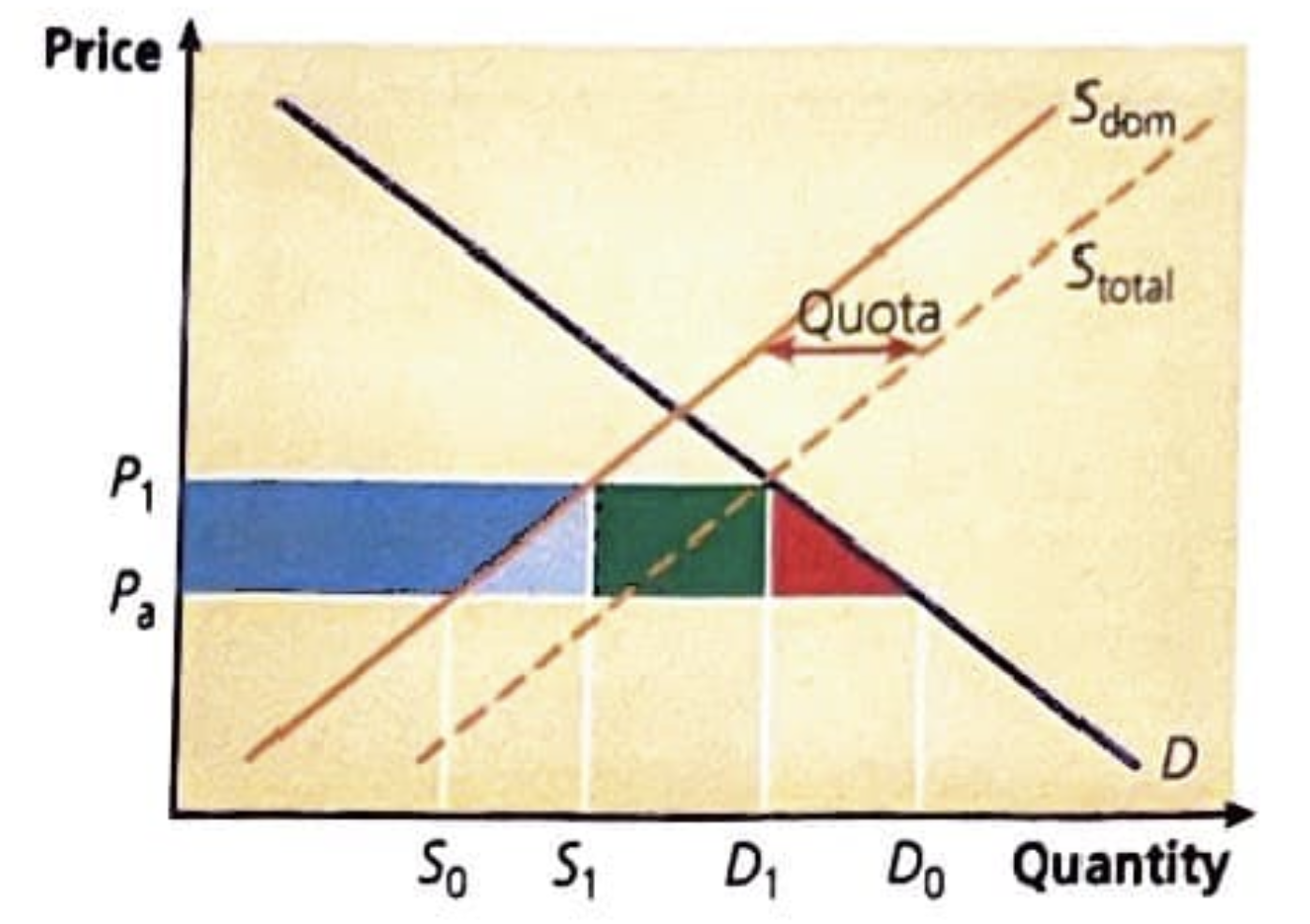
how do domestic producers gain in the event of a quota
they are able to sell at a higher price and generate more revenue as the imported goods raise the overall market price
how can domestic producers suffer in the event of a quota
they may develop poor attitudes to expanding productive potential as competition is low (less imports) which can lead to x-inefficiency
x-inefficiency
a lack of competition in a market leads to producers operate with a higher average cost of production than necessary as there is no incentive to reduce costs
non-tariff barrier with examples
barrier other than tariffs that is used to limit trade such as quality control or licensing requirements
sunset industry
industry that is in decline resulting in displaced workers
examples of sunset industries
steel industry, coal industry, oil and gas extraction
infant industry
growing industries that require protection in the short run as international competition can dismantle them
examples of infant industries
domestic automotive industries, steel industries
what is the international threat for infant industries
global exporters can have cheaper goods so placing barriers in place leads to domestic trade, as production expands prices fall and the infant industry can enter the global market
what are some pros of protectionism
countries can improve domestic industries, reduces global reliance especially in economic shocks such as war, reduces high unemployment from sunset industries, helps infant industries
what are some cons of protectionism
reduces specialism (EOS GAINS!!) and skill development especially in developing countries, hard to remove protectionism once in place, infant industries may fail which makes protectionist measures pointless
what are some producer impacts of protectionism
higher producer surplus as they can sell their goods for more, low incentives to produce efficiently so possibility of x-inefficiencies
what is the issue with domestic supply and protectionism measures
if protectionist measures are put in place to boost domestic supply, governments must consider the productive capacity of industries as they may not have the facilities to respond (lack of elastic demand) and prices may increase = inflation :(
what are some consumer impacts of protectionism
rise in prices due to tariffs and quotas, rise in equality as domestic jobs are protected, welfare losses from tariffs and quotas can create a drop in living standards, tax revenue from tariffs can be reinvested into society
what are some government impacts from protectionism
tariffs increase tax revenue, can increase equality and living standards, can help or put balance of payments at a disadvantage as imports fall
free trade
the practice of international trade without any barriers put in place such as tariffs or quotas
why may some countries argue against free trade
lack of ability to generate revenue from tariffs and protect domestic industries in terms of trade, especially in a recession where global prices may be up and affordability is low, governments cannot generate extra revenue to help their economic position, dependencies on international suppliers for imports is very volatile and can be bad in events of war
what is the global pattern of free trade and protectionism
increase in protectionism after the 2008 financial crisis due to local unemployment and a lack of domestic demand, still many free trade areas yet globally, trade is becoming fragmented
explain the trade policy patterns of the industrial revolution
free trade played a key role in importing materials and components that Britain used in its manufacturing such as cotton, yet Britain swiftly moved to protectionism measures to increase the revenue from exported goods and keep domestic industries in high demand by domestic consumers
what is the issue with a fragmented global trade market using both free trade and protectionist measures
protectionism heightens the barriers to international trade and increases inequality between developing and developed nations, trade wars pose significant affects on inflation and exchange rates
why is free global trade unlikely to happen
not all countries can agree on one singular policy / set of policies to follow
trading bloc
group of countries that agree to cooperate in international trade through some sort of free trade area or association, they usually reduce or remove barriers to trade
what are some examples of trading blocs
EU, USMCA
what are the benefits of trading blocs
allows countries to tap into the gains of free trade as well as specialise and integrate regional trade, has multiple benefits
free trade area
