UNIT B:CHEMISTRY AND MATTER SCIENCE 9
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/71
Last updated 2:23 AM on 3/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
1
New cards
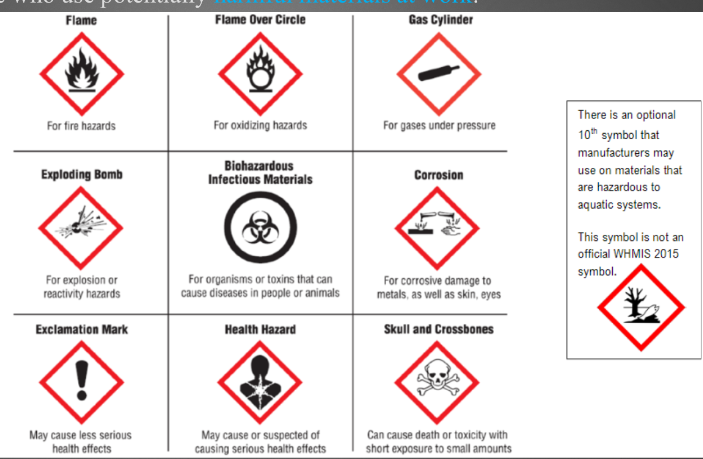
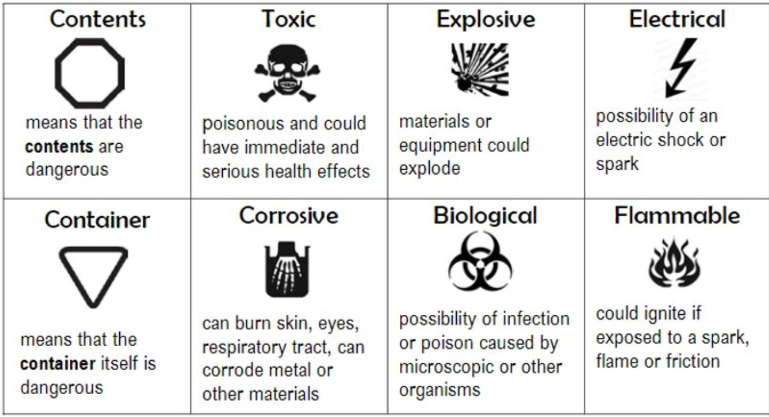
WHMIS
Workplace hazardous informative system, are symbols that indicate some sort of hazard. If a symbol is in an octagon that means its contents is the hazard, if the symbol is in a triangle, the container is hazardous.
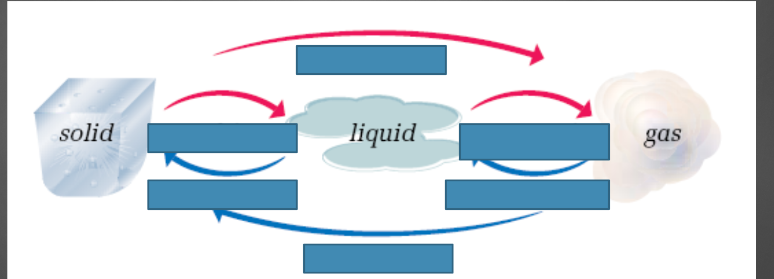
2
New cards
Matter
matter can be grouped into 3 different categories, solid, liquid, and gas, depending on the temperature
Freezing-liquid to solid
melting-solid to liquid
condensation-gas to liquid
boiling-liquid to gas
sublimation-solid to gas
deposition-gas to solid
Freezing-liquid to solid
melting-solid to liquid
condensation-gas to liquid
boiling-liquid to gas
sublimation-solid to gas
deposition-gas to solid
3
New cards
Physical properties
Physical properties are the physical characteristics of a substance, when a substance goes through a physical change, or change of state, no new substance is made and can be easily reversed.
