Comprehensive Nucleic Acids: DNA, RNA, Replication, Mutations & Protein Synthesis
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Nucleic Acids
One of the four macromolecules that make up living things.
Monomer
Nucleotide.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
One of the two main types of nucleic acids.
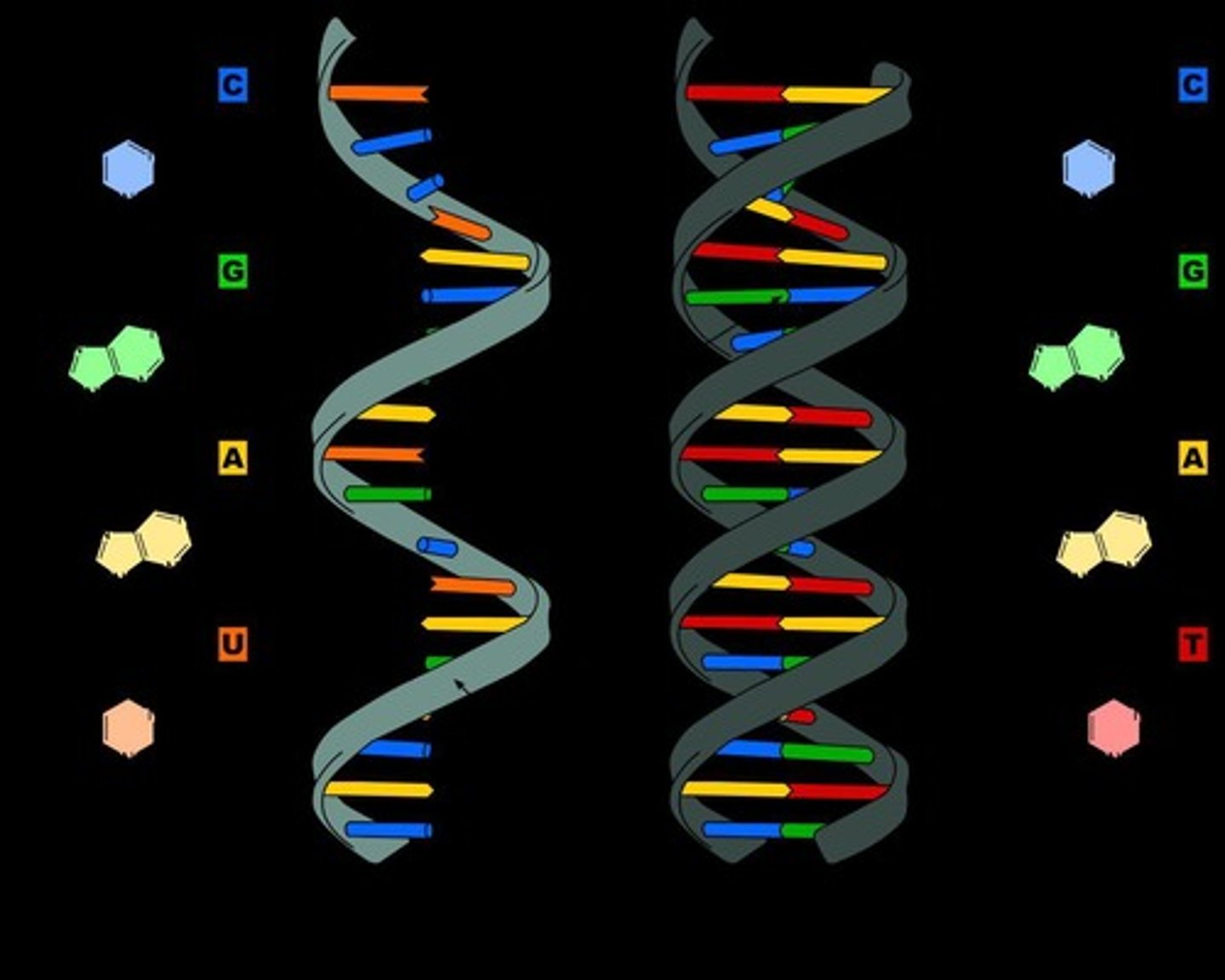
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
One of the two main types of nucleic acids.
Rosalind Franklin
Provided the X-ray photo of DNA.
Watson & Crick
Described the DNA molecule from Franklin's X-ray as a twisted ladder (3D double helix shape).
The Zipper Theory
Proposed by Watson & Crick regarding the structure of DNA.
Nucleotide Structure
Each DNA nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, deoxyribose, and one of four nitrogenous bases.
