Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA)
1/439
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
440 Terms
amb
ambulatory
BM
bowel movement
BP, B/P
blood pressure
c̄
with
c/o
complains of
DX
diagnosis
f/u
follow up
isol
isolation
p.c.
after meals (post cibum)
prn
as necessary
q (with a bar over it)
every
q.2h.
every 2 hours
q.h.
every hour
s (with line above)
without
stat
immediately
T
temperature
TID
three times a day (ter in die)
TPR
temperature, pulse, respiration
v.s.
vital signs
w/c
wheelchair
confusion can be caused by
UTI
low blood sugar
CVA
head trauma or head injury
dehydration
nutritional problems
fever
sudden drop in body temp
lack of oxygen
medication
infection
brain tumor
illness
loss of sleep
seizures
not using a hearing aid when necessary
cerebral palsy (CP)
condition characterized by lack of muscle control and partial paralysis, caused by a brain defect or lesion present at birth or shortly after
Spina Bifida
a congenital defect that occurs during early pregnancy when the spinal canal fails to close completely around the spinal cord to protect it
localized infection
redness
swelling
pain
heat
drainage
systemic infection
fever
chills
headache
change in other vital signs
nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
mental confusion
activities of daily living (ADLs)
personal daily care tasks, including bathing, skin, nail, and hair care, walking, eating and drinking, mouth care, dressing, transferring, and toileting
acute care
24-hour skilled care for short-term illnesses or injuries; generally given in hospitals and ambulatory surgical centers
animal-assisted therapy (AAT)
the practice of bringing pets into a facility or home to provide stimulation and companionship
assisted living
residences for people who do not need skilled, 24-hour care, but do require some help with daily care
charge nurse
a nurse responsible for a team of healthcare workers
cite
in a long-term care facility, to find a problem through a survey
continuity of care
an ongoing coordination of a resident's care over time, during which the care team is regularly exchanging information and is working toward shared goals
functional nursing
method of care that involves assigning specific tasks to each team member
holistic care
care that involves the whole person; this includes his or her physical, social, emotional, and spiritual needs
hospice care
holistic, compassionate care for people who have approximately six months or less to live; care is available until the person dies
Joint Commission
an independent, not-for-profit organization that evaluates and accredits healthcare organizations
long-term care
24-hour skilled care provided for people with ongoing conditions who are generally unable to manage their ADLs
Medicaid
a medical assistance program for people with low incomes, as well as for people with disabilities
Medicare
A federal program of health insurance for persons 65 years of age and older, have certain disabilities or permanent kidney failure, or are ill and cannot work
Who makes up the majority of residents in long-term care - men or women?
women
what are three tasks that NAs do not usually perform?
1) insert or remove tubes
2) give tube feedings
3) change sterile dressings
Who is the most important member of the care team?
patient
List the "five rights" of delegation.
1. Right task
2. Right circumstance
3. Right person
4. Right direction/communication
5. Right supervision/evaluation
person-centered care
a type of care that places the emphasis on the person needing care and his or her individuality and capabilities
When surveyors visit a facility, what do they study and observe?
How well the staff cares for residents. They focus on how residents' nutritional, physical, social, emotional, and spiritual needs are met. They observe how staff interact with residents/patients.
When a surveyor asks an NA a question she does not know the answer to, how should she respond?
Tell the surveyor that you do not know the answer but will find out as quickly as possible. Follow up with the surveyor after you have the answer.
If an NA is following the chain of command, to whom would she normally report a problem?
Nurse
If an NA has forgotten the correct order in which to perform a procedure, which of the following would be the best way for her to proceed?
The NA should review the procedure before beginning.
age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
a condition in which the macula degenerates, gradually causing central vision loss

Alzheimer's disease (AD)
a progressive disease that destroys the brain's neurons, gradually impairing memory, thinking, language, and other cognitive functions, resulting in the complete inability to care for oneself; the most common cause of dementia.