4
New cards
Examples of physical properties
melting point-the temperature in which a substance changes from solid to liquid
boiling point-temperature in which substance changes from liquid to gas
hardness-substance ability from getting scratched
malleability-substance can be pounded into sheets
ductility-substance can be stretched into long wire
crystal shape-shape of substance
solubility-ability of substance to be dissolved in another
density-how dense a substance is/mass in given volume
conductivity-substance ability to conduct heat and or electricity
boiling point-temperature in which substance changes from liquid to gas
hardness-substance ability from getting scratched
malleability-substance can be pounded into sheets
ductility-substance can be stretched into long wire
crystal shape-shape of substance
solubility-ability of substance to be dissolved in another
density-how dense a substance is/mass in given volume
conductivity-substance ability to conduct heat and or electricity
5
New cards
Chemical properties
Chemical properties explain how a substance can interact with other substances, they cannot be easily reversed.
For example:Cooking an egg, when you cook an egg you cannot uncook it.
For example:Cooking an egg, when you cook an egg you cannot uncook it.
6
New cards
Chemical properties examples
\-reaction with acid
\-ability of getting burned
\-reaction in water
\-behaviour in air
\-reaction to heat
\-ability of getting burned
\-reaction in water
\-behaviour in air
\-reaction to heat
7
New cards
Pure substances
Pure substances is matter that cannot be broken down, they can be either elements or compounds
8
New cards
elements
element(s) are substances that cannot be broken down to any simpler substance, it is only one kind of matter.
Ex:Hg(mercury), O(oxygen), C(carbon), N(nitrogen)
Ex:Hg(mercury), O(oxygen), C(carbon), N(nitrogen)
9
New cards
compounds
when 2 or more elements combine chemically it creates a compound which is also considered a pure substance.
Ex:CO2(Carbon dioxide),H2O(hydrogen dioxide)
Ex:CO2(Carbon dioxide),H2O(hydrogen dioxide)
10
New cards
Mixtures
Mixtures is a combination of elements and pure substances, however they are not a pure substance because they aren’t chemically combined. The pure substances making up mixtures remain in original form even if they cannot be seen distinctively.
11
New cards
Mechanical mixtures aka heterogenous mixtures
Mechanical mixtures are mixtures that you can see the substances that make up the mixture.
ex:salad or soil
ex:salad or soil

12
New cards
Solutions
Solutions are homogenous mixtures where a substance gets dissolved in another, and you cannot see the substances that make up the mixture
13
New cards
suspension
cloudy mixture that can be separated easily
14
New cards
colloid
cloudy mixture that cannot be separated easily
15
New cards
physical change
material changes from one state to another
16
New cards
chemical change
2 or more materials react and creates a new substance
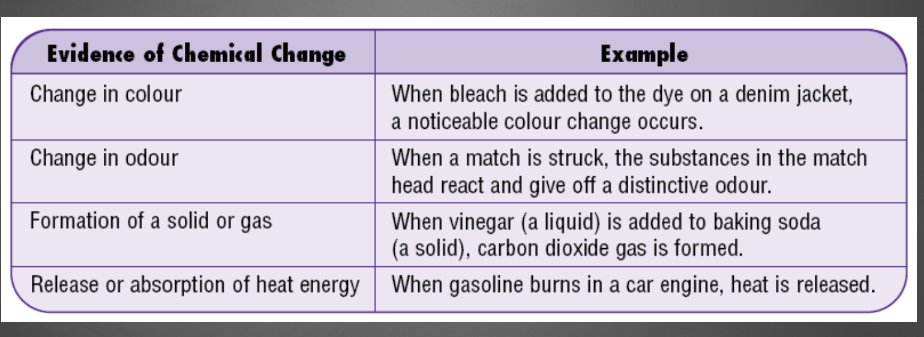
17
New cards
Democritus
First used the word atomos(atoms), to describe the smallest particles that cannot be broke down anymore. Believed each type of matter was made up of different matters, and each material had its unique set of properties
18
New cards
Aristotle
Greek philisopher
19
New cards
Chemistry
Chemistry came from the word khemia was greek for juice or plant, juice from juniper tree was used to mummify bodies
20
New cards
Alchemy
early form of investigation of nature, combined science and spiritualism. Alchemists are not considered scientists, but was first to do chemical experiments having influence on modern chemistry and science.
21
New cards
Robert Boyle
He believed gases can be compressed, and believed that everything was made up of tiny particles, like democritus, that could group together in different combinations to form substances
22
New cards
Antoine Lavisier
Developed a naming system for chemicals, and defined hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and other substances at that time. Is also known the father of chemistry
23
New cards
Combusion(1780)
Scientists found out air was necessary for combustion to occur
24
New cards
John Dalton theory aka billard ball model
First to define elements are pure substances, all atoms in an element had the same mass but no 2 elements had the same mass

25
New cards
JJ thomson theory aka rasin bun model
He used a cathode ray to find subatomic particles called electrons. He proposed the raisin bun model, which shows a positively charged sphere, with negative electrons embedded in it, making it balance out.
