A1.1 Water (copy)
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Where do most life processes occur?
Water
Where did the first cells originate from?
Water
How are hydrogen bonds formed?
Due to the polarity of covalent bonds in water.
Draw the molecular structure of water (using charges)
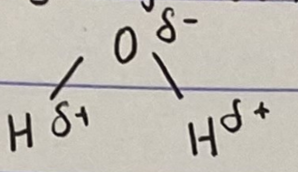
Draw the covalent structure of water
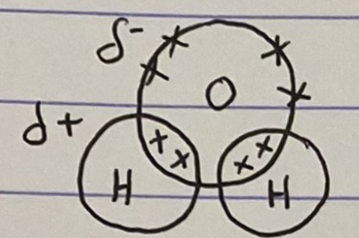
What causes polarity?
The unequal distribution of electrons.
What is the charge on oxygen?
Negative
What is the charge on hydrogen?
Positive
Define cohesion
Force by which individual molecules of the same type attract and associate.
What causes cohesion in water molecules?
Hydrogen bonds
How strong are hydrogen bonds? And what is it’s effect on water?
Hydrogen bonds are weak and are therefore always breaking and reforming. But can be strong in large numbers.
Give an example of the cohesive property of water.
Water flows up the inside the xylem vessel under tension due to the transpiration stream.
What other property does a transpiration stream have?
It’s a continuous stream
Define surface tension
Property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force, due to the cohesion between water molecules
What does surface tension allow for aquatic life?
It allows smaller organisms to the move along the surface
Give an example of an animal that moves across the surface of a water.
Pondskater
Define adhesion
The force by which individual molecules are able to bond, via hydrogen bonds, to other molecules which are polar, or charged.
Name a molecule that water adheres to in the xylem vessel
Cellulose
Define capillary action
The tendency of a liquid to move up against gravity when confined within a narrow tube, also known as a capillary.
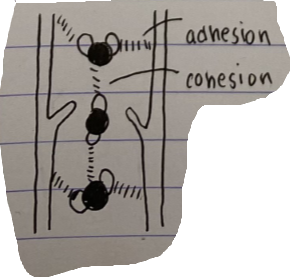
Draw a diagram showing water moving up a xylem vessel, label adhesion and cohesion and describe the process
Water is drawn up narrow tubes in the soil and into the plant via capillary action, when drawn into the plant, the water can move up the vessel through adhesions, by sticking to the walls of the plan.
Define hydrophilic
Attracted to water (e.g. hydrogen bonds are easily formed between a hydrophilic molecule and water)
Define hydrophobic
repelled by water (e.g. cannot form hydrogen bonds)
What is a molecule forming a hydrogen bond with water more commonly known as?
Dissolving
Is a polar molecule hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Hydrophilic
Is non-polar hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Hydrophobic
Give an example of cell function dependent on polarity
Phospholipid have hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails form the hydrophobic core of cell membranes
Where do most enzymes catalyse reactions?
In aqueous solution
Where do matabolic reactions take place?
Water
Why do most metabolic reactions take place in water?
Water has a neutral pH, and water can also store large amounts of heat, and water is also electrically neutral
Define buoyancy
The ability of any fluid to provide an upward vertical force on an object placed in or on it.
What is water’s buoyancy?
Water has a high buoyancy (animals can float on water)
Define viscosity
A measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow
What is water’s viscosity?
Water has a high viscosity (it’s easier to walk through air, low viscosity, than through water).
Define thermal conductivity
The measure of how easily heat flows through a specific type of material
What’s water’s thermal conductivity?
Water has a high thermal conductivity (it’s easier to lose heat in water than in air, i.e. you get colder in water)
Define specific heat capacity
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of substance.
What’s water’s thermal heat capacity?
Water has a high thermal conductivity (you need more energy to raise the temperature of water than to raise the temperature of air)
Give two examples of animals that use the properties of water to live
The ringed seal and the black throated loon
Explain how the black throated loon used the properties of water to live
Thermal conductivity: the loon’s feathers trap a layer of air between it’s feathers to keep in the heat
Buoyancy: Loons have hollow bones, it solid bones, which allows them to sink beneath the water to catch their prey
Buoyancy: Loons are covered in a thin layer of oil to allow for better floating
Viscosity: Loons have webbed feet which allow for quicker movement in water
Explain how the ringed seal uses the properties of water to live
Buoyancy: Seals live on the ice, as it can float on water
Viscosity: Seals have flippers that are used to propel themselves
Thermal conductivity: Seals have a layer of blubber (fat) to keep warm