bipolar disease
a type of mental health disorder that causes a person to have mood swings and changes in energy levels and the ability to function
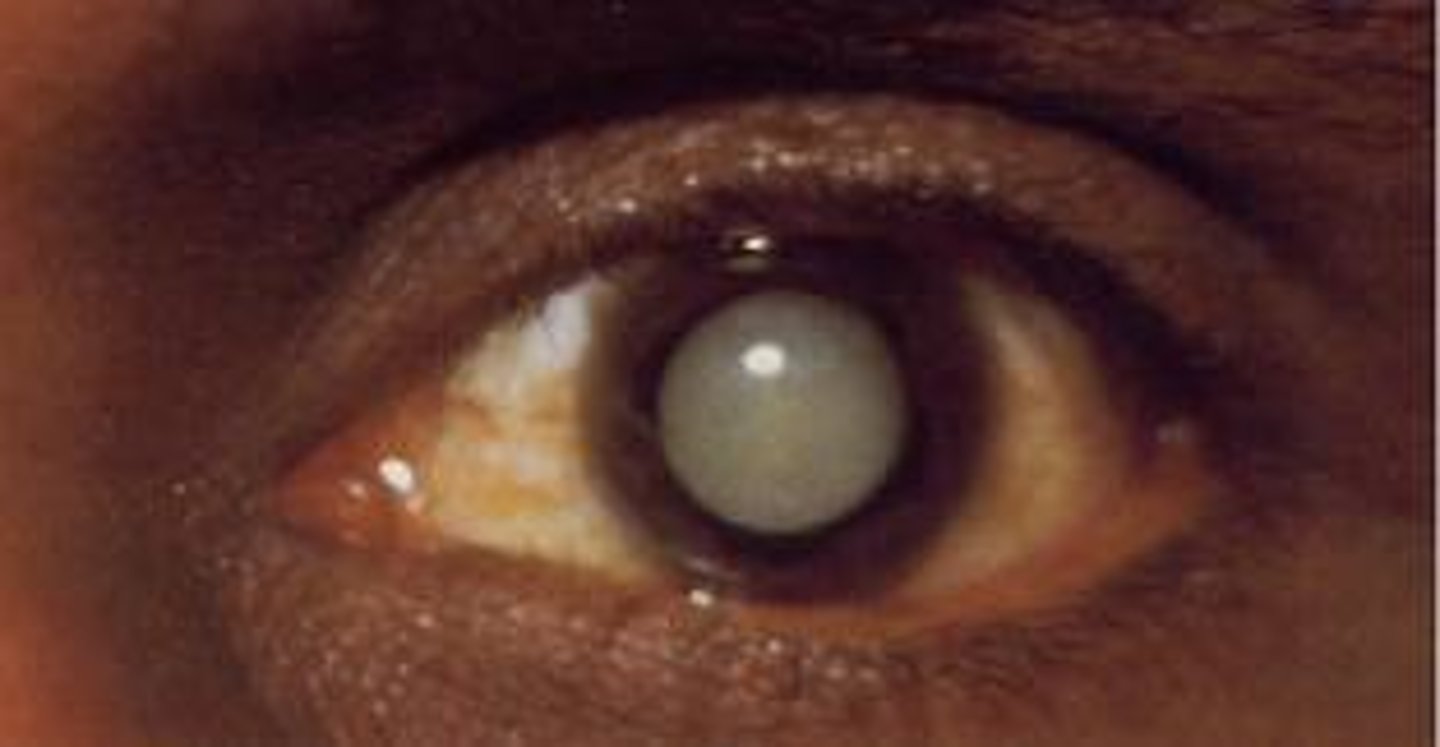
cataract
a condition in which the lens of the eye becomes cloudy, causing vision loss
catastrophic reaction
reacting to something in an unreasonable, exaggerated way
central nervous system
the part of the nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal cord
cerebral vascular accident (CVA)
a condition that occurs when blood supply to a part of the brain is blocked or a blood vessel leaks or ruptures within the brain; also called a stroke
cogntive behavioral therapy (CBT)
a type of psychotherapy that is usually short-term and focuses on skills and solutions that a person can use to modify negative thinking and behavior patterns; often used to treat anxiety disorders
concussion
a head injury that occurs from a banging movement of the brain against the skull
dementia
