Biol 226 (A&P II) Lab Exercise 11 - Renal Anatomy and Physiology; Urinalysis
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
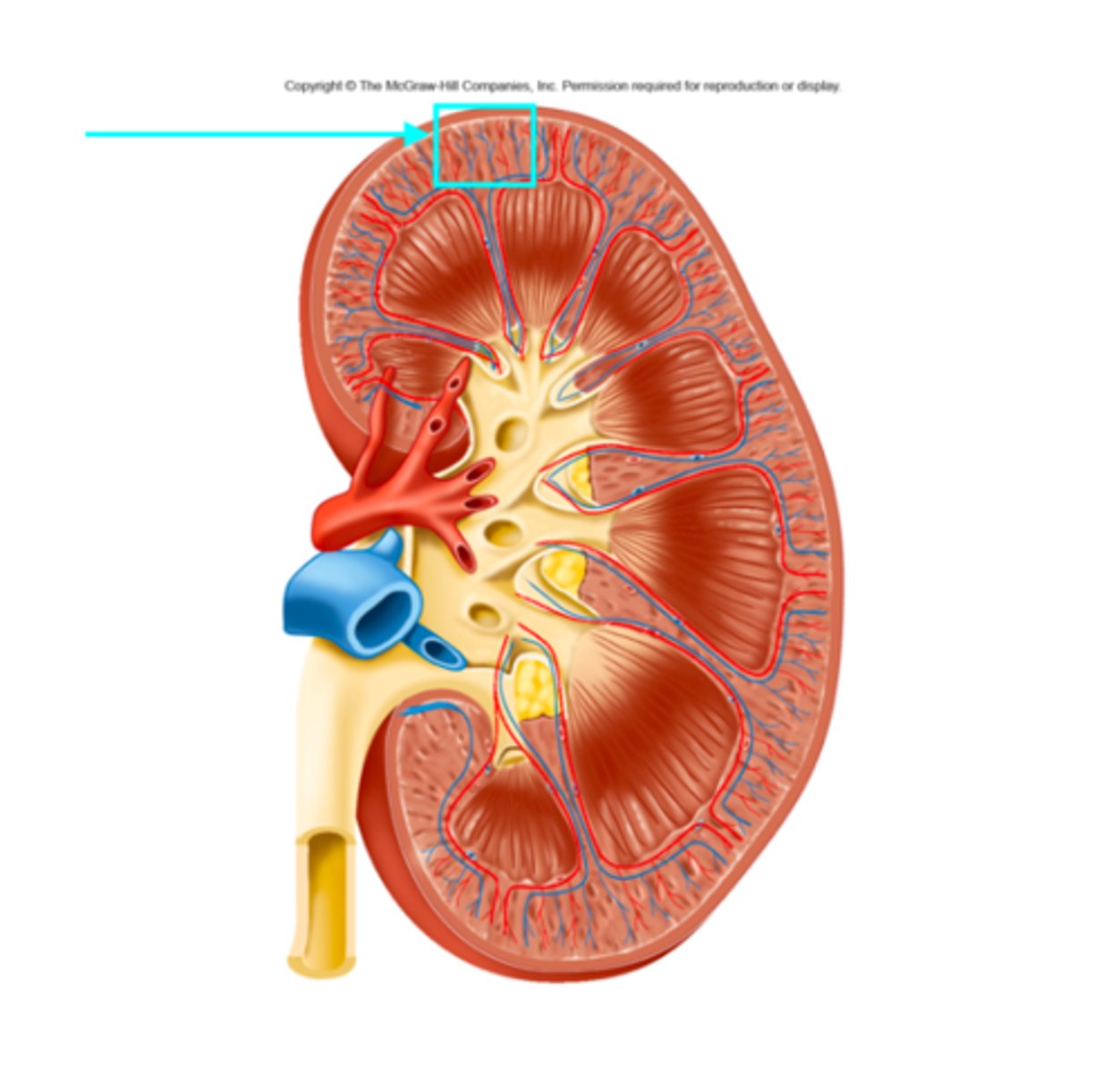
Cortex
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
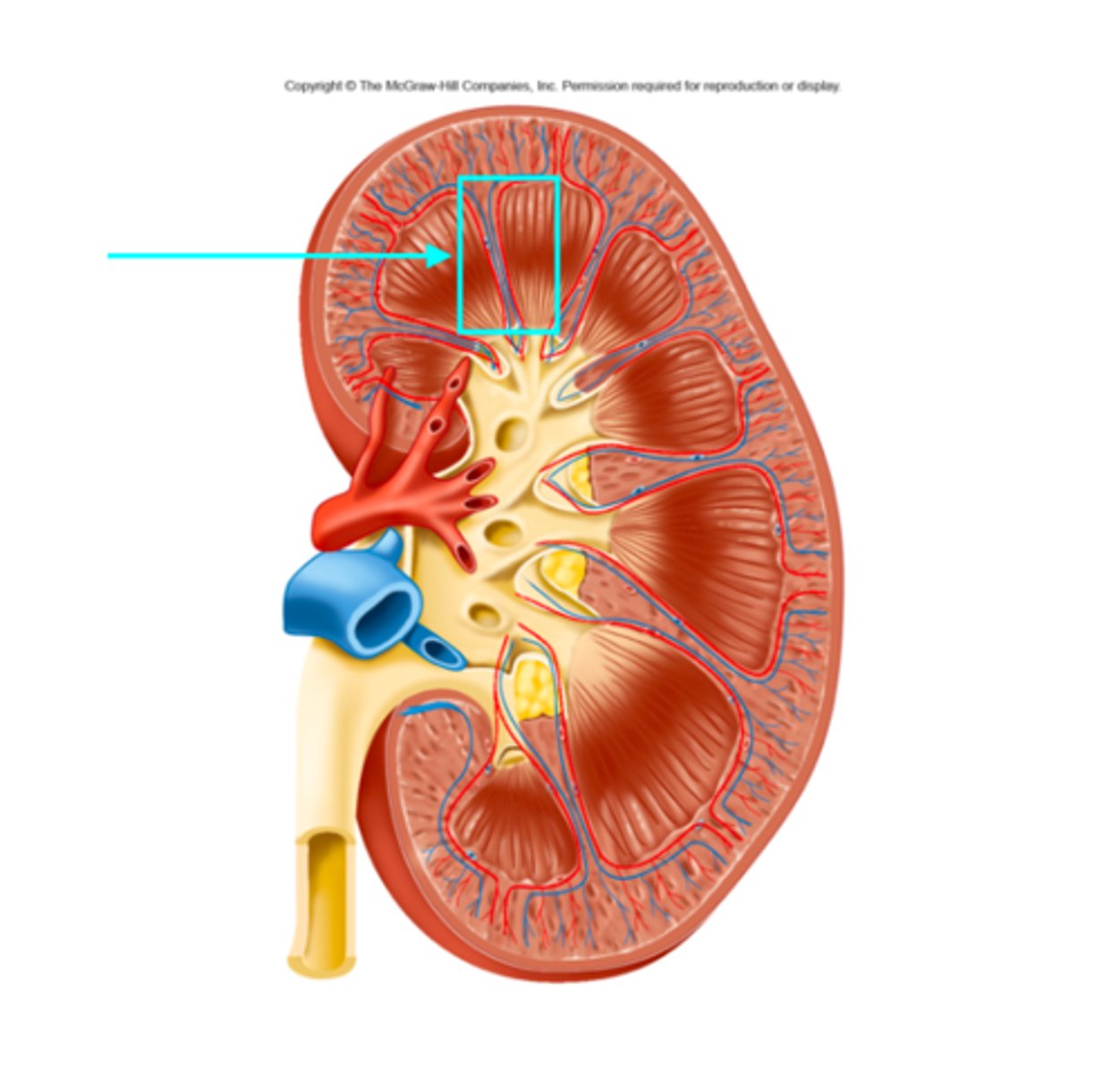
Medulla
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
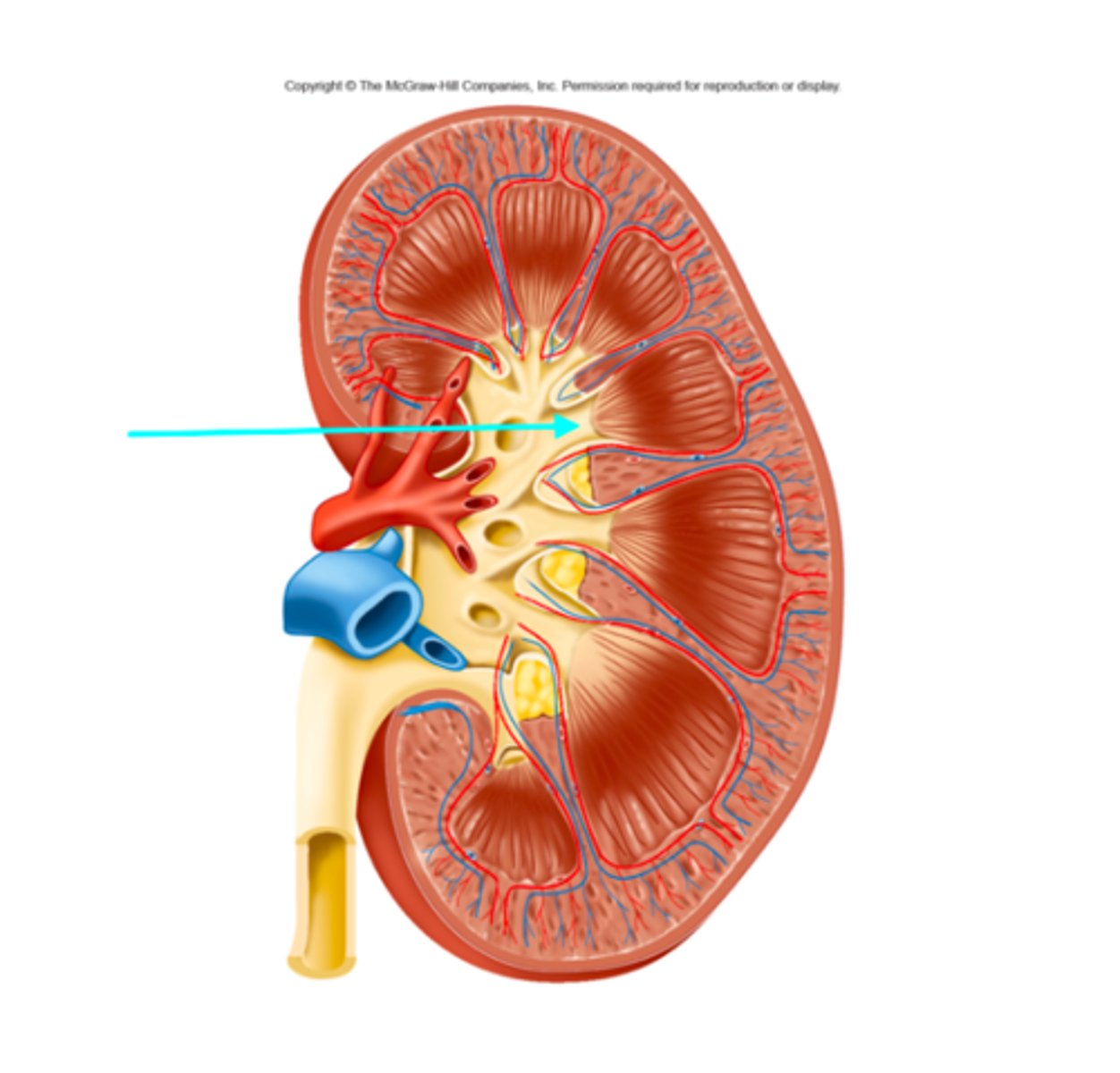
Minor calyx
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
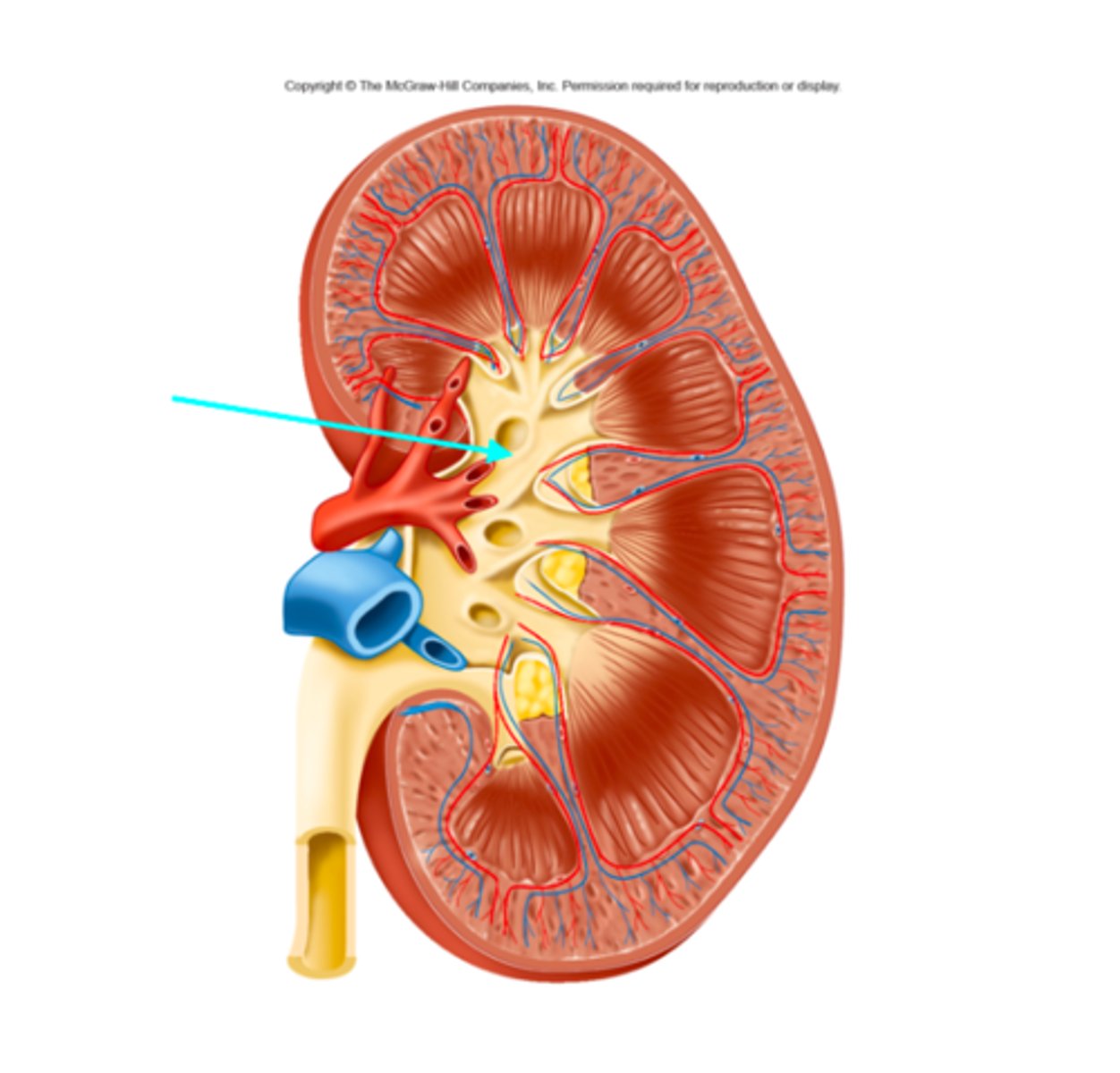
Major calyx
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
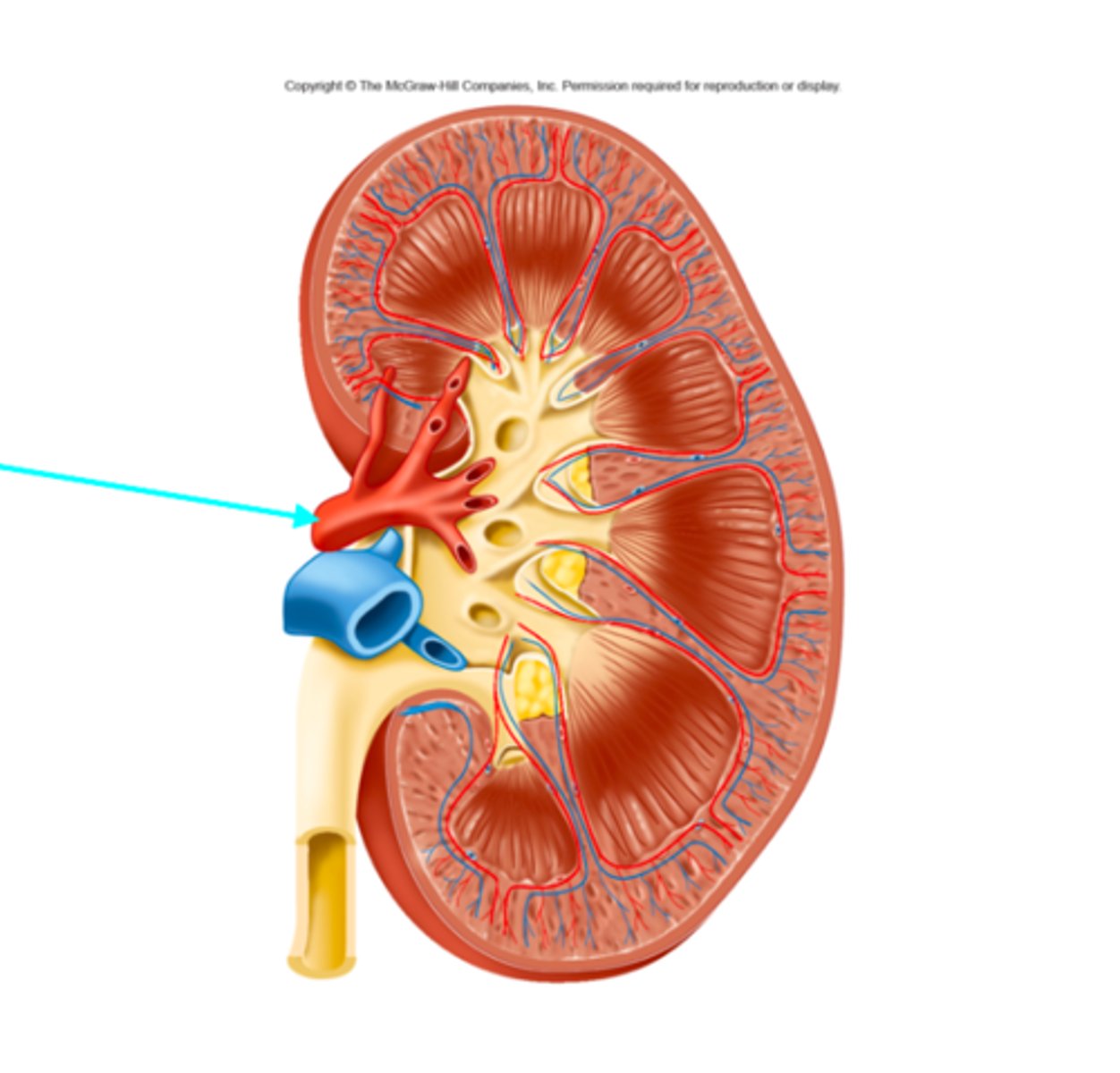
Renal artery
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
Renal vein
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
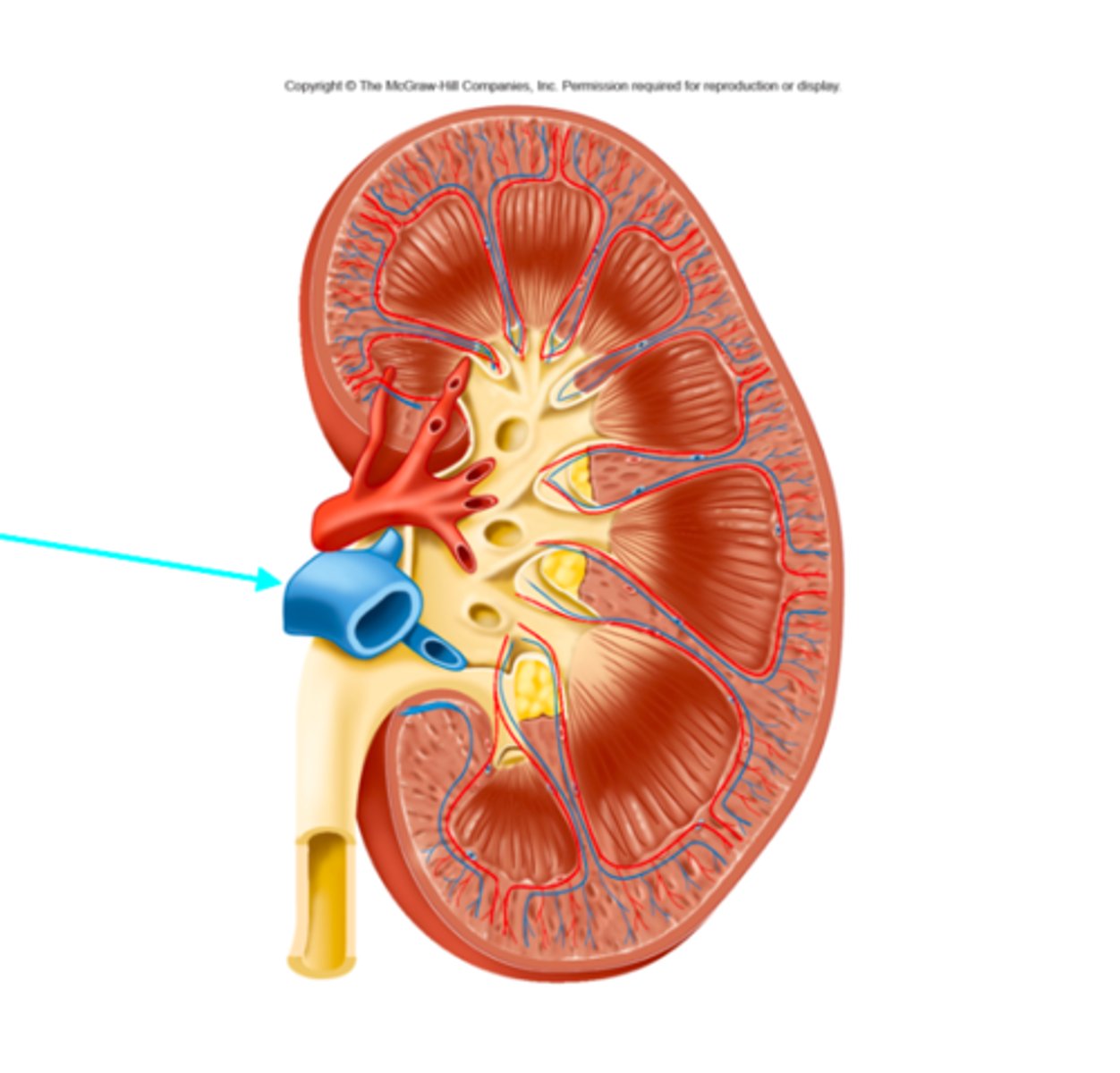
Renal pelvis
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
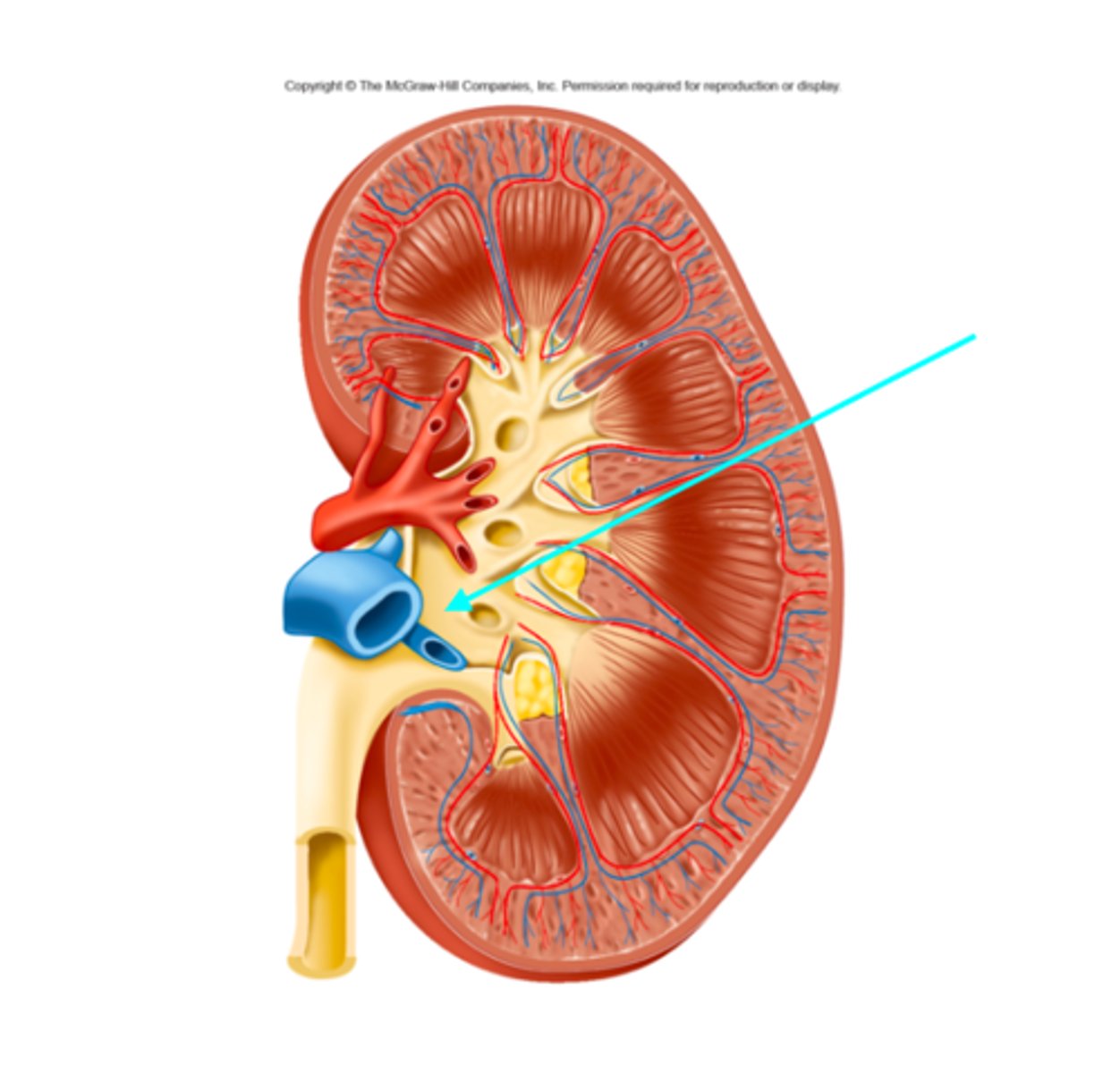
Renal pyramid
What individual structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
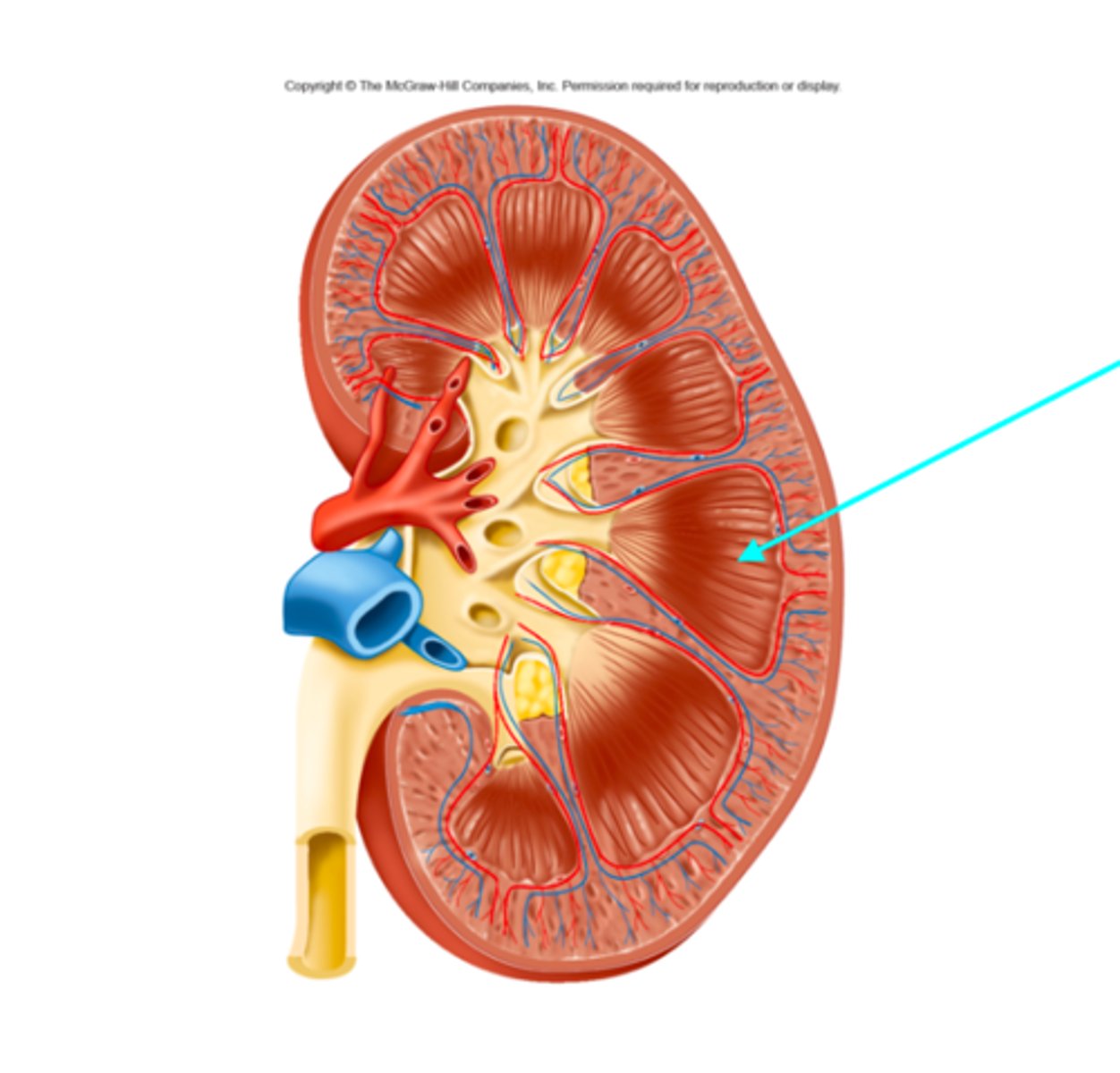
Ureter
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
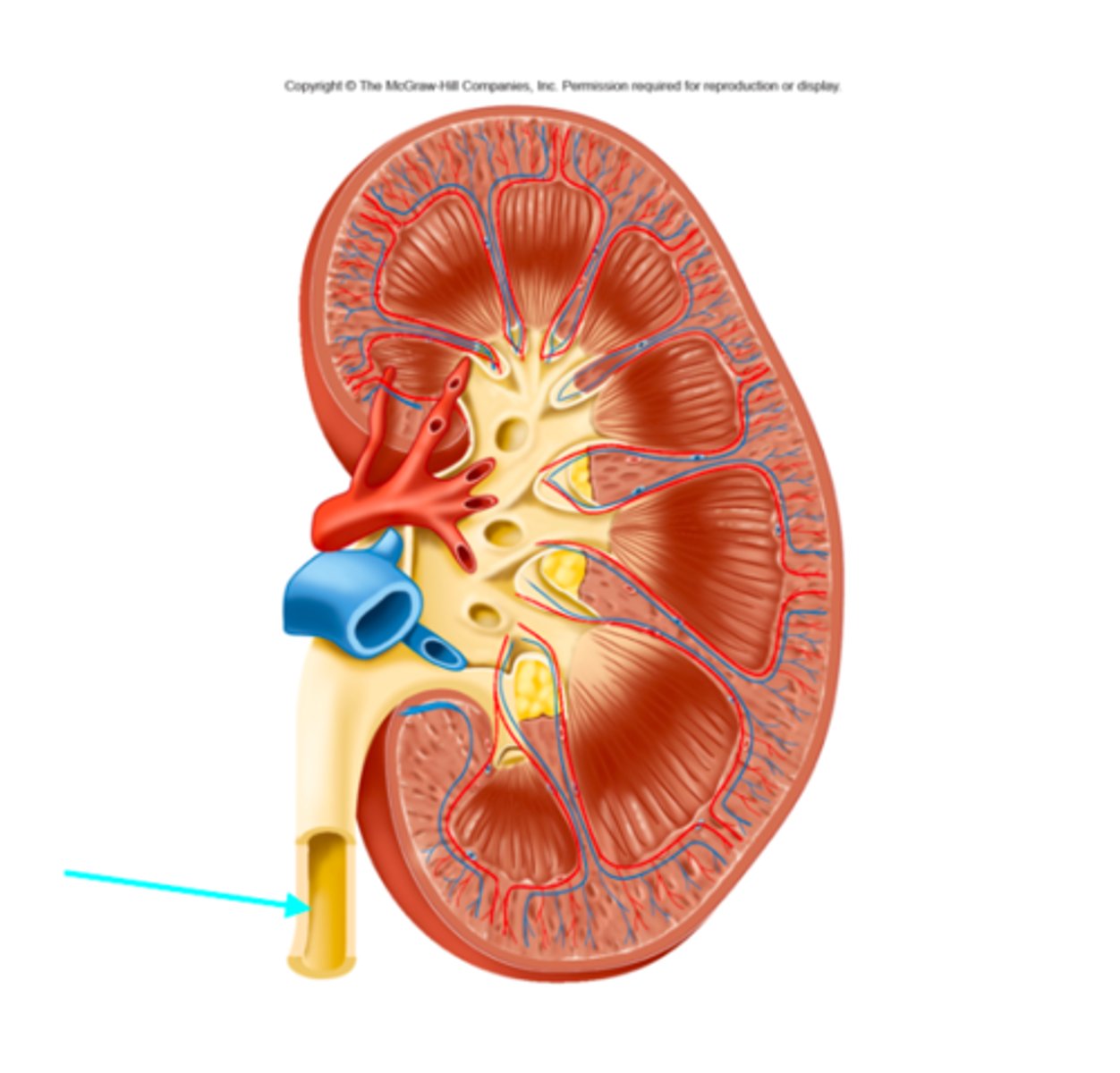
Interlobar arteries and veins
What structures of the kidneys are located where the blue arrow is pointing?
