GENERAL HISTOLOGY - EPITHELIAL TISSUES A
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
CHOOSE YES OR NO
The ciliated cells are present in the simple columnar resorbtive epithelium
A. yes
B. no
B. no (microvilli)
CHOOSE YES OR NO
The simple squamous epithelium is found in some endocrine glands (thyroid glands)
A. yes
B. no
B. no
(simple cuboidal epithelium)
CHOOSE YES OR NO
The pseudostratified epithelium is usually associated with resorbtion
A. yes
B. no
B. no
(absorption and secretion of mucus, protection from foreign particles (dust, pathogens, and allergens), and transport of materials such as hormones and enzymes.)
CHOOSE YES OR NO
The stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium originates from the ectoblast
A. yes
B. no
A. yes
Ectoblast: the outer wall of a cell; the ectoderm or epiblast.
CHOOSE YES OR NO
The superficial cells of stratified squamous non- keratinizing epithelium preserve their nuclei
A. yes
B. no
A. yes
CHOOSE YES OR NO
The simple exocrine glands have a system of branching ducts
A. yes
B. no
B. no
Exocrine glands secrete onto a surface and possess 'ducts' lined with epithelium; they can either be simple or compound. Simple glands - these have a single, unbranched duct. Examples include sebaceous glands, intestinal crypts and uterine glands.
CHOOSE YES OR NO
The mucous cells contain well developed rough surfaced endoplasmic reticulum
A. yes
B. no
B. no
Mucus is a slippery, gelatinous goo produced by your mucous membranes. It lines your mouth, nose, throat, sinuses, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. It's made up of 95% water, with a mix of glycoproteins, proteoglycans, lipids, proteins, and DNA
CHOOSE YES OR NO
The regeneration of the simple epithelia is through the substitutive (germiantive) cells localized between the mature epithelial cells
A. yes
B, no
A. yes
CHOOSE YES OR NO
The epithelial tissue is devoid of own blood or lymph vessels
A. yes
B. no
A. yes
The epithelial cells are nourished by substances diffusing from blood vessels in the underlying connective tissue.
CHOOSE YES OR NO
Two parts of the cytoplasm, an apical and basal portion are recognized in some epithelial cells
A. yes
B, no
A. yes
CHOOSE YES OR NO
The goblet cells evident in the epithelium of organs of the digestive system are described as "unicellular glands"
A. yes
B. no
A.yes
CHOOSE YES OR NO
The regeneration of the simple epithelia is through the germinative (substitutive) cells that are localized between the mature epithelial cells
A. yes
B. no
A. yes
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
Which of the following types is the epithelium of blood and lymph vessels:
a. simple cuboidal epithelium
b. simple squamous epithelium
c. pseudostratified columnar epithelium
d. simple columnar resorbtive epithelium
b. simple squamous epithelium
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
Which of the following types is the epithelium of lung alveoli:
a. simple cuboidal epithelium
b. simple squamous epithelium
c. pseudostratified columnar epithelium
d. simple columnar resorbtive epithelium
b. simple squamous epithelium
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
The goblet cells in functional aspect are:
a. resorbtive
b. secretory
c. covering
d. substitutive (germinative)
b. secretory
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
The microvilli containing cells in functional aspect are:
a. covering
b. stem
c. secretory
d. resorbtive
d. resorbtive
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
Simple cuboidal epithelium is evident in:
a. thyroid gland (follicles)
b. ureter
c. trachea
d. blood capillaries
a. thyroid gland (follicles)
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium is evident in:
a. ureter
b. trachea
c. small intestine
d. esophagus
b. trachea
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
Transitional epithelium of Henle is evident in:
a. ureter
b. trachea
c. small intestine
d. esophagus
a. ureter
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
The epithelial cells connect to the basal lamina (membrane) through:
a. nexus
b. desmosomes
c. hemi-desmosomes
d. tight junction (zonula occludens)
c. hemi-desmosomes
Hemidesmosomes are multiprotein complexes that facilitate the stable adhesion of basal epithelial cells to the underlying basement membrane.
