enzymes
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Using your knowledge of enzyme structure explain why this is the only reaction succinate dehydrogenase can catalyse
The active site of succinate dehydrogenase has a specific shape , succinct (the substrate) has a complementary shape and therefore fits into/ binds to the active site
Graph showing energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction
Drawing a line to show energy change that would take place if an enzyme was present —> line starting and finishing must be at the same point but the activation energy is lower
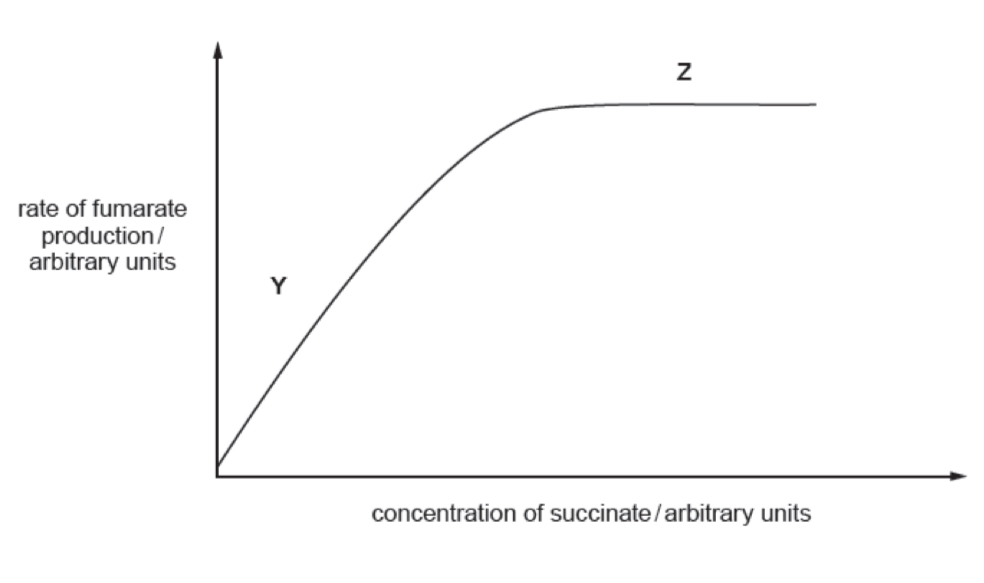
State the factor that is limiting the rate of reaction and give evidence from graph to support your answer
Concentration of succinate (substrate) because as the concentration of substrate increases the rate of reaction / rate of production of product increases
Explain what is limiting the RoR when the graph plateaus
The concentration of enzyme (succinate dehydrogenase) as all of the active sites are occupied
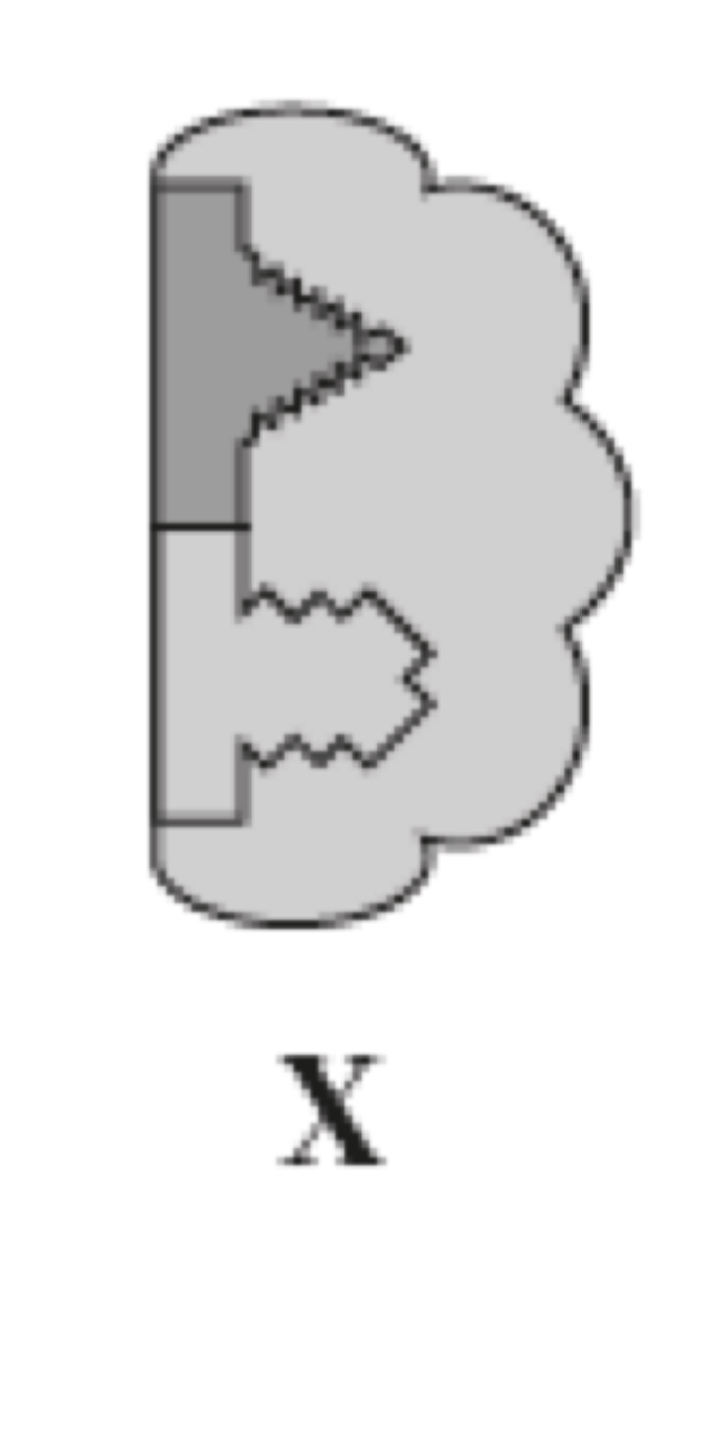
Using the diagram of succinate and malonate to explain how malonate inhibits succinate dehydrogenase
malonate has a similar structure to succinate (substrate) has a complementary shape to the active site, malonate binds to the active site preventing succinate (substrate) binding so fewer ESC are formed
Describe and explain the effect of temp on the rate of activity of the enzyme
Increase in rate from ..° to …°, increase in KE so molecules move faster , more successful collisions so more ESC formed up to optimum temp , there is a fall from …° to …° as above optimum temp there is a increased vibration causing hydrogen bonds to break resulting in loss or change of shape of the active site, enzyme denatures
Graph shows effect of temp on bacterial amylase, state the diff between bacterial amylase and amylase found in humans
Enzymes have different optimum temps, human amylase has an optimum temp of 37°C bacterial amylase has an optimum temp of .. (shown in the graph) so human amylase denatures at a lower temp
Which theory represents activity of lysozyme
Induced fit model
Name given to structure
Enzyme substrate complex
How do enzymes bring about thier effect of speeding up reactions
Lower the activation energy
What characteristic of the enzyme at the end of a reaction is visible in both diagrams
Enzyme/ active site is unchanged so can be reused
3 factors which affect enzyme activity
Temp
pH
Enzyme concentration
Substrate concentration
Distinguish between intercellular and extracellular enzymes
Intracellular→ inside the cell
Extra cellular → outside the cell
Advantage of immobilising enzymes
Product not contaminated with enzyme
Enzyme can be reused
Can withstand/ tolerate a wider range of pH
Can be used in a continuous process