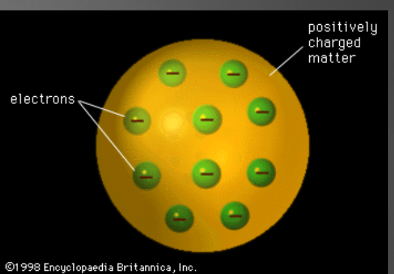
26
New cards
Hantaro Nagaoka theory
His theory was that negatively charged particles electrons orbited a positively charged nucleus. His theory was originally rejected because previous theories could not explain his
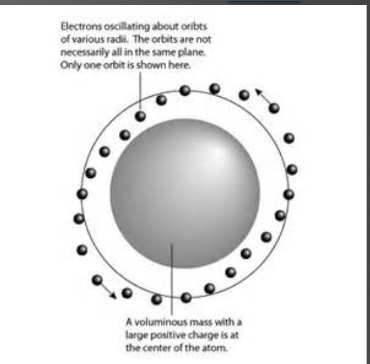
27
New cards
Rutherford model
From an experiment he did, he discovered a nucleus thats 1/10000th size of the atom, and it is positive. Also electrons surrounded the nucleus
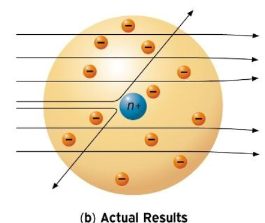
28
New cards
Niels Bohr theory
Bohr discovered electron shells, electrons move in a specific orbit and can jump from each shell if the element loses or gains energy
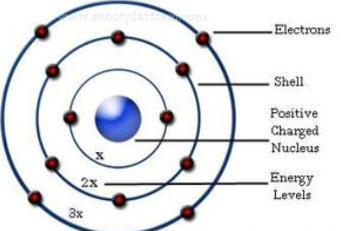
29
New cards
Chadwick theory
Discovered that nucleus was made up of neutrons(neutral charged subatomic particle), and protons(positively charged subatomic particle). Protons and neutrons are similar in mass while electrons are lighter
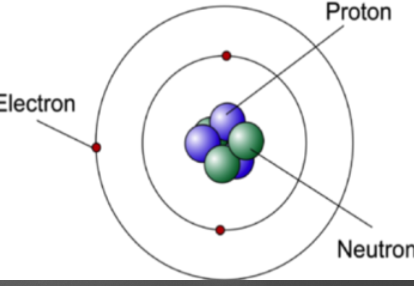
30
New cards
Quantum Model
describes an atom of a cloud of electrons surrounding a nucleus.

31
New cards
Atom
Smallest part of an element that represents that element. Has a positively charged nucleus, that composes of neutrons(neutral) and protons(positive), and has a cloud of electrons(negative) surrounding it. The electrons are in electron shells, and can jump from each shell if the atom loses or gains energy. It is neutrally charged.
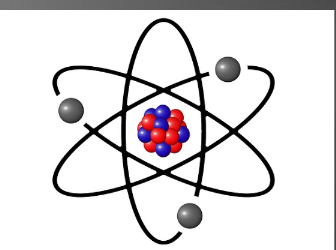
32
New cards
EXTRA INFO(you need to know)
\# of protons = # of electrons
centre of atoms aka nucleus are positively charged
centre of atoms aka nucleus are positively charged
33
New cards
Naming system of chemicals
John dalton developed a set of symbols to help communicate between chemists, then berzelius revised this by making it so that chemicals use the first or first 2 letters in its english or latin name, and making the 1st letter uppercase and 2nd letter lowercase
34
New cards
sorting out elements
Elements were listed based on atomic mass(mass number of one atom). John Newland created the law of octaves, which is a pattern in the periodic table which says that every 8 elements, or interval or 8 elements, had similar properties.
35
New cards
Mendeleev
He collected 63 elements at that time and sorted them based on their physical properties, boiling point, melting point, density, reactivity, etc. This allowed him to predict elements that didn’t exist yet.