a serious, progressive loss of mental abilities such as thinking, remembering, reasoning, and communicating
elope
in medicine, when a person with Alzheimer's disease wanders away from a protected area and does not return
epilespsy
a disorder of the nervous system that is characterized by recurrent seizures
Farsightedness
the ability to see distant objects more clearly than objects that are near; also called hyperopia
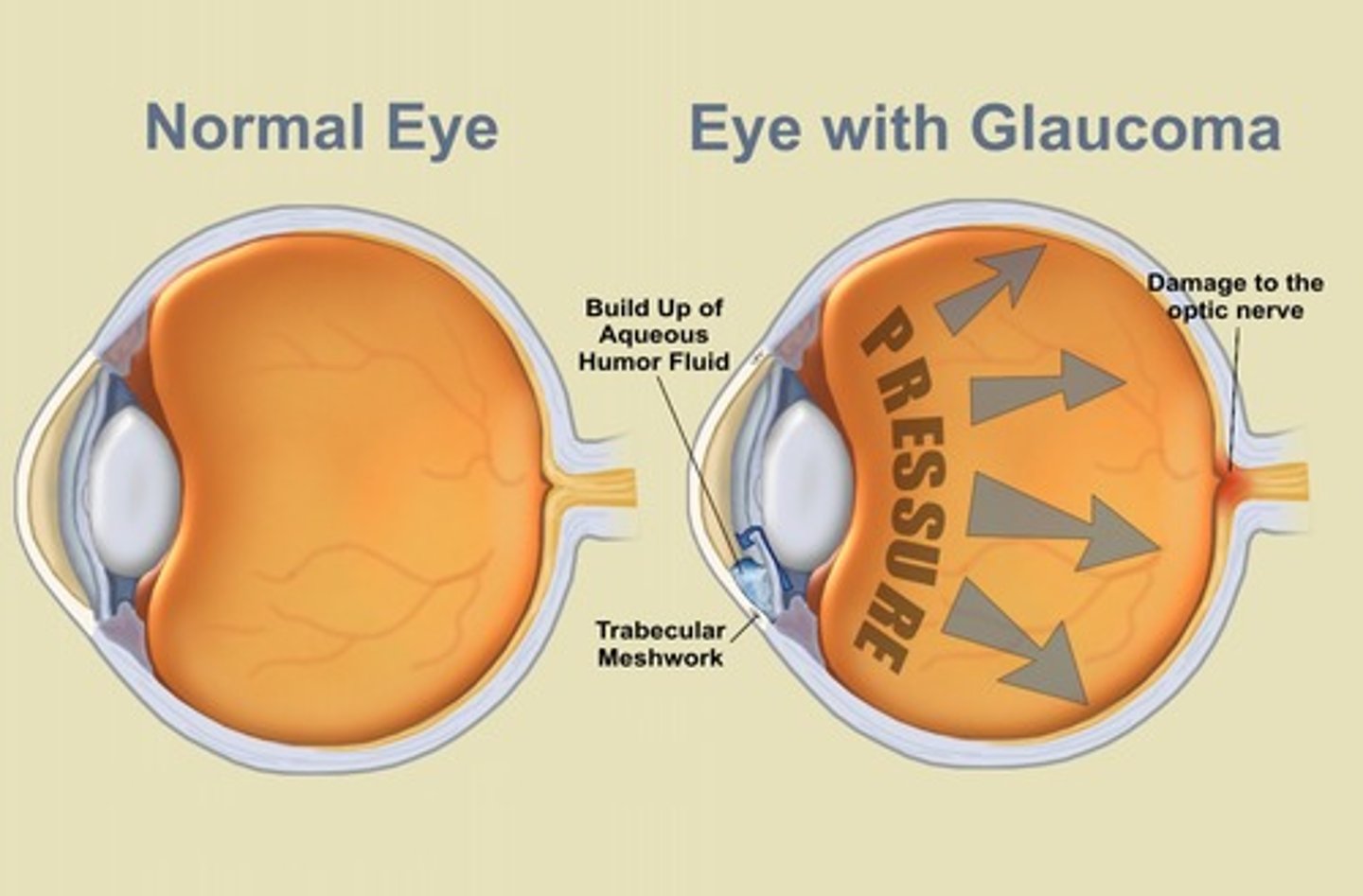
Glaucoma
a condition of increased pressure within the eyeball, causing gradual loss of sight.
Hallucinations
seeing, hearing, smelling, tasting, or feeling things that are not there
hearing aid
a small device placed in the ear that amplifies sound
hemianopsia; hemianopia
loss of vision in one-half of the visual field, due to CVA, tumor, or trauma

Ménière's disease
A disorder of the inner ear caused by a build-up of fluid, which causes vertigo (dizziness), hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ear), pain, or pressure.