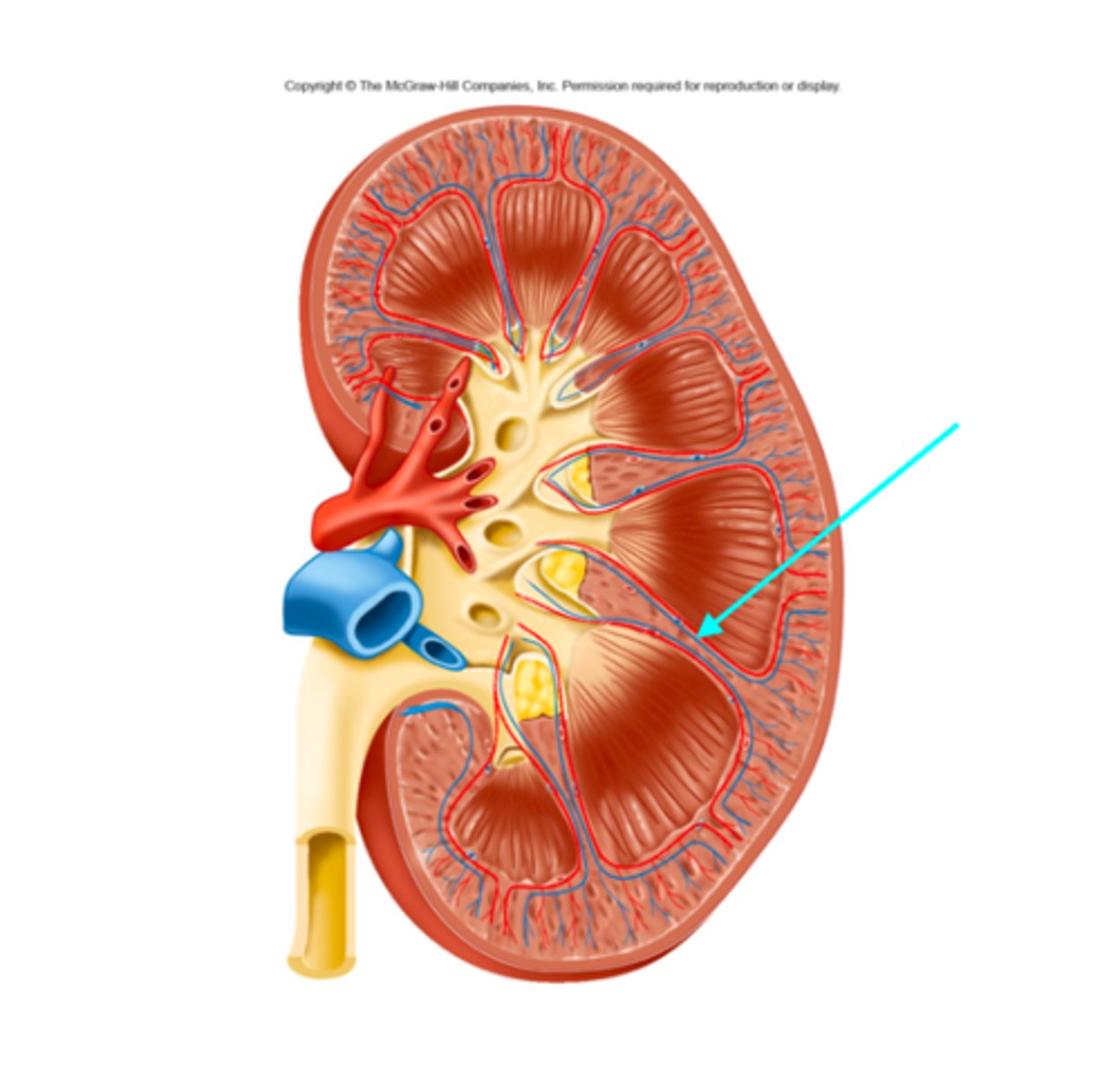
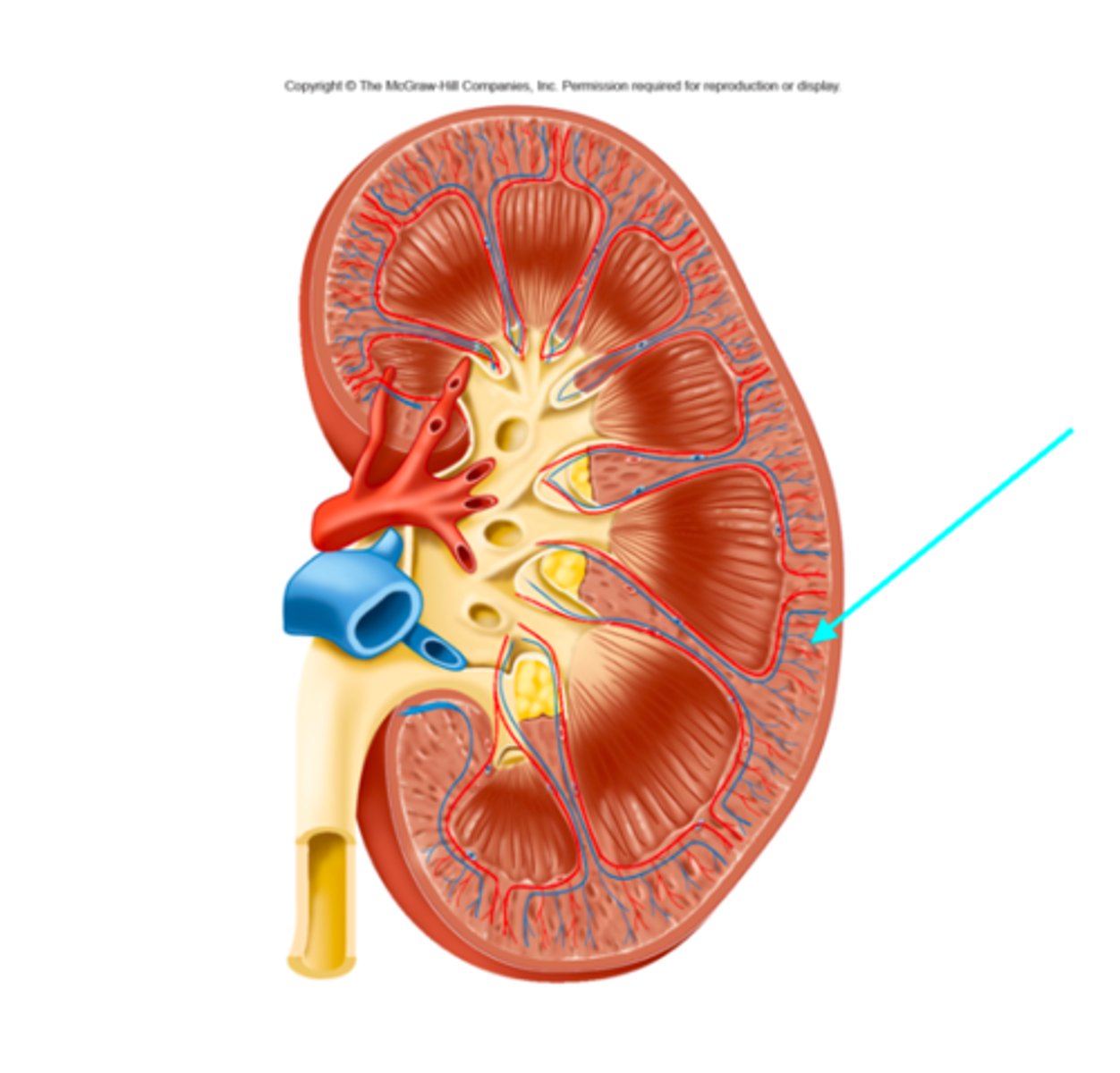
Cortical radiate arteries and veins
What structures of the kidneys are located where the blue arrow is pointing?
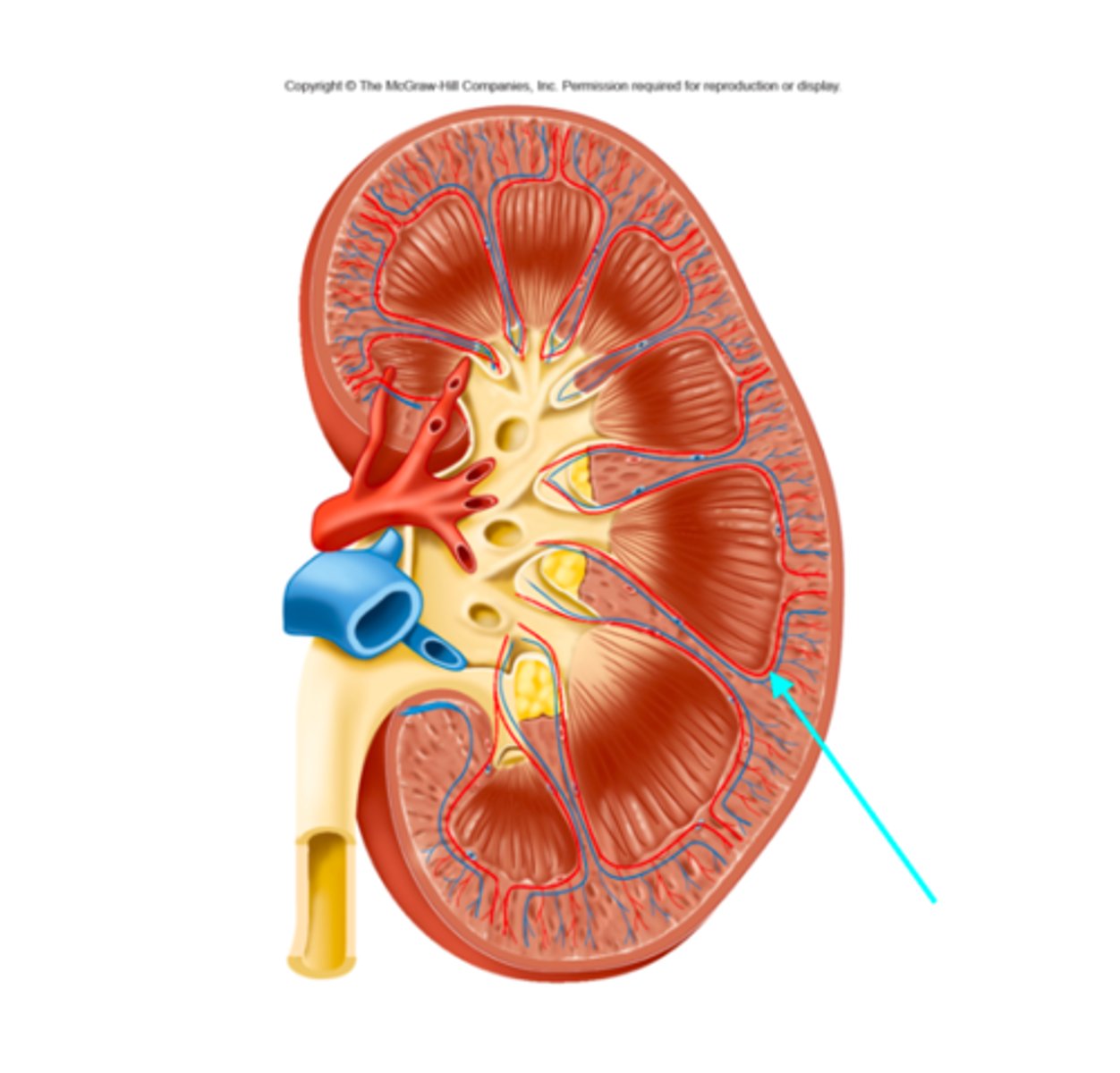
Arcuate arteries and veins
What structures of the kidneys are located where the blue arrow is pointing?
Cortical nephron
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
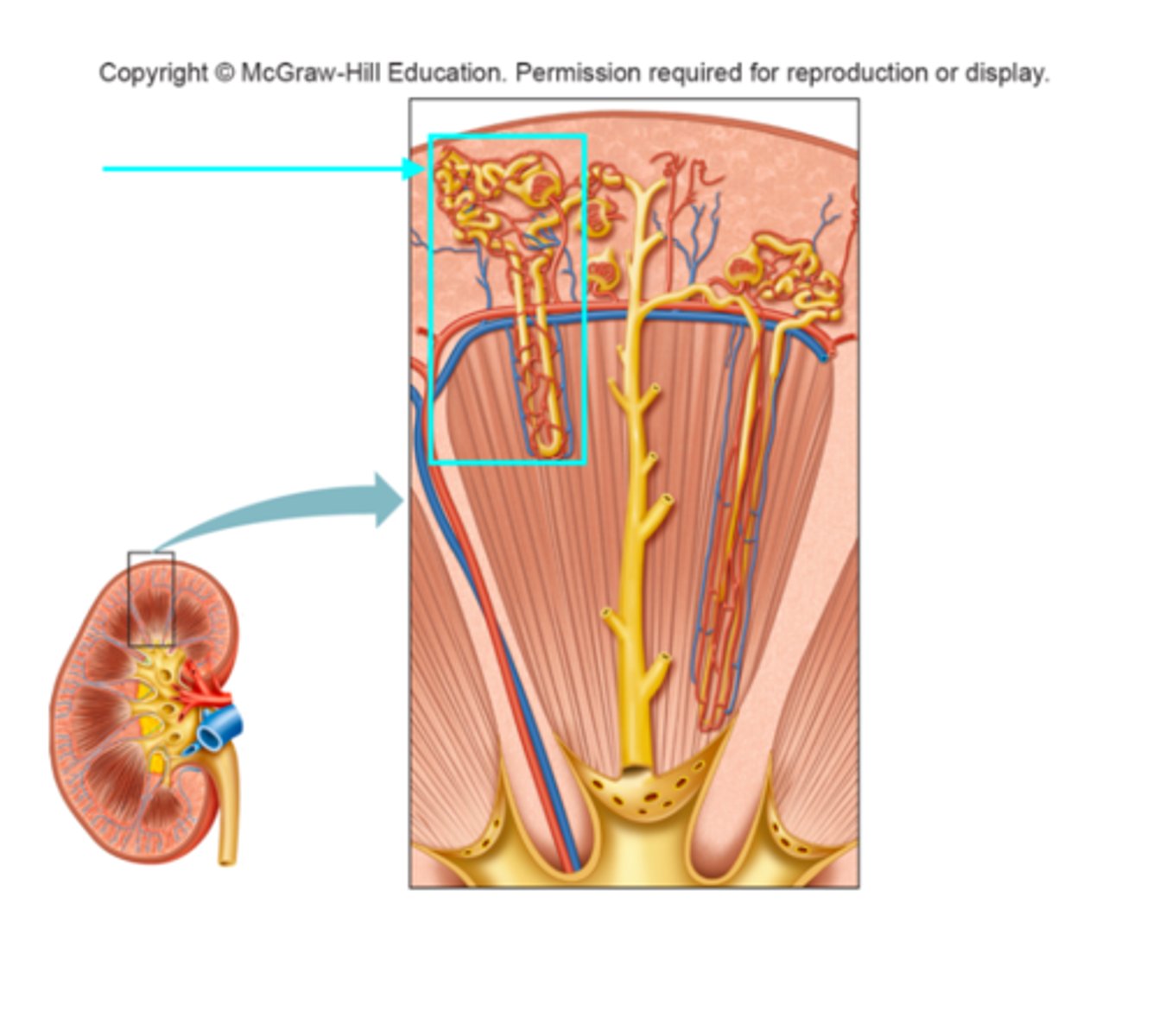
Juxtamedullary nephron
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
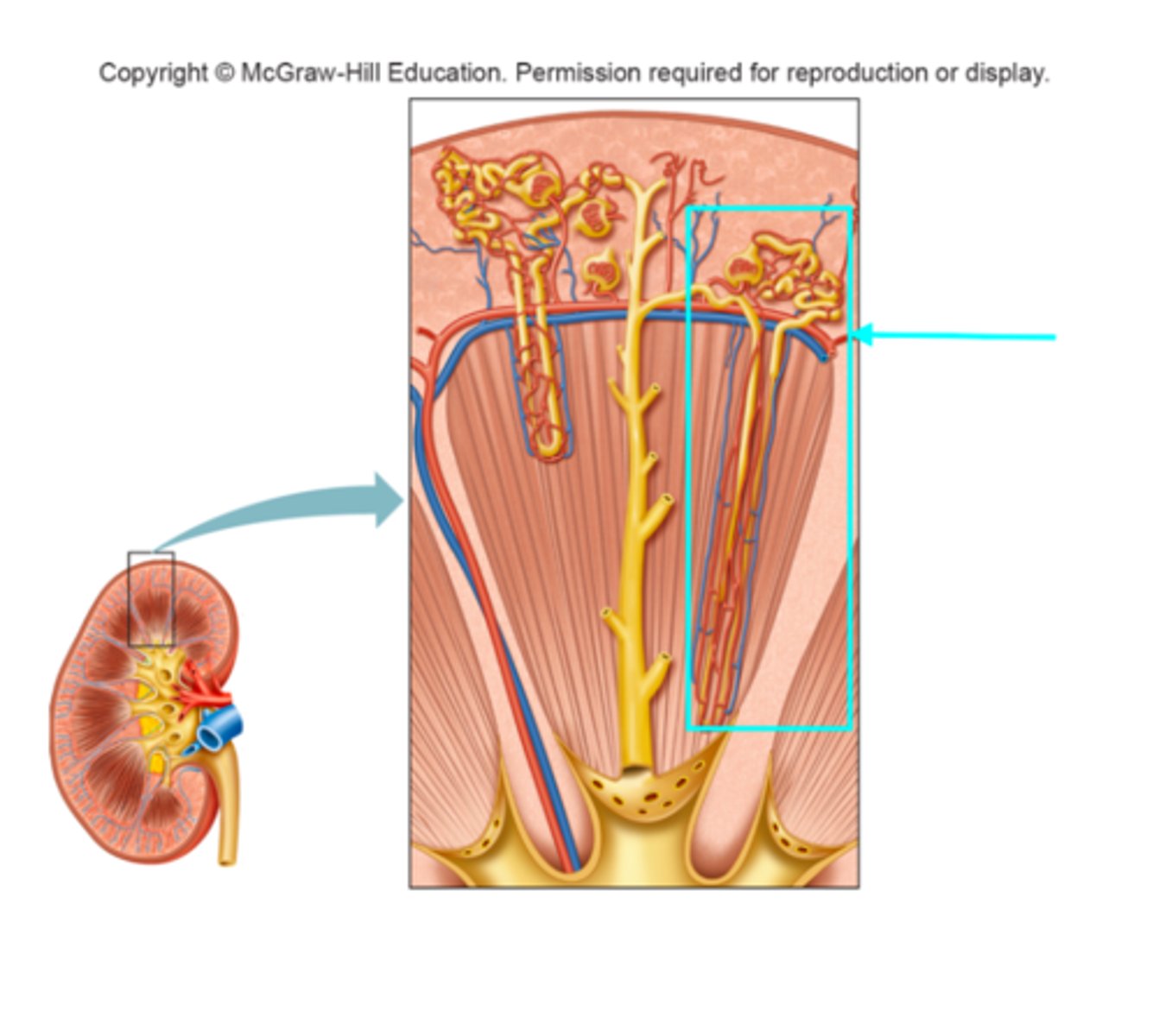
Collecting duct
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
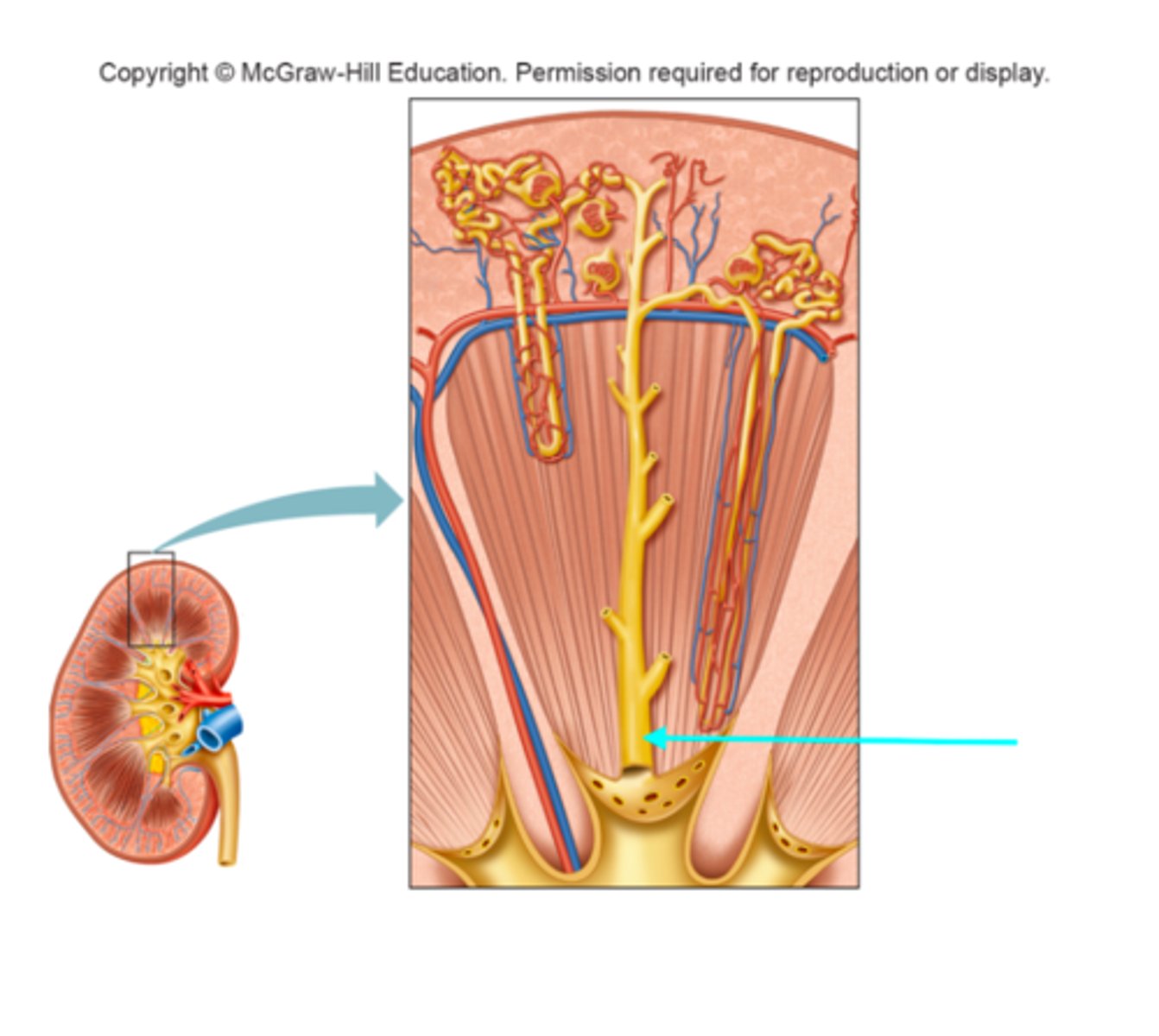
Interlobar vein
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
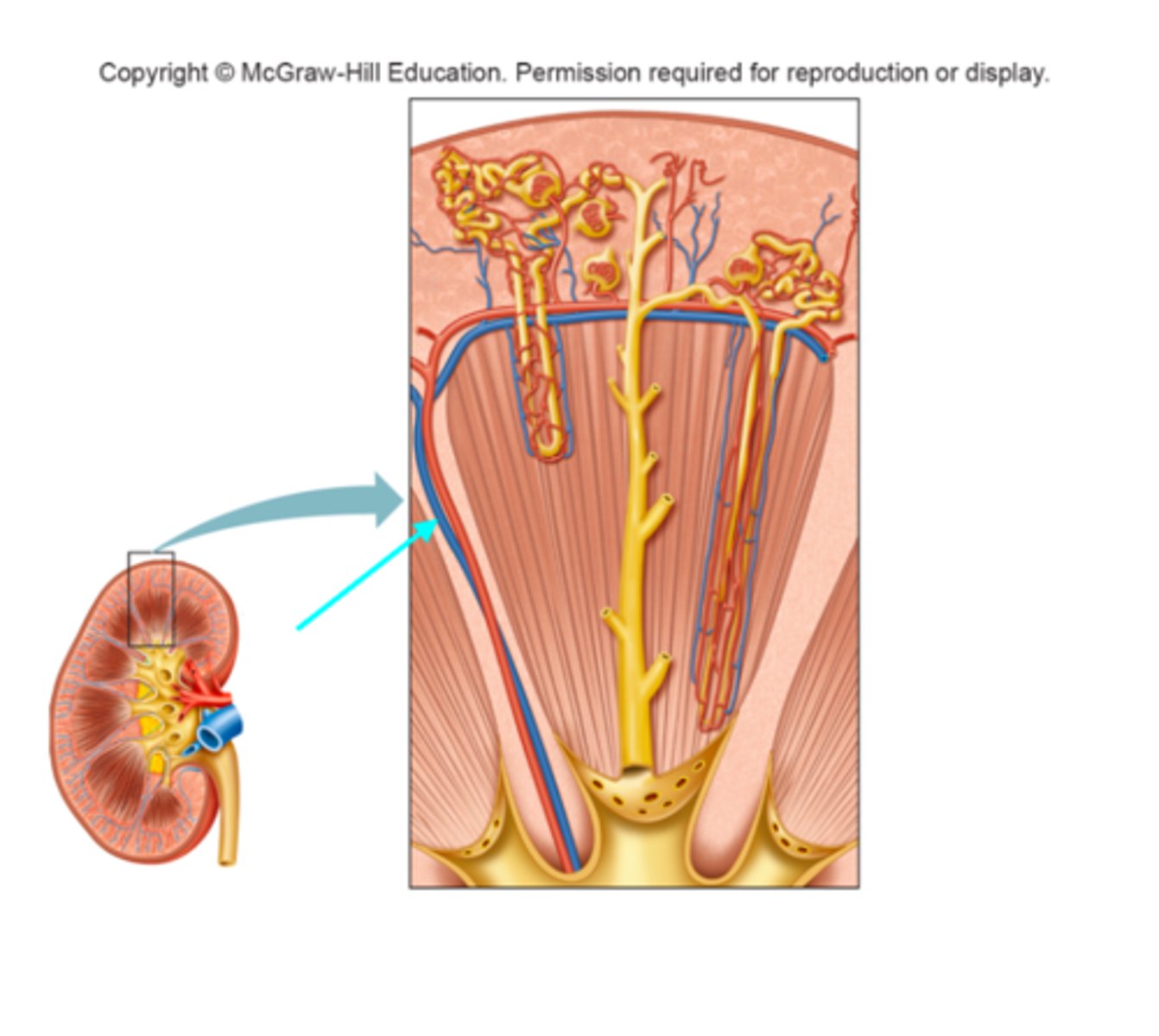
Interlobar artery
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
