BIO112 Exam 3
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Bryophytes
A moss, liverwort, or hornwort; a nonvascular plant that inhabits the land but lacks many of the terrestrial adaptations of vascular plants.

Tracheophytes
Plants that have transport vessels, xylem and phloem
Streptophytes
group that includes green algae and land plants
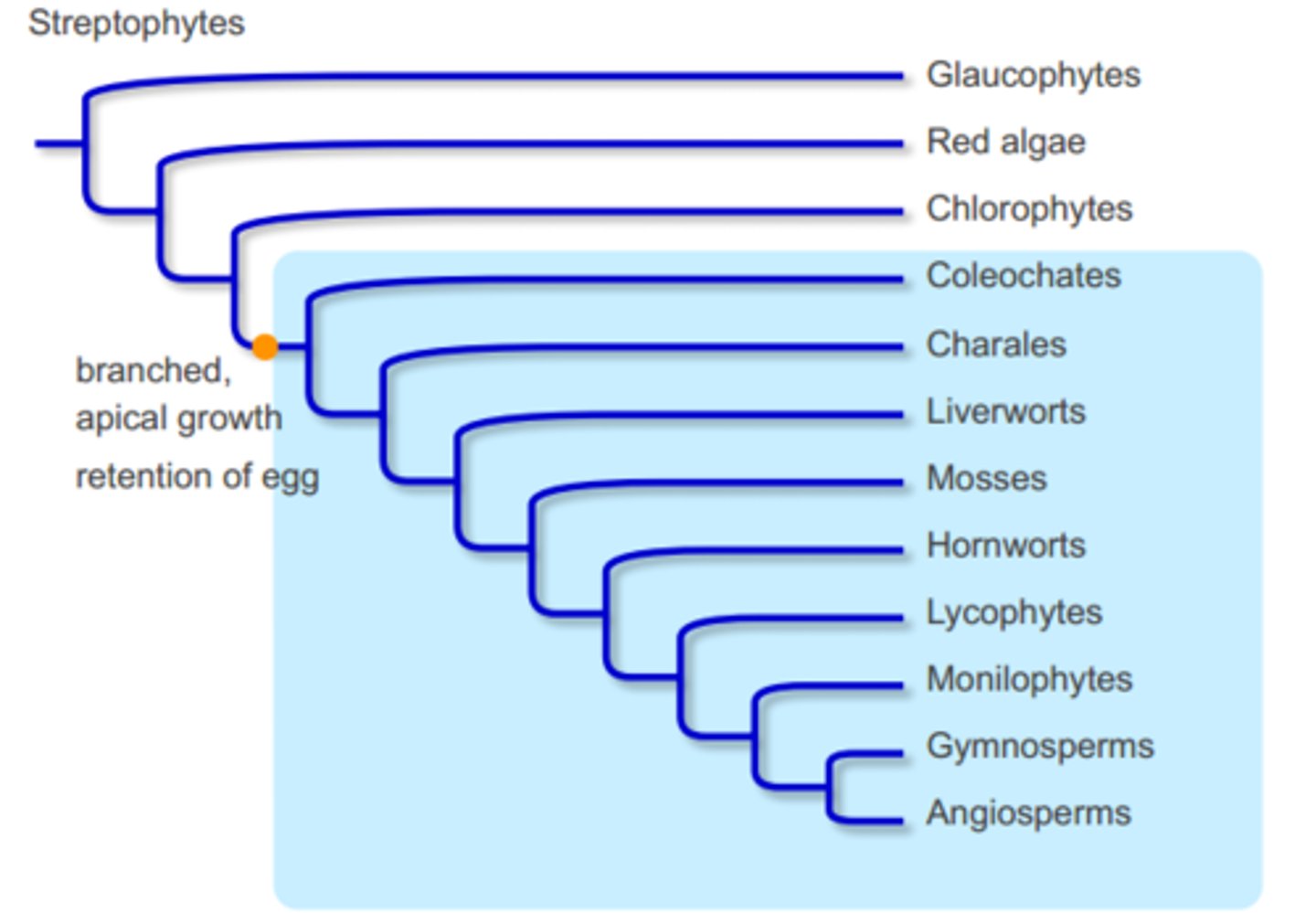
Alternation of Generations
A life cycle in which there is both a multicellular diploid form, the sporophyte, and a multicellular haploid form, the gametophyte; characteristic of plants and some algae.
