Proteins, Nucleic Acids, the Nitrogen Cycle, and the Phosphorus Cycle Quiz
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Protein
a functional biological molecule consisting of one or more polypeptides folded into a 3D structure
What is the monomer of proteins?
Amino acids
Do proteins have simple or complex structures?
complex and varied
proteins act as __ that regulate chemical reactions within cells
enzymes
What makes up ligaments and tendons?
proteins
The function of proteins depend on…
shape
Denaturation
When a protein unravels, losing its specific structure and function
ex) the separation of DNA strands
Amino acids
an organic molecule containing a carboxyl group and an amino group
Peptide bond
the covalent bond between two amino acids in a polypeptide
polypeptide
a chain of amino acids
Primary structure of proteins
the 1st level of structure that is just a chain of amino acids (polypeptide)
secondary structure of proteins
the regular pattern of coils or folds of a polypeptide chain
Tertiary structure of proteins
The 3D shape formed by folded proteins
Quaternary structure of proteins
The 3D structure of many polypeptide chains folded and linked together through peptide bonds
Where is nitrogen found?
Soil and atmosphere
What’s the largest reservoir for nitrogen?
Atmosphere
Nitrogen fixation
The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to nitrogen compounds (NH4+ and NO3-) that plants can absorb and use
What do plants use nitrogen for?
Building proteins
Can plants and animals directly absorb nitrogen from the atmosphere?
No
How do animals get nitrogen?
Eating plants
The ______ of plants and animals and the ___ of animals release nitrogen
The death/decomposition and the waste
What is phosphorus in (atomically)?
Nucleus acids, phospholipids, and ATP
What’s the only source of phosphorus on earth?
Rocks (meteorites and earth lithosphere/crust)
What’s the function of Human Growth Hormone?
● Allows for tissues, organs, cartilage, and
bones to grow in the human body
● It stimulates protein synthesis and increases fat hydrolysis, which gives the body more energy to allow for tissue growth (mitosis)
Insulin function
Insulin clears glucose from the blood and stores it as glycogen. If a person lacks insulin (has diabetes), glucose builds up in the bloodstream instead of going into your cells for energy, so they have to inject insulin into their blood.
Keratin
Forms the hair, skin, and nails. Also aids the body in healing wounds and strengthening skin
Collagen
Improves hair health and growth and promotes bone and muscle growth.
Hemoglobin
Found in the bloodstream. Carries oxygen to and CO2 from cells
Myosin and actin
Proteins that allow muscle movement by pulling on one another
Melanin
Produces skin, eye, and hair pigmentation and protects skin from UV rays
Salivary amylase
Initiates digestion of carbs and breaks down complex starches
Thyroxine
Controls how much energy the body uses
Albumin
Keeps fluid from leaking out of the cells into body tissues
What are the general functions of proteins?
Enzyme, storage, signal, contractile, defense, transport, receptor, structural
What elements are proteins made of?
C, O, H, N
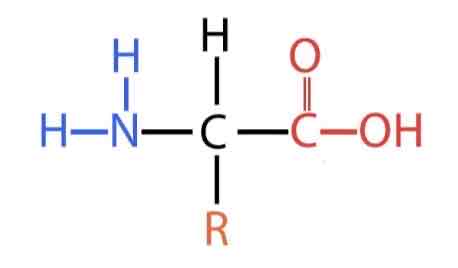
What does this show?
A monomer of proteins
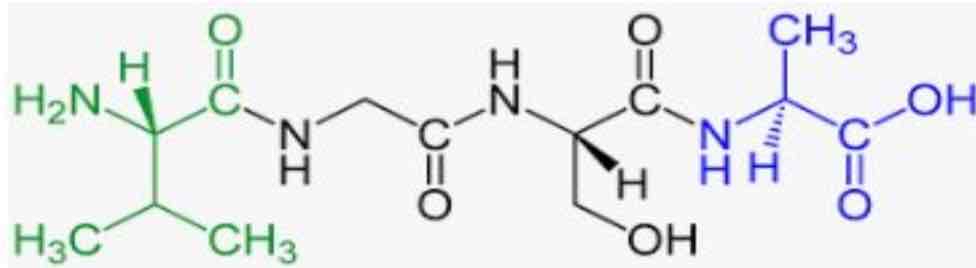
What does this image show?
Polymer of proteins
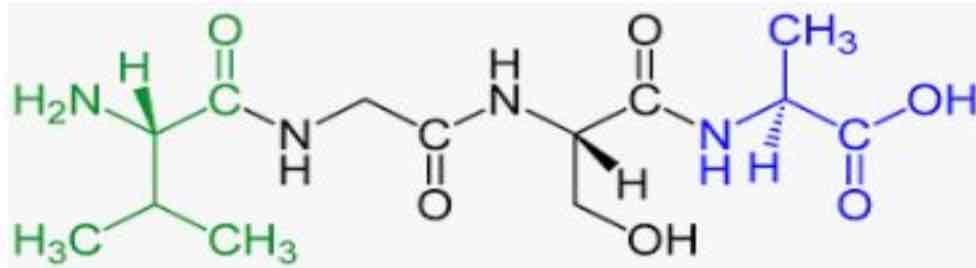
How many proteins are in this image?