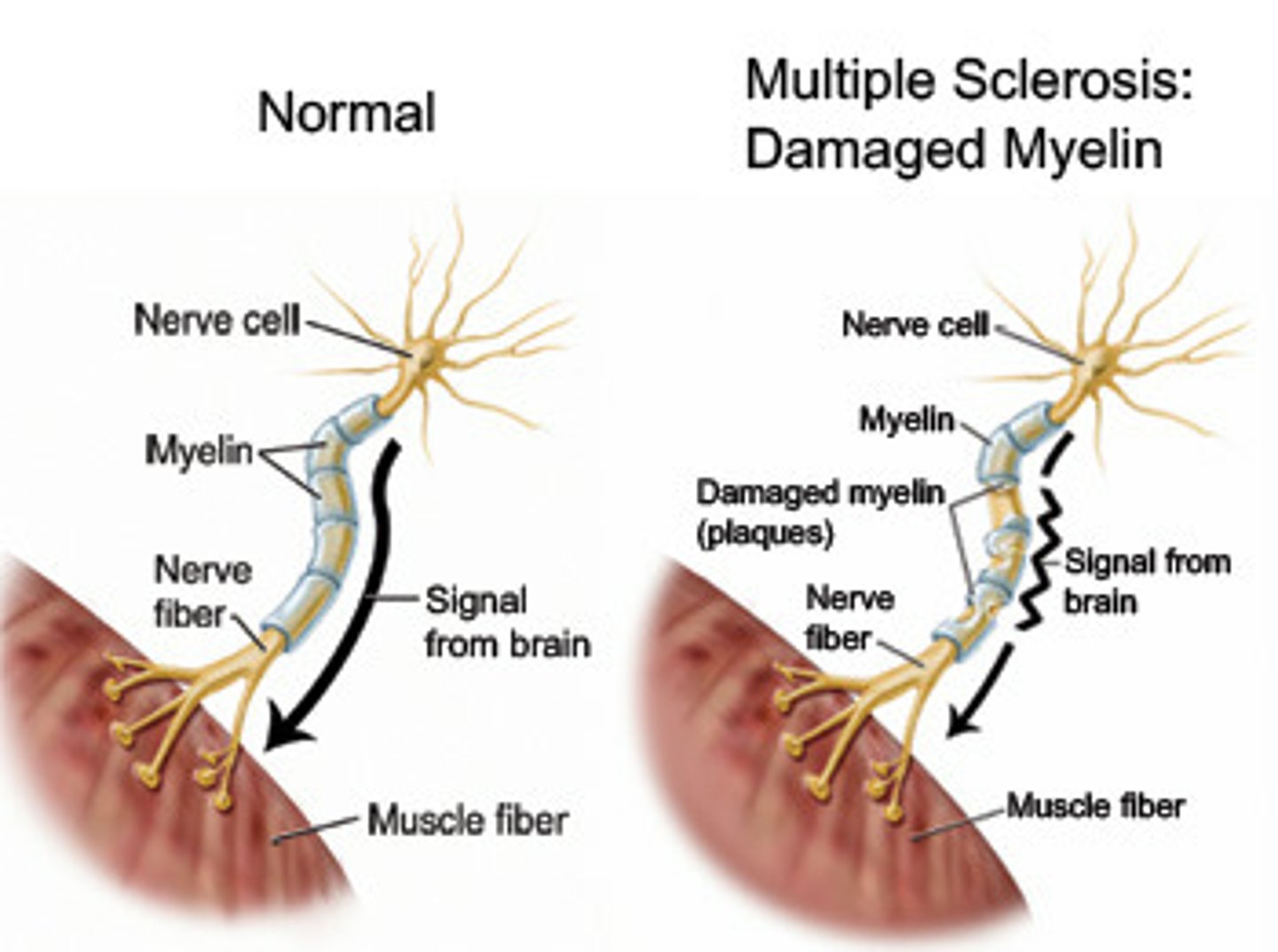
multiple sclerosis (MS)
a progressive disease in which the protective covering of the nerves, spinal cord, and white matter of the brain breaks down over time; without this covering, nerves cannot send clear messages to and from the brain in a normal way
nearsightedness
the ability to see objects that are near more clearly than distant objects; also called myopia
obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
a type of mental health disorder characterized by intrusive, repetitive thoughts or behaviors that cause anxiety or stress
otits media
an infection in the middle ear that causes pain, pressure, fever, and reduced ability to hear
panic disorder
a type of mental health disorder characterized by panic attacks, which are repeated episodes of intense fear, along with physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, dizziness, chest pain, shortness of breath, and an upset stomach
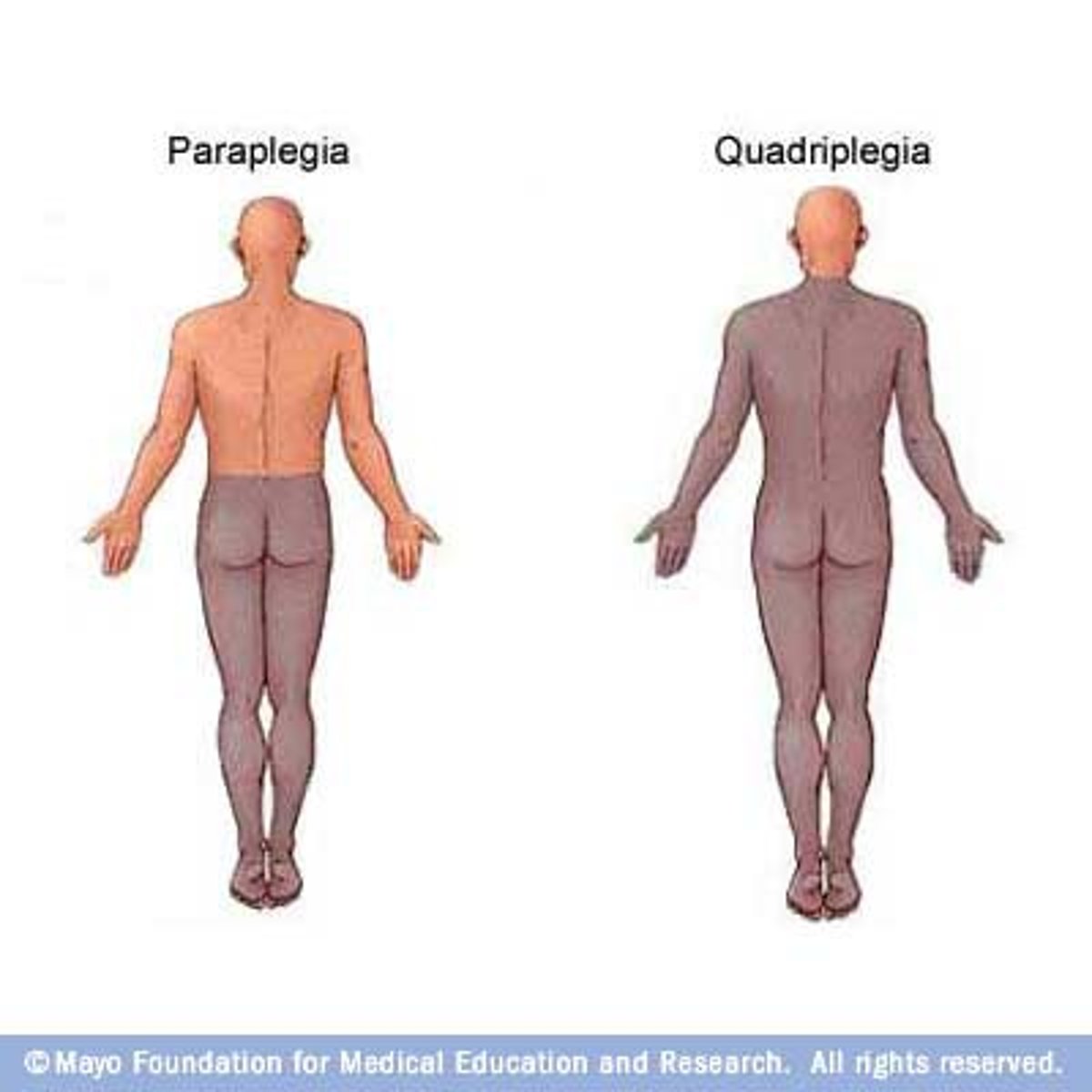