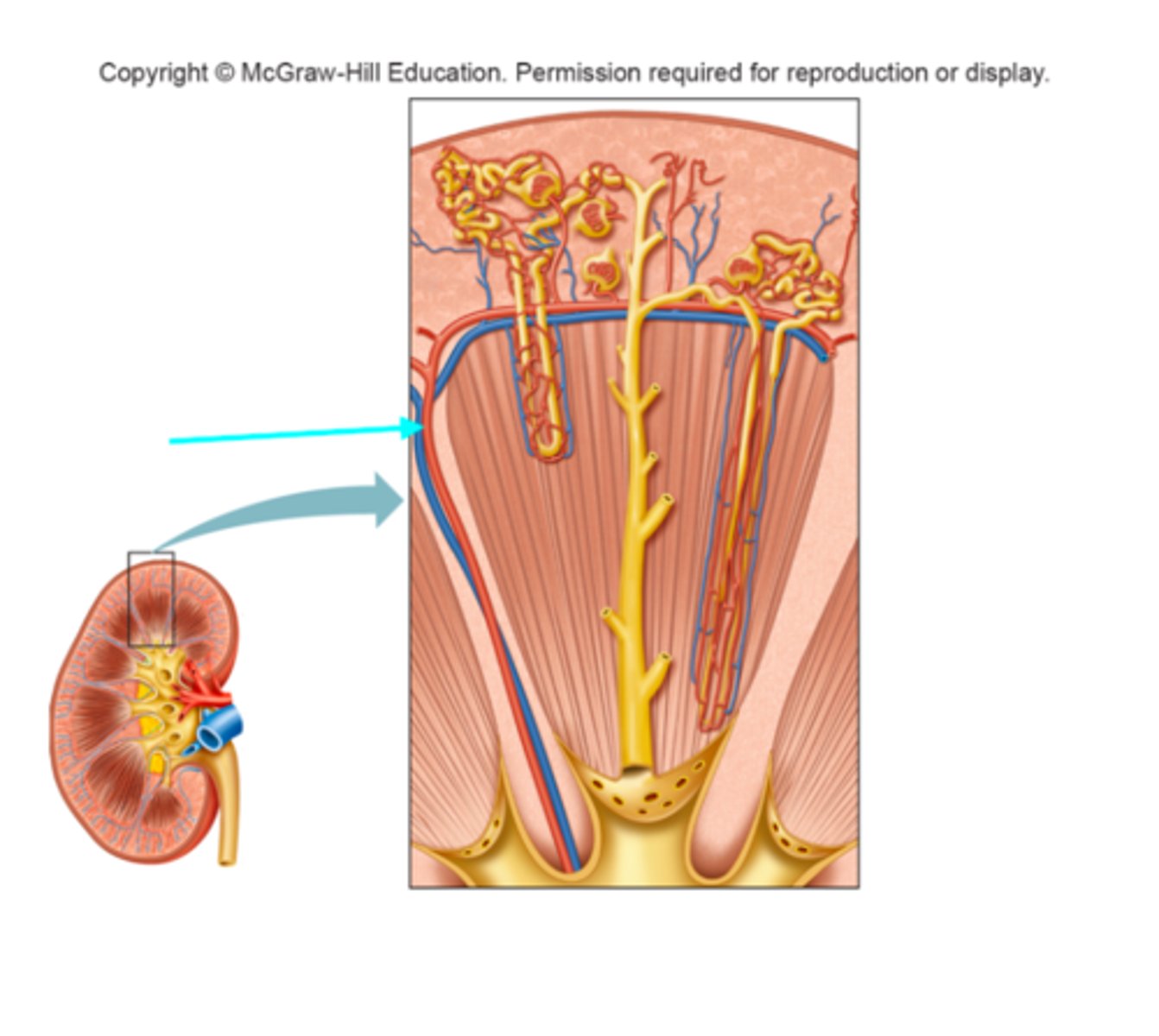
Arcuate vein
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
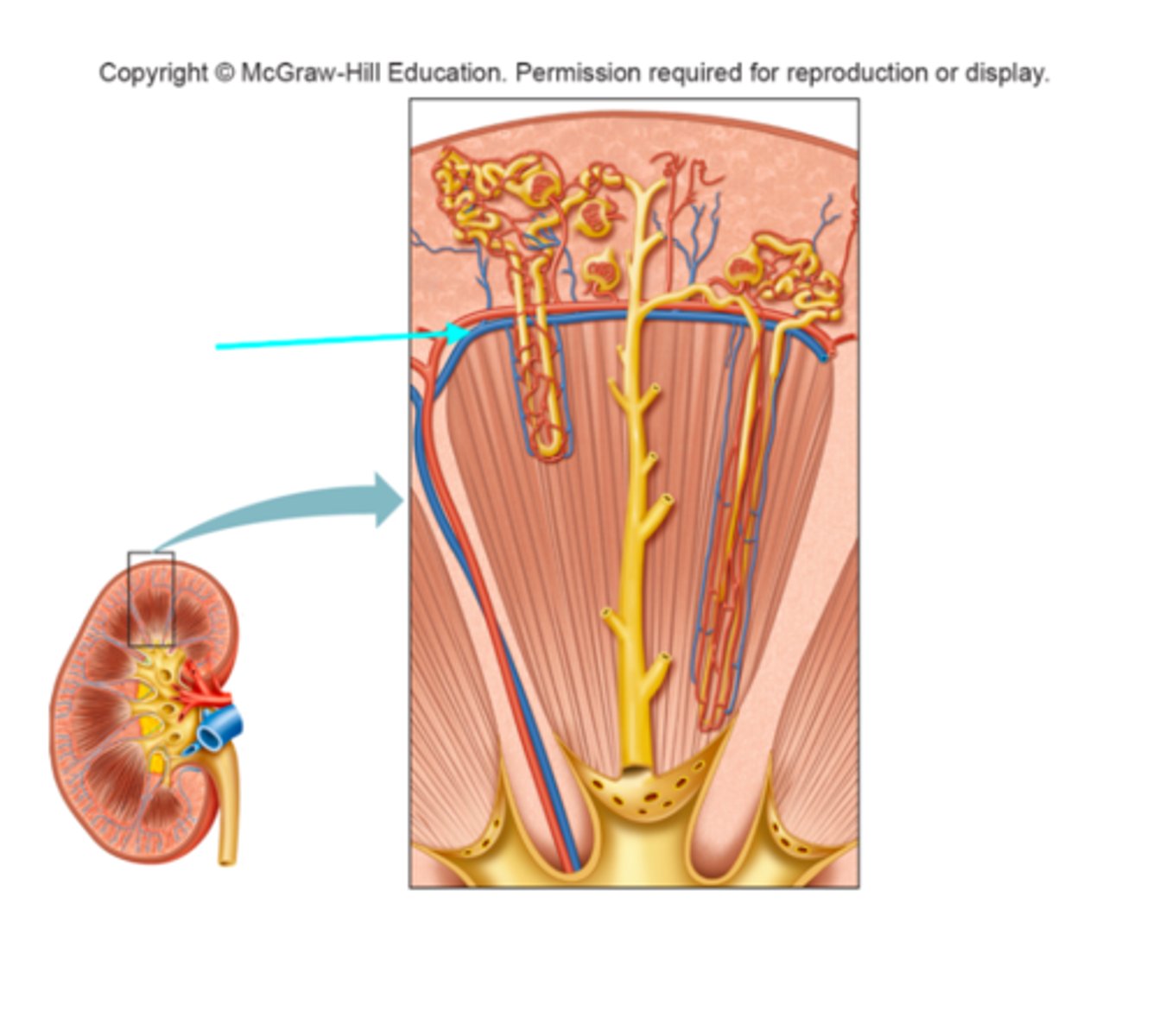
Arcuate artery
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
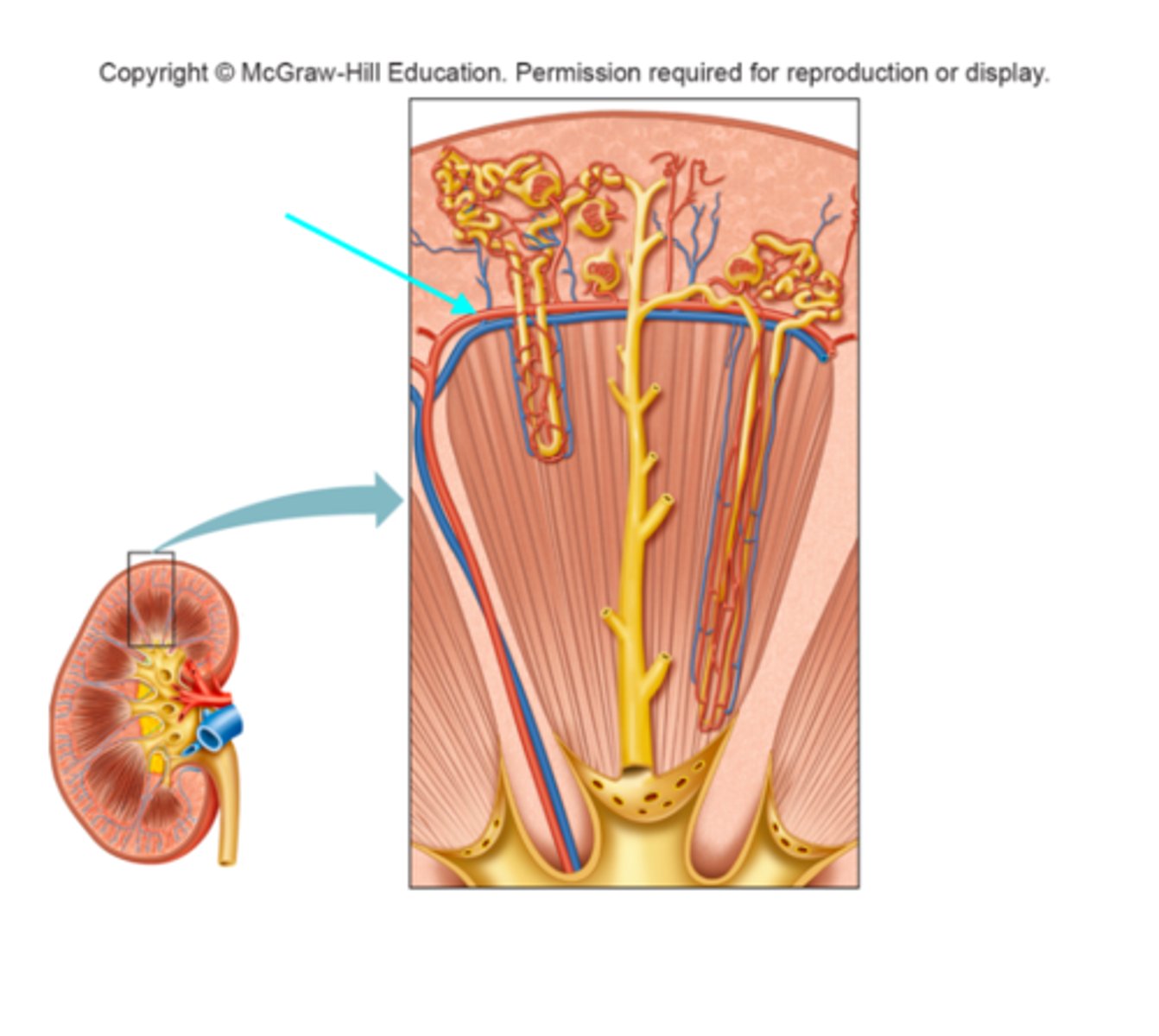
Cortical radiate vein
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
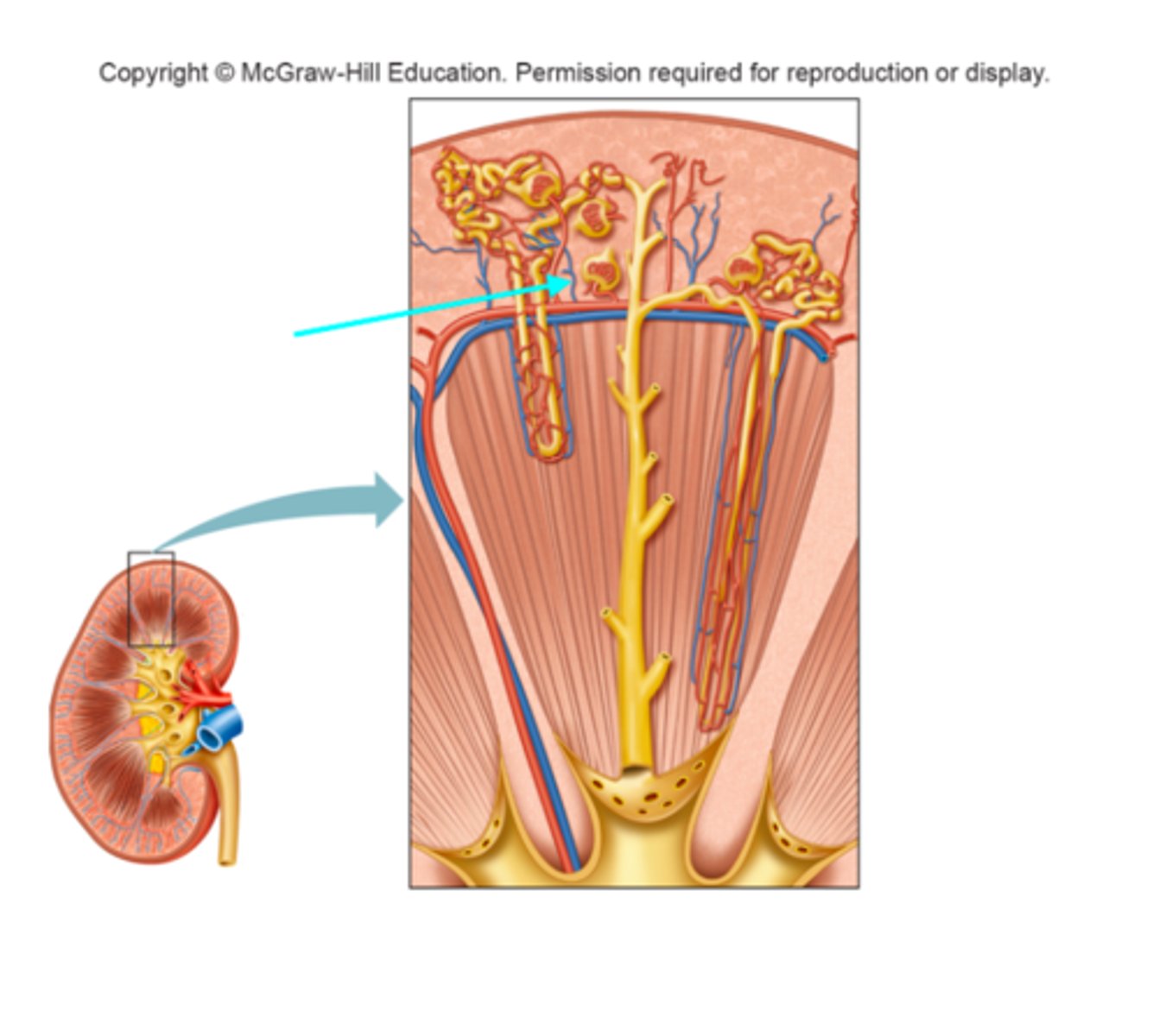
Cortical radiate artery
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
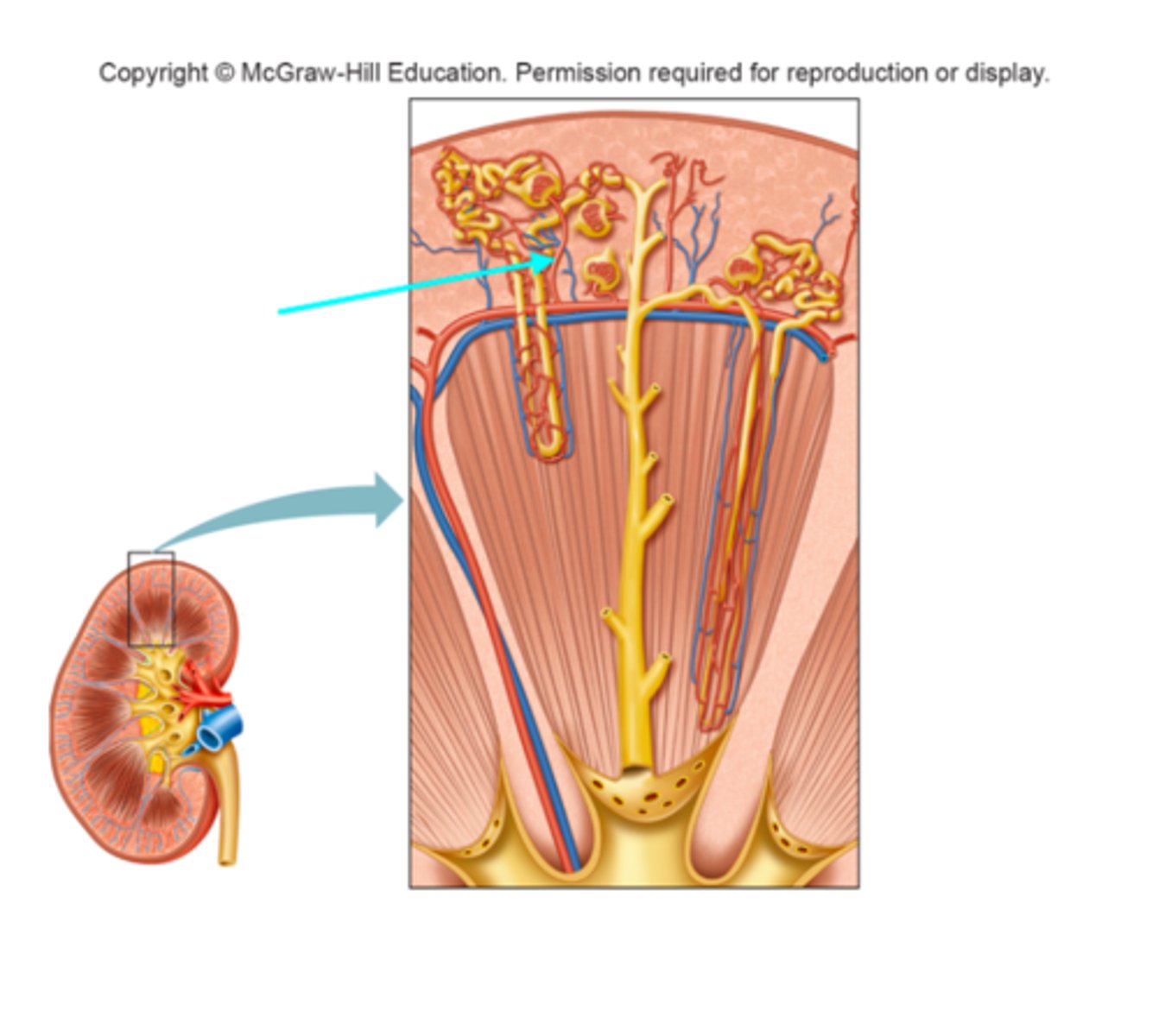
Afferent arteriole
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
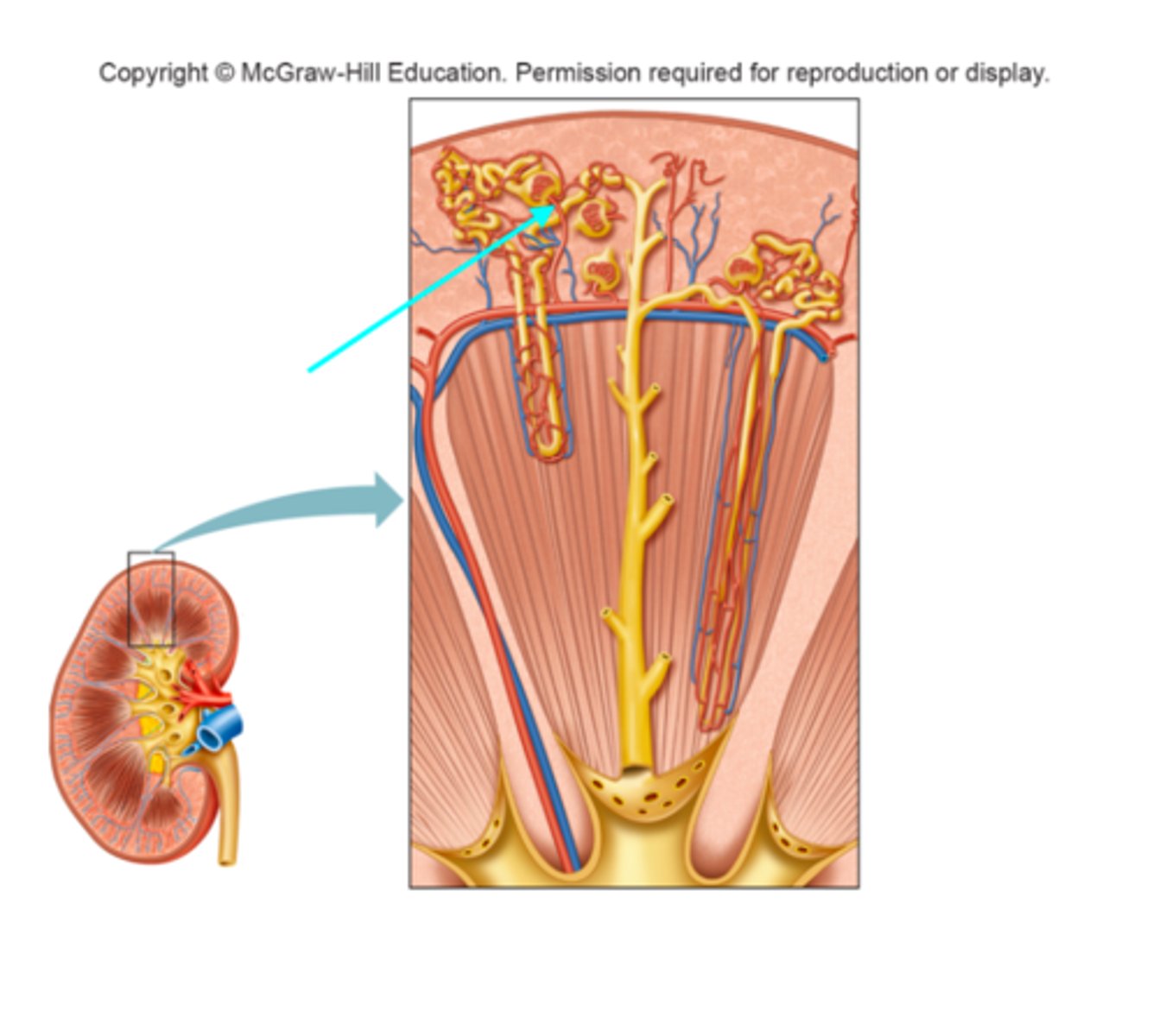
Efferent arteriole
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
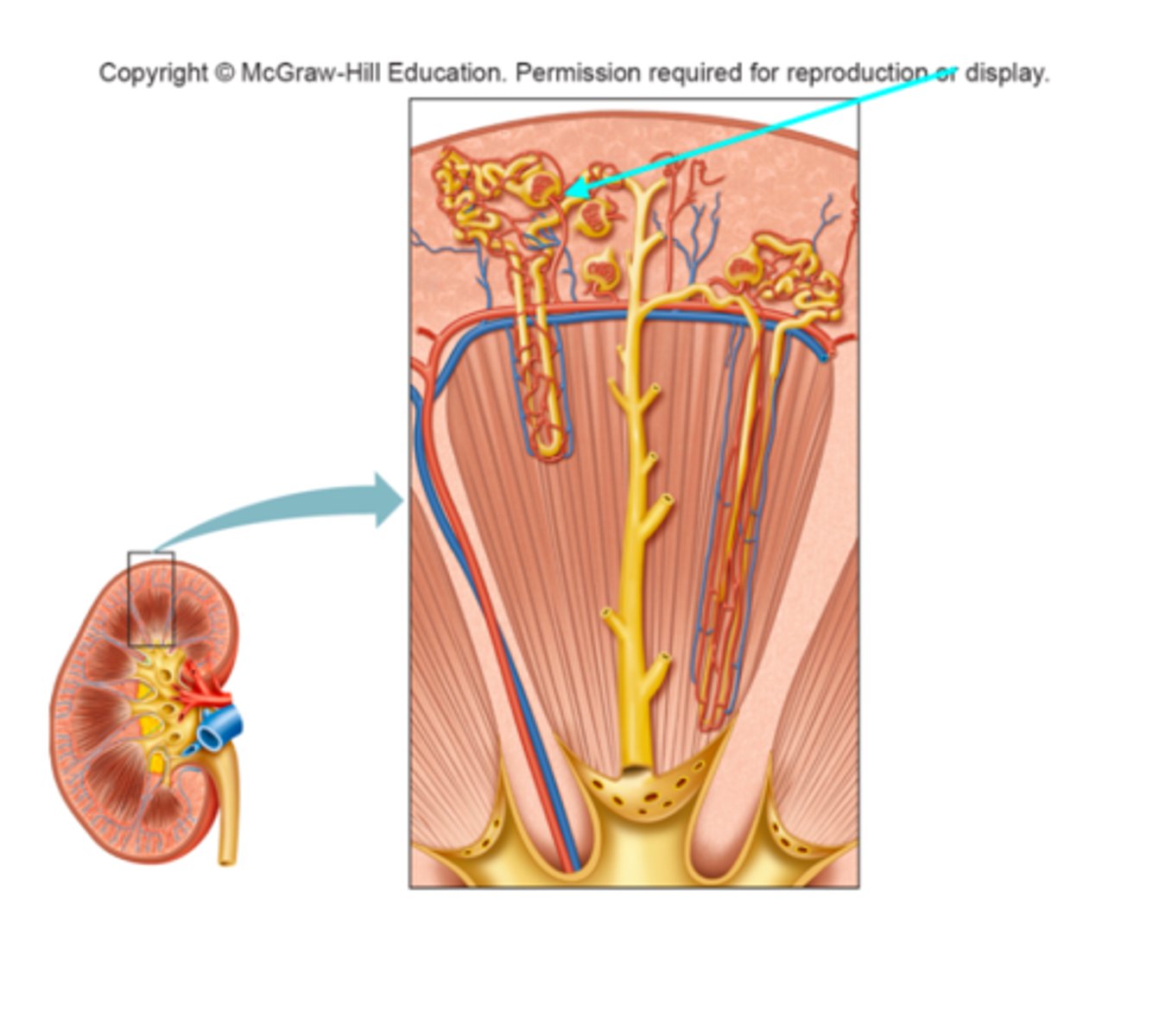
Peritubular capillaries
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
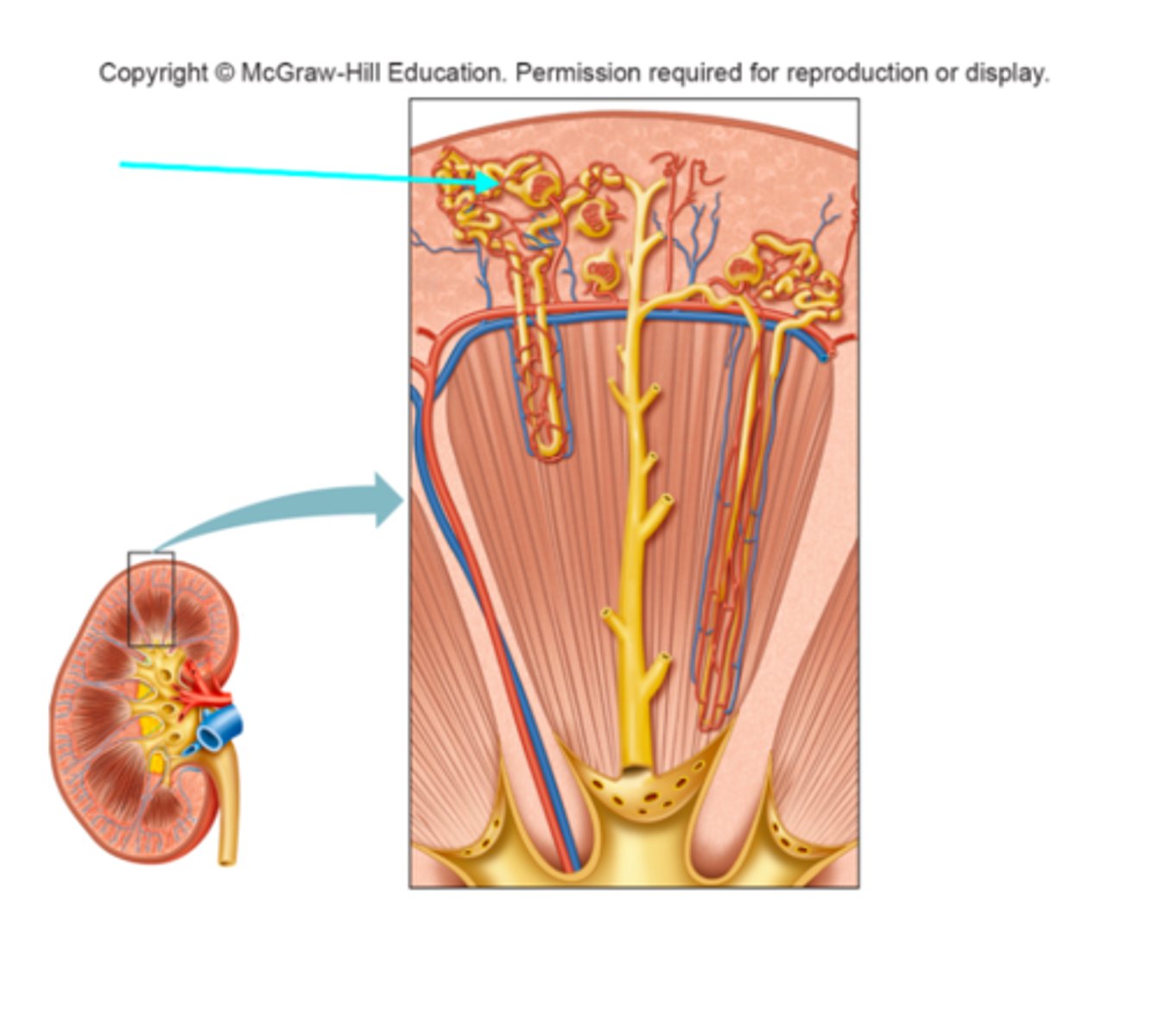
