2.1 CELLS AND CELL STRUCTURE + MICROSOPES
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
WHAT DO ALL CELLS CONTAIN?
Cell surface membrane, enclosing cell contents.
Cytoplasm.
Genetic material made of DNA.
EVIDENCE THAT EUKARYOTIC MIGHT BE DERIVED FROM PROKARYOTIC?
Indirect evidence; they have extra features.
IN WHICH MANNER DO CHEMICAL REACTIOSN OCCUR IN EUKARYOTIC CELLS AND HOW?
Have membrane bound organelles.
Being in a compartment, the chemicals involved in a particular process are kept separate from the rest of the cytoplasm.
This allows chemical reactions to occur quickly and efficiently.
ANIMALS
CELL MEMBRANE
NUCLEUS
MITOCHONDRIA
RER
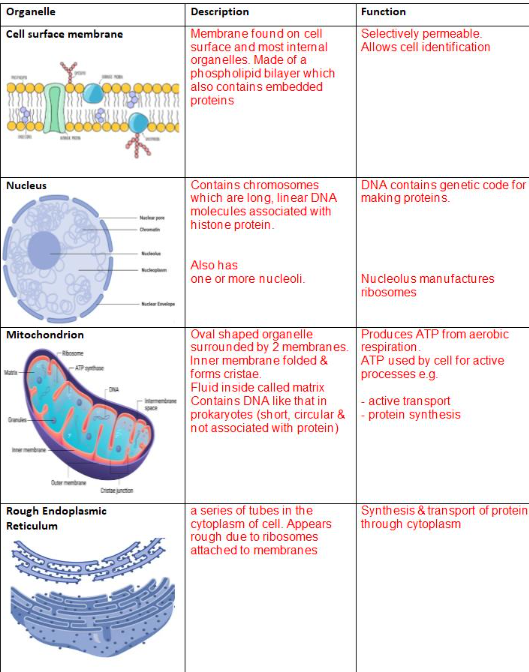
ADVANTAGE OF HAVING MITOCHONDRIA?
(1) Able to respire aerobically.
(1) So it can make (more) ATP/release more energy.
ANIMALS:
RIBOSOMES
SER
GOLGI
LYOSOMES
GOLGI: MODIFIES, TRANSPORTS AND PROCESSED GLYCOPROTIENS.
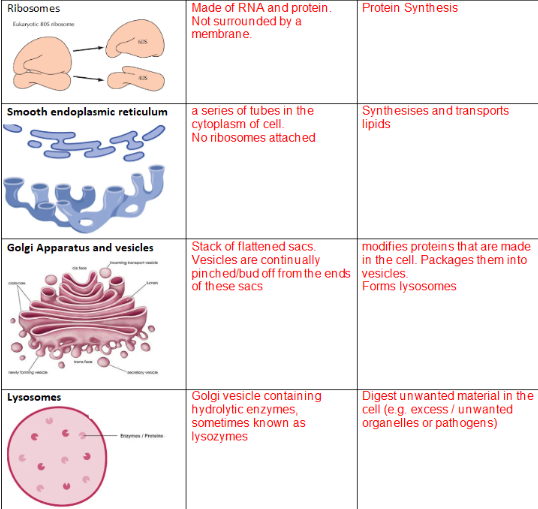
CYTOPLASM: (ANIMALS)
This is the site of many metabolic reactions, including anaerobic respiration.
CELL WALL IN PLANTS
Make of cellulose.
High tensile strength.
Osmotic lysis.
HOW TO MAKE A TEMPORARY MOUNT?
This is for starch (hint: use stain) grains with an optical microscope.

VACUOLE
Cell sap.
Weak solution of sugars and salts - rigidity.
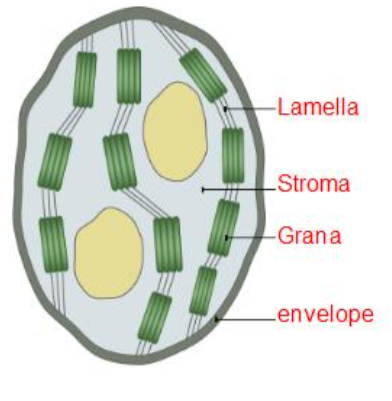
CHLOROPLASTS
Plants and algal cells, site of photosynthesis.