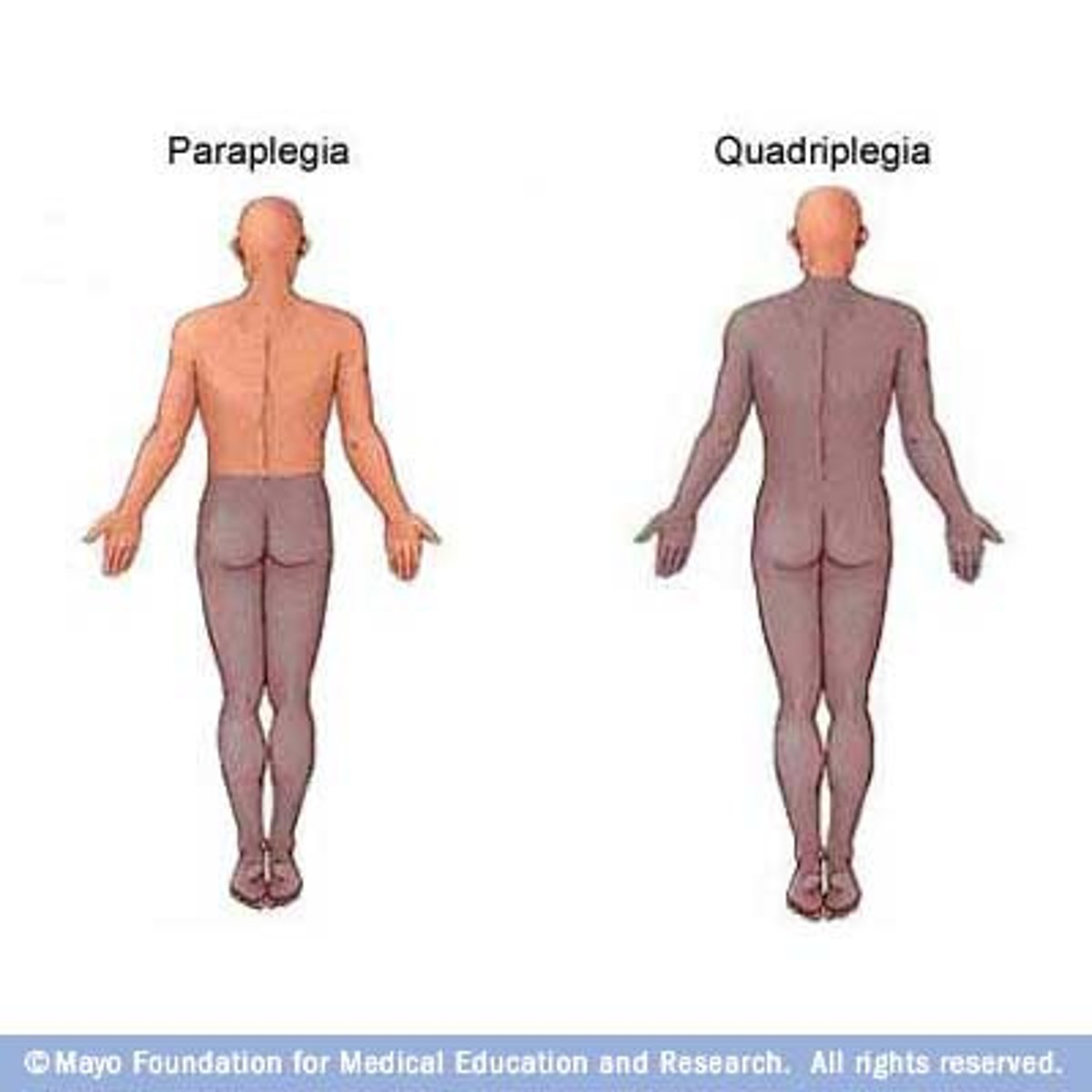
paraplegia
paralysis from the waist down
Parkinson's disease
a progressive disease that causes a portion of the brain to degenerate; causes rigid muscles, shuffling gait, pill-rolling, mask-like face, and tremors
peripheral nervous system
part of the nervous system made up of nerves that extend throughout the body and connect to the spinal cord
perseveration
the repetition of words, phrases, questions, or actions
phobia
an intense and irrational fear of a particular object or situation
posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
a type of mental health disorder caused by witnessing or experiencing a traumatic event
Psychotherapy
a method of treating mental health disorders that involves talking about one's problems with mental health professionals
quadriplegia
paralysis of all four limbs
reminiscence therapy
type of therapy that encourages people with Alzheimer's disease to remember and talk about the past
remotivation therapy
type of group therapy that promotes self-esteem, self-awareness, and socialization for people with Alzheimer's disease
rummaging
going through items that belong to other people
Schizophrenia
a type of mental health disorder that may involve acute episodes; affects a person's ability to think, communicate, make decisions, and understand reality
social anxiety disorder
a type of mental health disorder characterized by excessive anxiety about social situations; also called social phobia
spinal cord
the part of the nervous system inside the vertebral canal that conducts messages between the brain and the body and control spinal reflexes
sundowning
a condition in which a person gets restless and agitated in the late afternoon, evening, or night
validation therapy
a type of therapy that lets people with Alzheimer's disease believe they are living in the past or in imaginary circumstances
abandonment
Leaving a patient after care has been initiated and before the patient has been transferred to someone with equal or greater medical training.