Increases temp range over which they can be used
Suggest why reducing the flow rate of material through the column would result in an increased volume of products
Increases contact time between enzymes and substrates , more time for immobilised enzymes to digest substrate, more successful collisions/ more enzyme substrate complexes formed
Explain the results for temp above 40°C (graph decreases from 40° and falls to 0 at 60°C)
Between 40 to 60°C there is a decrease in the product produced, enzymes are denaturing, above 60°C no product is produced so enzymes are denatured hydrogen bonds break, tertiary structure deformed active site changes shape, substrate can longer fit into active site so fewer ESC formed
Explain why a higher yield of products was produced using free enzymes between these temps than using immobilised enzymes
Free enzymes can move, increase chance of successful collisions, more ESC form
Explain why enzyme bound to gel membrane surface produces more product than enzymes immobilised inside beads
Membrane bound enzymes are more accessible to substrate, for enzymes immobilised inside beads substrate has to diffuse or pass into bead
Describe what is meant by the term biological catalyst
A protein Produced by living cells, speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up or changed themselves
Suggest why different enzymes are needed for remove different types of stains
Enzymes are specific
Each stain / protein has a diff shape, diff shaped substrate
Would not fit one active site, three different active sites are needed
Explain using graphs why reaction at 60° wouldn’t be recommended
(Graph shows all enzymes denature at 50°) → at this temp all three enzymes are denatured, have no activity due to breaking of hydrogen bonds, active site deforms, prevents enzyme substrate complexes forming so no ESC form, prevents successful collisions
Graph shows 3 enzymes, explain why reactions works best at this temp
all 3 enzymes have high activity/ are working well at this temp
Explain how molecule works as a competitive inhibitor
It has a similar structure to substrate, complementary to the active site of enzyme
Less ESC formed, more enzyme inhibitor complexes formed, fewer successful collisions
Less substrate is converted and reaction decreases so concent of product decreases there is less product
Increasing comment of substrate reduced effect of inhibitor
Suggest why this might be useful to a cell
Prevents build up/ overproduction of end product, stops when sufficient or enough product is made, regulating production of … product, stops …( product) reaching toxic levels
Describe how enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase can catalyse conversion of ethanol into ethanal