Large organelles, oval.
In mesophyll cells of leaves.
Thylakoid membranes have chlorophyll in them.
Stroma contains starch grains and enzymes for photosynthesis.
Double membrane is an envelope.
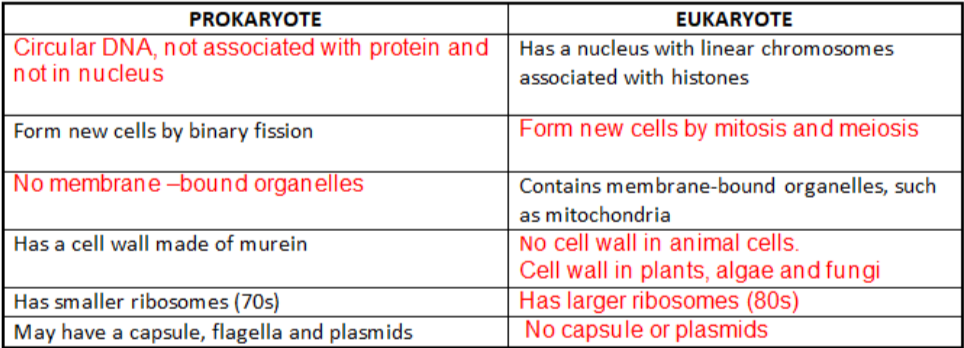
PROKARYOTIC CELL ORGANELLES:
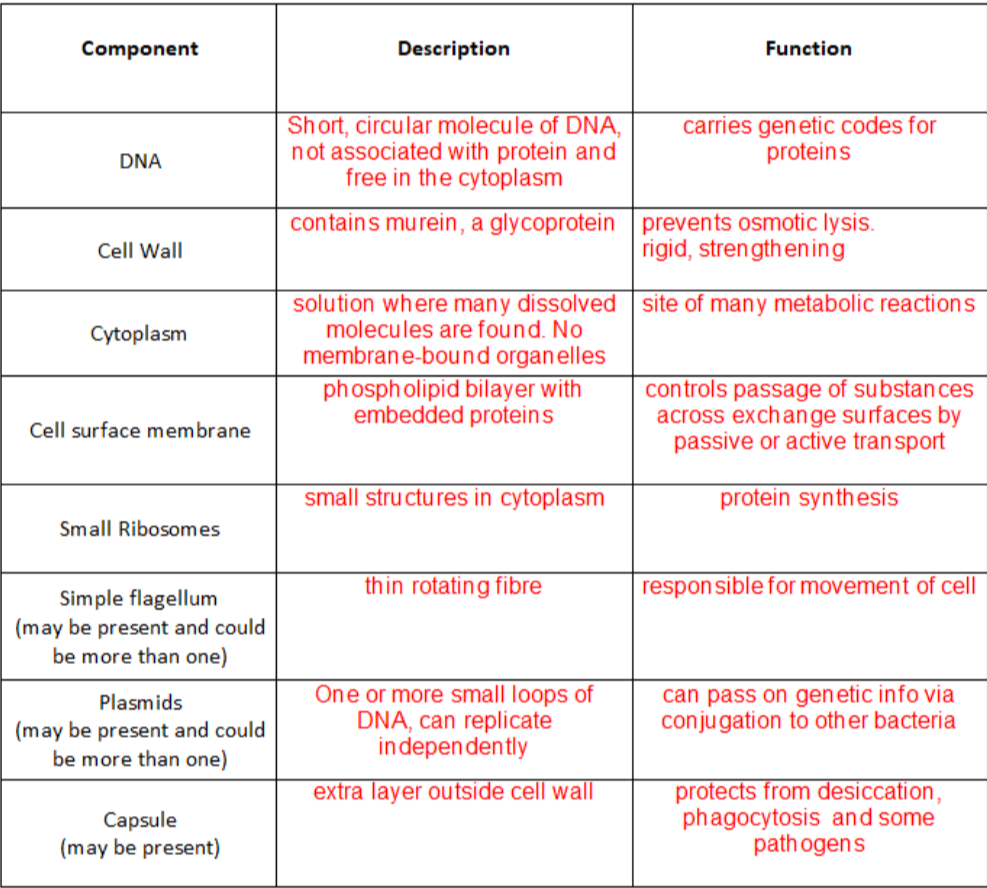
FEATURES THAT ARE IN ALL PROKARYOTIC CELLS THAT ARE NOT IN EUKARYOTIC CELLS:

COMPARE PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS
WHY MAY CELLS BECOME SPECIALIZED?