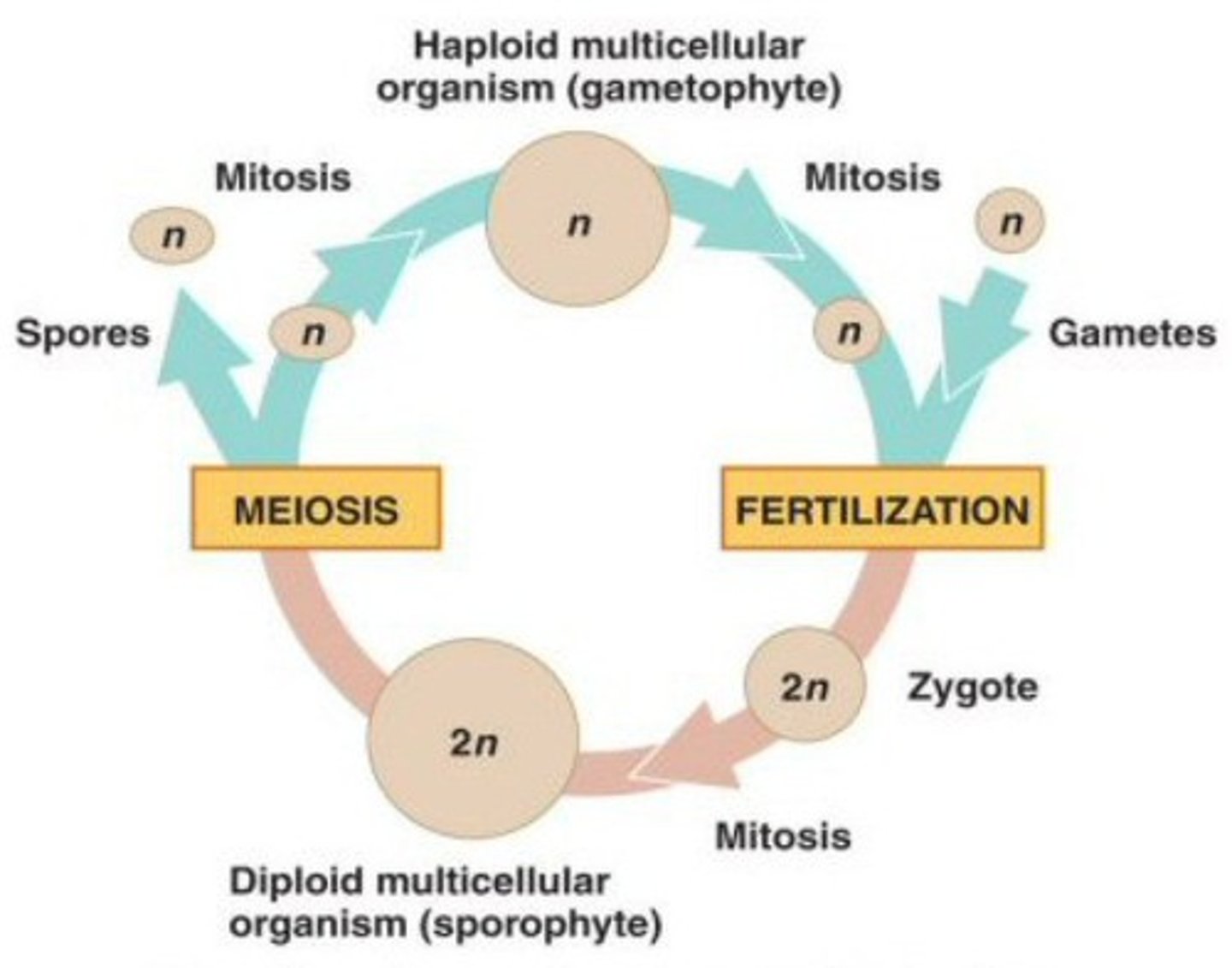
Tracheid
A water-conducting and supportive element of xylem composed of long, thin cells with tapered ends and walls hardened with lignin.