Enzyme has a specific shaped active site , ethanol substrate has a complementary shape, the two fit together to form an enzyme substrate complex
Fixed mass of ethanol was added to test tube containing enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase, test tube was incubated and the mass of ethanal produced over time was recorded shown in a curve graph (time against mass of product)
reason for difference in rate at the start (time 0) and when time is 30s → at the start the rate of reaction is higher as the concent of substrate is high, the concent of the enzyme is the limiting factor
At 30s→ the rate of reaction is lower and the concent of substrate decreases, the convent of substrate becomes the limiting factor
Explain how the induced fit mechanism differs from lock and key model
Lock and key active site shape already fixed, complementary to substrate
Induced fit active site changes shape when substrate binds
Protein ADK is an enzyme involved in regeneration of ATP in a muscle, suggest why the activity of ADK would be an advantage to muscle
ATP can be regenerated quickly, more ATP for muscle contraction
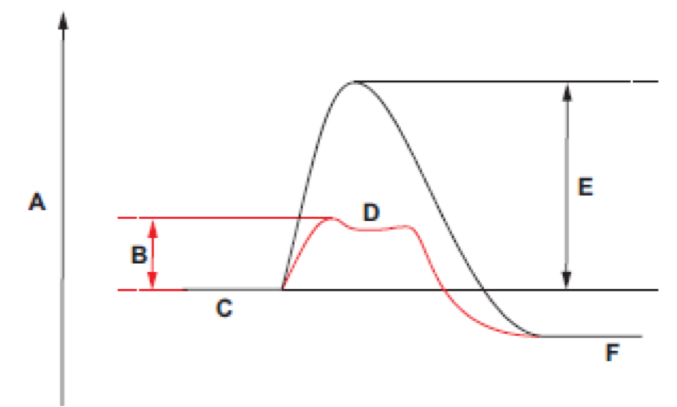
Energy level of the products of an enzyme catalysed reaction: F
Activation energy of an enzyme catalysed reaction: B
energy level of an ESC: D
Energy level of the reactants: C
Activation energy of a non enzyme reaction: E
Ethylene glycol is converted into glycoaldehyde, this reaction is catalysed by alcohol dehydrogenase, treatment of ethylene glycol involves giving patient alcohol, graph shows rate of glycoaldehyde production when ethanol present and when absent against concent of ethylene glycol
Ethanol and ethylene glycol (substrate) must have a similar structure, must both be complementary to the shape of the a five site of the enzyme (ADH), ethanol act as a competitive inhibitor, when ethanol binds to the active site it prevents ethylene glycol from binding , fewer ESC formed which reduces the rate of rpsouvripn of glycoaldehyde/ product
Describe what is meant by the term enzyme
Biological catalysts that speed up rate of reactions, lowers activation energy
explain why the tertiary structure of the enzyme is important to the function of the enzyme
Active site is complementary to the substrate, lock and key theory, substrate fits into/ binds to the active site so enzyme substrate complexes can form
Term given to enzymes that work outside of cells
Extracellular
Explain why several different types of lipase enzymes are released by the pancreas
Different triglycerides have different structures for example different lengths of fatty acids, some are unsaturated and some are saturated
Needs diff shaped/ complementary/specific active sites
When vinegar (ethanoic acid) is added to potato chips, enzyme A (produced in the mouth) is unable to break down the starch they contain. Suggest the reason for this.