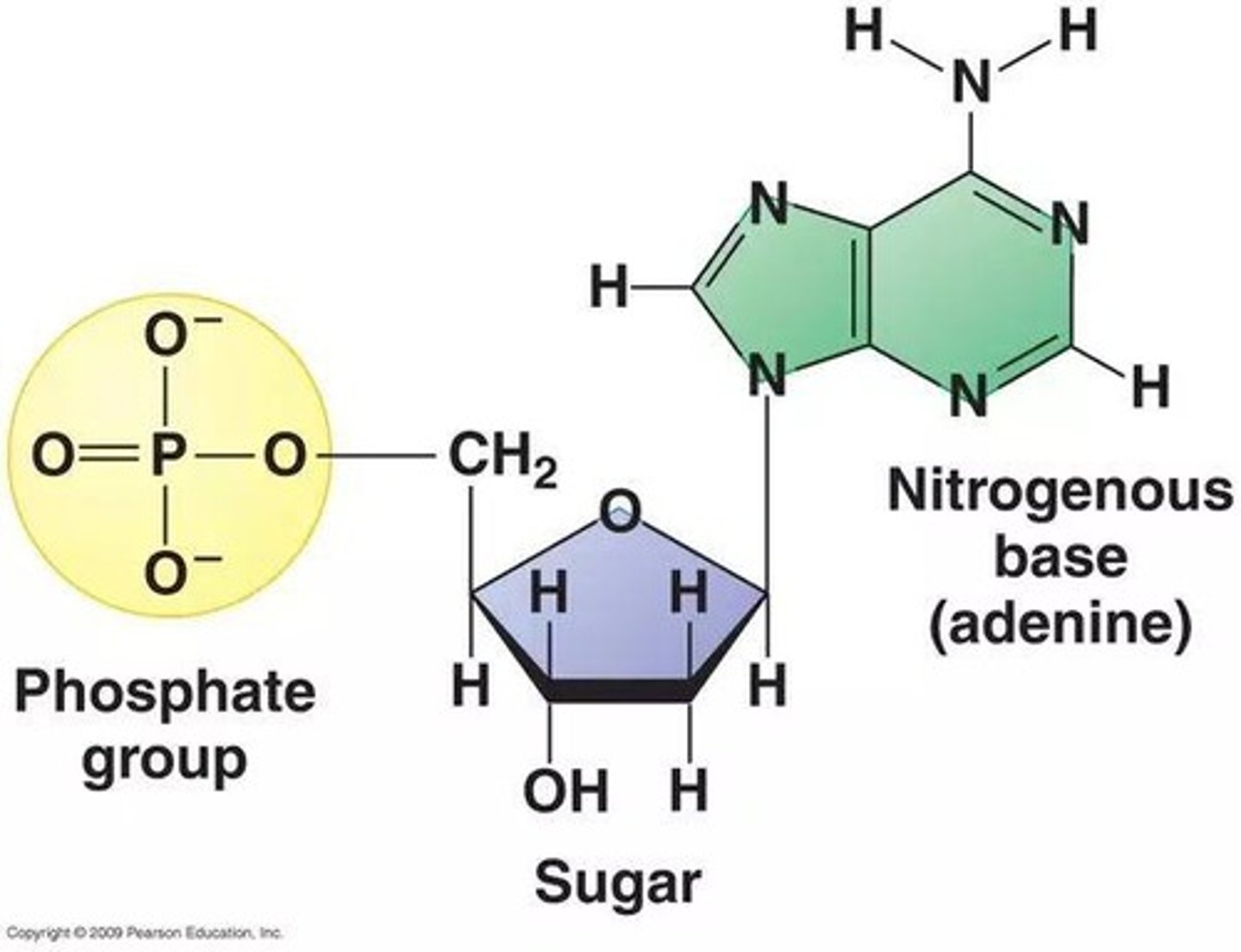
Nitrogenous Bases
Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T).
DNA Function
Genetic Code (stores the information in genes for making proteins) and Replication (makes copies of itself).
Interphase
The stage of the cell cycle when DNA replication occurs.