abdominal thrust
a method of attempting to remove an object from the airway of someone who is choking
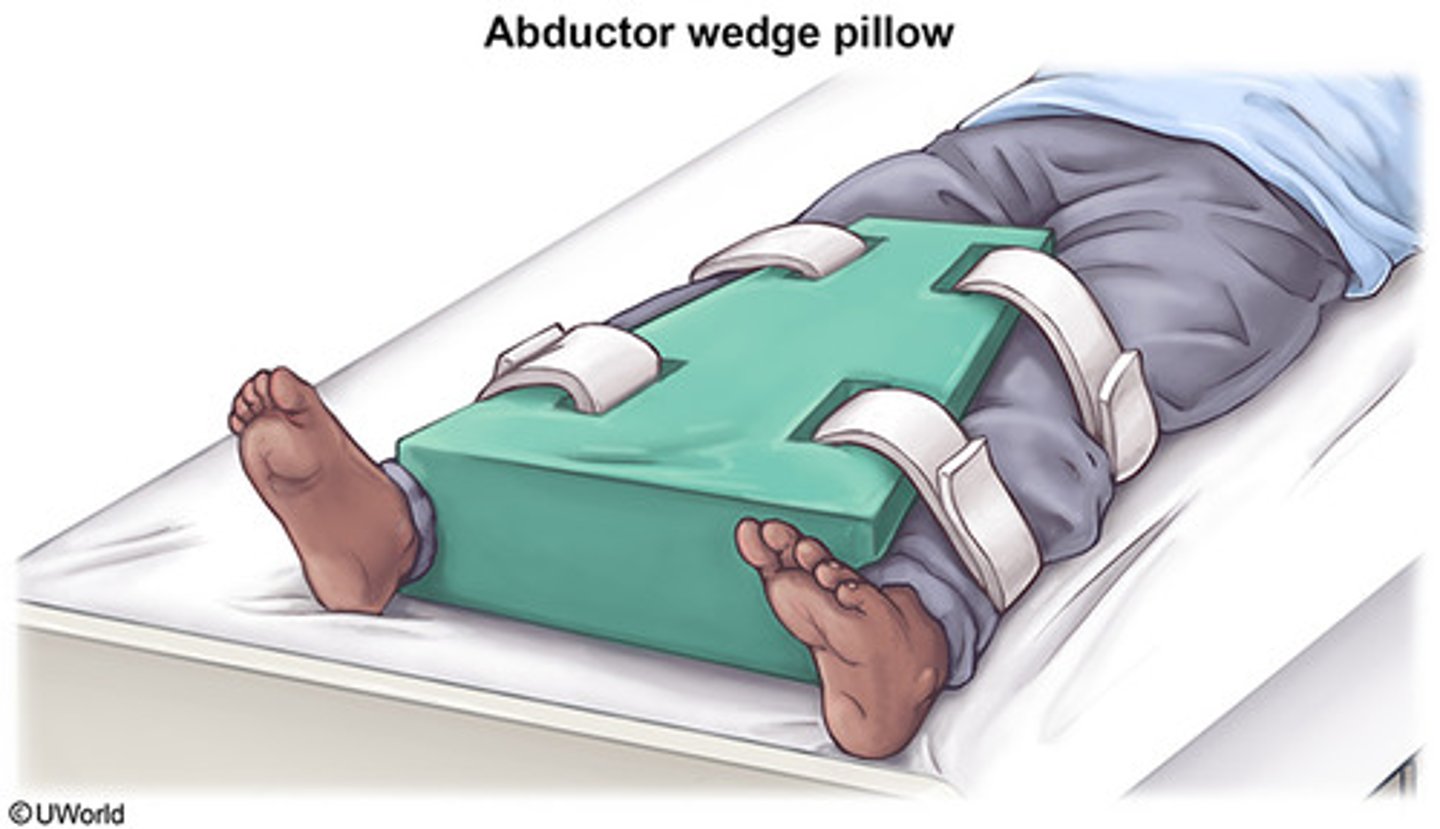
abductor wedge
designed to separate the legs of a patient. It is often used after hip surgery to prevent the new hip from "popping out". Prevents adduction.
abnormal vital signs
any reading outside of these ranges: Heart Rate 60-100, Blood Pressure 120/80, Temperature 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit, 37 degrees Celsius, Respiratory rate 12-20 breaths/minute, Pulse Ox >95%; You report/Communicate to charge nurse.