vinegar {inactivates / denatures} enzyme
Describe how they could test the resulting liquid to show that no enzyme had left the column. Explain why this test is used.
Add biuret, stays blue, Enzyme is a protein
Give one example where ATP is used in an anabolic reaction
protein synthesis / condensation reaction/
Give one example where ATP is used in a catabolic reaction
digestion/ respiration/ hydrolysis/
Explain how an ATP molecule could act as a non-competitive inhibitor.
ATP binds to allosteric site / to enzyme but not to active site (1) Changes shape of active site.
Explain why the solutions were left in the thermostatic water bath for 5 minutes before combining, lipids and lipase enzyme
Both solutions reach the same temperature

Suggest two sources of inaccuracy in this experimental method that could account for the variation within these results.
Difficulty deciding the end-point 1) Use a colorimeter/ use colour standard (1) Difficulty in mixing the solutions (1) Agitate at regular intervals / or reasonable suggestion (1) Difficulty deciding when to start the stop clock (1) Start as soon as solutions are completely mixed
Explain the term allosteric inhibition.
inhibitor binds to a site away from/ other then the active site changing the shape of the active site substrate no longer fits in active site
Explain one reason why the volume of juice collected may be lower than expected using the filtration method shown in
filter blocked by pulp / not left for long enough / juice absorbed by filter paper / did not squeeze the pul
describe and explain the effect of increasing the concentration of enzyme
y four (x1) from A - As the concentration of enzyme increases, juice volume increases (1) B – {Above 0.6% / at 1%}the increase in volume is not as great / same volume (1) C - Increased successful collisions / increase E-S complexes formed (1) D - At low concentrations (there is lower volume due to) enzyme concentration being a limiting factor (1) E - At higher enzyme concentrations (0.6 – 1.0%), Pectin is (becoming) the limiting factor / not enough substrate / substrate all broken down
The pectinase and pineapple mixture was placed in a water bath at the optimum temperature for the enzyme. If incubation temperature was less than the optimum, the volume of juice extracted would have changed. Suggest how the volume of juice extracted would have changed. Explain your answer
volume reduced (1) Less successful collisions / less KE / Less ES complexes
Describe the induced fit hypothesis.
Active site shape changes to fit the substrate (1) Enzyme-Substrate complex forms (1) Lowers activation energy (1) Active site returns to original shape after reactio
Describe how the lock and key hypothesis is different from the induced fit hypothesis.
Substrate complementary shape to active site (1) Active site does not change shape
Predict and explain what would happen to the concentration of substrate as the concentration of inhibitor increases
increase or remains the same, As the concentration of inhibitor increases, the rate of activity of enzyme decreases, fewer enzyme-substrate complexes formed, so less substrate is converted, allowing its concentration to increase
Predict the relationship between bead diameter and rate of hydrolysis. Explain your answer.