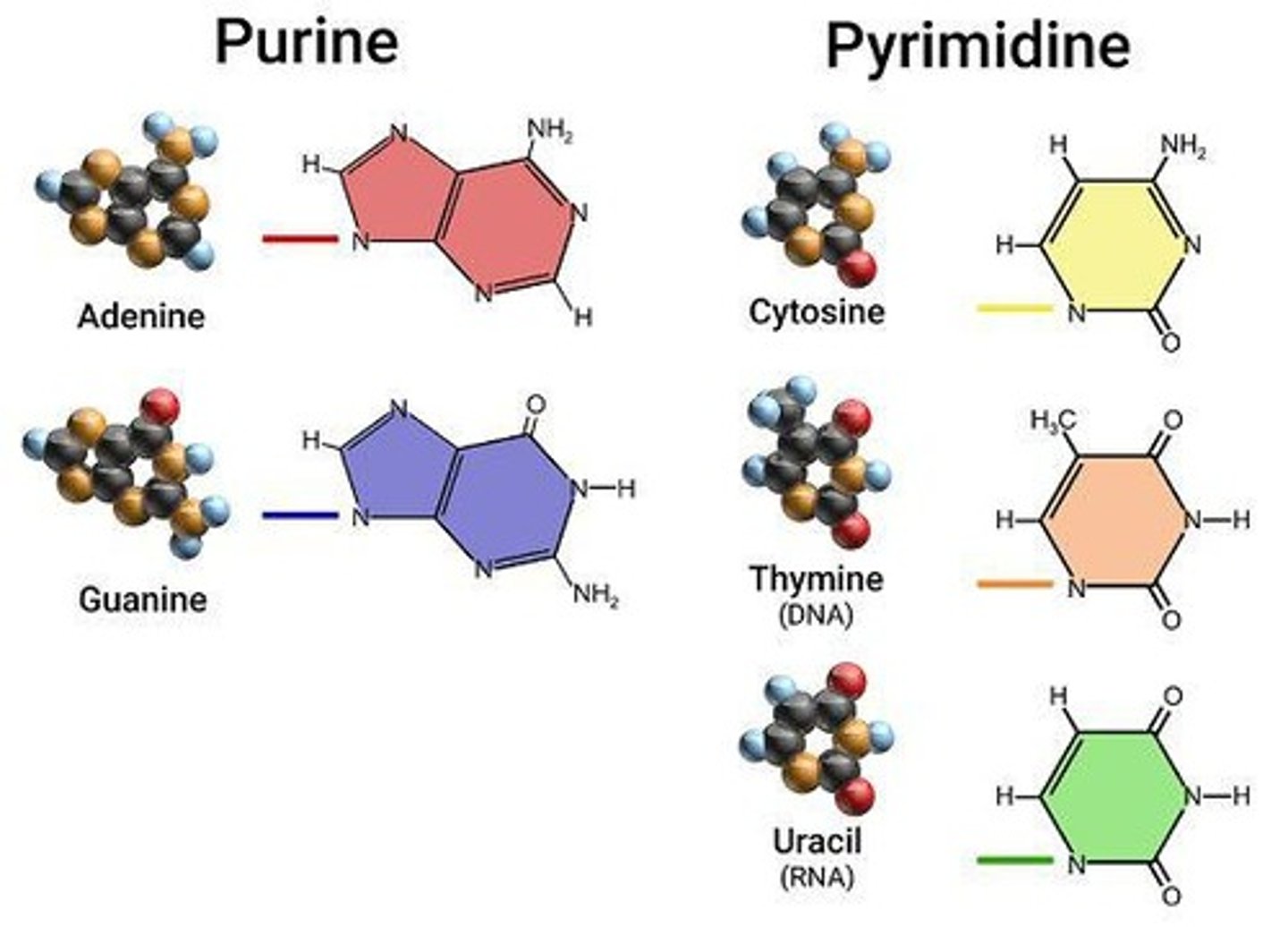
Purines
Double ring of carbon and nitrogen; includes Adenine (A) and Guanine (G).
Pyrimidine
Single ring of carbon and nitrogen; includes Thymine (T) and Cytosine (C).
Base Pair Rule
A (adenine) binds to T (thymine) forming a double hydrogen bond; C (cytosine) binds to G (guanine) forming a triple hydrogen bond.