absorption
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of the digestive system into the blood
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
(AIDS)
group of clinical signs and symptoms associated with suppression of the immune system and marked by opportunistic infections, secondary neoplasms, and neurologic problems
acute
New, usually of rapid onset and of concern, opposite of chronic
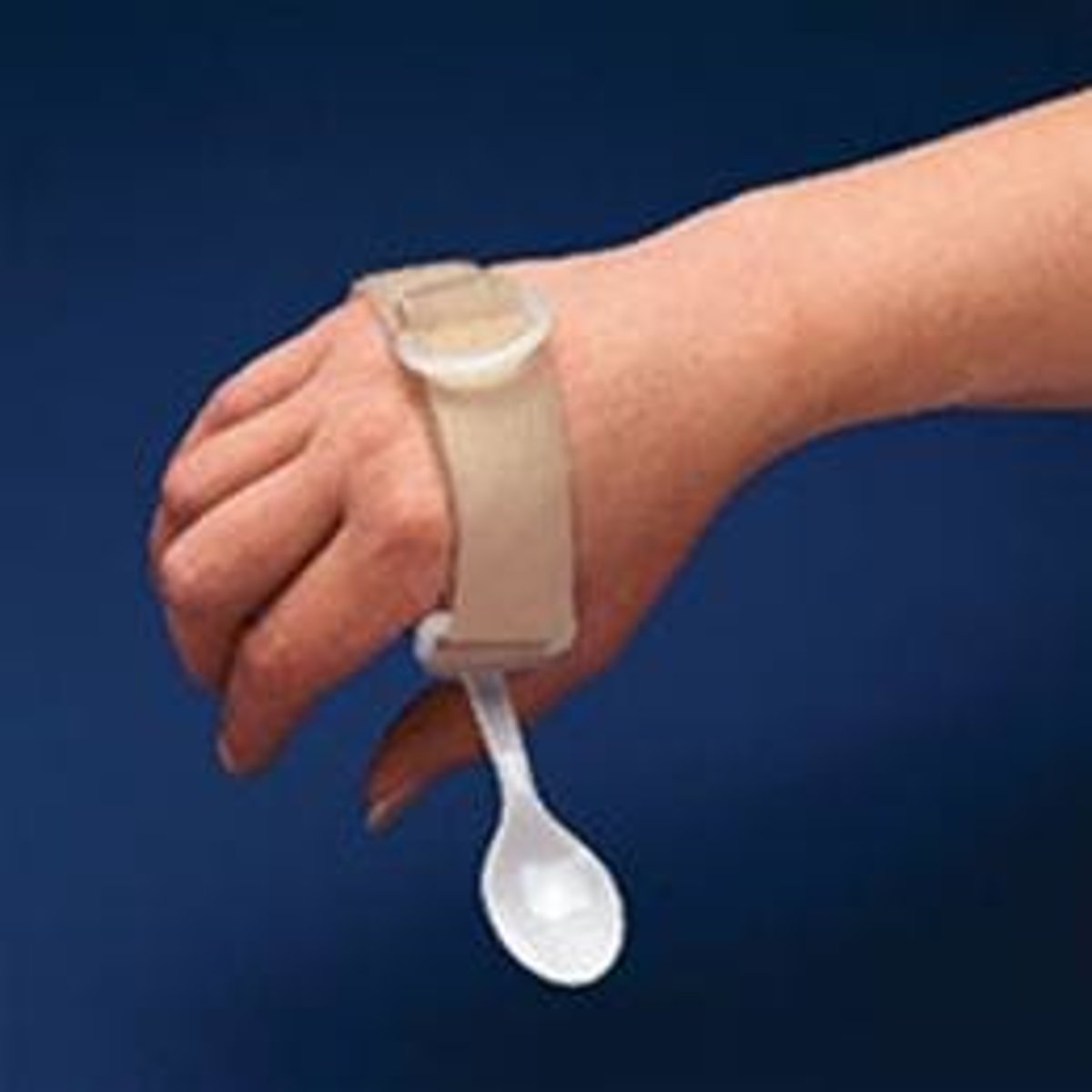
adaptive equipment
Items such as eating utensils which are altered to make them easier to use by residents with functional limitations
adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
advance directives
legal documents that allow people to choose what medical care they wish to have if they are unable to make those decisions themselves
afebrile
without fever
ambulation
walking
anemia
A condition in which the blood is deficient in red blood cells, in hemoglobin, or in total volume.