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
By which of the following epithelia a convoluted basal lamina (membrane) is found:
a. simple epithelia
b. stratified epithelia
c. glandular epithelia
d. neuroepithelium
b. stratified epithelia
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
Which of the following specializations are described by the stratified epithelia:
a/ microvilli
b/ cilia
c/ tonofibrils
d/ myofibrils
c. tonofibrils
Tonofibrils are cytoplasmic protein structures in epithelial tissues that converge at desmosomes and hemidesmosomes.
tonofibrils are a bundle of fine filaments found in epithelial tissues. They help in anchorage to cytoskeleton.
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
the melanocytes are:
a/ adipose connective tissue cells
b/ pigmentous connective tissue cells
c/ secretory cells
d/ pigmentous neuroepithelial cells
d. pigmentous neuroepithelial cells
Melanocytes are cells of neural crest origin. In the human epidermis, they form a close association with keratinocytes via their dendrites.
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
Which of the following substances is present in the granular layer (stratum granulosum) of the stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium:
a/ eleidin
b/ keratohyaline
c/ keratin
d/ mucopolysaccharides
b. keratohyaline
Keratohyalin is a protein structure found in cytoplasmic granules of the keratinocytes in the stratum granulosum of the epidermis.
What is the difference between keratin and keratohyalin?
is that keratin is (protein) a protein which hair and nails are comprised of while keratohyalin is (biology) a protein structure found in granules in the stratum granulosum of the epidermis, which may be involved in keratinization, and in hassall corpuscles in the thymus.
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
Which of the following substances is present in the lucent layer (stratum lucidum ) of the stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium:
a/ eleidin
b/ keratohyaline
c/ keratin
d/ mucopolysaccharides
a. eleidin