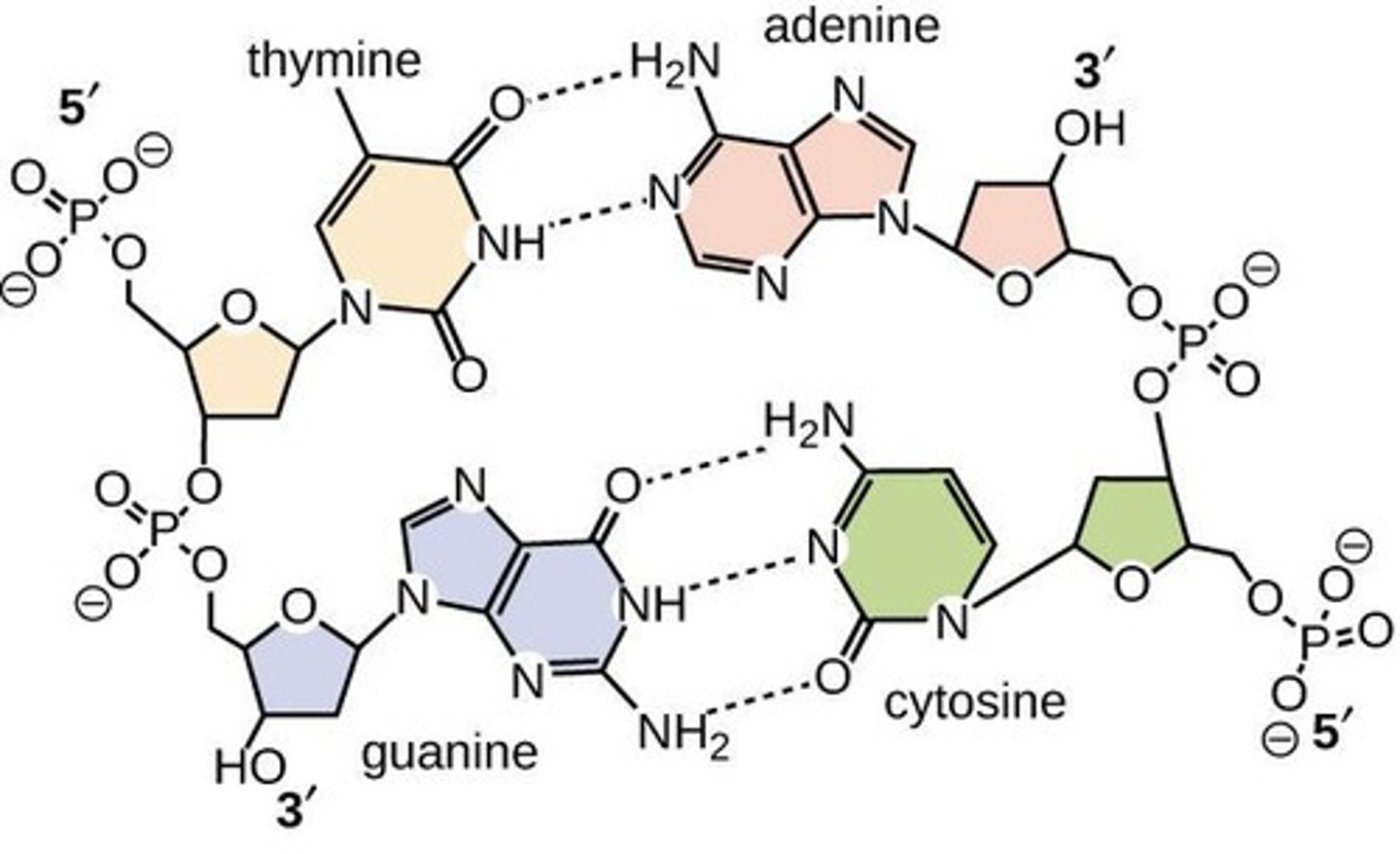
Antiparallel
The orientation of DNA strands running in opposite directions.
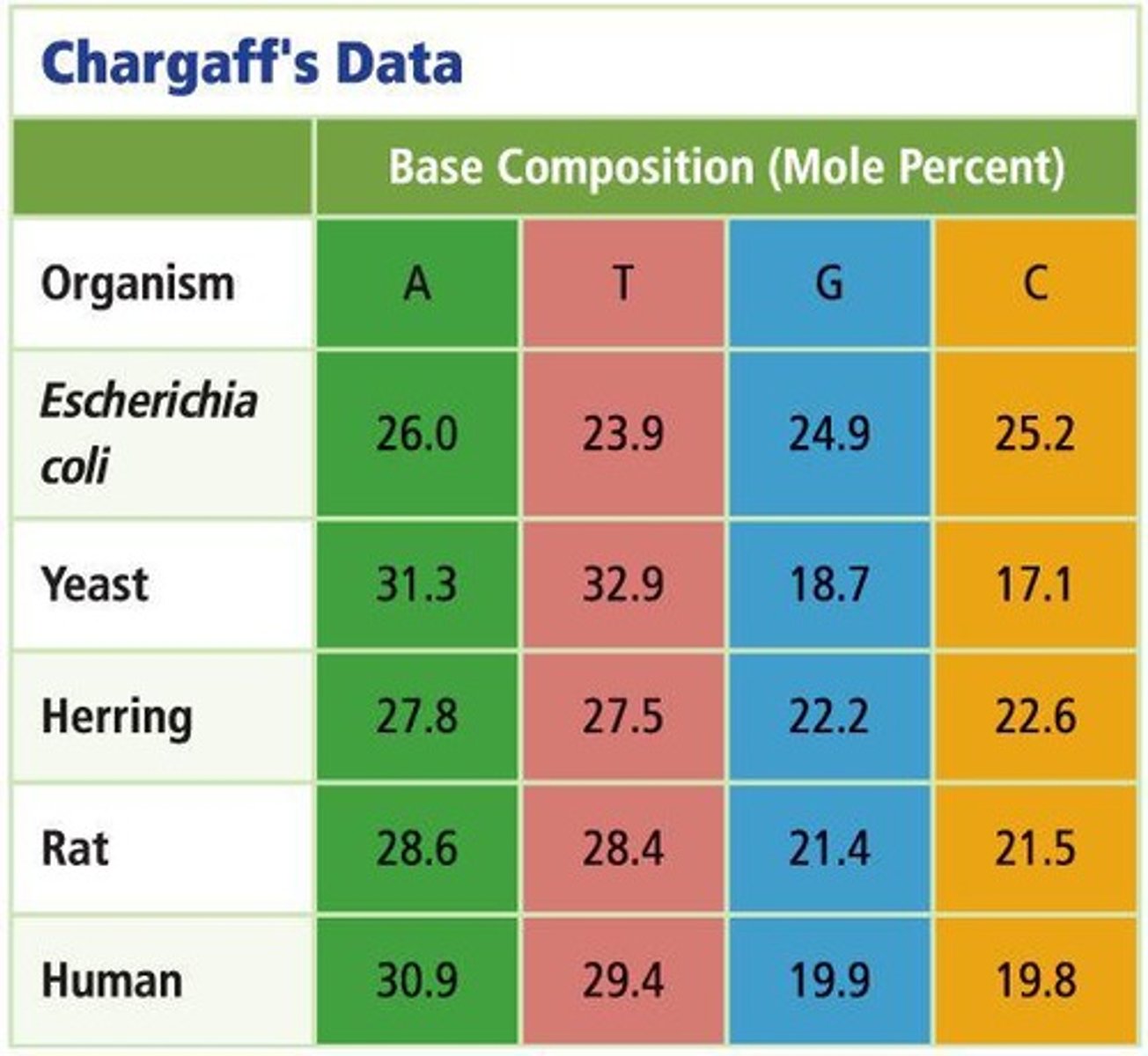
Chargaff Rule
In DNA, there is always equality in quantity between the bases A and T and between the bases G and C.
