Band Theory & Unit Cells (9/25)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Describe the electron sea model.
Valence electrons are delocalized and free to move throughout the crystal.
Why do metals have the malleability and ductility properties that they have?
the behavior of mobile valence electrons
True/false: Molten states conduct electricity.
True
What is it called when molecular orbital theory is applied to crystals?
band theory
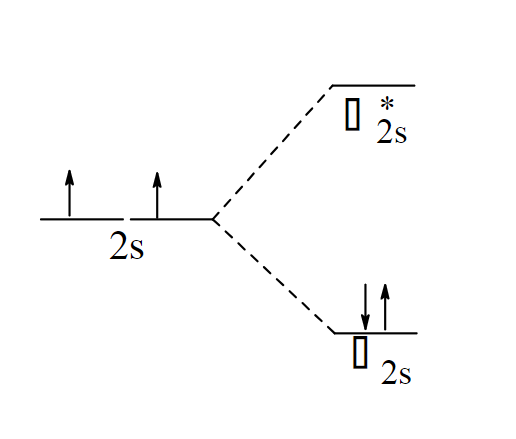
Draw the band theory model of 2s orbitals from two Li atoms interacting.
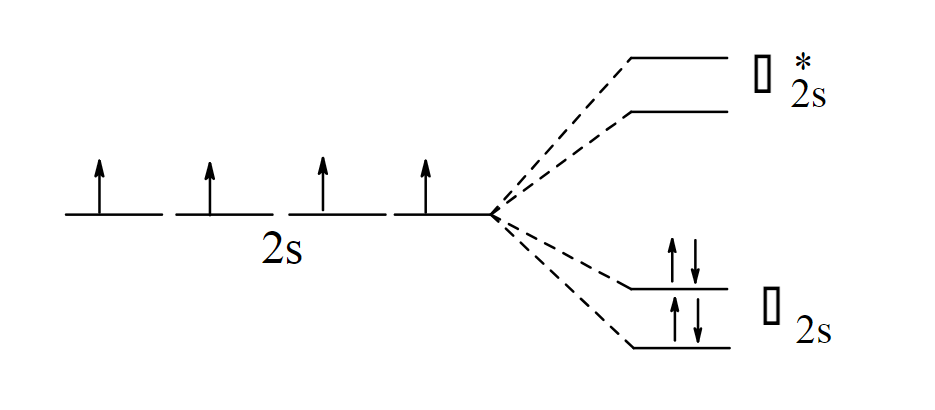
Draw the band theory model for four Li atoms interactions.
What is a band in band theory?
A bunch of atomic orbitals stacked on top of each other
What is band width? How do you calculate it?
The width of a continuous band. (Energy of highest atomic orbital) - (energy of lowest atomic orbital).
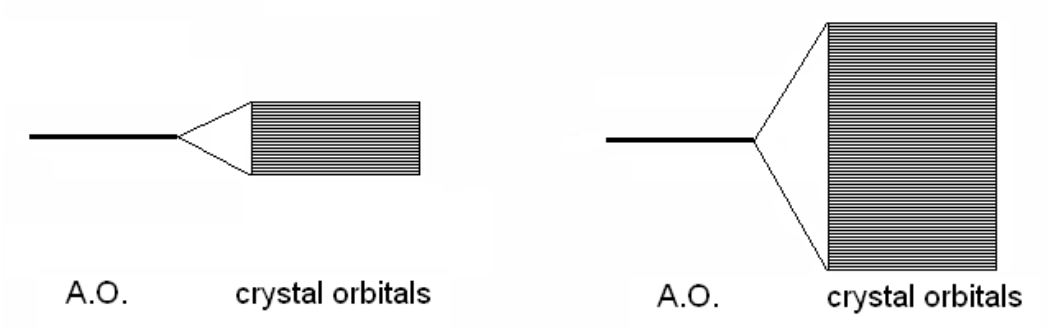
In the following image, which of these is weak bonding and which is strong bonding?
left is weak; right is strong
What does band gap depend on?
energy gap between AOs in the atom; widths of the bands
Which is bigger: the band gap or the atomic orbital gap?
atomic orbital gaps
Why do insulators have large band gaps?