Eleidin is clear intracellular protein which is present in the stratum lucidum of the skin. Eleidin is a transformation product of the amino acid complex keratohyalin,
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
The stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium of cornea is found in:
a/ esophagus
b/ skin
c/ cornea of the eye
d/ oral cavity
c. cornea of the eye
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
Which of the following functions is specific for the glandular epithelium:
a/ covering
b/ secretory
c/ resorbtive
d/ protective
b. secretory
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
Which of the following concepts is not designated to the shape of secretory portions by the exocrine glands:
a/ acinar (alveolar)
b/ tubular
c/ mixed
d/ tubuloalveolar (tubulonacinar)
c/ mixed
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
The serous type of secret contains:
a/ proteins
b/glycogen
c/ mucopolysaccharides
d/ steroids
a. proteins
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
The nuclei of mucous acinar cells are:
a/ flattened
b/ round (spherical)
c/ fragmented
d/ irregular
a. flattened
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
The serous crescents or demilunes of Giannuci are:
a/ serous cells in mixed acini
b/ mucous cells in mixed acini
c/ serous acini
d/ mucous acin
a. serous cells in mixed acini
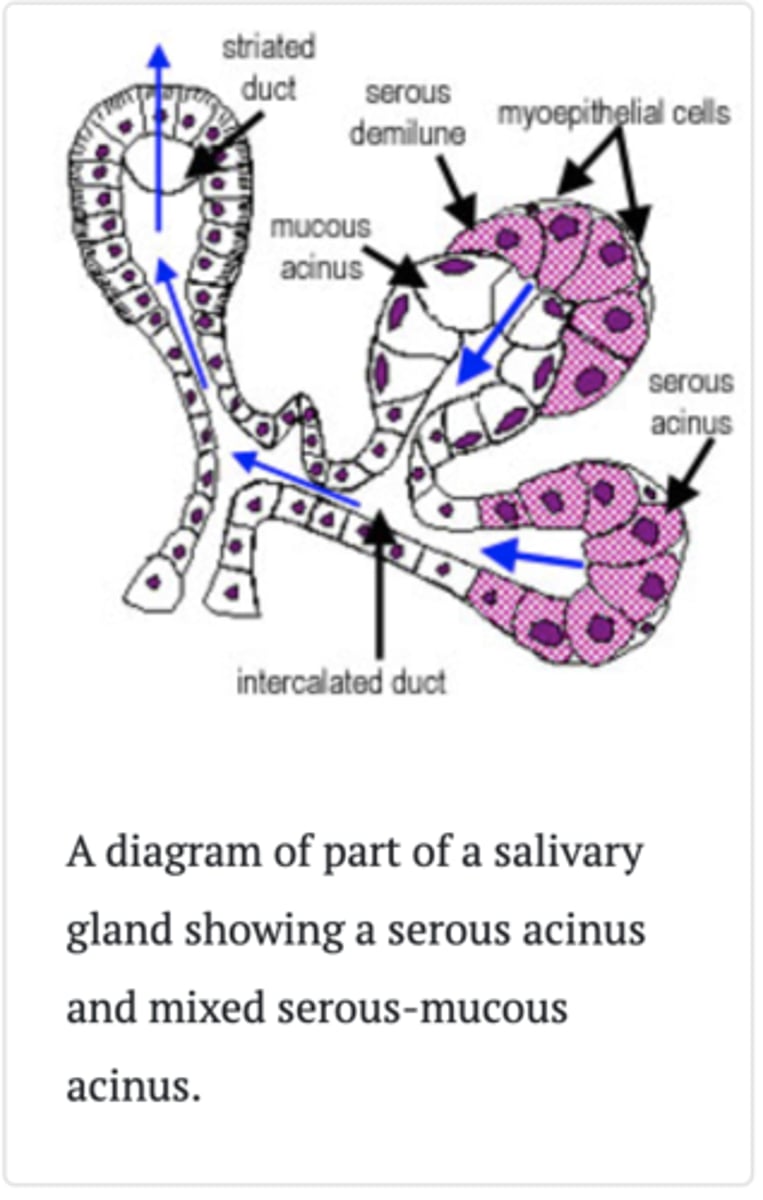
https://www.histology.leeds.ac.uk/oral/salivary.php#:~:text=In%20a%20mixed%20serous%2Dmucous,continue%20on%20as%20striated%20ducts.
Salivary glands are made up of secretory acini (acini - means a rounded secretory unit) and ducts. There are two types of secretions - serous and mucous. The acini can either be serous, mucous, or a mixture of serous and mucous.
A serous acinus secretes proteins in an isotonic watery fluid.A mucous acinuss secretes secretes mucin - lubricant
In a mixed serous-mucous acinus, the serous acinus forms a serous demilune around mucous acinus, as shown in the diagram.
The secretory units merge into intercalated ducts, which are lined by simple low cuboidal epithelium, and surrounded by myoepithelial cells.
These ducts continue on as striated ducts.