Smaller beads would give higher rate of hydrolysis (1) Larger S.A.: Vol. / overall surface area (1) Higher chance of enzyme – substrate complex forming
Carrying out the experiment at room temperature reduces reproducibility. Explain why and suggest how this could be improved
Room temperature varies (1) Carry out in thermostatically controlled waterbath
Explain how the shape of the molecule is related to its function
The shape is globular / specific (3D) shape (1) Reference to active site being complementary to substrate
Some bacteria produce a protease which breaks down milk protein. When the enzyme is added to milk the milk gradually becomes clear as the protein in milk is broken down. A student investigated the effect of temperature on this protease using the following method. • Set up five water baths in beakers using ice, hot and cold water at the following approximate temperatures; 10ºC, 20ºC, 30ºC, 40ºC, 50ºC. • Record the actual temperature of the water baths. • Add 10cm3 of milk to one test tube. • Add 1cm3 of protease at pH 7 to a separate test tube. • Place both test tubes in the first water bath for five minutes. • Pour the milk into the protease. • Record the time taken for the milk to become clear. • Repeat for the other temperatures.
Identify two sources of inaccuracy in this experimental method
Maintaining a constant temperature, Use thermostatic / constant temperature water baths (1) Difficult to determine exactly when the milk has become clear (1) + Use a colorimeter to determine when the milk has become clear/ colour standard
Describe and explain the results of the experiment.
The mean time taken for the milk to turn clear decreases until 42º C and then increases (1) • Due to increased kinetic energy (1) • Leading to more successful collisions (1) • Ref to denaturing at higher temp (1) • Ref to optimum temperature
Explain why galactose can act as a competitive inhibitor of lactase.
Shape: Galactose is similar to {lactose/ substrate} / complementary to active site and prevent {successful collisions/ enzyme substrate complexes}
Explain how the results show that galactose acts as a competitive inhibitor of lactase.
Rate reduced at lower concentration (1) Accept ORA Reach the same rate at high concentration as ‘without inhibitor’
Describe how the graph would look if galactose was a non-competitive inhibitor of lactase.
Reduced rate at all concentrations/ maximum rate not achieved
Explain why the immobilised lactase works at its maximum rate over a wider range of temperatures than the free lactase.
{Stability/ protection} from {increased / higher} temperature / more energy required to overcome weak bonds/ Reference to bonds forming stability (1) shape of active site is maintained at higher temperatures
Explain why the substance used to immobilise the lactase must be inert
Substance used for immobilisation must not affect the shape of the active site / does not react with enzyme or substrate
Compare the activity of the free lactase and immobilised lactase below 50°C
free lactase has higher energy, more active below 50 because lactase and lactose can move freely, more chance of successful collisions, ESC forming
Takes longer for lactose to diffuse through the beads when immobilised
Compare the activity of the free lactase and immobilised lactase above 50°C
Immobilised lactase is more active above 50, free lactase is denatured, because the immobilisation stabilised lactase/ maintains shape of the active site
Why could you not use Benedict’s solution to monitor digestion of lactose by lactase
All give a blue to orange colour change with Benedict’s, reactants and products would both give a blue to orange colour change, all monosaccharides/ glucose/ galactose are reducing sugars
Explain why it is important to rinse beads with distilled water before use
To wash off any excess enzyme
Explain why the same solution of alignste and lactase was used to make all different sizes of bead
To ensure all bead sizes have the same concent of lactase
investigating effect of temp on enzyme protease by changing the temp of the water bath, pursing milk into protease , control variables
Same type of milk, concentration of milk
Concentration of enzyme/ protease
Method of mixing
Explaining results of investigation
time taken for milk to turn clear decreases until ..°C and then increased
Due to increased KE leading to more successful collisions, more ESC formed
Enzymes denature at high temps
Explain the shape of the curve when a boiled enzyme was used to break down hydrogen peroxide into oxygen
Slight reaction is due to decomposition of hydrogen peroxide in the air
Explain how the experiment could be modified to investigate the affect of concent of Catalse on the rate of reaction
The subst concent is constant , use optimum pH value, vary concent of Catalse by dilution of liver
Explain why initial rate of reaction is higher than any other rate
Higher concentration of substrate
All of active sites occupied