36
New cards
Periodic table
Periods are the 7 horizontal rows, and families/groups are the 18 vertical rows
37
New cards
Atomic Number
\# of protons in element
\
\*\*# of protons=# of electrons
\
\*\*# of protons=# of electrons
38
New cards
Mass number
\# of protons + # of electrons
39
New cards
Atomic Mass vs Mass number
Mass number is mass of one atom, atomic number is mass average of all atoms in element(decimal number because of isotopes)
40
New cards
Ion charge
An Ion is an atom of group of atoms that lost or gain electrons
41
New cards
metals vs non metals
Metals
\-shiny, malleable ductile
\-conductors
\-usually solid
\
Non metal
\-dull and brittle
\-insulators
\-shiny, malleable ductile
\-conductors
\-usually solid
\
Non metal
\-dull and brittle
\-insulators
42
New cards
Metalloids
Has both Metal and Non Metal properties
43
New cards
Akali metals
\-In group 1
\-Most reactive elements \*\*
\-Most reactive elements \*\*
44
New cards
Alkaline earth metals
\-Group 2
\-EXTREMELY REACTIVE, but not as reactive as alkaline metals,
\-2nd most reactive elements\*\*
\-EXTREMELY REACTIVE, but not as reactive as alkaline metals,
\-2nd most reactive elements\*\*
45
New cards
Halogens
\-group 17
\-most reactive non metals\*\*
\-most reactive non metals\*\*
46
New cards
Noble gases
\-group 18
\-MOST STABLE ELEMENTS\*\*\*\*
\-MOST STABLE ELEMENTS\*\*\*\*
47
New cards
Naming chemical formulas
Chemical formulas should always identify the elements that make up the compound, and how much of each elements. Metal always go first, and naming system is called nomenclature.
48
New cards
subscripts
subscripts is the little number beside a letter showing how much there is of that element
49
New cards
State + aqueous notation
When there is a little letters in brackets beside a compound, that basically says what state it is in. (s) stands for solid, (l) stands for liquid, (g) stands for gas, and (aq) says its in an aqueous solution
50
New cards
Polyatomic ions
A polyatomic ion is a group of atoms of certain elements combine to create a certain ion charge
51
New cards
Naming Ionic compounds
1\.Write the Metal element 1st
2\.write the non metal element 2nd and use the -ide suffix
or
2\.Write polyatomic ion BUT DO NOT USE -IDE SUFFIX
2\.write the non metal element 2nd and use the -ide suffix
or
2\.Write polyatomic ion BUT DO NOT USE -IDE SUFFIX
52
New cards
Elements with more than one ion charge
when elements use more than one ion charge we have to use roman numerals to distinguish which charge the element has
ex:Copper has 2 ion charges, 2+ and 1+, if it uses 2+ we write the element like Copper(II), but if it uses 1+ we use Copper(I)
ex:Copper has 2 ion charges, 2+ and 1+, if it uses 2+ we write the element like Copper(II), but if it uses 1+ we use Copper(I)
53
New cards
Naming compounds
1\.Print out the elements name, metal first than non metal
2\.find out the charges of each element
3\.balance them out, so that both are equal
ex:
calcium chloride
Ca2+ Cl1-
CaCl2
2\.find out the charges of each element
3\.balance them out, so that both are equal
ex:
calcium chloride
Ca2+ Cl1-
CaCl2
54
New cards
Naming ionic compounds with polyatomic ions
if there is a polyatomic ion, and it balances out perfectly, then just write it out how its written. But if its unbalanced and the polyatomic ion has more than 1 atom write the polyatomic ion is brackets, then put the number of the polyatomic ion on the outside..