MULTIPLE CHOICE - ONE ANSWER
Which of the following staining is applied for visualization of the mucous acini:
a/ hematoxylin-eosin
b/ PAS reaction
c/ Sudan III
d/ silver impregnation (with AgNO3)
b. PAS reaction
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
the simple columnar secretory epithelium is found in:
a/ ducts of exocrine glands
b/ stomach
c/ small intestine
d/ large intestine
e/ esophagus
b/ stomach
d/ large intestine
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
Which of the following cells are specific for the transitional epithelium of Henle:
a/ basal
b/ cells with microvilli
c/ polyhedral
d/ superficial binucleate, ("umbrella-like" cells)
e/ columnar ciliate
a/ basal
c/ polyhedral
d/ superficial binucleate
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
Which of the following features are specific for the stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium:
a/ convoluted basal membrane
b/ keratohyaline granules
c/ superficial cells with preserved nuclei
d/ presence of different in shape cells
e/ presence of nonliving keratinized cells
a/ convoluted basal membrane
c/ superficial cells with preserved nuclei
d/ presence of different in shape cells
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
Which of the following features are specific for the stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium:
a/ convoluted basal membrane
b/ keratohyaline granules
c/ superficial cells with preserved nuclei
d/ presence of different in shape cells
e/ presence of columnar ciliated cells
a/ convoluted basal membrane
b/ keratohyaline granules
d/ presence of different in shape cells
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
Which of the following features are specific for the serous acini:
a/ cells with flattened nuclei
b/ cells with spherical nuclei
c/ wide lumen
d/ basophilic cytoplasm
e/ narrow lumen
b/ cells with spherical nuclei
d/ basophilic cytoplasm
e/ narrow lumen
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
Which of the following features are specific for the mucous acini:
a/ PAS positive reaction
b/ cells with flattened nuclei
c/ cells with spherical nuclei
d/ narrow lumen
e/ wide lumen
a/ PAS positive reaction
b/ cells with flattened nuclei
e/ wide lumen
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
Which of the following features are specific for the exocrine glandular epithelium:
a/ the secretory cells are arranged in groups, follicles, or strands
b/ the secretory product is transported to a surface
c/ releasing of hormones
d/ presence of capillary network surrounding the cells
e/ secretion of enzymes
b/ secretory product is transported to surface
e/ secretion of enzymes
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
Which of the following features are specific for the endocrine glandular epithelium:
a/ lack of excretory ducts
b/ the secretory product is transported to a surface
c/ presence of myoepithelial cells
d/ presence of excretory duct system
e/ releasing of hormones
a/ lack of excretory ducts
e/ releasing of hormones
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
Which of the following substances are designed as keratin precursors:
a/ glycogen
b/ tonofibrils
c/ mucopolysaccharide
d/ keratohyaline
e/ eleidin
b/ tonofibrils
d/ keratohyaline
e/ eleidin
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
Which of the following features are specific for the stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium of cornea:
a/ non-convoluted basal membrane (lamina)
b/ convoluted basal membrane (lamina)
c/ 20-30 layers of cells
d/ 10 layers of cells
e/ synthesis of keratin
a/ non-convoluted basal membrane (lamina)
d/ 10 layers of cells
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
Which of the following cells are present in the simple columnar resorbtive epithelium:
a/ basal (germinative)
b/ columnar cells with microvilli
c/ goblet cells
d/ binucleate ("umbrella-like" cells)
e/ ciliated cells
a/ basal
b/ columnar cells with microvilli
c/ goblet cells
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
Which of the following features are specific for the epithelial tissue:
a/ is found as packing between organ structures
b/ is covering the hollow organs
c/ the cells posses an apical and basal portions (part)
d/ presence of numerous nerves and nerves endings
e/ presence of abundant intercellular substance
b/ is covering the hollow organs
c/ the cells posses an apical and basal portions
d/ presence of numerous nerves and nerve endings
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
The main functions of the epithelial tissue are:
a/ contractile
b/ covering
c/ supporting
d/ secretory
e/ resorbtive
b/ covering
d/ secretory
e/ resorbtive
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
Which of the following features are specific for the covering type of epithelium:
a/ the cells possess apical and basal portion (part)
b/ the cells are arranged in single or multiple layers
c/ there are specializations of the cell surface
d/ the cells are arranged in isogenous groups
e/ the cells possess high phagocytic activity
a/ cells possess apical and basal portion
b/ cells arranged in single or multiple layers
c/ there are specialisations of cell surface
MULTIPLE CHOICE - MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
Which of the following features are specific for the pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium:
a/ convoluted basal membrane (lamina)
b/ presence of ciliated cells
c/ presence of goblet cells
d/ all cells are adjacent to the basal lamina
e/ presence of cells with microvilli
b/ presence of ciliated cells
c/ presence of goblet cells
d/ all cells are adjacent to basal lamina
DEFINE AND FILL IN CORRECT ANSWERS
the types of simple epithelia are:
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
a/ Simple Squameus epithelium
b/ simple cuboidal epithelium
c/ simple columnar epithelium
d/ pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
e/ transitional epithelium of Henle
DEFINE AND FILL IN CORRECT ANSWERS
the cellular types of evident in simple columnar resorbtive epithelium are:
a.