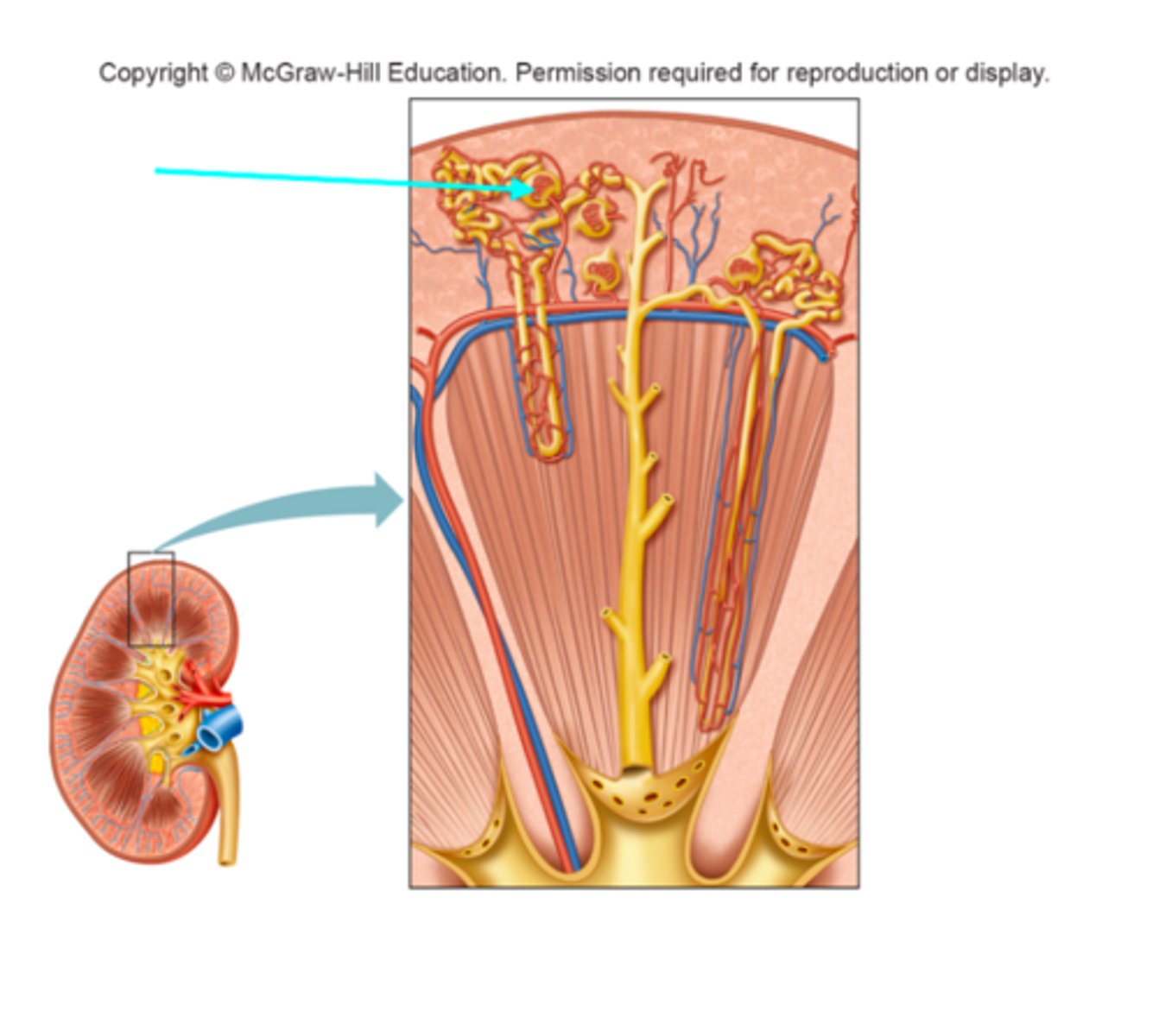
Glomerulus
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
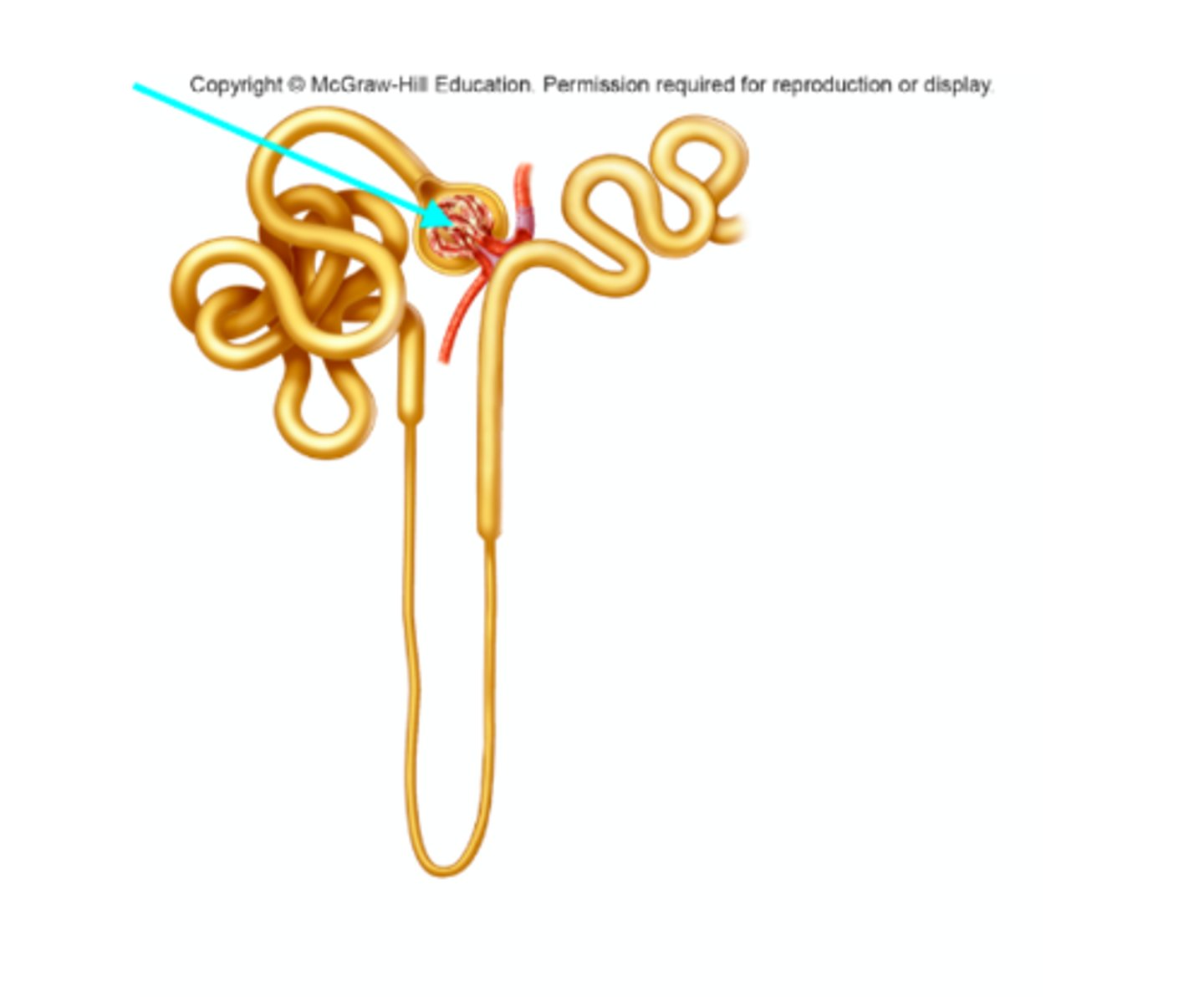
Glomerulus
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
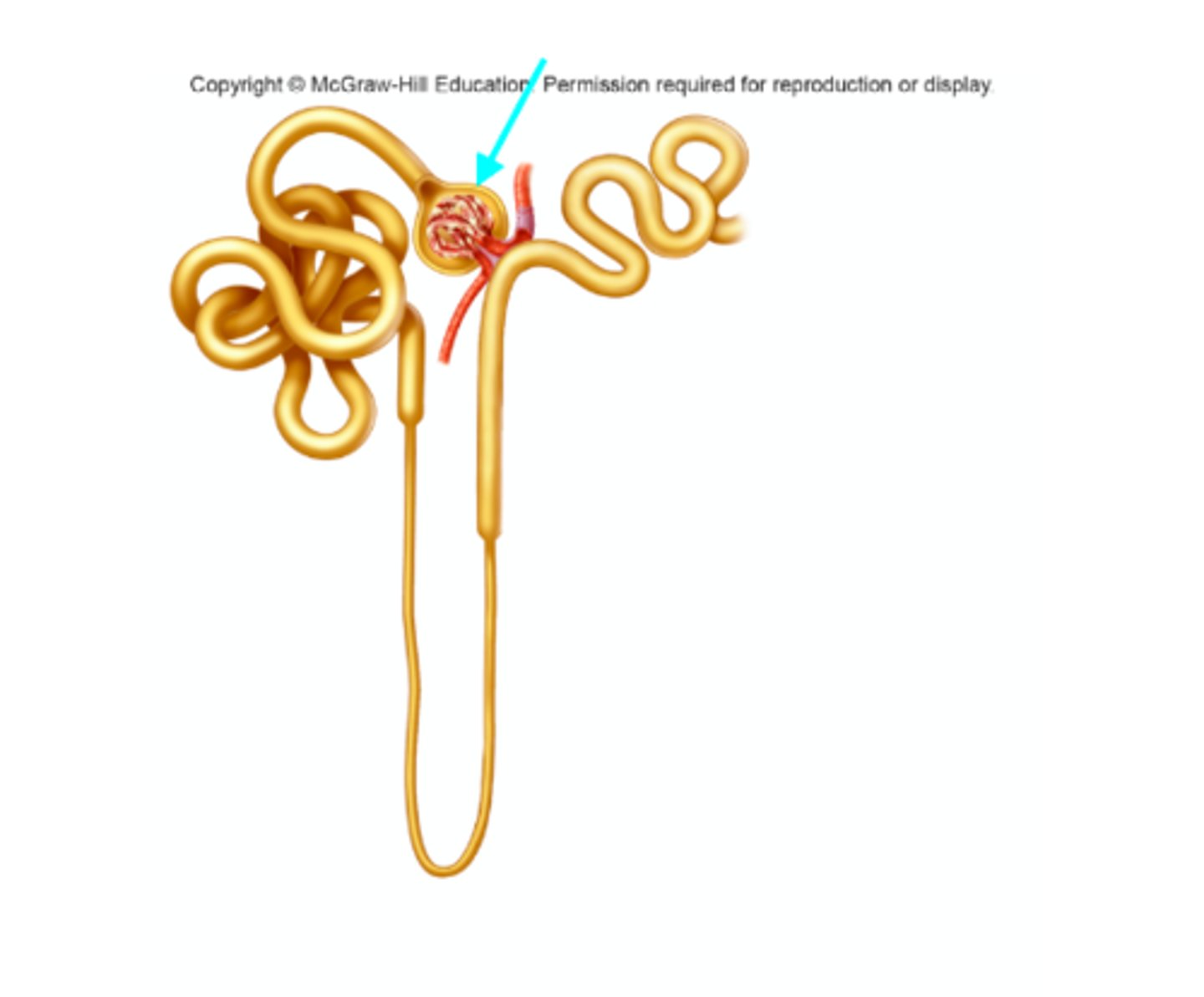
Glomerular capsule
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
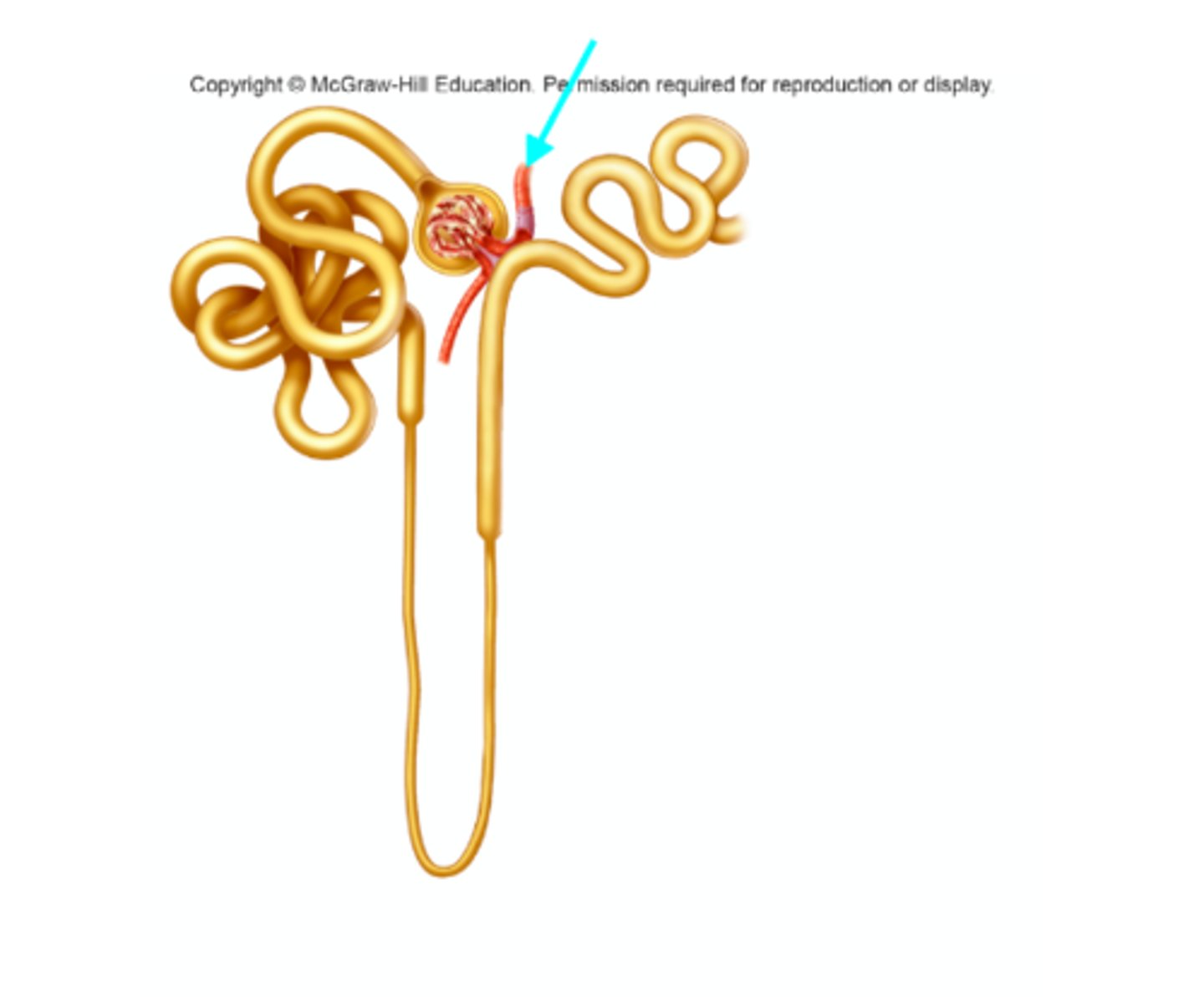
Afferent arteriole
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
Efferent arteriole
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
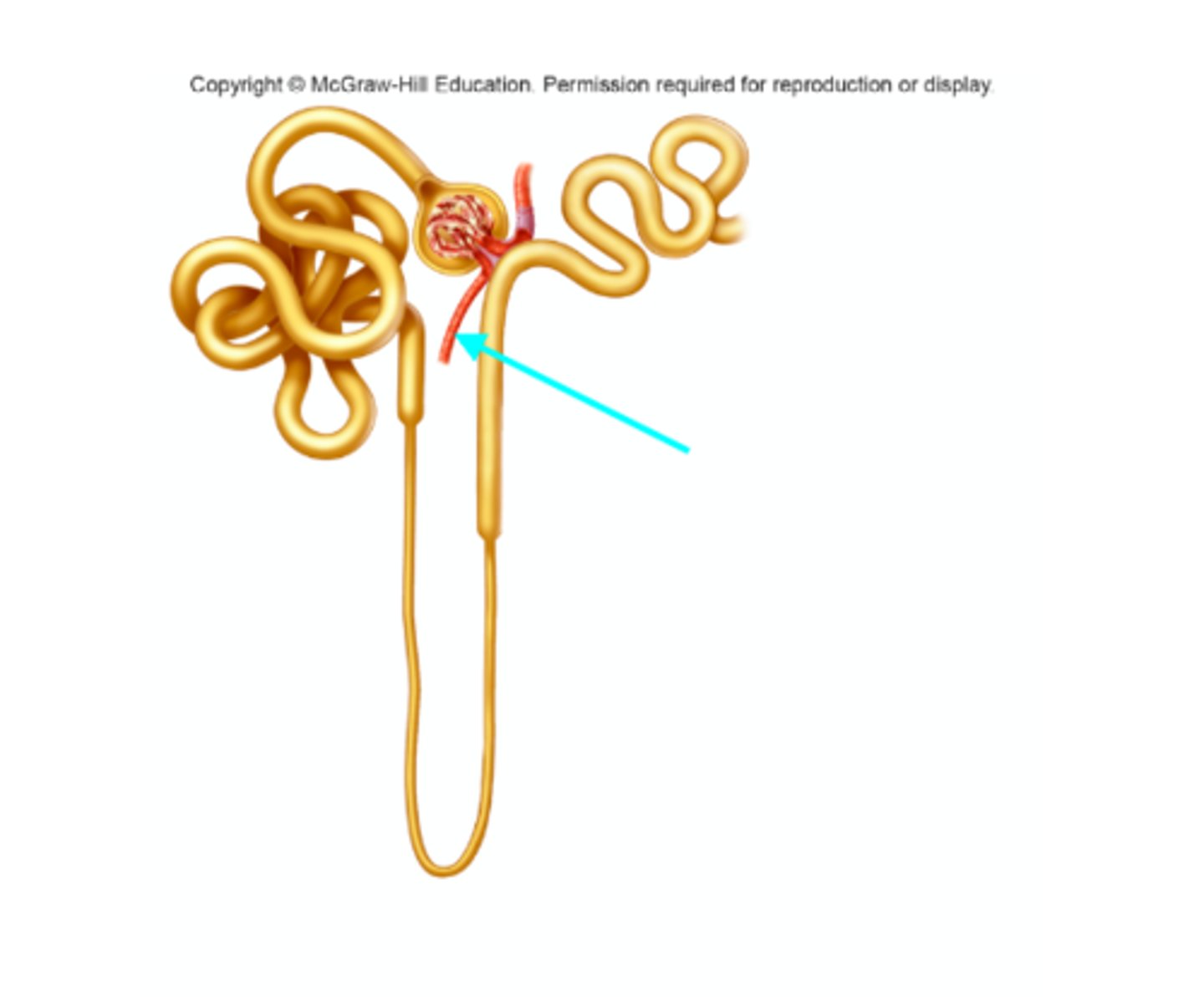
Distal convoluted tubule
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
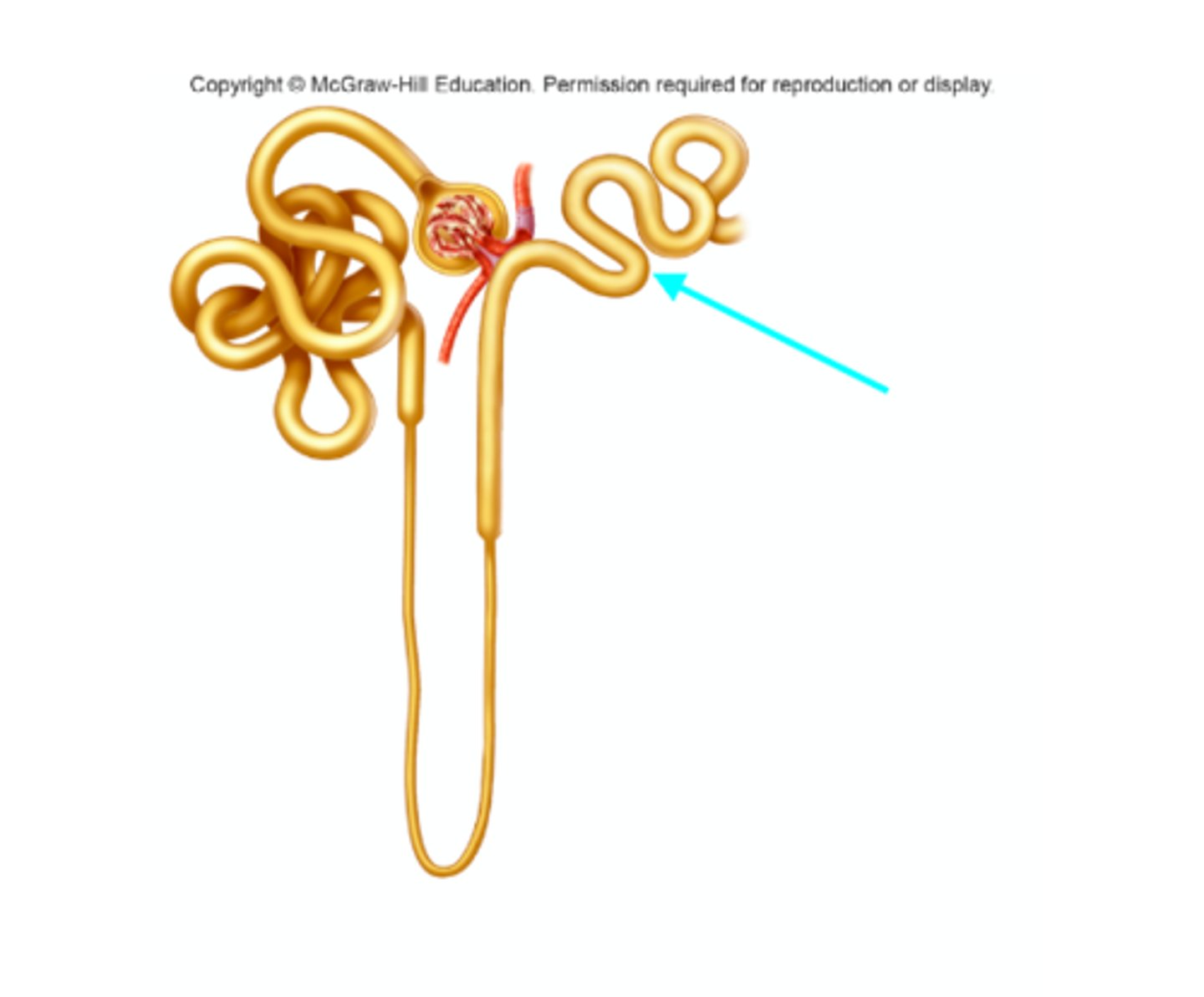
Proximal convoluted tubule
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
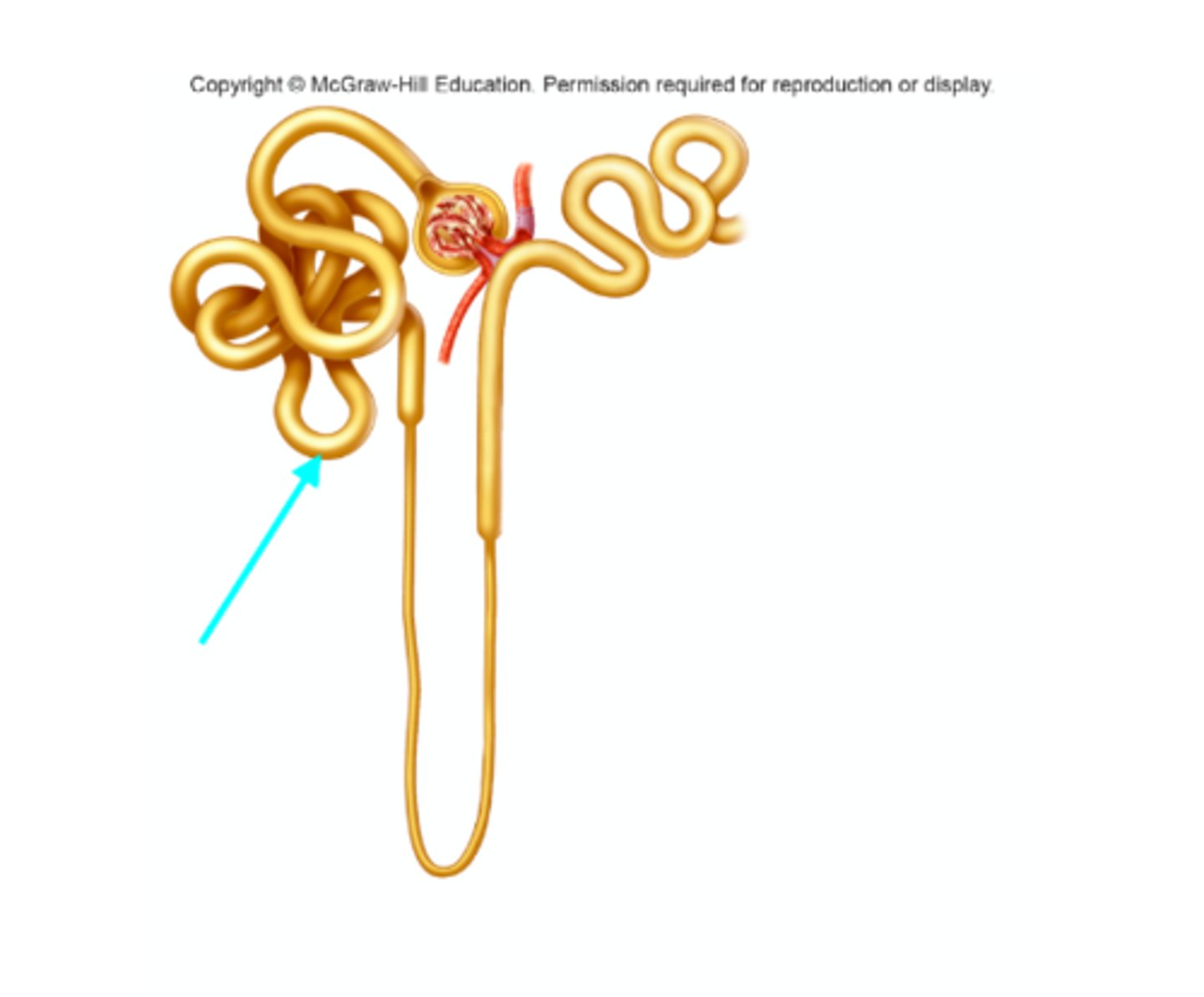
Descending limb of the nephron loop
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
