MRI (copy) (copy)
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
MRI measures
measures amount of Hydrogen in the area of interest by converting magnetism into electrical energy + mapping this on Image matrix
Advantages of MRI
Excellent Soft Contrast Direct acquisition in all orthogonal planes & in-between planes
Evaluate morphology & physiology Diffusion & perfusion measurements
No known adverse biological effects (caveats – risk associated w/ MR environment)
Ability to image arterial and venous blood flow
Disadvantages of MRI
Not ideal for pts w/ claustrophobia + contraindication
Not as readily available as other modalities
Higher cost
Can only image tissue containing hydrogen
Long scanning times
Challenging environment
Modes
Multi-Planar Imaging: Direct acquisition in 3 orthogonal planes/Oblique Planes- can see between planes like in shoulder to see between joints + in aorta to see through folds.
Cine Mode & 3D/Cine- stack images, good for planing surgery esp orthopaedic for complex #
MR can image
Morphological Studies- tumours, anatomy
Physiological Studies- arteries, veins, diffusion, perfusion, blood supply to anatomy
Contrast
Controlled by TE +TR
can be altered by user
TR- how much T1 relaxation occurs- short TR + TE= T1-weighted images
TE - how much T2 relaxation occurs- long TR + TE= T2-weighted images
Inherent and secondary contrast
gadolinium introduced as a secondary contrast so we can visualise just the tumor not just fluid/inflammation caused by tumour
Saturating Signal
technique for contrast- reducing impact of wither water or fat on image/ saturating out signal
T2 Negative Contrast
not common
conrast technique
just for liver
uses iron filing
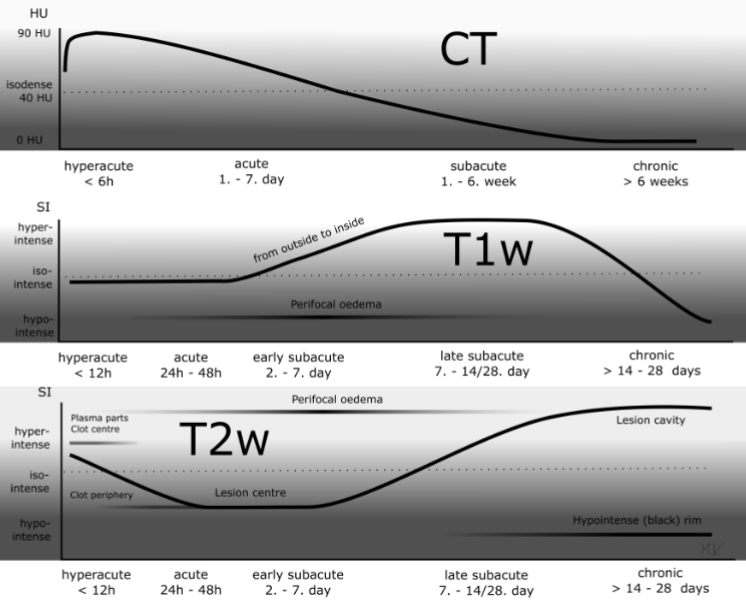
MRI v CT Brain Bleed
Haemorrhage on MRI has differing imaging characteristics that depend on:
the age of the blood
type of haemoglobin present: oxy-, deoxy- or met-
whether or not RBC walls are intact: i.e. intra- vs extracellular
the MRI sequence
Phase Mismapping
common artefact- when MR tries to get signal but proton has moved, like breathing
Chemical Shift Artefact
common at border of starkly different tissue. signals very different cause incorrect mapping
Magnetic Susceptibility Artefact
where piece of metal becomes ferrous magnetic/magnetised e.g., dental work
secure environment
Zone I- all areas freely accessible to general public where the magnet field poses no hazards, such as the entrance to the MR facility.
Zone II- located between Zone I and more restrictive E.G., waiting room
Zone III- access restricted by physical barriers e.g., doors w/ coded access.
Risks
Magnetic field- metals, tattoos
Radiofrquency waves- behave like microwave + overheat pt. MR built to stop this
Quenching- overheating of cryogen bath liquid turns to gas + can create vacuum/ suffocation
Image contrast
high signal, low signal + intermediate signal- diff tissues= diff signal return
knowing normal signal means when signal is abnormal we know tissue may be pathological