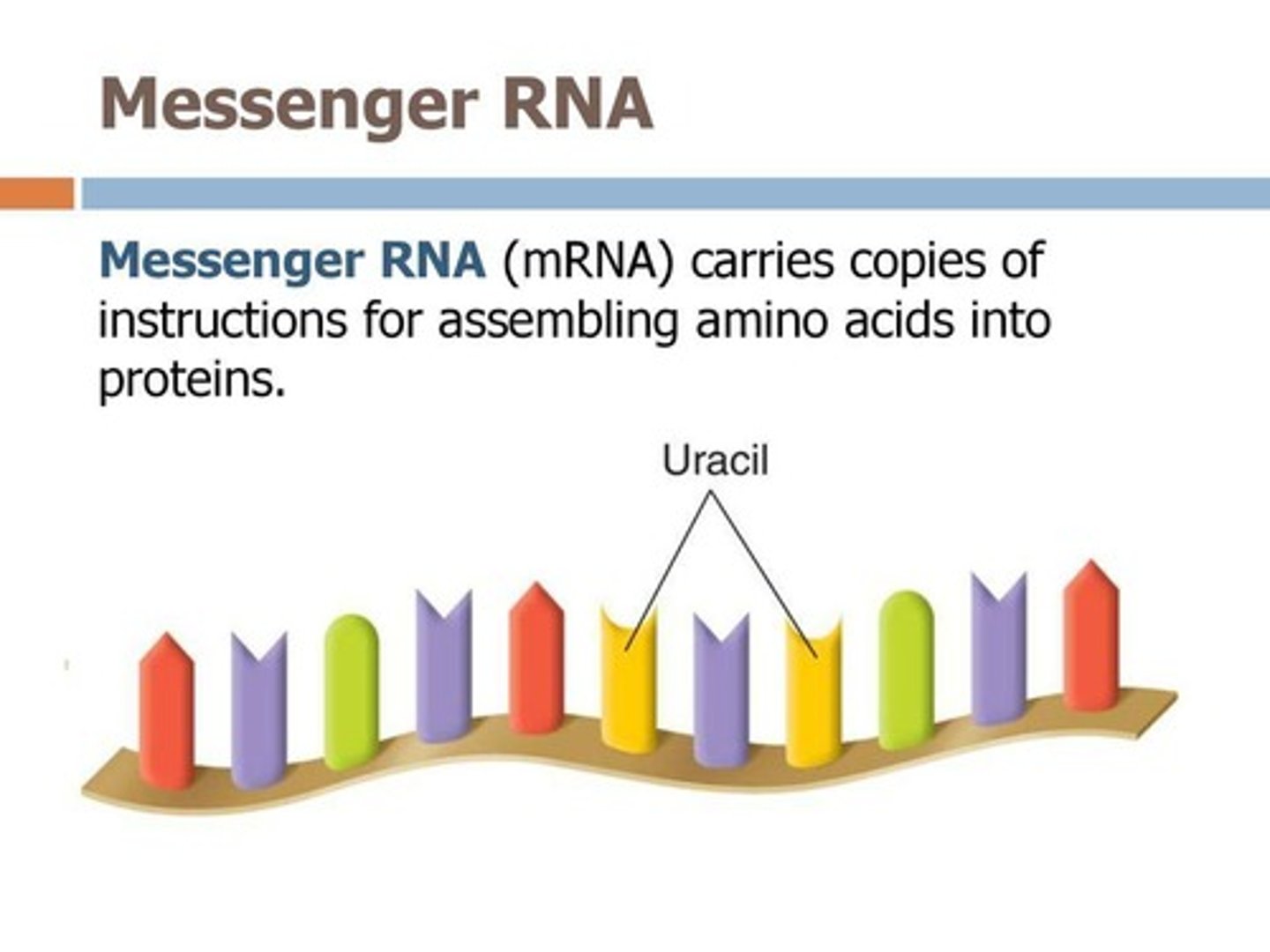
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid; monomer is nucleotide composed of phosphate group, ribose, and one of four nitrogenous bases.