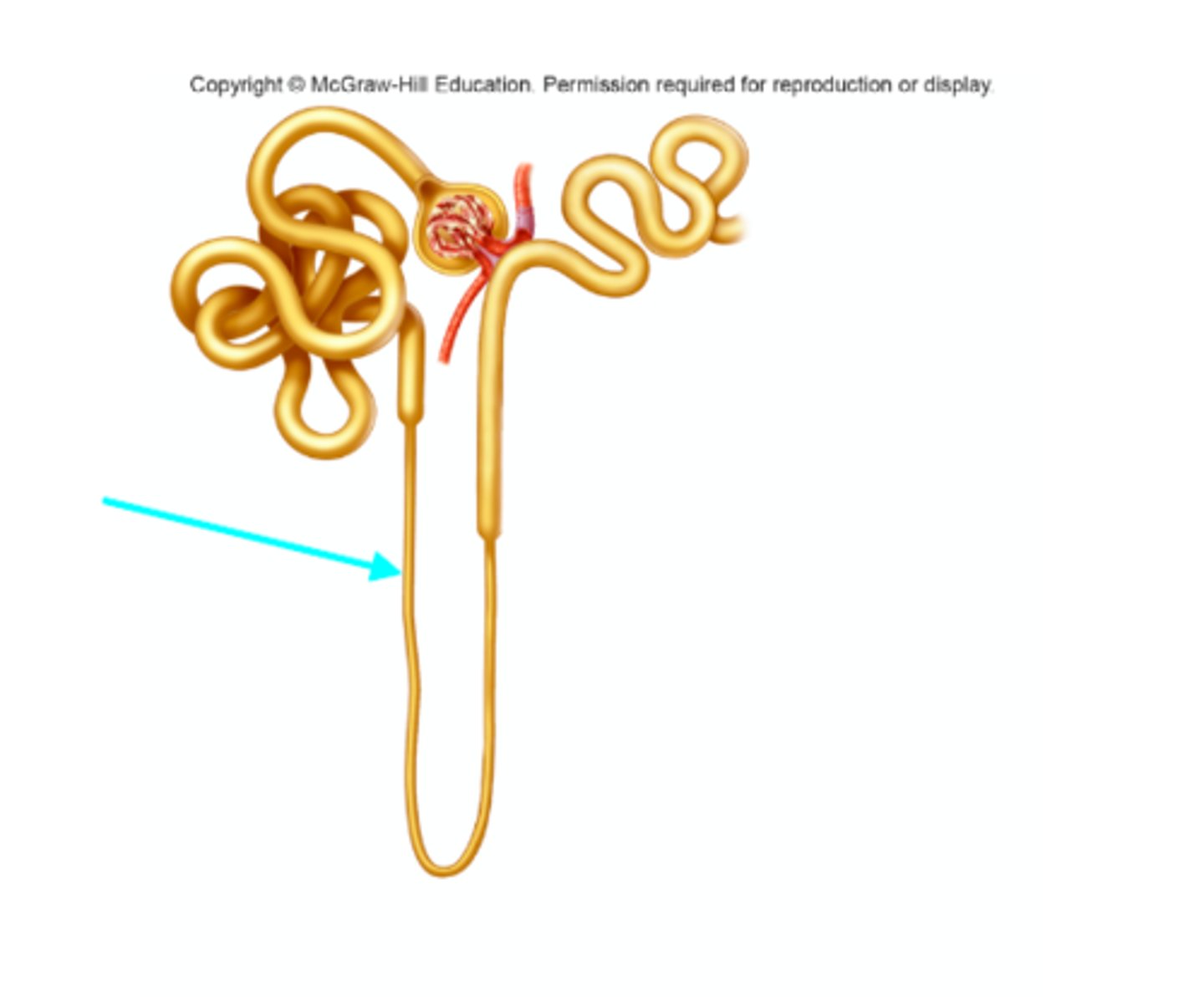
Ascending limb of the nephron loop
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
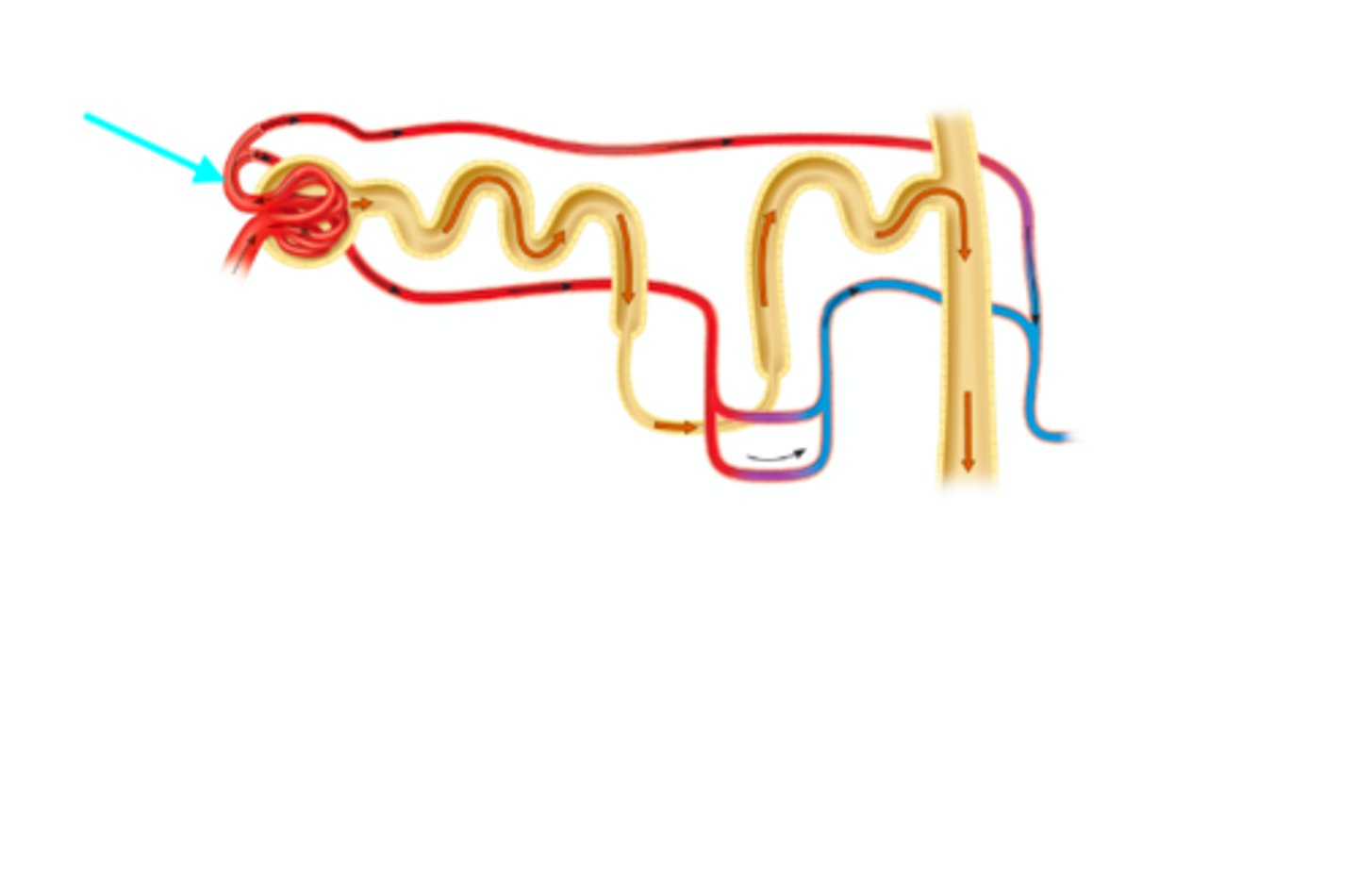
Nephron loop
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
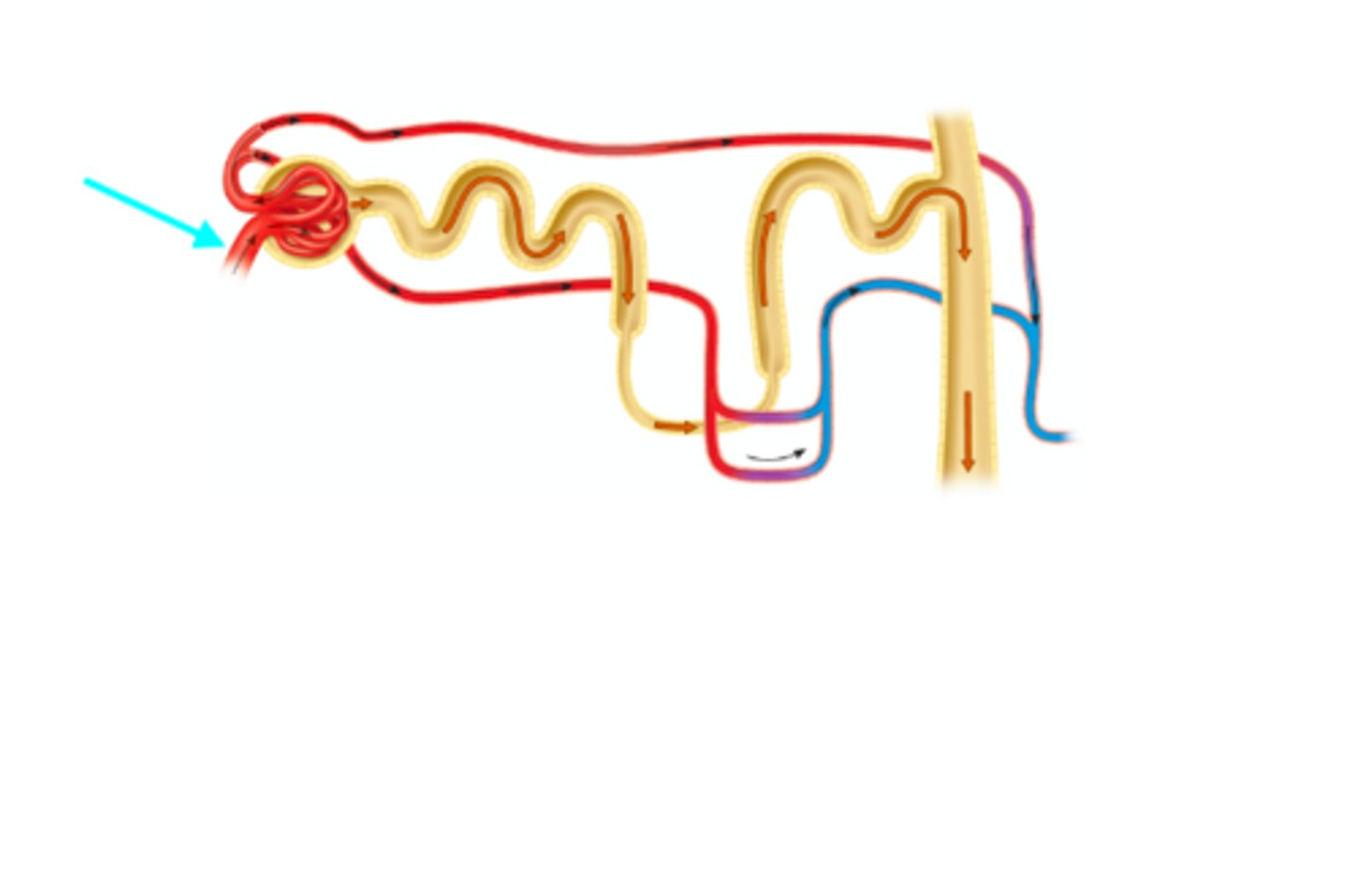
Efferent arteriole
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
Afferent arteriole
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
Glomerulus
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
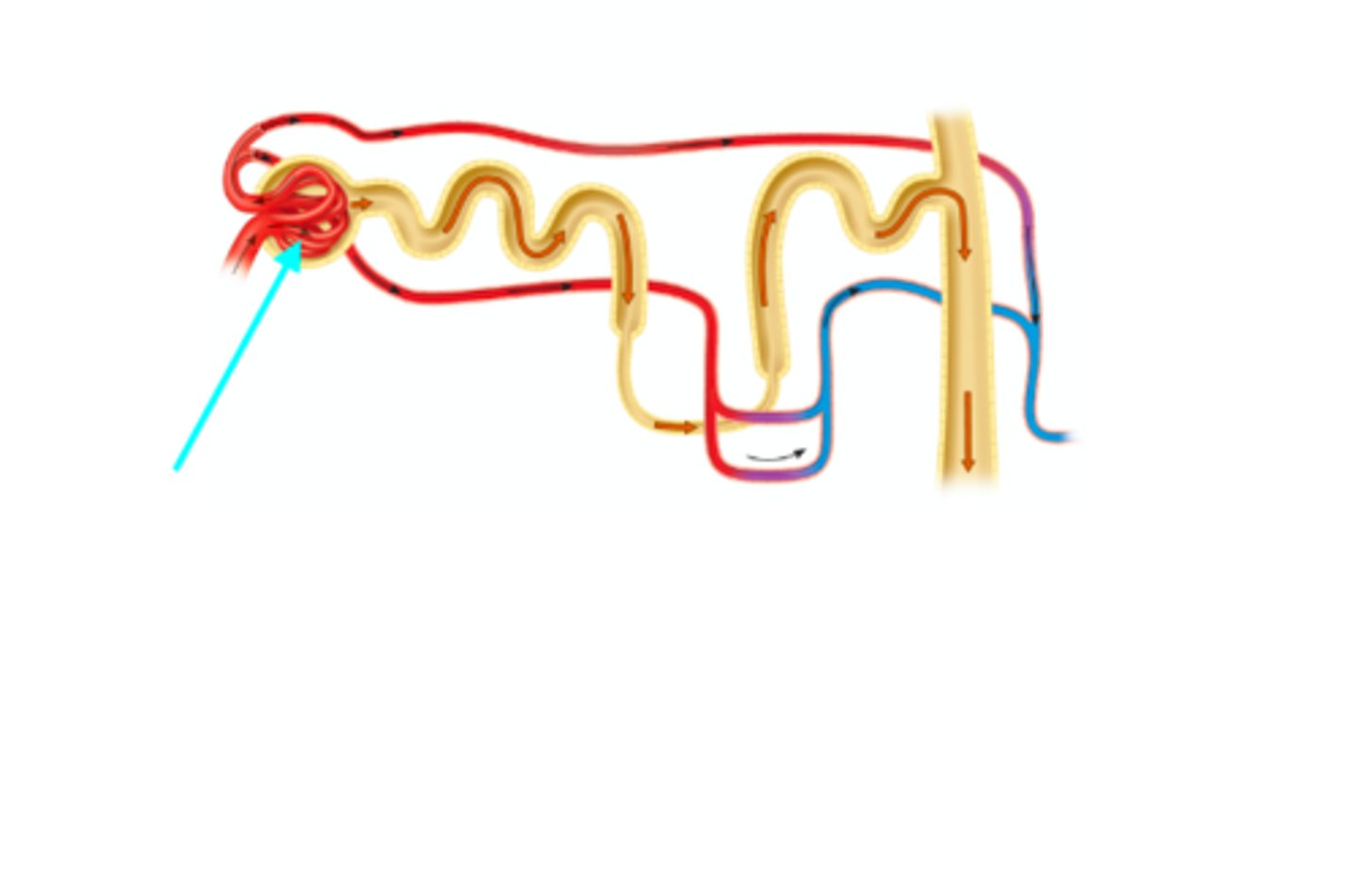
Glomerular capsule
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
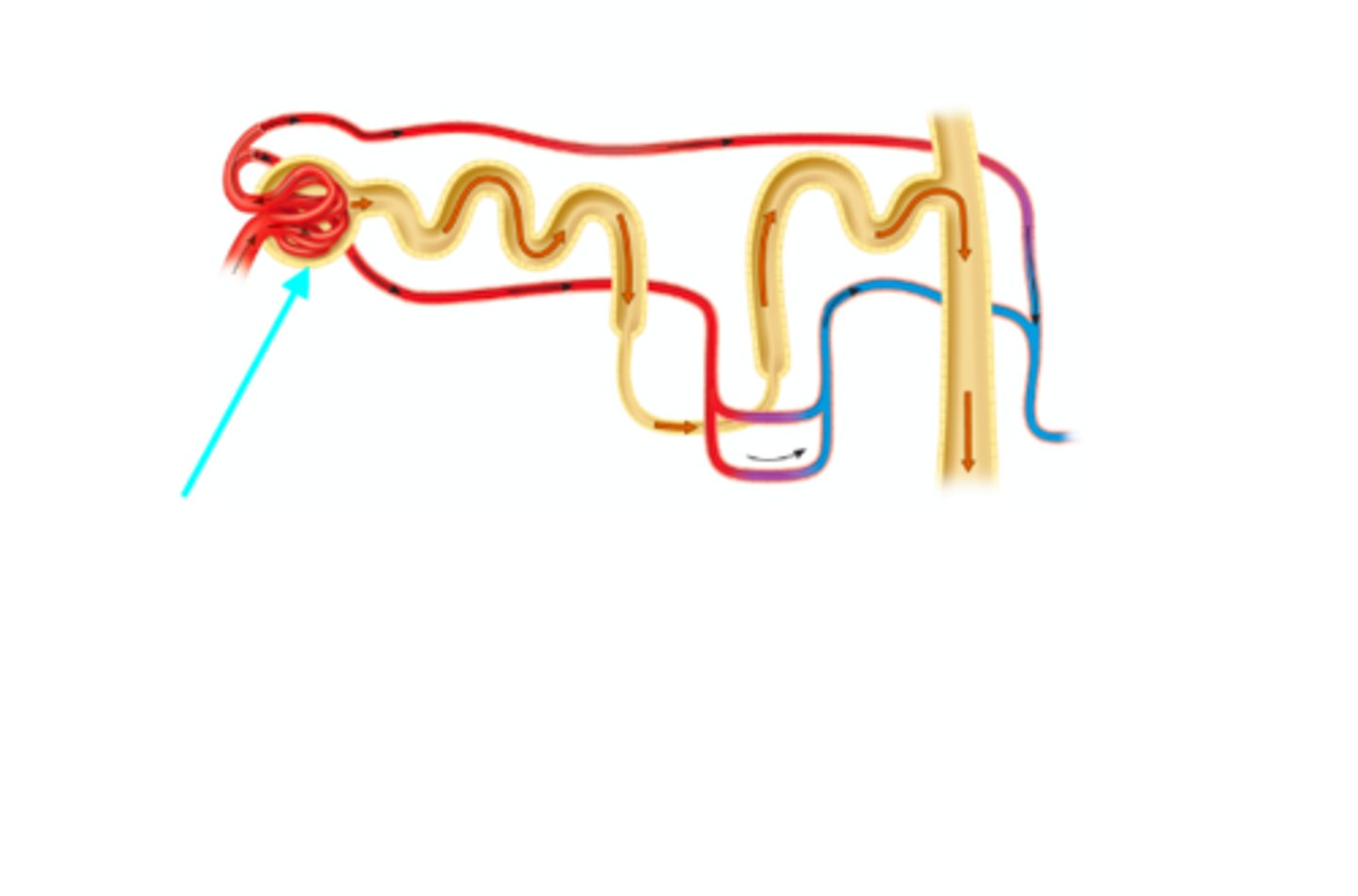
Proximal convoluted tubule
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
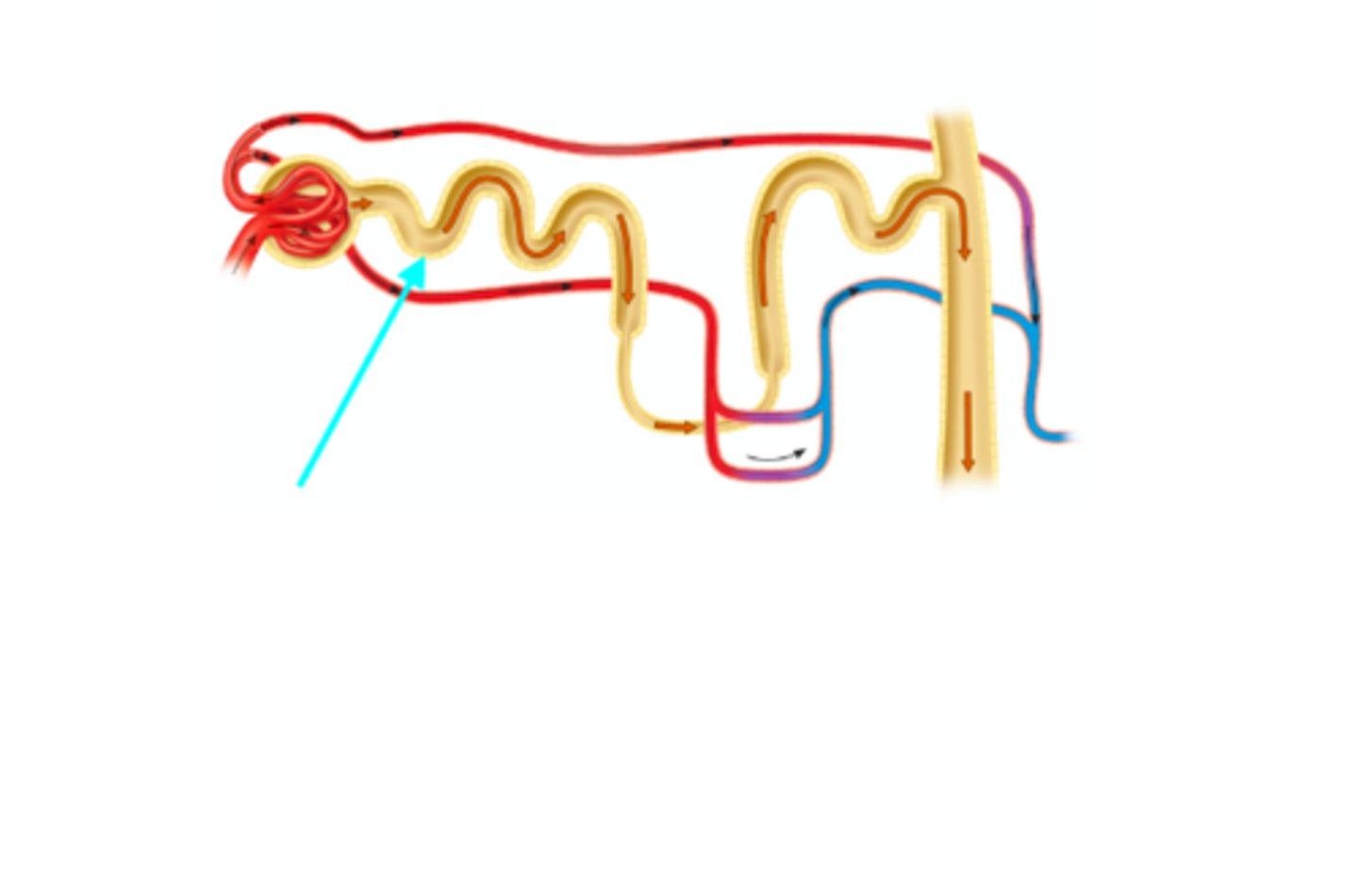
Descending limb of the nephron loop
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?