group of countries that agree to remove trade restrictions with each other but have no formal agreement on the barriers against non-members
what are some common issues with free trade areas
tariffs to non members can differ so trade can flow in and out of the FTA even though it originated from the FTA, can create some unnecessary transaction costs, doesn’t include the free flow of labour
what was one free trade area that failed and why, what was it replaced with
NAFTA (north american free trade area) caused a loss of US manufacturing jobs as production moved to Mexico, replaced with USMCA (us mexico canada trading bloc )
custom union
group of countries that agree to remove trade restrictions between each other and set a common agreement of trade policies against non-member states
what are some benefits of custom unions
smaller countries can benefit from economies of scale and protection from global markets as they grow, benefits from external economies of scale within the union such as transport links, more competition than protectionist measures allows resistance built by firms, sharing technology and innovation
what are some drawbacks of custom unions
transactional costs when setting up the union, difficulty in setting common barriers against non-members, must overcome geopolitical barriers, some industries may move to the geographical centre of the union to reduce transport costs which concentrates labour in one area and increases inequality
what is the largest custom union in the world
EU (27 states), have a common tariff rate to non members of 1.39%
what are the three types of custom unions
common market, monetary/ currency union, full economic and currency union
common market
group of countries with no trade restrictions, common barriers to non-members and a free movement of labour and capital with common procurement policies to encourage equality and so that governments don’t favour their own firms
monetary/ currency unions with example
groups of countries that share a common currency e.g eurozone that share the euro
full economic unions
common market agreements with common currencies, a blend of monetary unions and common markets
what is the fragility surrounding full economic unions
if one country enters a recession, it can affect the whole union, policies put in place must be carefully considered as it affects many unions
what is the structural issue with full economic unions
lots of structural changes when entering a full economic union as you have to move industries and retain workers e.g shift to financial services in the uk
what is trade creation
importing cheaper goods and resources from within trading blocs to exploit comparative advantages
why would trading blocs engage in trade creation
leads to more trade overseas and is cheaper to do than trade with those overseas, can use the raw materials to make more goods to export.
what was the large economic trade split that occurred in the uk and when
Brexit in 2016 from a referendum
why was brexit encouraged (from a trade perspective)
meant that the UK didn’t have to follow EU trade restrictions such as forming trade agreements with other countries
what do the UK need to do to preserve and create trade relations
make more trade deals with countries to gain from international trade
why may countries protest against the WTO
more integration and free trade can lead to a loss of jobs and a higher likelihood that recession will spread between trading blocs, transactional costs can also be very high
who can deal with trade disputes
the world trade organisation
what agenda was brought in by the WTO to improve trade conditions
the doha development agenda
outline the doha development agenda
set of initiatives set by the WTO to lower trade barriers and increase global trade, works on developing countries especially : removing non-agricultural tariffs, using anti dumping tariffs, subsidies and investment and being more transparent with procurement
what was the nairobi package including one of its effects
a set of initiatives by the WTO against LDCs trade, one policy was the elimination of export subsidies (money going to developed countries from their governments to incentivise them to export goods to improve the trade balance)
anti dumping tariff
tax that is added onto cheap imports to not interfere with competition domestically
what are some arguments against globalisation and close trade integration
loss of jobs, fragmenting production has a negative environmental effect, more transport is needed so affects the environment more, countries have incentives to lower their emission policies to attract MNCs for cheap production, rich countries benefit the most as they have the market power to ensure trade conditions work in their favour