Specialized cells are more efficient and can carry out their functions more effectively than undifferentiated ones.
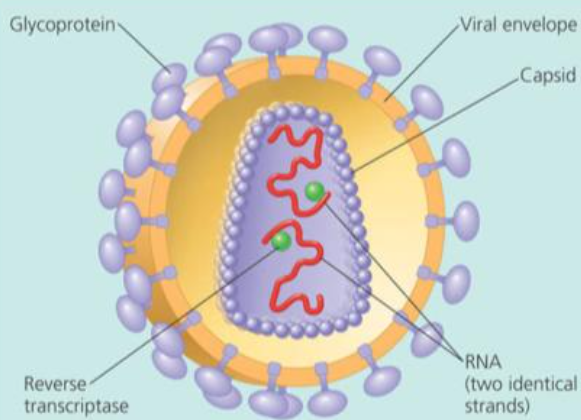
WHAT IS A VIRUS?
Infectious particle.
Parasitic because of the way they reproduce.
WHY ARE VIRUSES NON-LIVING?
No metabolic processes.
Can’t live independently/ move/ respire/ replicate/ reproduce/ excrete.
Have no nutrition.
WHY ARE VIRUSES ACELLULAR?
Have no cell-surface-membrane.
Not made of cells.
No organelles/cytoplasm.
HOW DO VIRUSES DIVIDE?
Viruses cannot cell divide because they are not cells.
So they attach to and enter a host cell and use that cell’s machinery to replicate.
Use ribosomes to produce new viral particles.
WHICH THREE COMPONENTS DO ALL VIRUSES CONSIST OF?
GENETIC MATERIAL.
CAPSID.
ATTACHMENT PROTEINS.
GENETIC MATERIAL IN A VIRUS?
Either DNA or RNA.
Single or double stranded.
Genome/ genetic codes for viral proteins.
(Nucleic acid core.)
CAPSID IN VIRUSES
A protein coat.
Protects the genetic material.
Glycoproteins.
ATTACHMENT PROTIENS IN VIRUSES
Allows the virus to attach to a host cell.
Complementary to the receptors on the host cell’s membranes.
Binds to receptors on cell.
WHAT IS A POTENTIAL FOURTH STRUCTURE?
Envelope
Formed from the membrane - phospholipids because of the cell they were made in.
WHAT TYPE OF VIRUS IS HIV?
Retrovirus because it has RNA.
So it needs the enzyme reverse transcriptase.