They don’t conduct - mobile electrons have trouble jumping the bands to become mobile
What type of band gap do metallic conductors use?
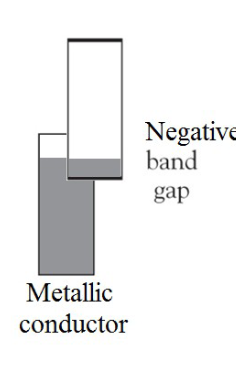
What is the bottom band and what is the top band called?
bottom band: valence band; top band: conductive band
What is a major difference between conductors and semiconductors?
as temperature increase:
conductors decrease conductivity
semiconductors increase conductivity
What is doping?
adding a small impurity to a host metal to changes its behavior
What is the main difference between n-type and p-type doping?
n-type: dope valence electrons > host valence electrons
p-type: dope valence electrons < host valence electrons
They both increase conductivity.
Describe the impurity band of an n-type dope.
N-type doping adds more electrons and creates a negatively charged semiconductor.

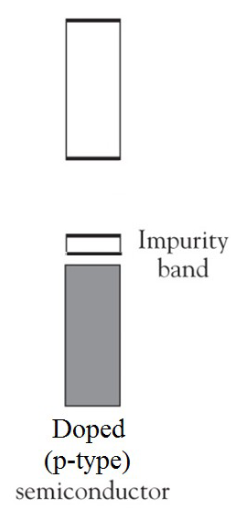
Describe the impurity band of an p-type dope.
P-type bonding creates more holes where electrons should be and creates a positively charged semiconductor.
How is maximum attraction obtained?
each atom is surrounded by the largest possible number of other atoms
simple cubic: % efficiency?
52
simple cubic: coordination number
6
simple cubic: net atoms per unit cell
1
simple cubic: examples
po
simple cubic: e equation
e = 2r
body centered cubic: % efficiency
68
body centered cubic: net atoms per unit cell
2
body centered cubic: coordination number
8
body centered cubic: examples
Na, V, K, Fe (low temp)
body centered cubic: e equation
e = (4/root 3)r
face centered cubic: % efficiency
74
face centered cubic: net atoms per unit cell
4
face centered cubic: coordination number
12
face centered cubic: examples
Cu, Al, Ag, Au, Fe (high temp)
face centered cubic: e equation
e = (4/root 2)r
hexagonal close packing: % efficiency
74
hexagonal close packing: coordination number
12
hexagonal close packing: net atoms per unit cell
2
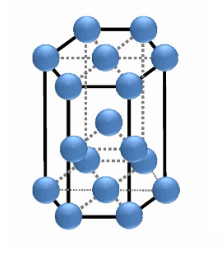
hexagonal close packing: examples
Mg, Ru, Co, Re, Os
Draw the unit cell for simple cubic.
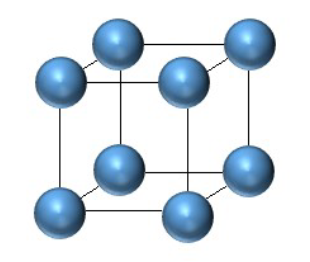
Draw the unit cell for body centered cubic.
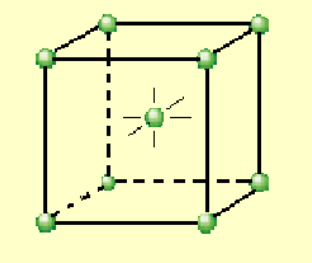
Draw the unit cell for face centered cubic.
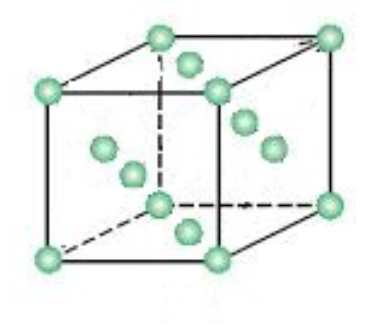
Draw the unit cell for hexagonal close packing.