Codons
Sequence of three nucleotides.
mRNA
Messenger RNA; a copy of a specific gene on a DNA molecule that carries the message for making a specific protein to the site of protein synthesis.
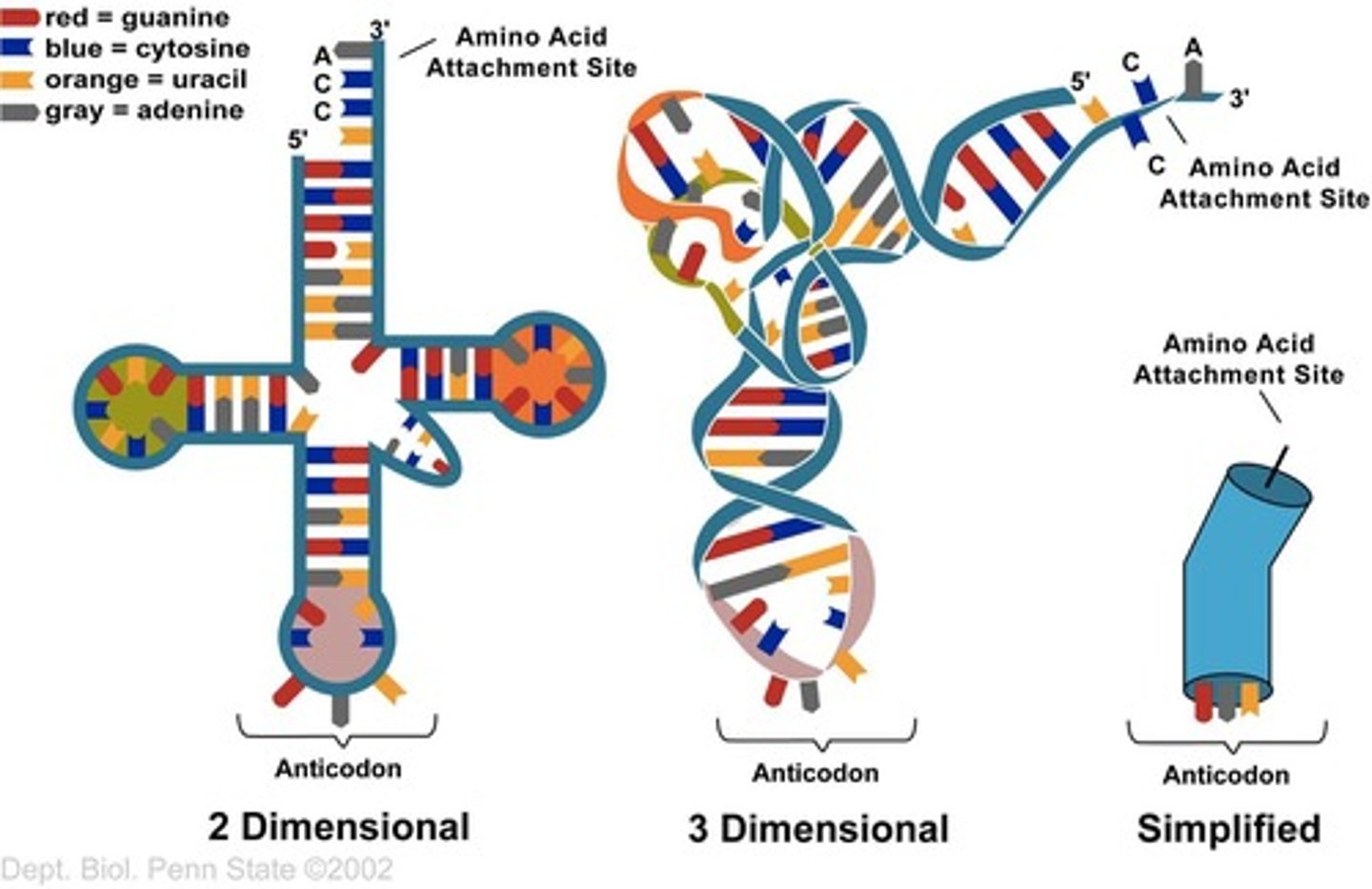
tRNA
Transfer RNA; carries the amino acid that the mRNA codes for and has an anticodon that is complementary to the mRNA codon.
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA; makes up the ribosome and is involved in protein synthesis.