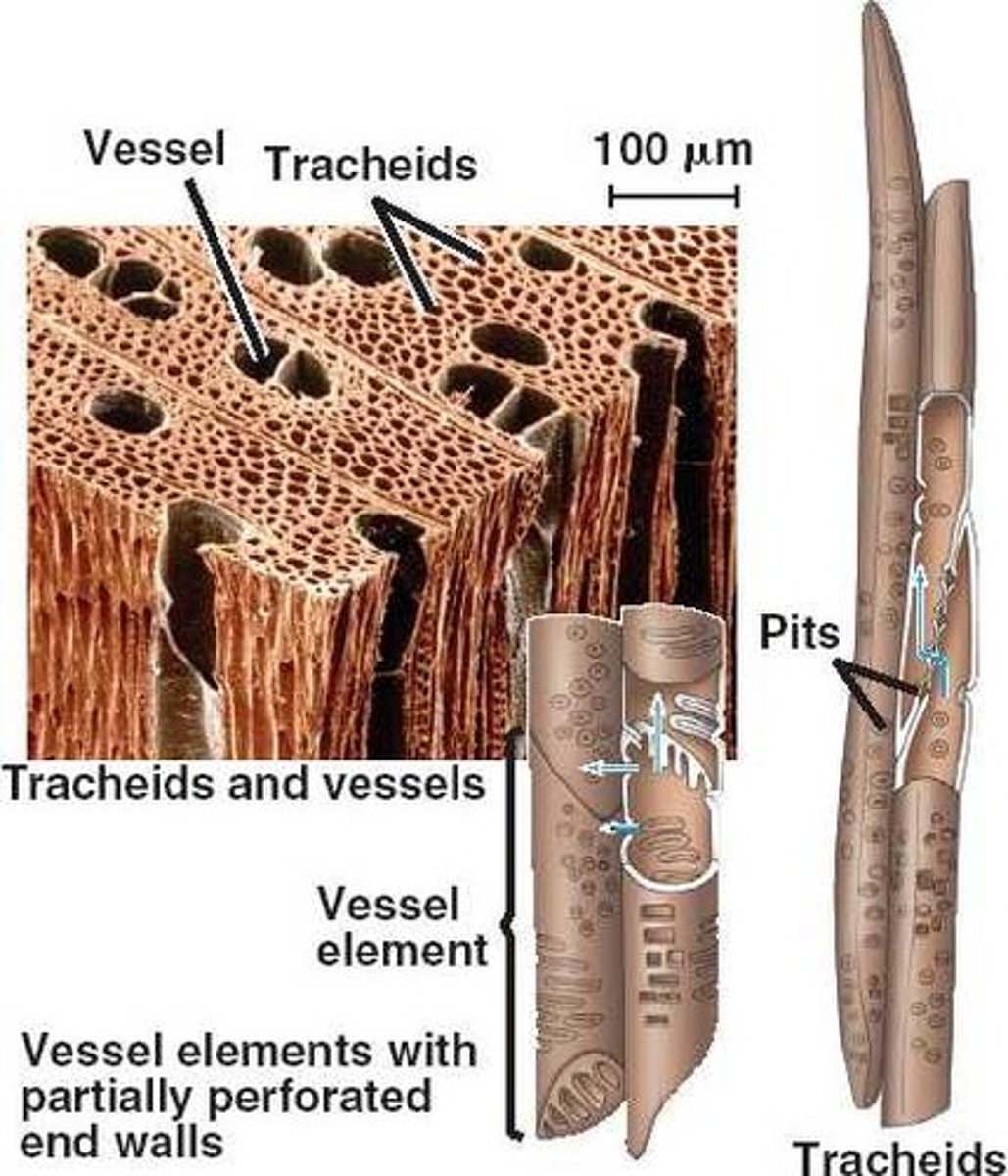
Endosperm
A nutrient-rich tissue formed by the union of a sperm cell with two polar nuclei during double fertilization, which provides nourishment to the developing embryo in angiosperm seeds.