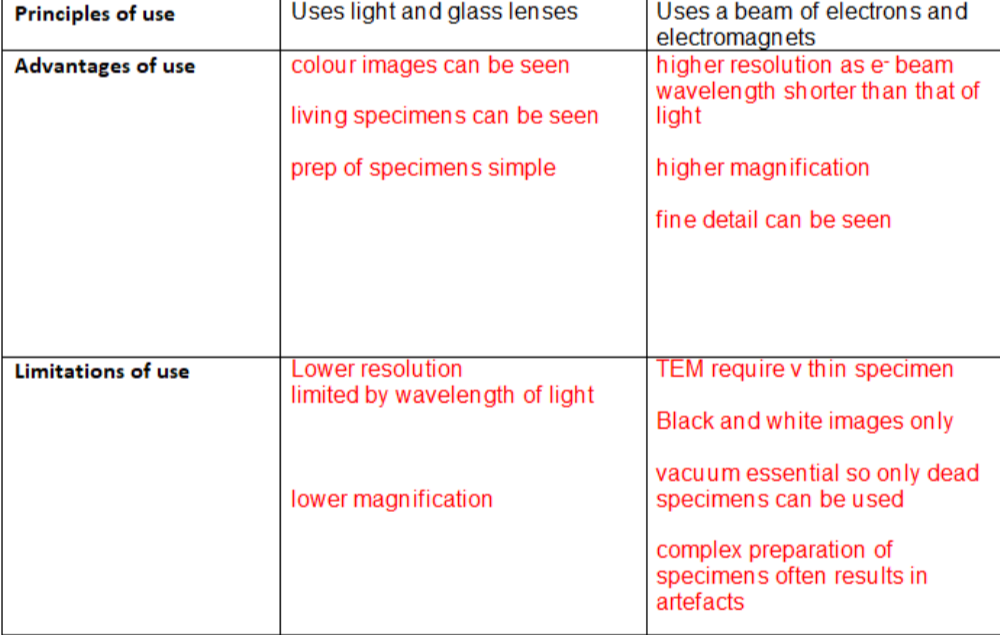
COMPARE LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPES
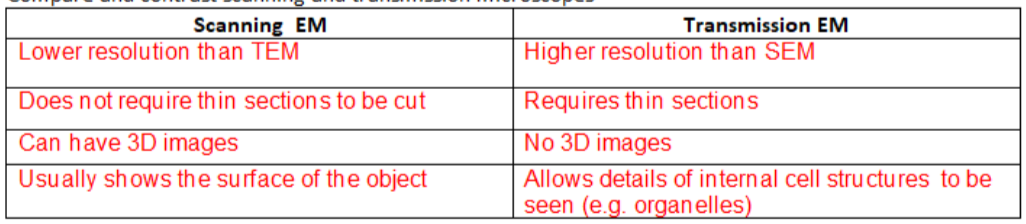
SEM VS TEM
1mm = x micrometers.
1000nm = x micrometers.
1mm = 1000 micrometers.
1000nm = 1 micrometers.
COMMON LENGTHS OF ANIMAL CELLS, THE NUCLEUS,AND PLANT CELLS.
Animals Cells: 30-50microm.
Nucleus: 10microm.
Plant Cells: 150microm.
HOW DO YOU MEASURE DIAMETER OF A CELL?
Measure diameter of field of view using a stage micrometer
OR Estimate the proportion of field of view occupied by one cell
OR Eye piece graticule (which is engraved by an arbitrary scale):
Calibrate it against a stage micrometer scale.
To work out the length that each eyepiece graticule division represents at a particular magnification.
Eyepiece scale used to measure an object under the microscope - it will be super imposed over the image.
WHAT OCCURS DURING CELL FRACTIONALISATION?
(Question is: Q15. (a) Describe and explain how cell fractionation and ultracentrifugation can be used to isolate mitochondria from a suspension of animal cells. (5))
Cell homogenisation to break open cells.
Filter to remove large debris.
Isotonic to prevent damage to organelles.
Cold to prevent damage by enzymes.
Centrifuge to desperate nucleus.
Re spin after removing supernatant at higher speed to get mitochondria pellet.

WHAT IS THE ORDER OF DENSITY IN ORGANELLES?
Nucleus,
Chloroplast.
Mitochondria.
Lysosomes.
Endoplasmic Reticulum.
Ribosomes.
N CM L E R
No canned meat left ever, Ronald.
WHY IS A COLD, BUFFERED, ISOTONIC SOLUTION USED?
Cold: Reduces enzyme activity ::: no digestion of organelles.
Isotonic: Same water potential, prevents osmotic lysis.
Buffer: Controls pH.
WHY DO SAMPLES NEED TO BE THIN FOR LIGHT MICROSCROPES?
To allow light to pass through.
To increase visibility.
PRINCIPLES AND LIMITATIONS OF TEM:
Electrons pass through thin specimen.
Denser parts absorb more electrons.
So they appear darker.
Electrons have short wavelength ::: high resolution.
Cannot look at living/ vacuum.
Very thin.
Artefacts present.
Long preparation time.
Only 2D images produced.