Ascending limb of the nephron loop
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
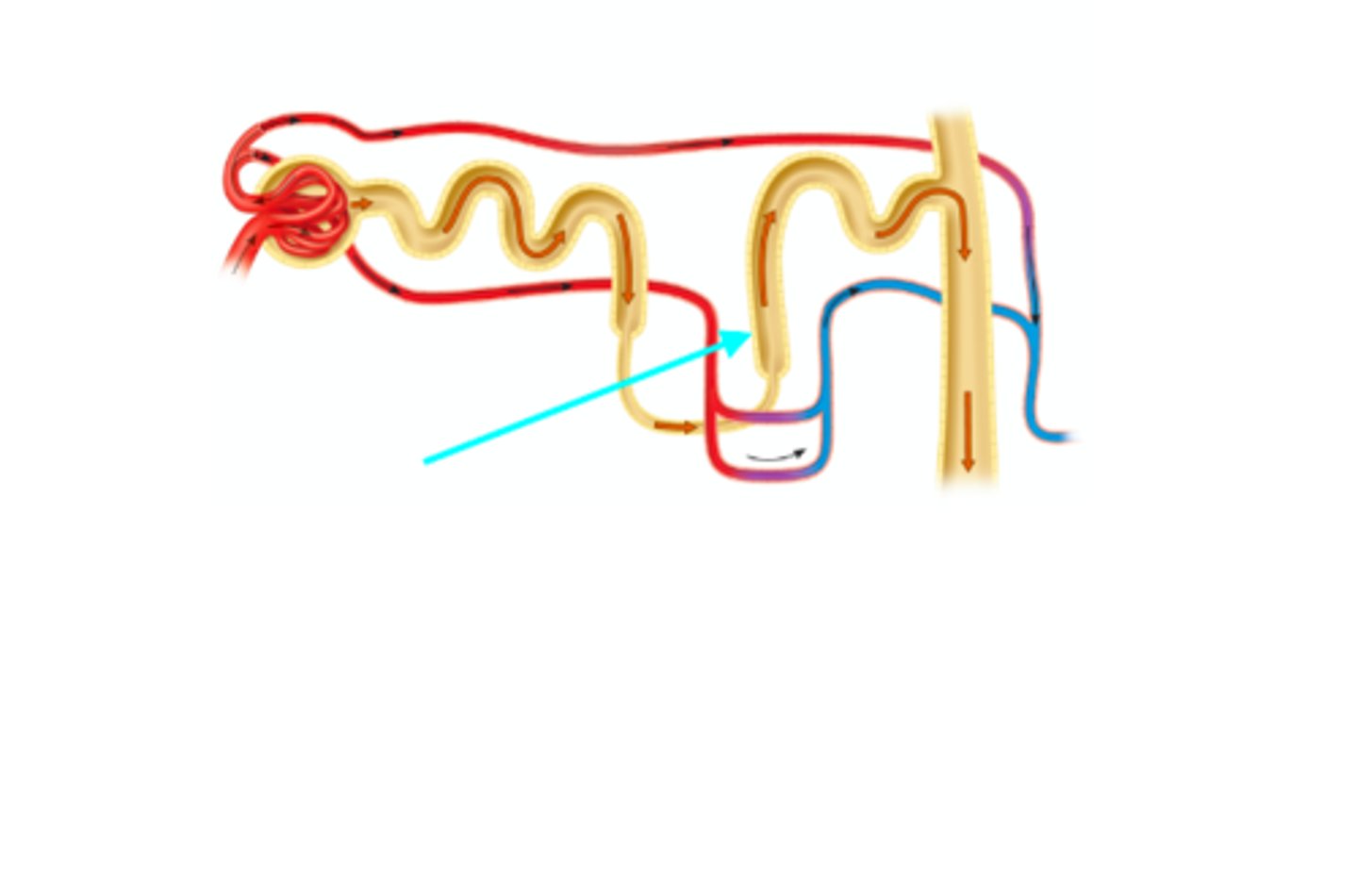
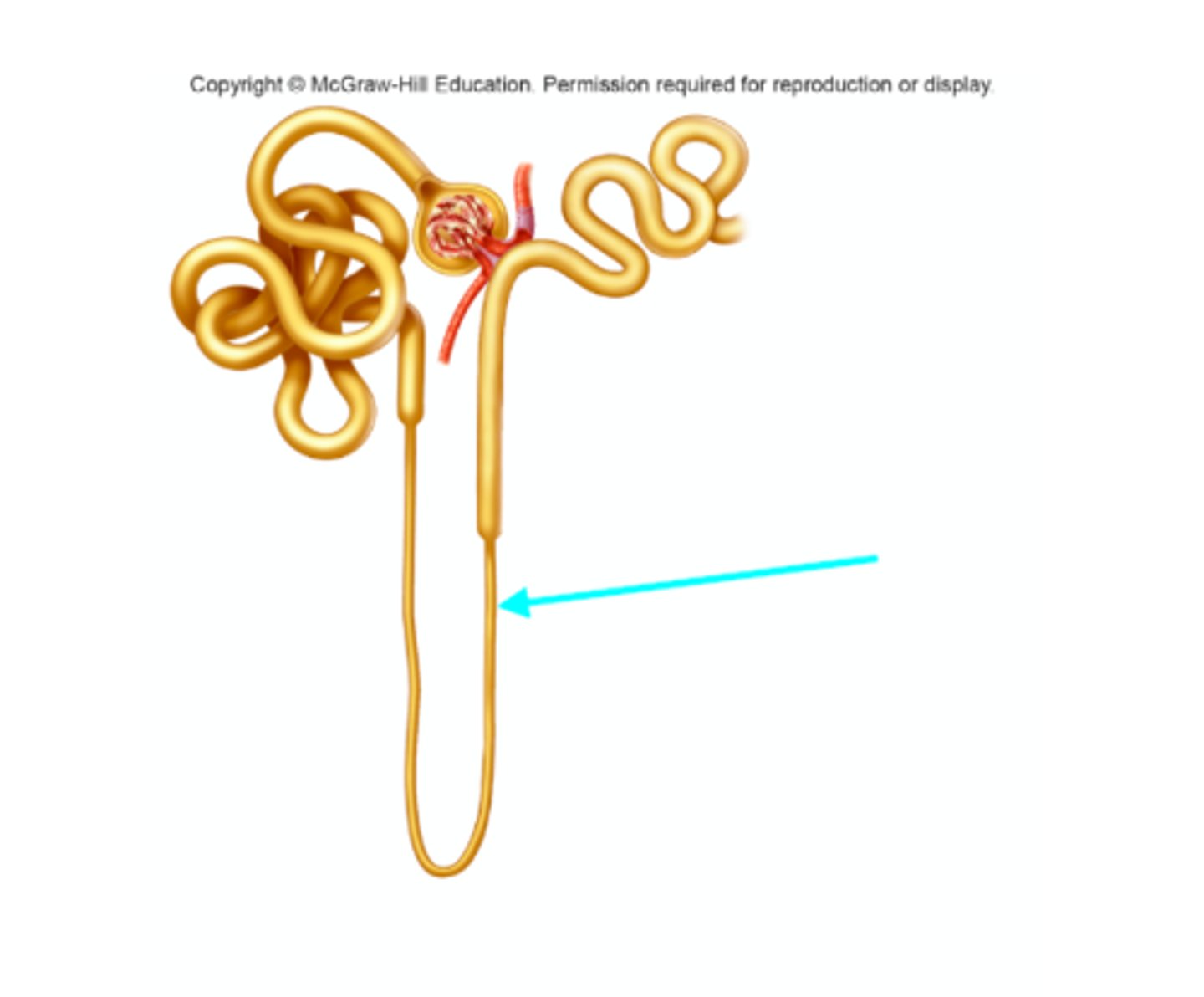
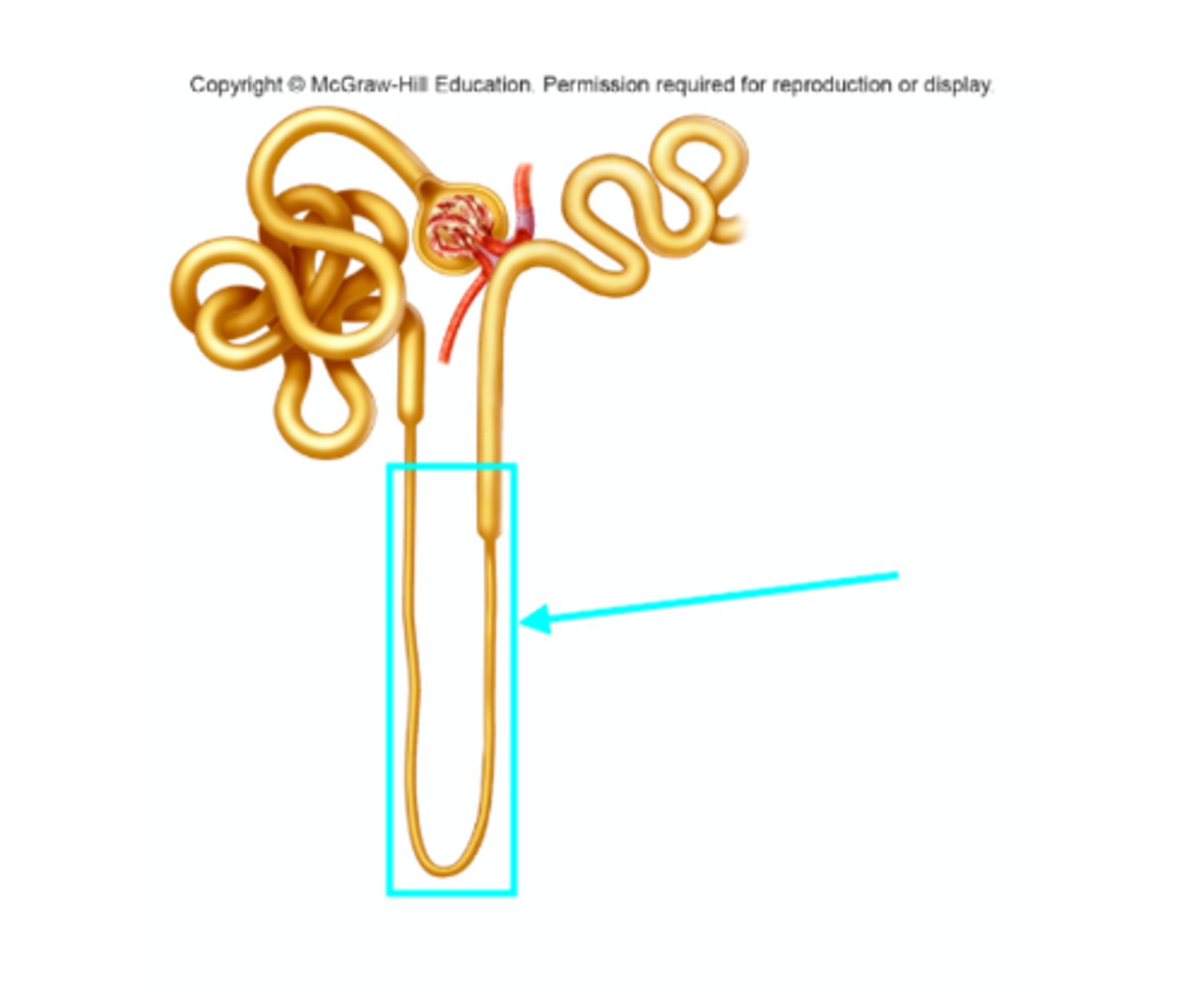
Nephron loop
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
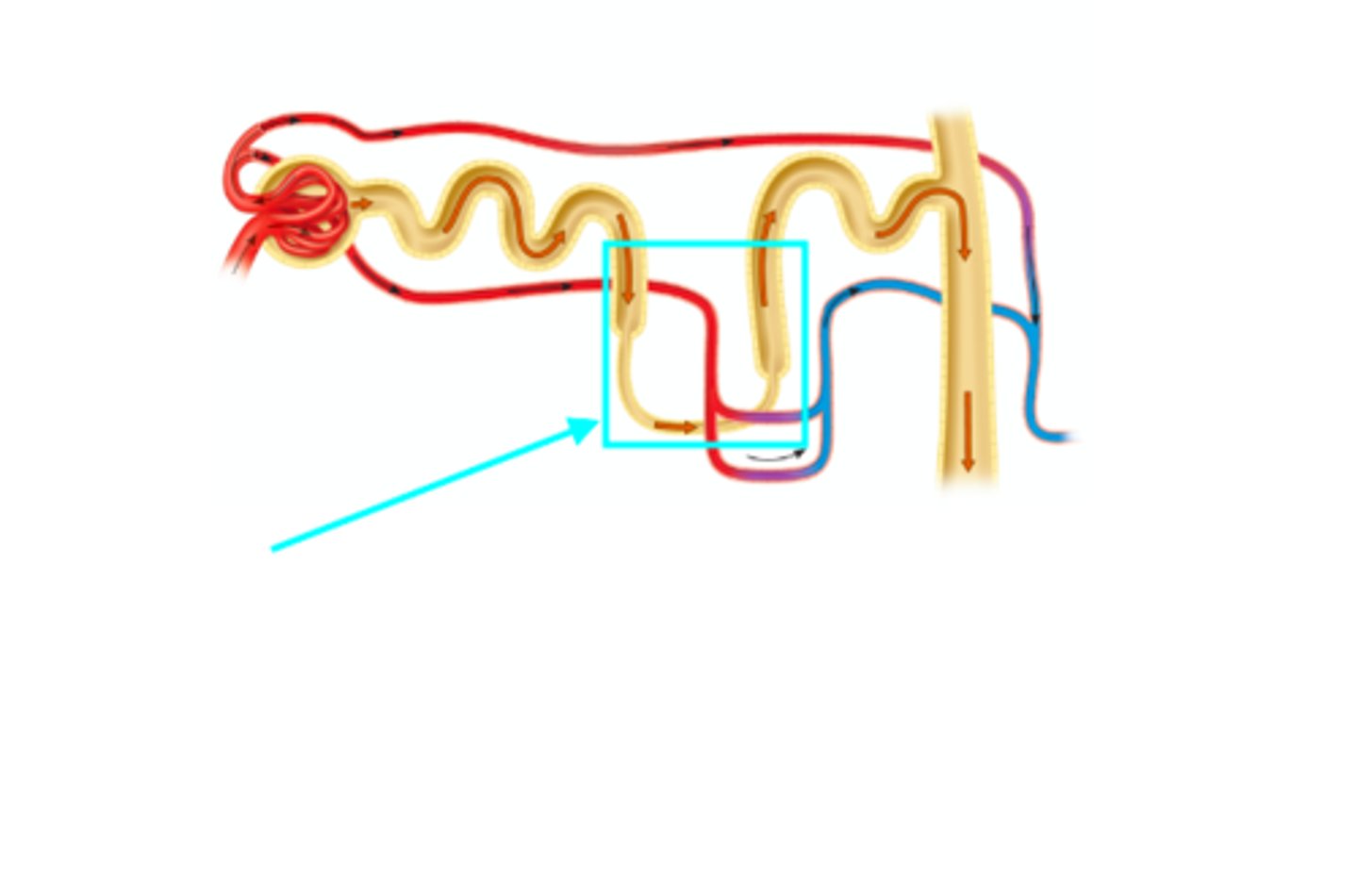
Peritubular capillary
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
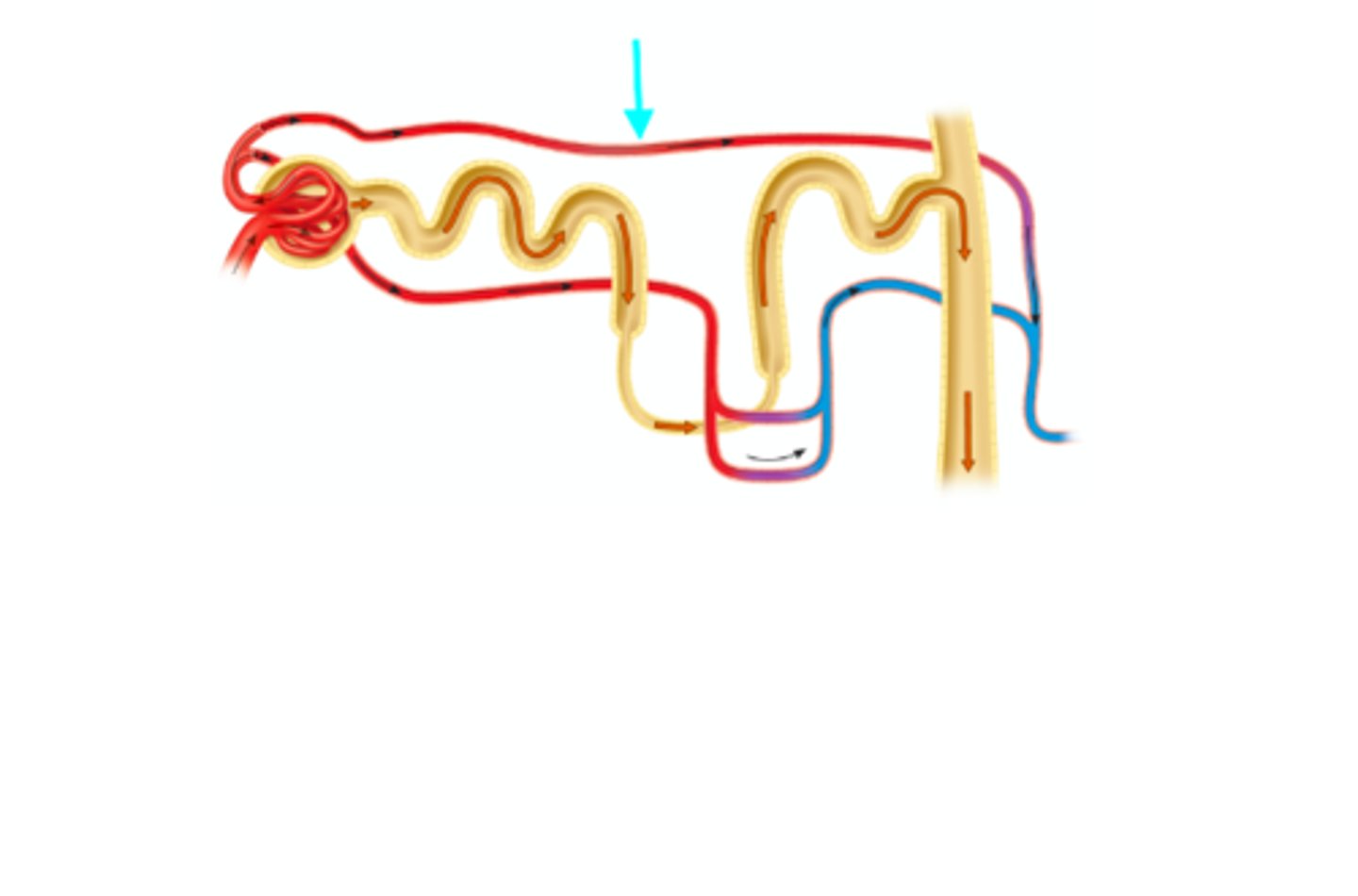
Distal convoluted tubule
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
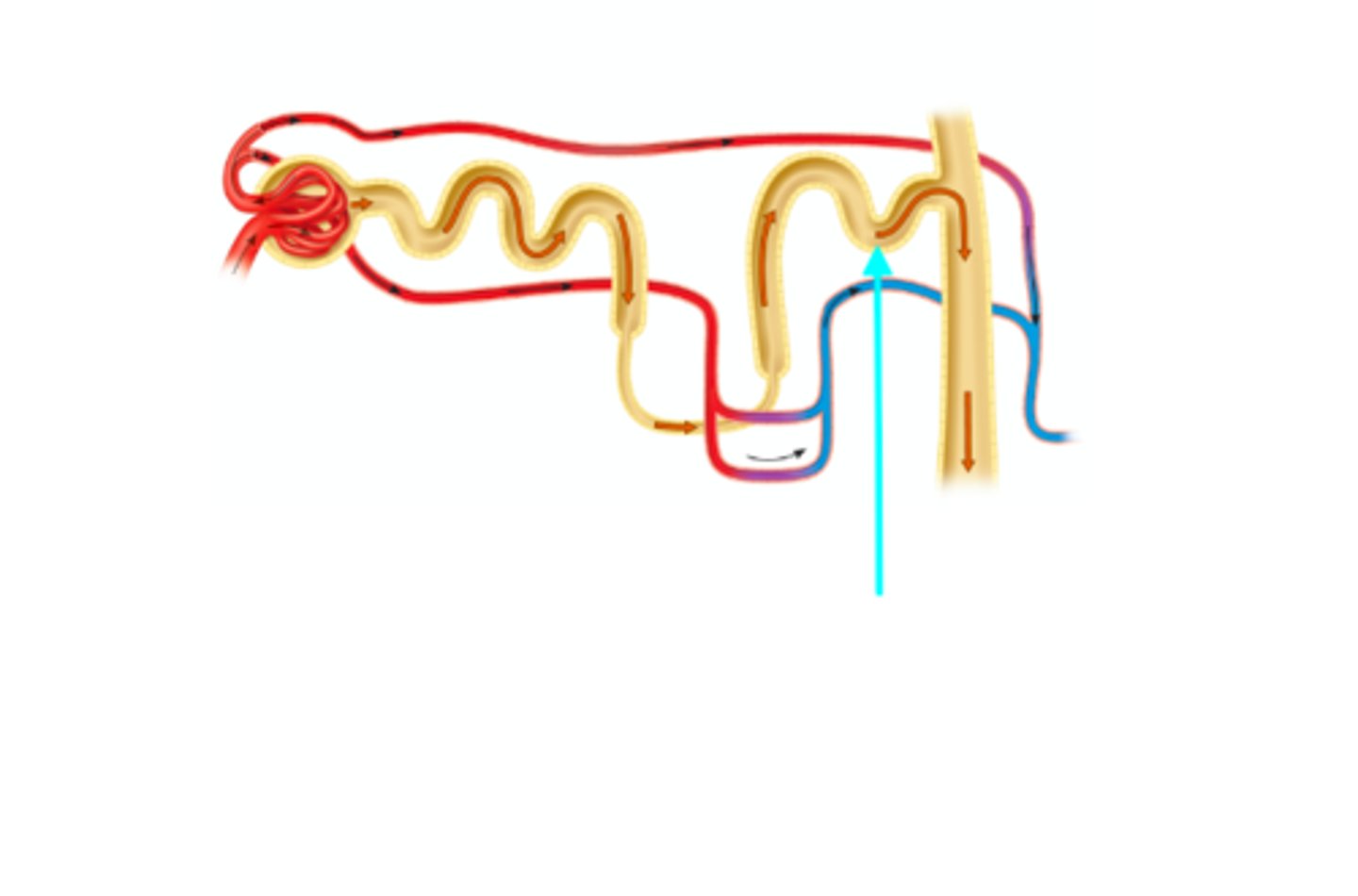
Collecting duct
What structure of the kidneys is the blue arrow pointing at?