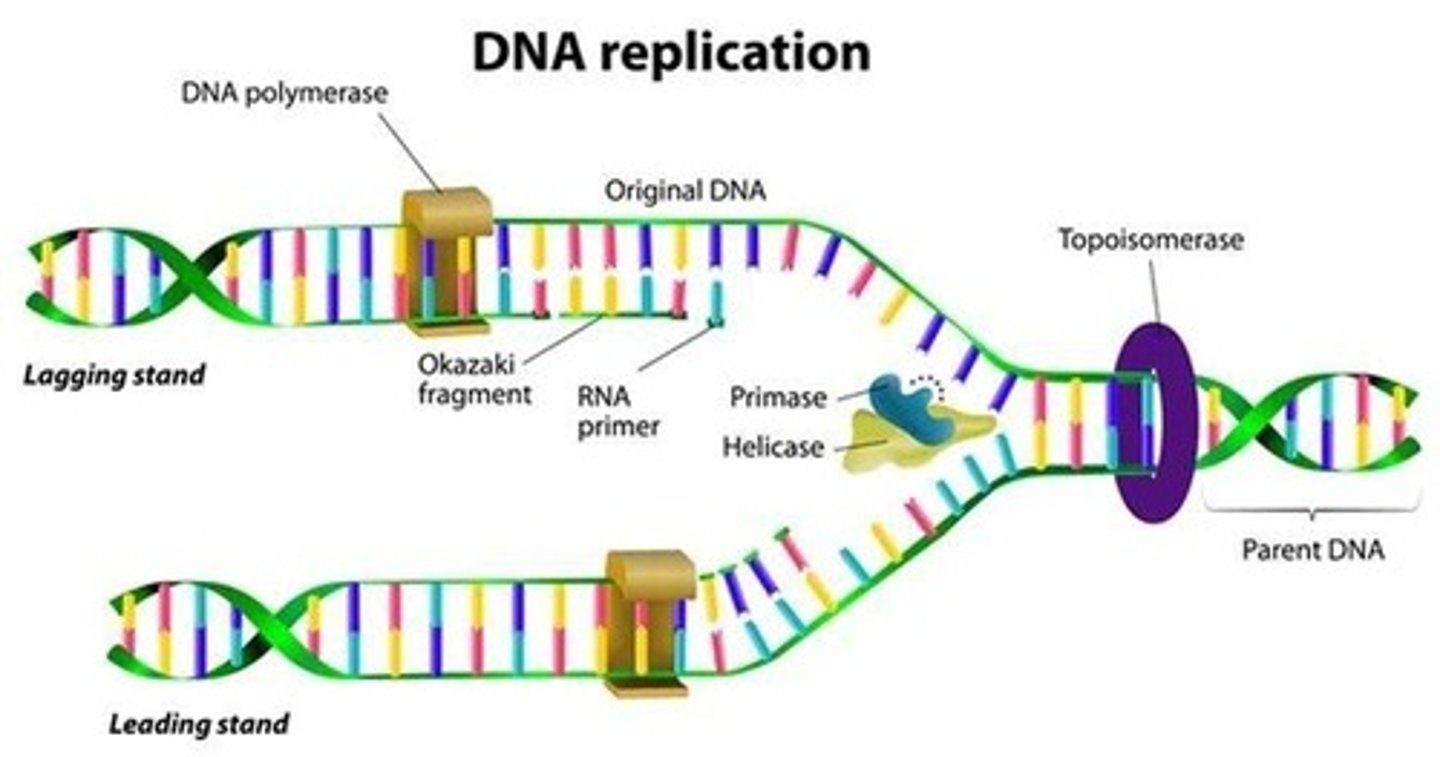
DNA Replication
Occurs during S phase of interphase, starting with one strand of DNA and producing two identical strands.
Semiconservative
After DNA replication, it consists of one original strand and one new strand of DNA.
5' and 3'
Indicate the carbon numbers in the DNA's sugar backbone; the 5' carbon has a phosphate group and the 3' carbon has a hydroxyl (-OH) group.
Leading strand
5' → 3'
Lagging strand
3' → 5'
Replication fork
Develops at the 'Origin of replication'
Helicase
Opens the DNA strand by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases
Topoisomerase
Functions at the replication fork to prevent DNA from coiling too tight
Single Stranded binding proteins (SSB's)
Bind to the newly split single stranded DNA and prevent it from coming back together
DNA polymerase
Adds DNA nucleotides to the leading and lagging strand following the complementary base pair rules
Leading strand addition
Bases can be added continuously [5'-3']
Lagging strand addition
Can only be made in fragments [3'-5']
Okazaki Fragments
RNA primer is added to allow for the fragments to be made
Ligase
Fills any gaps in the DNA lagging strand
Semi-conservative replication
Each new DNA molecule contains one original (parent) strand and one new strand
Genetic code
Universal; all living cells store hereditary information in double-stranded DNA
Building blocks of DNA
A, T, C, G
Genetic engineering
Theoretically, DNA from one organism can be placed into another organism
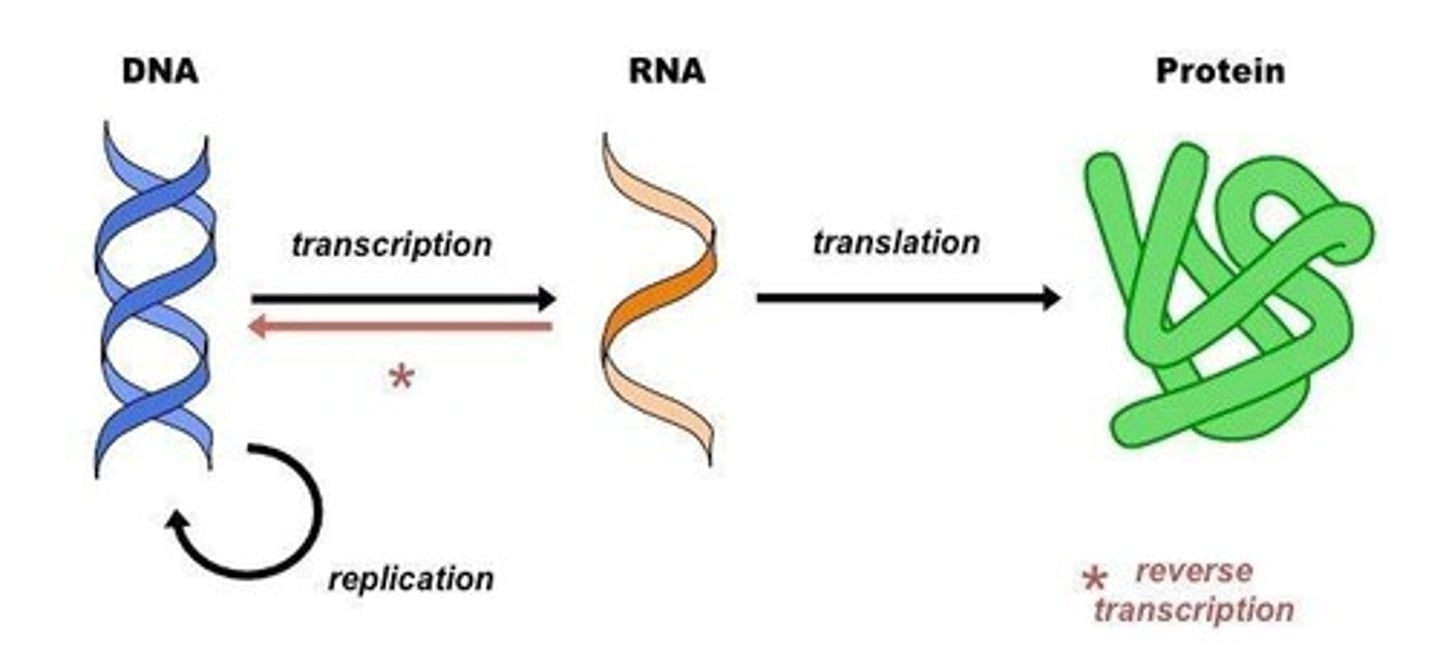
Central Dogma
DNA ⇒ RNA ⇒ Protein
Protein structure
Proteins are made up of amino acids connected by peptide bonds
Polypeptide chain
Many amino acids connected together
Functional protein
Formed when a polypeptide chain folds
Gene expression
Gene → Protein → Trait
Transcription
Process of making a copy of a gene on DNA [DNA → mRNA]
Translation
Process of converting RNA into Protein
RNA polymerase
Binds to DNA at a specific gene location and breaks the hydrogen bonds between DNA nucleotides
Transcription steps
1. Initiation 2. Elongation 3. Termination
Transcription vs Replication