b.
c.
a/ resorbtive cells
b/ mucous (goblet) cells
c/ substitutive cells (germinative cells )
DEFINE AND FILL IN CORRECT ANSWERS
the cellular types evident in transitional epithelium of Henle are:
a.
b.
c.
a/ Basal cells
b/ polyhedral cells
c/ superficial cells (binucleate cells, "umbrella-like" cells)
DEFINE AND FILL IN CORRECT ANSWERS
write some of the most specific microscopic features of the stratified epithelia:
a.
b.
c.
a/ convoluted basal membrane
b/ more than one cell layers
c/ different in shape cells
DEFINE AND FILL IN CORRECT ANSWERS
write the layers of the stratified squamous keratinising epithelium:
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
a/ stratum basale
b/ stratum spinosum
c/ stratum granulosum
d/ stratum lucidum
e/ stratum corneum
DEFINE AND FILL IN CORRECT ANSWERS
the regeneration of the stratified epithelia is associated to the _____ cells localises ______
a. substitutive cells
b. upon basal membrane
DEFINE AND FILL IN CORRECT ANSWERS
depending on type of secretion the glandular epithelia are:
a.
b.
a. exocrine epithelium
b. endocrine epithelium
DEFINE AND FILL IN CORRECT ANSWERS
depending on the type of their secret the acini are:
a.
b.
c.
a/ serous acini
b/ mucous acini
c/ mixed (compound) acini
DEFINE AND FILL IN CORRECT ANSWERS
depending on shape of their secretory units the exocrine glands are:
a.
b.
c.
a/ acinous (alveolar) glands
b/ tubular glands
c/ tubulo-acinar glans
DEFINE AND FILL IN CORRECT ANSWERS
write the types of stratified squamous epithelium:
a.
b.
c.
a/ stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium
b/ stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium of cornea
c/ stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium
GIVE THE CORRECT ANSWER
By light microscopic observation of paraffin section stained with hematoxylin-eosin, epithelial membrane resting upon basal membrane (lamina) is observed. The cell nuclei lying at different levels in a perpendicular section. Some of the epithelial cells have cilia on their apical part.
What type epithelial tissue is this?
pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
GIVE THE CORRECT ANSWER
By light microscopic observation of paraffin section stained with hematoxylin-eosin, epithelial membrane lying on straight basal membrane (lamina) is observed. The apical part of the cells is striated and their nuclei are ovoid, perpendicular oriented to the basal lamina. Some cells appear with unstained cytoplasm.
What type of epithelial tissue is this?
simple columnar resorbtive epithelium of small intestine
GIVE THE CORRECT ANSWER
By light microscopic observation of paraffin section stained with hematoxylin-eosin, epithelial membrane lying on convoluted basal membrane (lamina) is seen. The epithelial sheet is composed of different in shape cells- columnar, polygonal and flattened arranged in layers. There is no border between the epithelial layers. The most superficial cells appear with preserved nuclei. The deeper epithelial layers show basophilia of cell cytoplasm.
What type of epithelial tissue is this?
stratified squamous non-keratinising epithelium
GIVE THE CORRECT ANSWER
By light microscopic observation of paraffin section stained with hematoxylin-eosin, acini composed of high columnar cells with basal basophilic cytoplasm and apical secretory granules are found. The cell nuclei are large and localized in the basal portion of the cytoplasm. The acinus lumen appears very small, narrow.
What type of acini are these?
serous acinus
GIVE THE CORRECT ANSWER
by light microscopic observation of paraffin section stained with hematoxylin-eosin, acini composed of cells with unstained cytoplasm and flattened nuclei localized in its basal part are visible. The acinus lumen appears large, wide.
What type of acini are these?
mucous acinus