6.3.2 Populations and sustainability (do i need to know the "case studies"??
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Complete xx
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Population growth curve image
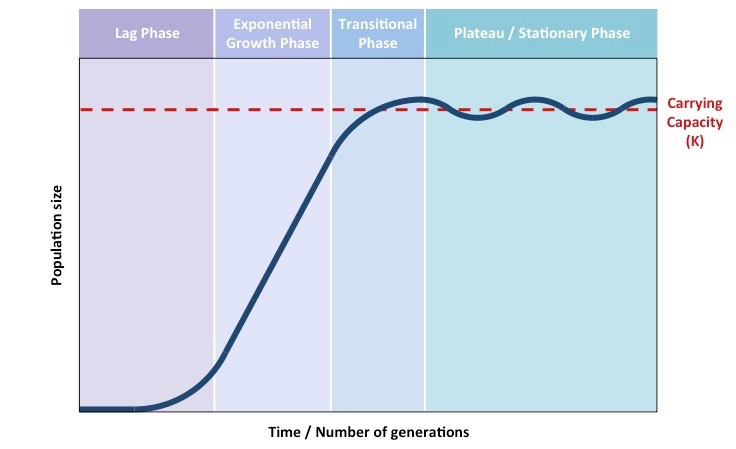
When would the population grow exponentially
When all recources = avaliable in a plentiful supply
Limiting factors to population growth
Abiotic and biotic
Immigration and emigration
Immigration definition
Movement of organisms into an area
Emigration definition
Movement of organisms out of the area
Carrying capacity definition
The population is the max population size an environment can support.
The populations are not subject to further succession
Interspecific competition
Competition between two different species
Intraspecific competition
Competition between members of the same species
Predation
Biotic factor - influence pop size
Predators have evolved ways to catch their prey and prey has evolved ways to avoid capture (mimicry, camouflage..)
Population decrease
Death rete is higher than birth rate
Predator prey relationship graph
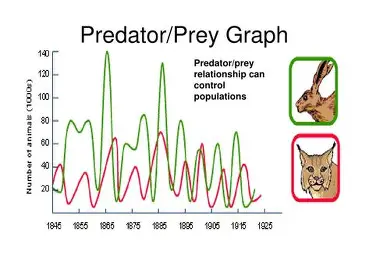
Interactions btw. the predator and prey relationships - simple
The population fluctuates
To do with the food availability of the predator and the over predation by the predator
Interactions btw. the predator and prey relationships - long winded.
As the rabbit population increases in size, more food for lynx. Therefore lynx pop. will increase. And as it increases, the hare pop. decreases cause its being eaten. And as the hare pop. decreases, the lynx = less food so it will decrease. And as there is less lynx, the hare pop can increase
Conservation definition
Maintenance/ management of nature to protect species/ habitats
Preservation definition
Leaves the environment/ lands not to be used by humans
(leaves the ecosystems untouched)
Why is conservation important for economic reasons
Ecotourism
A potential for future medicines
Why is conservation important for social reasons
Aesthetic
Stop the impact of deforestation
Why is conservation important for ethical reasons
Preserve biodiversity/ stop extinction
Support the indigenous populations
Sustaniablility deinition
Maintaining the numbers within a population size so that they can reproduce and so that the population isn’t going to decrease dramatically all the time
Aims of sustainability
Preserve the environment
Ensure resources are available for future generations
Allow humans in all societies to live comfortably
Enable less economically developed countries to develop through exploiting their natural resources
Create a more even balance in the consumption of these resources in more economically developed countries and less economically developed countries
Sustainable timber production ways
Coppicing
Selective felling
Rotational felling
Strip felling
What is coppicing
Tree trunk cut close to ground level
Several new shoots grow from cut surface
Process repeated after a certain time
Can be repeated indefinitely
Need to protect young shoots from grazers
Advantages of coppicing
New stems grow more rapidly than saplings
Lifespan of tree extended
Provides variety of light levels
Fewer larger trees = more light for smaller plants
Provides a variety of habitats
Maintains biodiversity
Roots prevent soil erosion
Maintains soil quality
Prevents succession
Large machinery not needed therefore less disturbance
What is selective felling
The cutting down of selected mature trees in a forest
Allows other trees to grow and mature and also leaves enough habitats for animals
What is rotational felling*
Planting a site and then felling the trees when they have reached maturity (after approx. 8-20 years)
What is strip felling
Cutting down selected, mature trees in a forest in a strip. Allows other trees to grow to maturity and also leaves enough habitats for animals
After you have felled a tree if appropriate what’s important to do
Replant
Why is it important to sustainably fish in our oceans*
Exploitation of fish = high
Sustainable fishing production ways
Introduce quotas
Net hole sizes
Time of year
How does introducing quotas help with sustainable fishing
Limits the number of certain species of fish that can be caught
How does changing net hole sizes help with sustainable fishing
Certain hole nets can allow smaller fish to escape and reach maturity and therefore breeding age - maintain sustainable population
How does allowing fishing only during certain times of the year help with sustainable fishing
Allows the pop. to reach a sustainable level