EX:Iron(III)carbonate
Fe 3+ CO3 2-
Fe2(CO3)3
EX:Iron(III)carbonate
Fe 3+ CO3 2-
Fe2(CO3)3
55
New cards
Prefix rules for molecular compounds
Use rules to show how much atoms while naming molecular compounds:
1=mono
2=di
3=tri
4=tetra
5=penta
\
WHEN FIRST NON-METAL HAS ONLY ONE ATOM, DO NOT USE PREFIX MONO, BUT WHEN HAS MORE THAN ONE ATOM USE PREFIX(only applies to the first element)
1=mono
2=di
3=tri
4=tetra
5=penta
\
WHEN FIRST NON-METAL HAS ONLY ONE ATOM, DO NOT USE PREFIX MONO, BUT WHEN HAS MORE THAN ONE ATOM USE PREFIX(only applies to the first element)
56
New cards
Naming molecular compounds
1. Print out first element
2. Print out second element with -ide suffix
3. use prefixes BUT if first element only has one atom, then don’t use prefix for first element, doesn’t apply to 2nd element
Ex:CO2
Carbon oxide
Carbon Dioxide
\
Ex 2:N2O
Nitrogen Oxide
Dinitrogen Monoxide
57
New cards
Ionic Vs molecular compounds
Ionic
\-High boiling and melting point
\-conductors
\-distinct/nicer crystal shape
\-uses non metal and metal
\-uses roman numerals
\-uses ion charge
\
Molecular
\-Low boiling and melting point
\-insulators
\-rougher crystal shape
\-both non metal
\-uses prefixes
\-doesn’t use ion charge
\-High boiling and melting point
\-conductors
\-distinct/nicer crystal shape
\-uses non metal and metal
\-uses roman numerals
\-uses ion charge
\
Molecular
\-Low boiling and melting point
\-insulators
\-rougher crystal shape
\-both non metal
\-uses prefixes
\-doesn’t use ion charge
58
New cards
Chemical reactions Reactants vs Products
Reactants are the materials at the start of the reaction, products are the materials and substances created from the reaction
59
New cards
Reactions(how to write them)
Plus symbols are used to separate reactants. A line is used to separate reactants from products, and plus symbol is used to separate products
EX:wood + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
EX:wood + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
60
New cards
Evidence of chemical change
\-odour
\-colour change
\-formation of solid or gas
\-release or absorption of energy
\-colour change
\-formation of solid or gas
\-release or absorption of energy
61
New cards
Exothermic reactions
Reactions where the energy is released. Energy would be placed with the products.
EX:If a beaker is hot, the beaker will be warm to touch because its __releasing energy__
EX:If a beaker is hot, the beaker will be warm to touch because its __releasing energy__
62
New cards
Endothermic reactions
Reactions will energy is being absorbed. Energy would be placed with the reactants.
EX:If a beaker is cold, the beaker is cold to touch because its __absorbing energy__
EX:If a beaker is cold, the beaker is cold to touch because its __absorbing energy__
63
New cards
Combustion
Chemical reaction that occurs when oxygen reacts with another substance to create a substance that gives off energy
* Reaction that causes something to burn or catch on fire
* known as a exothermic reaction
* Reaction that causes something to burn or catch on fire
* known as a exothermic reaction
64
New cards
Corrosion
Slow chemical change when oxygen reacts with metal
* Rusting occurs
* exothermic reaction
* Rusting occurs
* exothermic reaction
65
New cards
Cellular respiration
A chemical reaction/change that happens in our bodies
* Glucose reacts with oxygen to create carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
* exothermic reaction
* Glucose + oxygen →Carbon dioxide + water(hydrogen dioxide) + energy
* Glucose reacts with oxygen to create carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
* exothermic reaction
* Glucose + oxygen →Carbon dioxide + water(hydrogen dioxide) + energy
66
New cards
Law of conservation
Scientific law in which matter is not destroyed nor created during a chemical reaction. Proven in closed systems, and in open system, gas can escape still proven it exists
67
New cards
Closed systems
closed system means no extra material can enter nor leave, for matter to be conserved, the experiment must be done in a closed system.
68
New cards
Open systems
Open systems, the reaction is open to the environment. Even law of conservation cannot be proven in open systems, doesn’t mean it doesn’t happen. An opening allows gases to escape, meaning matter was still conserved.
69
New cards
Catalysts
Help a reaction go faster, doesn’t need to be apart of reaction, if there is no catalysts then there must be a higher temperature.
70
New cards
Concentration of reaction
The greater concentration of reactants, the faster the reaction. Because of higher concentrations, more atoms can react
71
New cards
Temperature of reaction
When heat is added to reactants, the faster the reaction. Since heating up a substance can make particles go faster, this can cause them to collide more often
72
New cards
Surface area of reaction
The high the surface area of reaction, there is more space exposed and available to react