Transcription copies a gene; replication copies all the DNA
Replication
Uses helicase & DNA polymerase.
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins.
Peptide Bonds
Amino acids connect via peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain.
Codon
A sequence found on mRNA that determines the amino acid.
Codon Combinations
There are 64 possible 3-letter codon combinations.
Ribosome
Takes place in ribosome for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Anticodon
A set of three nucleotides that is complementary to the mRNA codon, carried by tRNA.
Initiation
tRNA binds to a start codon on mRNA and signals the ribosome to assemble.
Start Codon
AUG, which codes for the amino acid Methionine (Met).
Elongation
tRNA molecules will continue to come into the ribosome and the amino acid from the first tRNA will be transferred to the second tRNA.
Termination
A stop codon will be reached, the ribosome will release the protein and will disassemble.
Stop Codons
UAG, UAA, UGA.
Mutation
Any change in an organism's DNA.
Somatic Mutations
Mutations in somatic (body) cells only impact the individual.
Germline Mutations
Mutations in gametes (sex cells) may impact offspring.
Gene Mutations
Typically involves one nucleotide and affects one single gene.
Chromosomal Mutations
Involves pieces of or even entire chromosomes.
Point Mutation
One nucleotide is substituted for another.
Missense Mutation
If the substitution changes the amino acid.
Silent Mutation
If the substitution does not change the amino acid.
Nonsense Mutation
If the substitution changes the amino acid to a 'stop' codon.
Frameshift Mutation
One nucleotide is inserted/deleted from sequence, changing the entire amino acid sequence after the point of mutation.
Insertion Mutation
Addition of base to the DNA sequence.
Deletion Mutation
Loss of base in the DNA sequence.
Translocation
When a segment of genetic material breaks from one chromosome and reattaches to another chromosome.
Nondisjunction
Chromatids fail to separate during meiosis.
Monosomy
Losing 1 chromosome.
Trisomy
Gaining an extra chromosome.
Polyploid
More than the correct number of chromosome sets.