4 —- four nitrogen atoms
What atom does every protein have one of?
Nitrogen
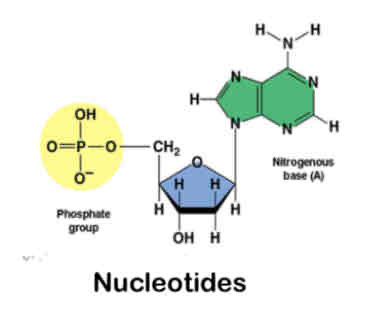
what does this image show?
Nucelic acid monomer
What determines the polarity and therefore function of amino acids?
R groups
How do protein polymers form?
Dehydration synthesis and peptide bonds
What organisms make proteins?
all living things
What cycles are necessary to make proteins?
Water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles
What elements are in nucleic acids?
CHONP
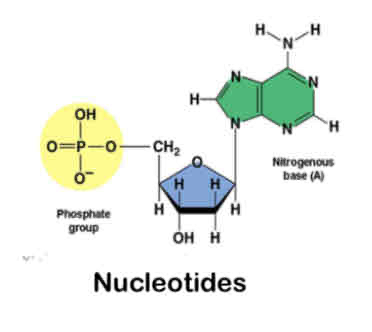
What does this image show?
monomer of nucleic acids
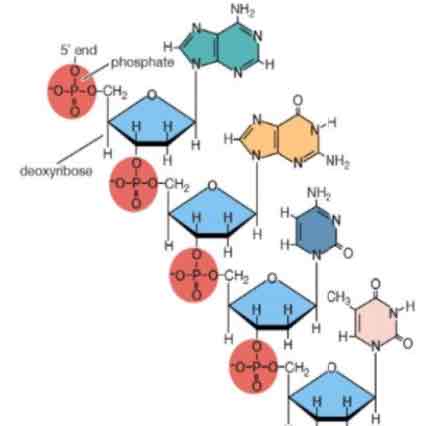
What does this image show?
Polymer of nucleic acids
What are the monomers of nucleic acids called?
Nucleotides
What are the polymers of nucleic acids called?
Polynucleotides
Function of nucleic acids
Protein synthesis and storage of genetic info
What cycles are needed to make nucleic acids?
Water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycle
What is the first step of the nitrogen cycle?
Bacteria traps nitrogen gas from the air (atmosphere) in the soil
How does nitrogen enter plants?
it is absorbed through the roots after being “fixed”
Why can’t plants absorb nitrogen from the atmosphere?
N2 is non-polar and can’t be absorbed by water
What is the second step of the nitrogen cycle?
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria changes nitrogen gas into (NH4+) solid ammonium
In the nitrogen cycle, once N2 is changed to NH4, what happens?
Hydrogen atoms in NH4 bond with oxygen atoms. The molecule is dissolved in water because it’s polar
What is the third step of the nitrogen cycle?
NH4 is dissolved in groundwater and absorbed into plant roots
In step 3, nitrogen is _____ into amino acids with carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms
Assimilated
What is the fourth step of the nitrogen cycle?
Bacteria converts some NH4 to NO3- which gets dissolved in water
What is the fifth step of the nitrogen cycle?
NO3- is absorbed by plant roots and assimilates into amino acids with C, H, and O
What is the sixth step of the nitrogen cycle?
Animals get proteins by eating plants and digesting them into amino acids
What is the seventh step of the nitrogen cycle?
Bacteria and fungi decompose dead plants and animals, releasing nitrogen into the atmosphere.
What is the eighth step of the nitrogen cycle?
Bacteria can convert NH4 and NO3 back into non-polar N2 and release it into the air
How do carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen first get into a plant?
Photosynthesis
Which cycles/processes come first, and which second?
photosynthesis and water cycle first, then nitrogen
Humans can’t make ____ but plants can
Organic molecules
plants need nitrogen atoms to be polar so the atoms are able to…
Dissolve in water (can be absorbed through the roots)
What is a major component in the breaking down, rearranging, and movement of nitrogen?
Bacteria
If there’s a __ atom, it’s a nucleic acid
Phosphorus
DNA and RNA
DNA is the instruction to make your traits. RNA follows instructions and makes proteins for the traits
What allows phosphorus to get into the lithosphere/crust?
Tectonic plate movements (converging, diverging, volcanic activity) and the weathering of rocks over time
The erosion of rocks goes into…
Bodies of water and soil