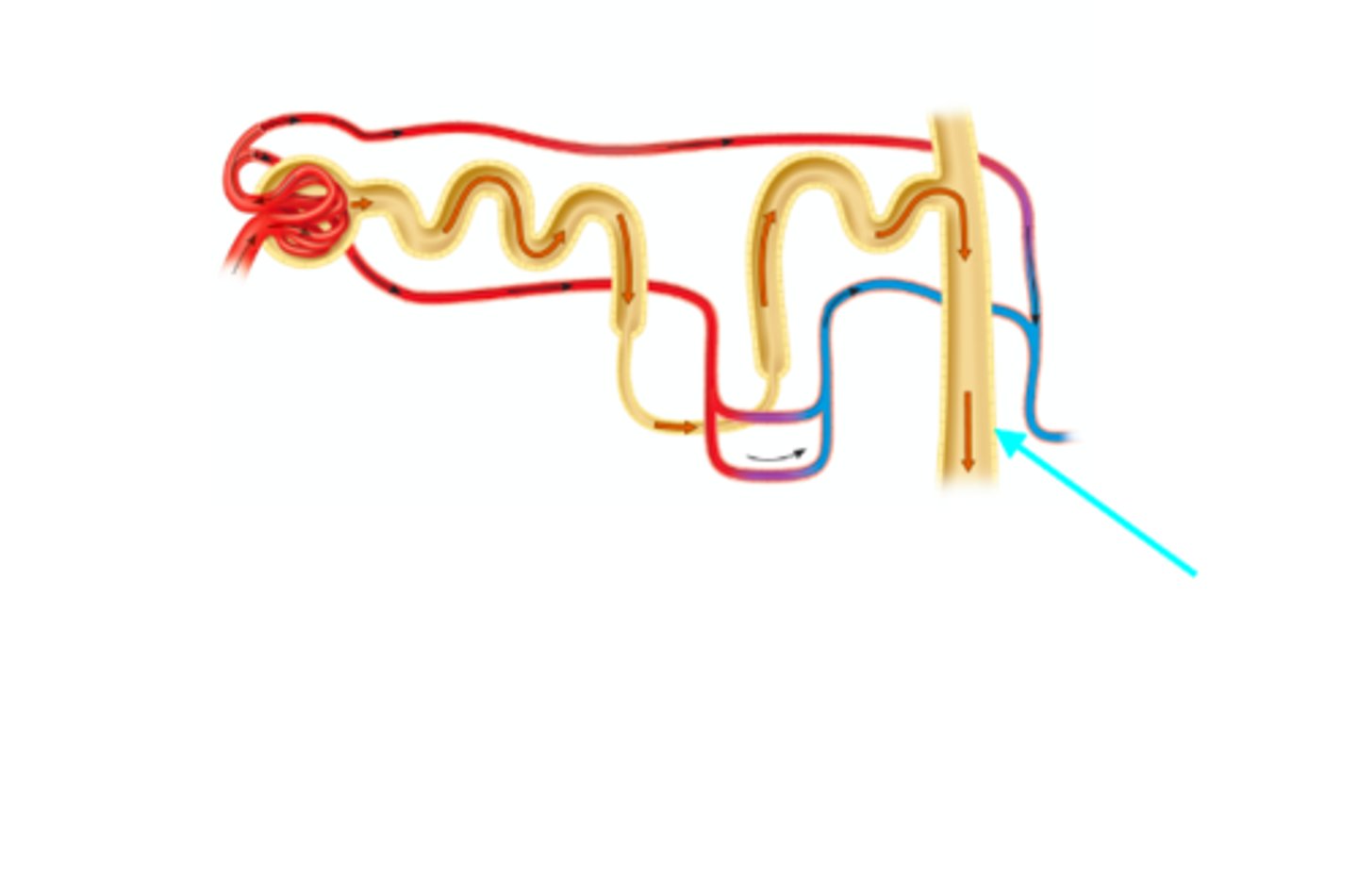
Transitional epithelium of the bladder
What tissue is depicted on the slide above the pointer?
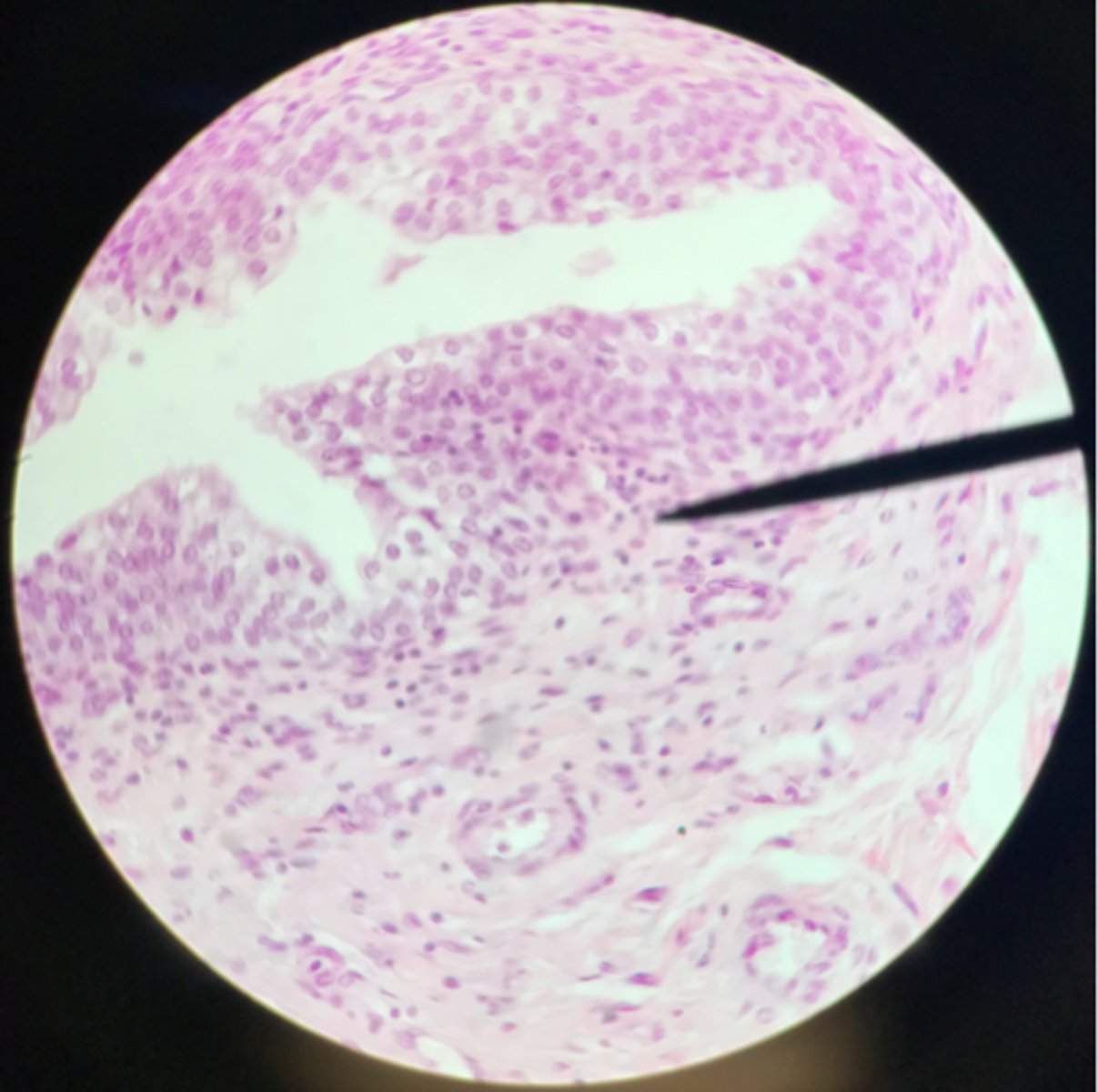
Basement membrane
What cells of transitional epithelium are located where the pointer is at?
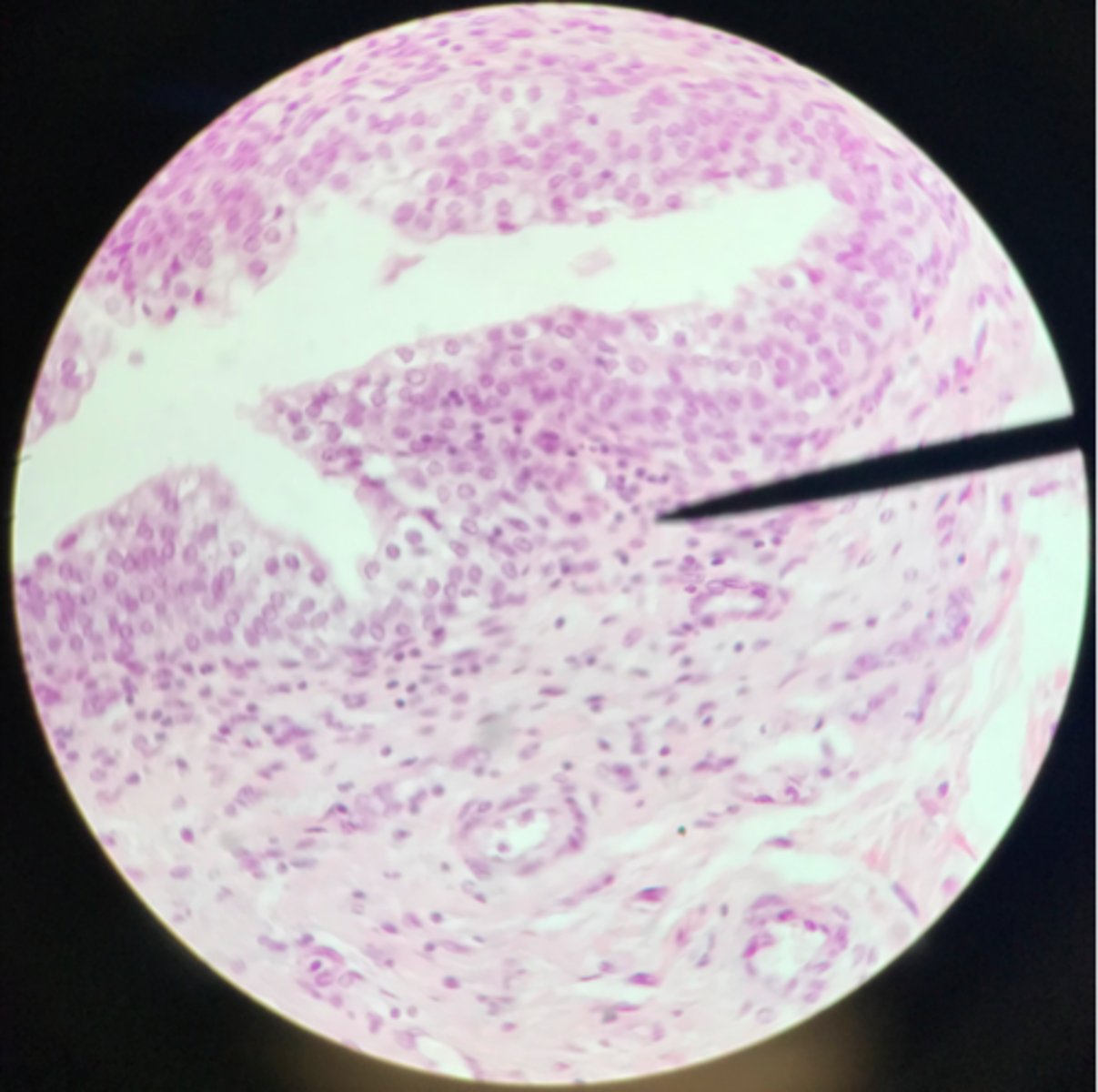
Ureter
Transitional epithelium
What structure/organ is depicted on this microscope slide?
What tissue makes up a majority of it?
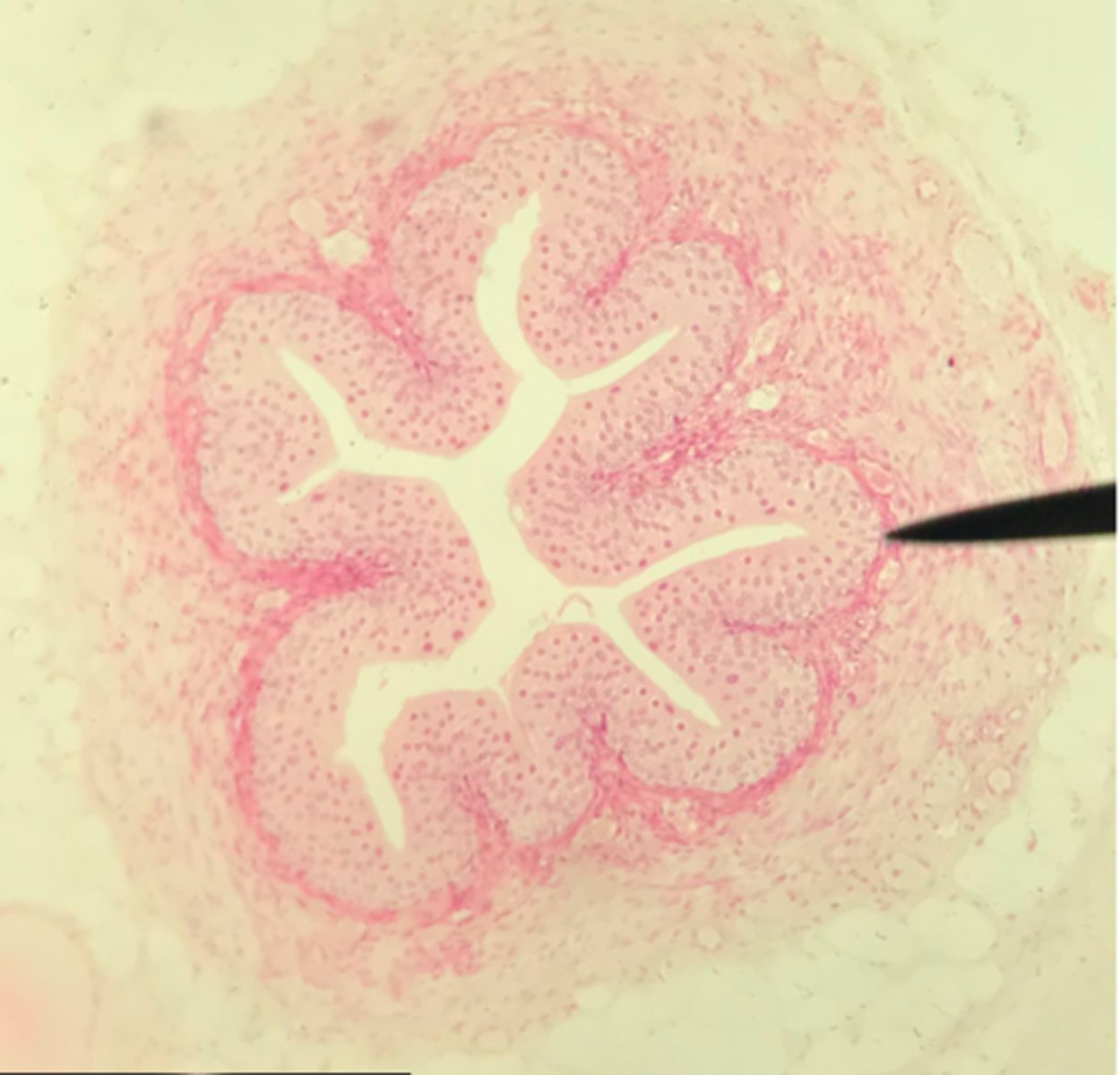
Transitional epithelium
What type of tissue makes up the inner lining of the ureter?
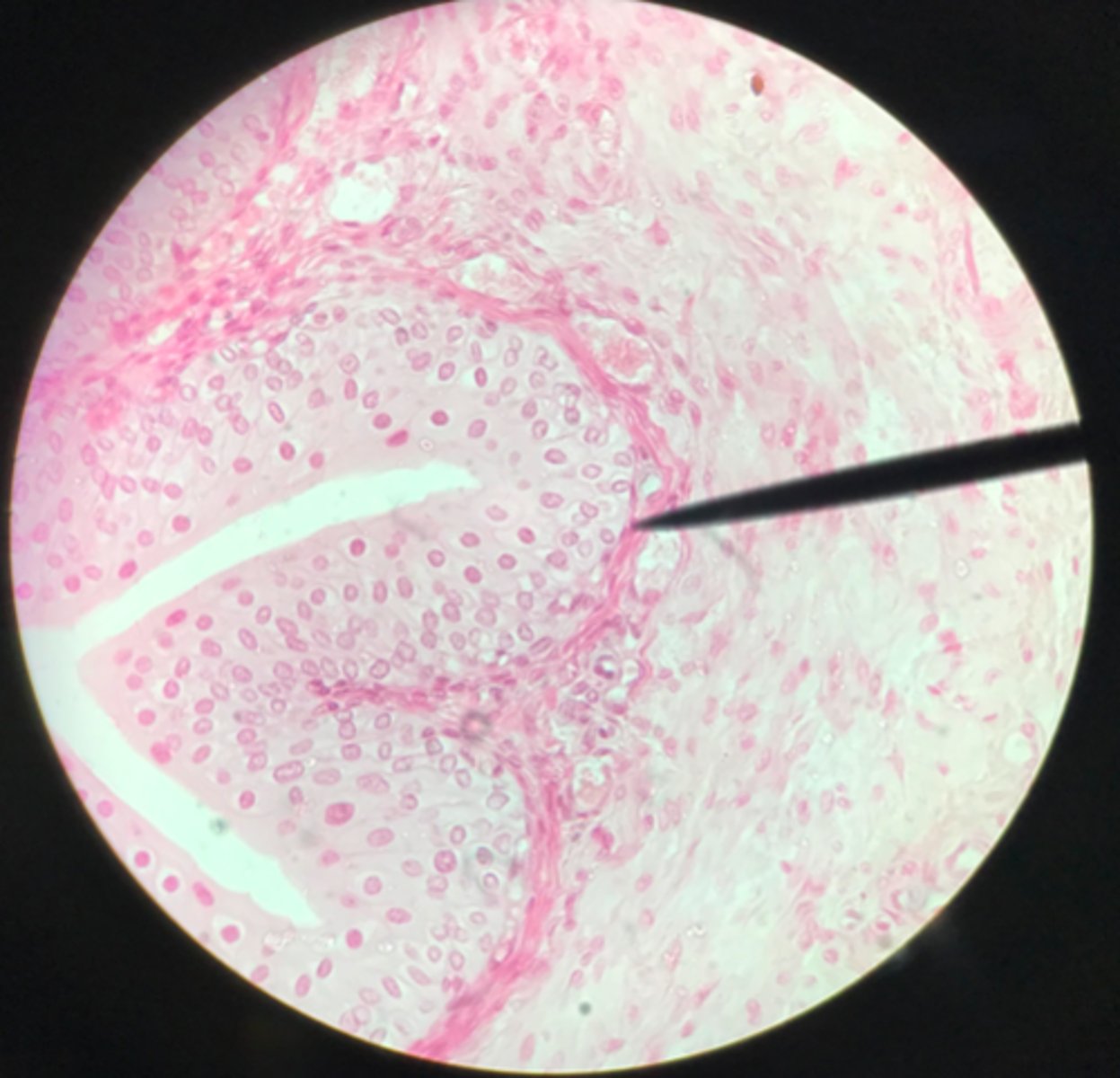
Cortex of the kidney
There are glomerular corpuscles present in the cortex. They are not present in the medulla
What layer of tissue of which organ is depicted on this slide? How can you tell?
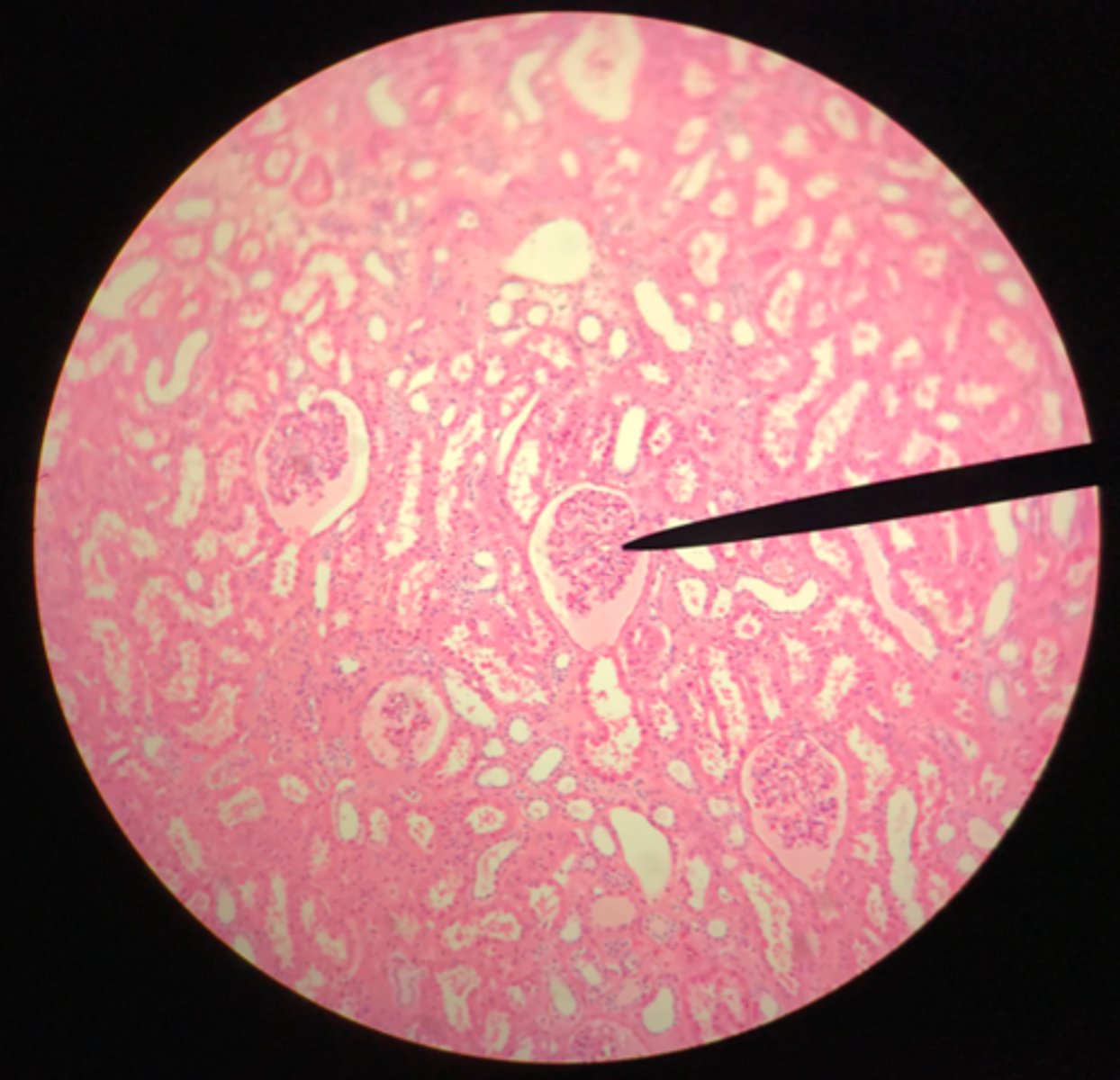
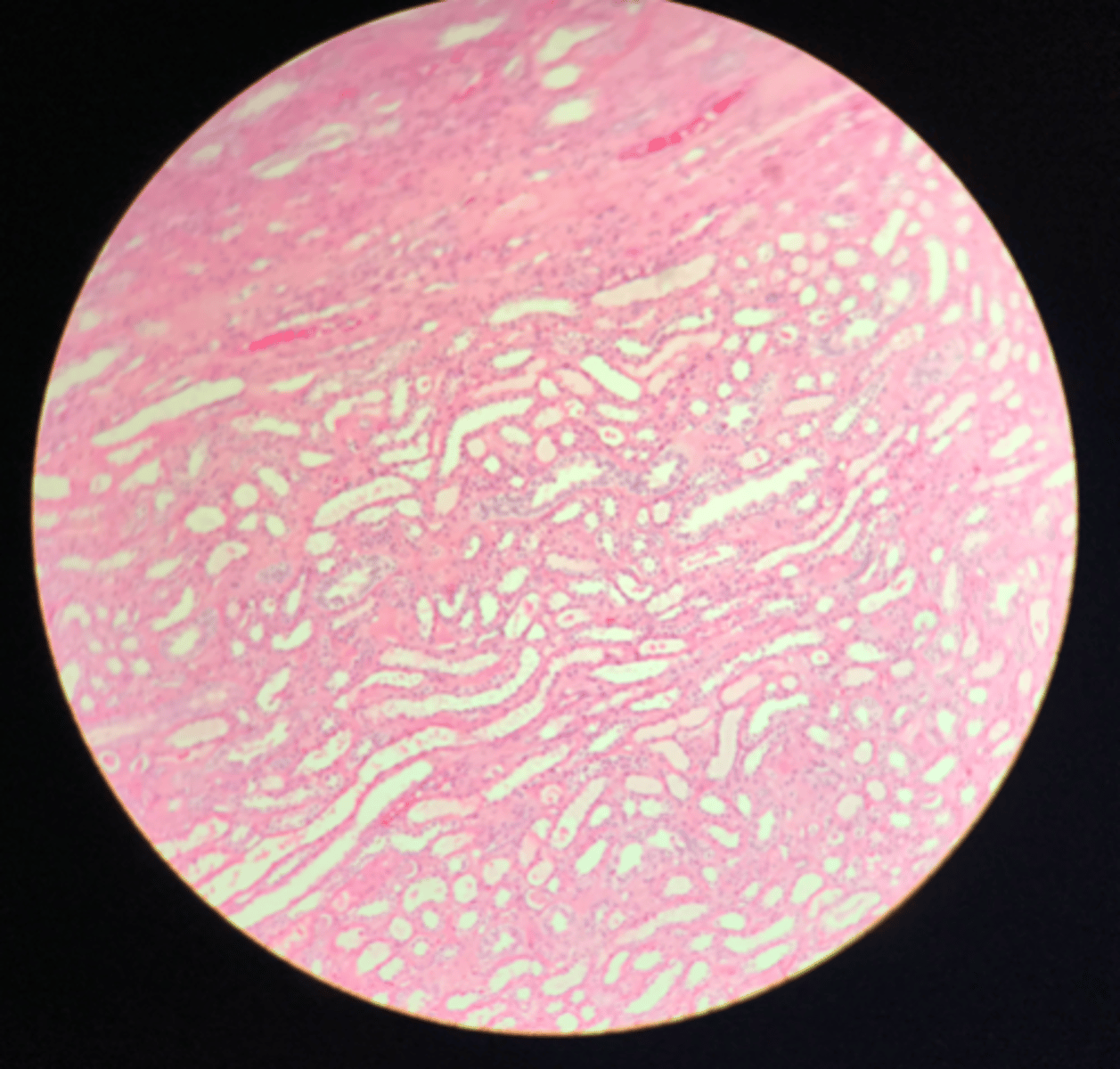
Medulla of the kidney
There are no glomerular corpuscles present and there are numerous visible collecting ducts
What layer of tissue of which organ is depicted on this slide? How can you tell?
Glomerular (Bowman's) capsule (in the cortex)
What structure of the kidney is the blue arrow pointing at?
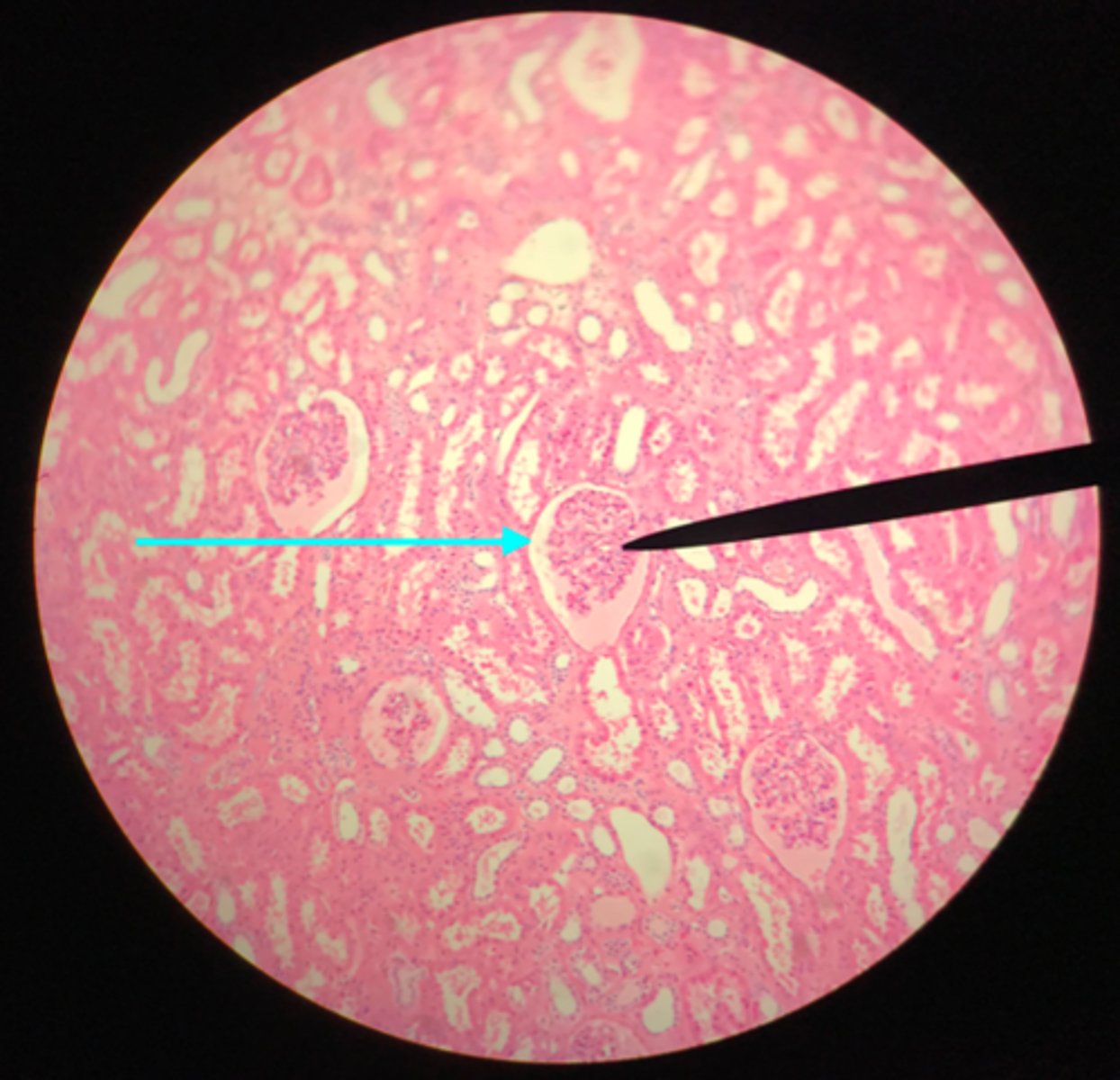
Collecting ducts (in the medulla)
What structure of the kidney are the blue arrows pointing at?
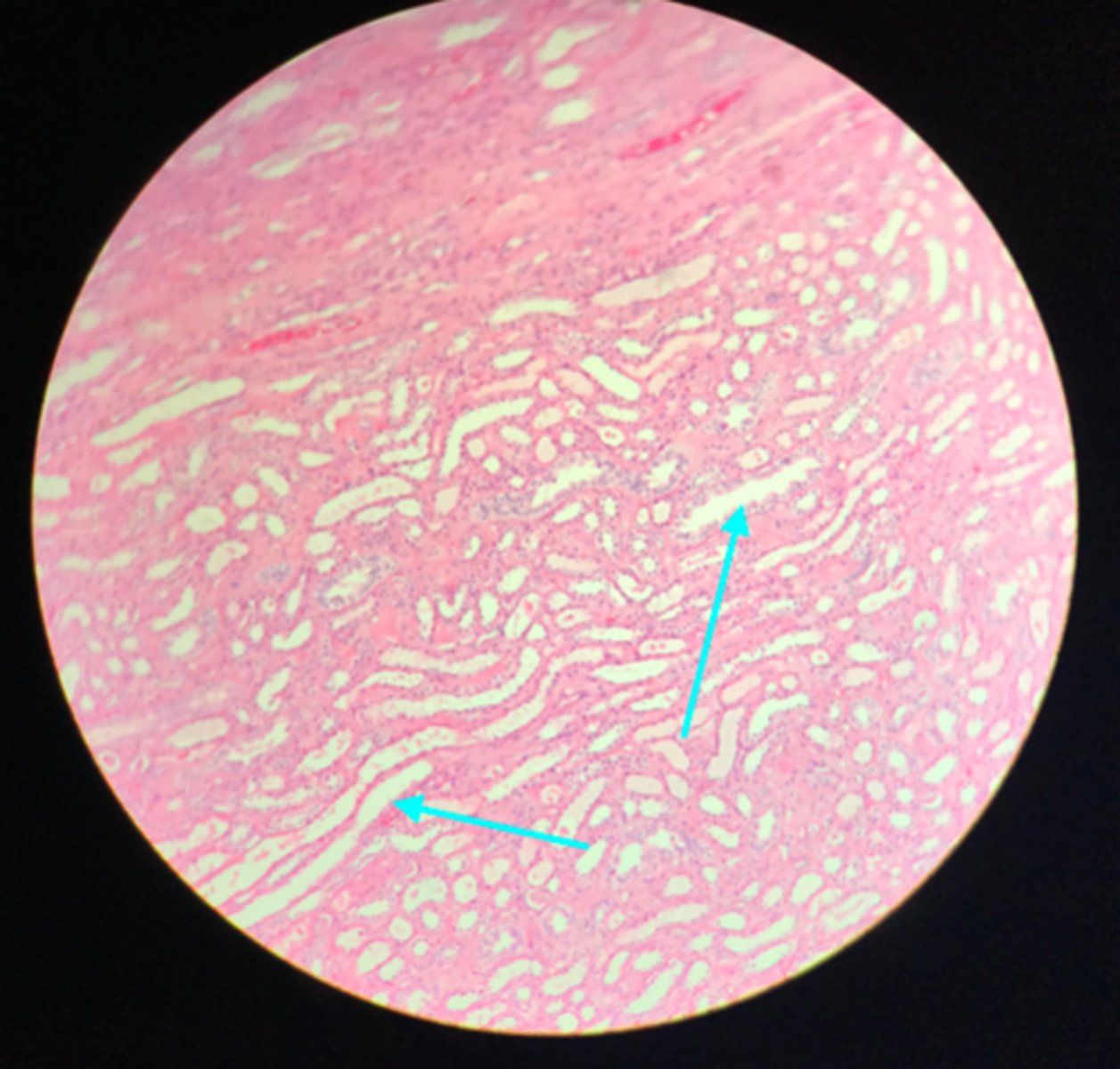
Glomerulus
What structure of the kidney is the pointer placed on?
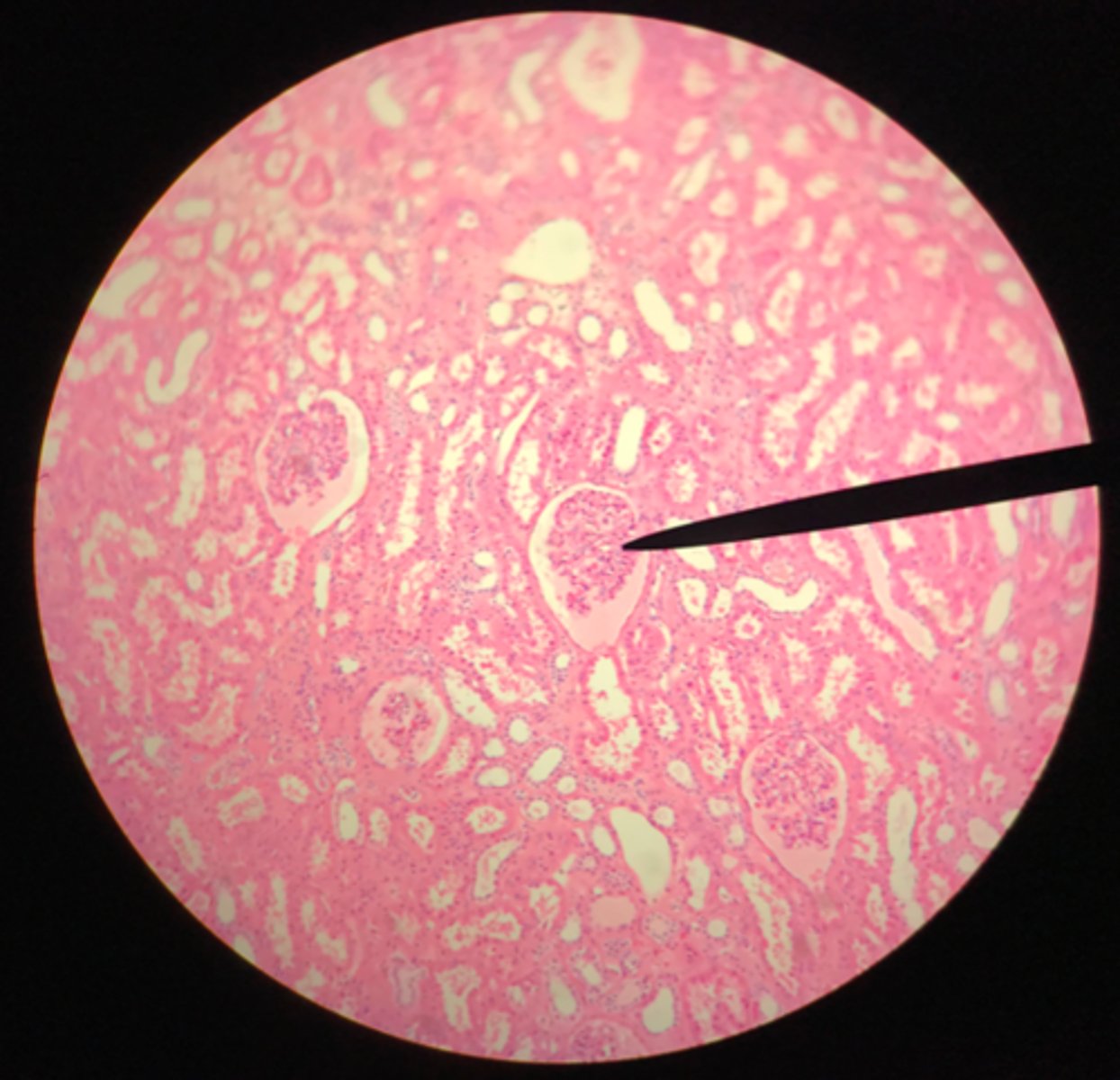
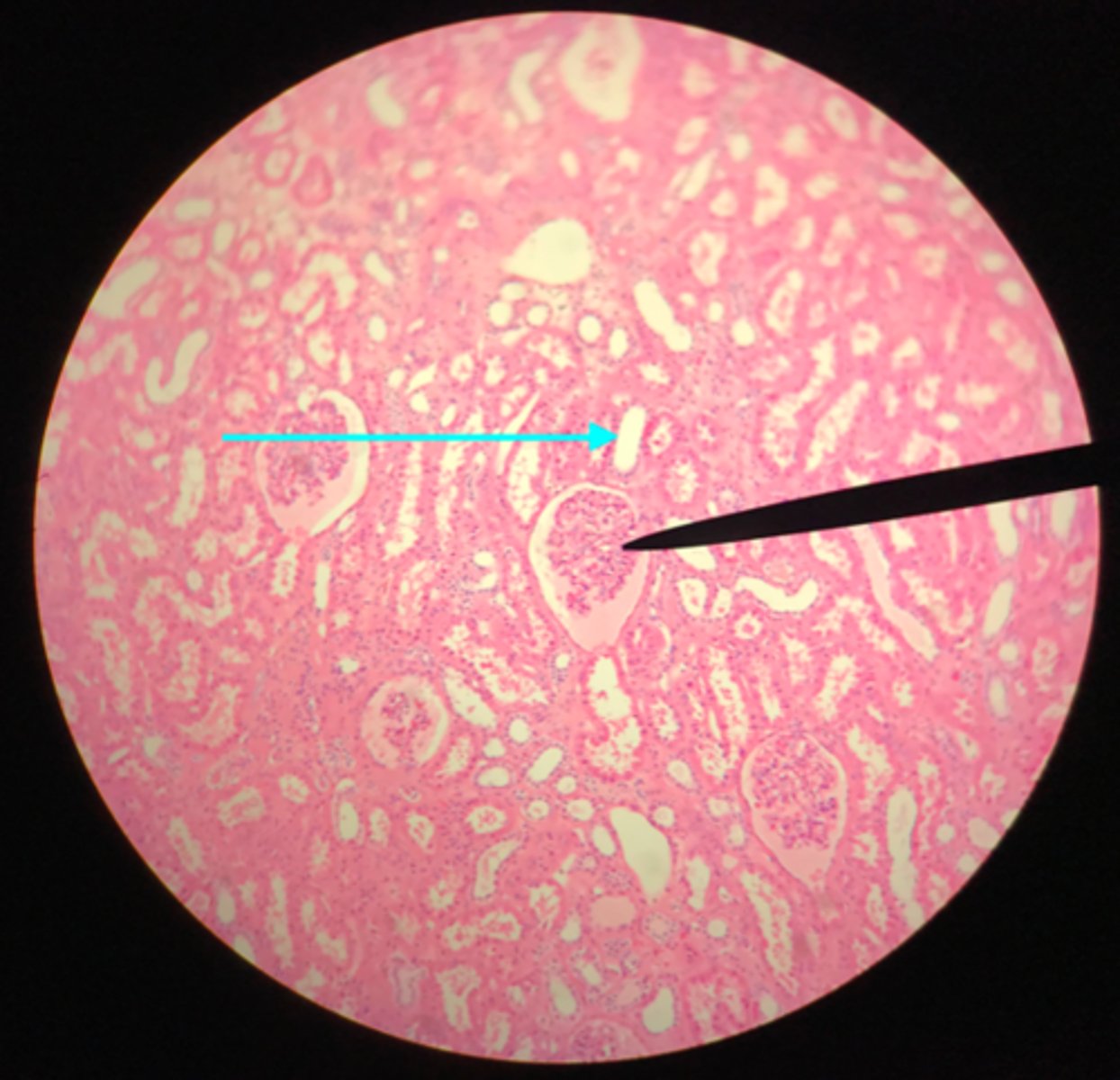
Renal tubules (in the cortex)
What structure of the kidney is the blue arrow pointing at?
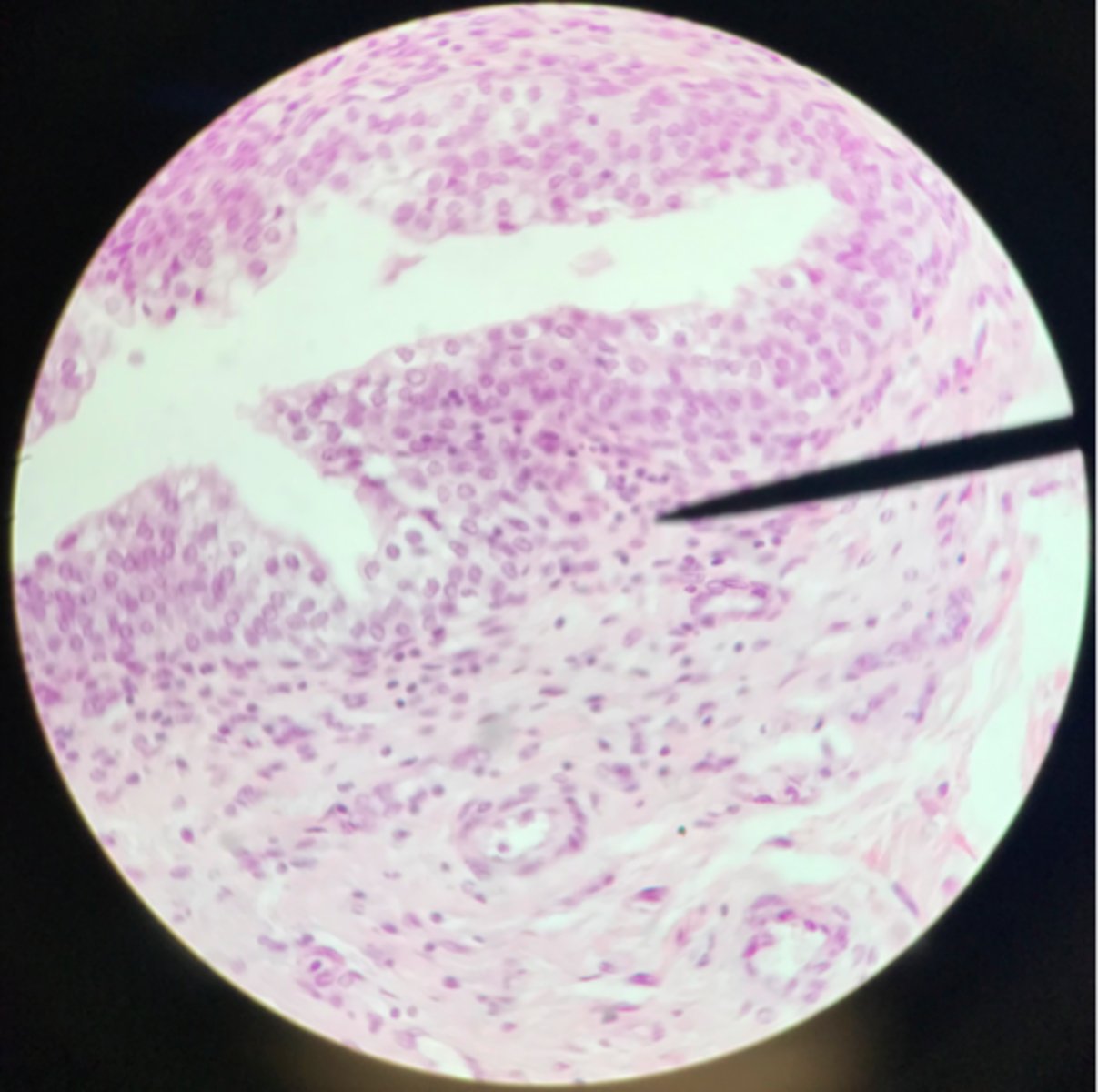
Urinary bladder
Transitional epithelium
What organ is depicted on the slide? What type of tissue is the main component?
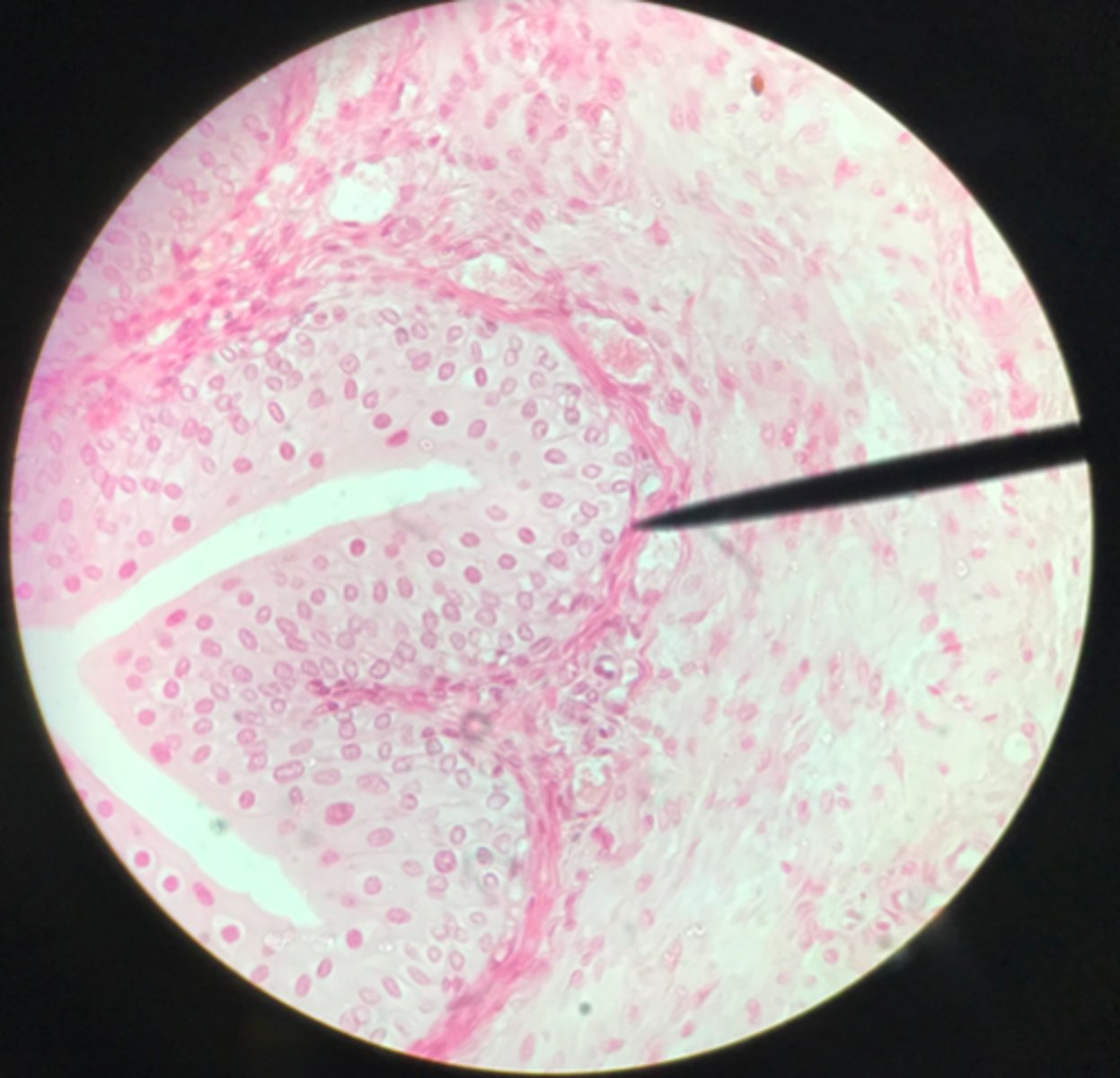
Ureter
Note the smooth muscle layer surrounding the transitional epithelium
What organ is depicted on this slide?
Renal artery → Interlobar arteries → arcuate arteries → cortical radiate arteries → afferent arteriole → glomerular capillaries → glomerular capsule → proximal convoluted tubule → descending limb of nephron loop → ascending limb of nephron loop → distal convoluted tubule → collecting duct → minor calyx → major calyx → renal pelvis → ureter → urinary bladder → urethra
What is the pathway of a molecule as it travels from the renal artery to the urethra? Assume this molecule freely filters and is not reabsorbed.
Renal artery → Interlobar arteries → arcuate arteries → cortical radiate arteries → afferent arteriole → glomerular capillaries → efferent arteriole → peritubular capillaries → proximal convoluted tubule → descending limb of nephron loop → ascending limb of nephron loop → distal convoluted tubule → collecting duct → minor calyx → major calyx → renal pelvis → ureter → urinary bladder → urethra
What is the pathway of a molecule as it travels from the renal artery to the urethra. Assume this molecule does not filter and is actively secreted
The main function of the kidneys is to regulate the composition and volume of body fluids. Volume directly impacts blood pressure.
Discuss the relationship between urinary function (primarily water and electrolyte balance) and cardiovascular function
The kidney functions to maintain fluid composition and volume in the body. This fluid composition and volume has an ideal concentration of water present, so if the volumes of water in the body change drastically, the kidneys change aspects of their function to retain or excrete water. The kidney's function to control water volume allows the removal or retention of H+ ions to regulate pH as well
Discuss the relationship between kidney function, the control of water volume, and pH regulation
The kidneys have the ability to to excrete H+ ions to raise pH or retain H+ to lower pH. The respiratory system can increase the amount of respirations to expel CO2 and raise pH; it can also decrease the amount of respirations to maintain CO2 and lower pH. Your respiratory system can either retain or lose CO2 to minimize changes in pH, and your renal system can either retain or lose H+ to correct problems with pH.
Discuss the relationship between urinary function and respiratory function as they work together to regulate blood pH
Be able to use a flow chart to arrive at a patient diagnosis using his/her medical history, information from a brief physical exam, patient statement, and urinalysis result.

Nephron
This is the basic functional unit of the kidney
Renal pelvis
This is the expanded superior end of a ureter located within a renal sinus
Arcuate artery and vein
These blood vessels run along the border between renal cortex and renal medulla
Medulla
This is the inner region of the kidney
Cortex
This is the outer region of the kidney where all renal corpuscles are located
Glomerular capsule
This is the expanded end of renal tubule systems that receive the filtrate
Afferent arteriole
This arteriole delivers blood to the glomerulus
Efferent arteriole
This arteriole takes blood away from the glomerulus
Renal artery and vein
These are the major blood vessels that deliver blood to and take blood away from the kidneys
Cortical radiate arteries
Afferent arterioles branch directly off of these arteries
Distal convoluted tubule and the collecting duct
These are the two regions of the renal tubule that anti-diuretic hormone binds to
Descending limb of nephron loop
This segment of the nephron loop is permeable to water
interlobar arteries and veins
These are blood vessels in the renal medulla that pass between renal pyramids
Proximal convoluted tubule
This is the region of the renal tubule where the majority of reabsorption occurs
Ureter
These are muscular, tube-like structures that carry urine away from the kidneys. This is capable of peristaltic contractions
Ascending limb of the nephron loop
This segment of the nephron loop is impermeable to water. Sodium ions are actively transported out of this segment
Peritubular capillaries
These are blood vessels found surrounding the renal tubules
Alcohol and caffeine both interfere with the action of ADH. Alcohol prevents ADH secretion while caffeine blocks ADH binding
A young lady goes to a wine tasting party and enjoys the many varieties of red wines. During the night she has to get up several times to urinate, and when she gets up in the morning her mouth is dry, she is very thirsty, and she feels dizzy. She decides that coffee will help her feel better, but after several cups she actually feels worse. Explain her symptoms and why coffee actually made her feel worse.
At 60 mm Hg, the forces favoring filtration do not exceed those opposing filtration. If MAP is this low, the last thing you want to do is lose more volume. Retaining volume will help maintain pressure
If mean arterial pressure (MAP) drops below approximately 60 mm Hg, filtration at the glomerulus stops. Discuss the reasons why filtration would stop if MAP fell below this level (consider the pressures necessary for filtration to occur) and why this response is advantageous.
ACE (angiotensinogen converting enzyme) activates angiotensin, which is a vasoconstrictor. Hypertension is characterized by high blood pressure, and vasoconstriction would act to increase pressure further. Inhibiting the activation of angiotensin could help keep blood pressure lower by promoting vasodilation
Explain why drugs called ACE inhibitors could be effective in treating hypertension.
Inhibition of ADH could limit the ability to conserve water, leading to dehydration. The patient will likely have to urinate frequently and be thirsty all the time
Lithium is used to treat certain psychiatric conditions. Chronic lithium ingestion, however, appears to affect the renal tubules by entering the collecting tubule cells through sodium channels, accumulating and interfering with the normal response to ADH in a mechanism that is not yet fully understood. Explain the effects this will have on the patient.
Retention of CO2 = respiratory acidosis
Kidneys should excrete H+ to raise pH
For this situation, discuss the impact this condition would have on the individual's blood pH, and how the individual's renal system (if respiratory origin) or respiratory system (if metabolic origin) would respond to compensate for this change in blood pH.
An individual is suffering from emphysema.
Hyperventilation = loss of CO2 = respiratory alkalosis
Kidneys should retain H+ to lower pH
For this situation, discuss the impact this condition would have on the individual's blood pH, and how the individual's renal system (if respiratory origin) or respiratory system (if metabolic origin) would respond to compensate for this change in blood pH.
An individual is placed in an experimental chamber in which the percentage of oxygen in the air is only 11% (nitrogen concentration is increased to 88%). The very low level of oxygen stimulates chemoreceptors in the carotid and aortic bodies.
Retention of acid = metabolic acidosis.
Respirations should increase to expel CO2 and raise pH
For this situation, discuss the impact this condition would have on the individual's blood pH, and how the individual's renal system (if respiratory origin) or respiratory system (if metabolic origin) would respond to compensate for this change in blood pH.
An individual is suffering from uremia, a condition in which the kidneys fail to excrete normal amounts of acid.
Loss of acid = metabolic alkalosis
Respirations should decrease to retain CO2 and lower pH
For this situation, discuss the impact this condition would have on the individual's blood pH, and how the individual's renal system (if respiratory origin) or respiratory system (if metabolic origin) would respond to compensate for this change in blood pH.
An individual is suffering from hypertension and has been given a prescription for a diuretic. One potential consequence of taking diuretics for an extended period of time is the excessive loss of H+ in the urine.