Fruit
A mature ovary of a flower that protects dormant seeds and aids in their dispersal.
Seed
Plant embryo and a food supply encased in a protective covering
Double Fertilization
A mechanism of fertilization in angiosperms, in which two sperm cells unite with two cells in the embryo sac to form the zygote and endosperm.
Cycad
gymnosperm that grows in tropical climates and resembles a palm tree; member of the phylum Cycadophyta

Microspores
Produced by small male cones and will develop into male gametophytes or pollen grains
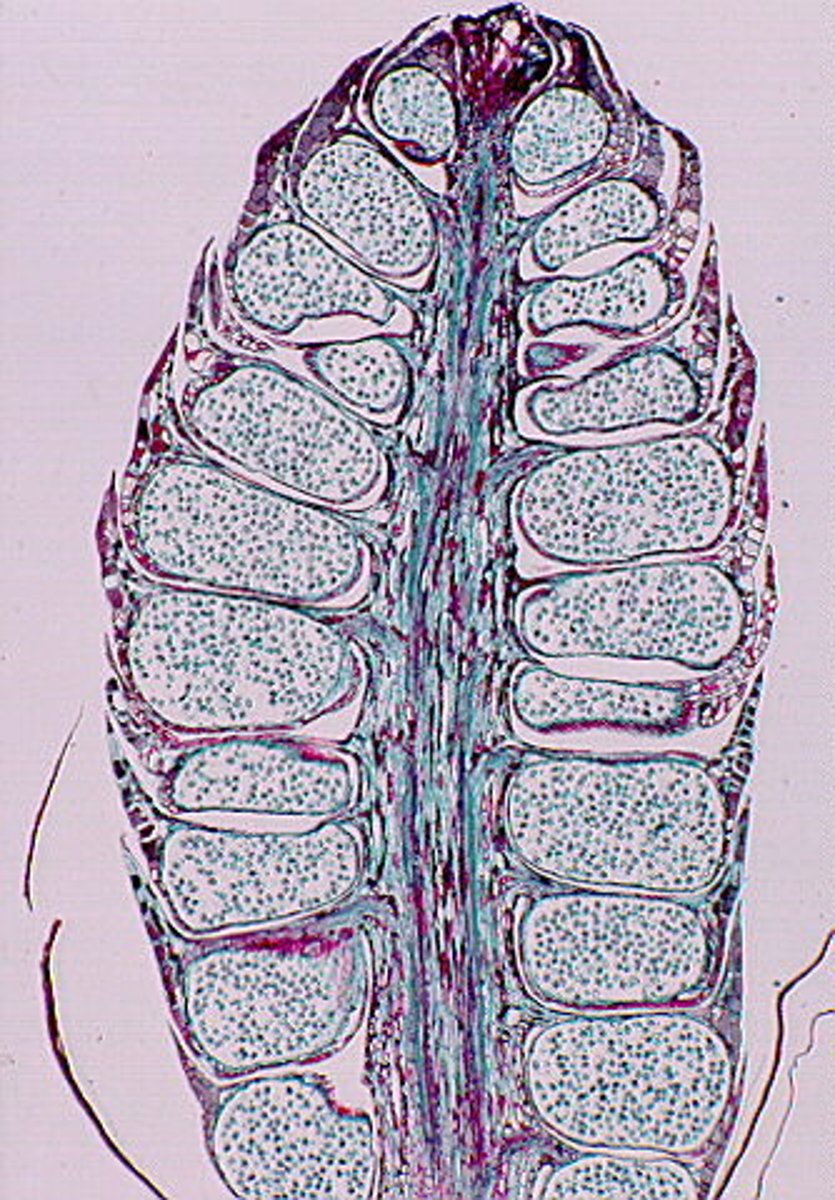
Angiosperm
a flowering plant that produces seeds within a fruit
Pollen Tube
A tube that forms after germination of the pollen grain and that functions in the delivery of sperm to the ovule.
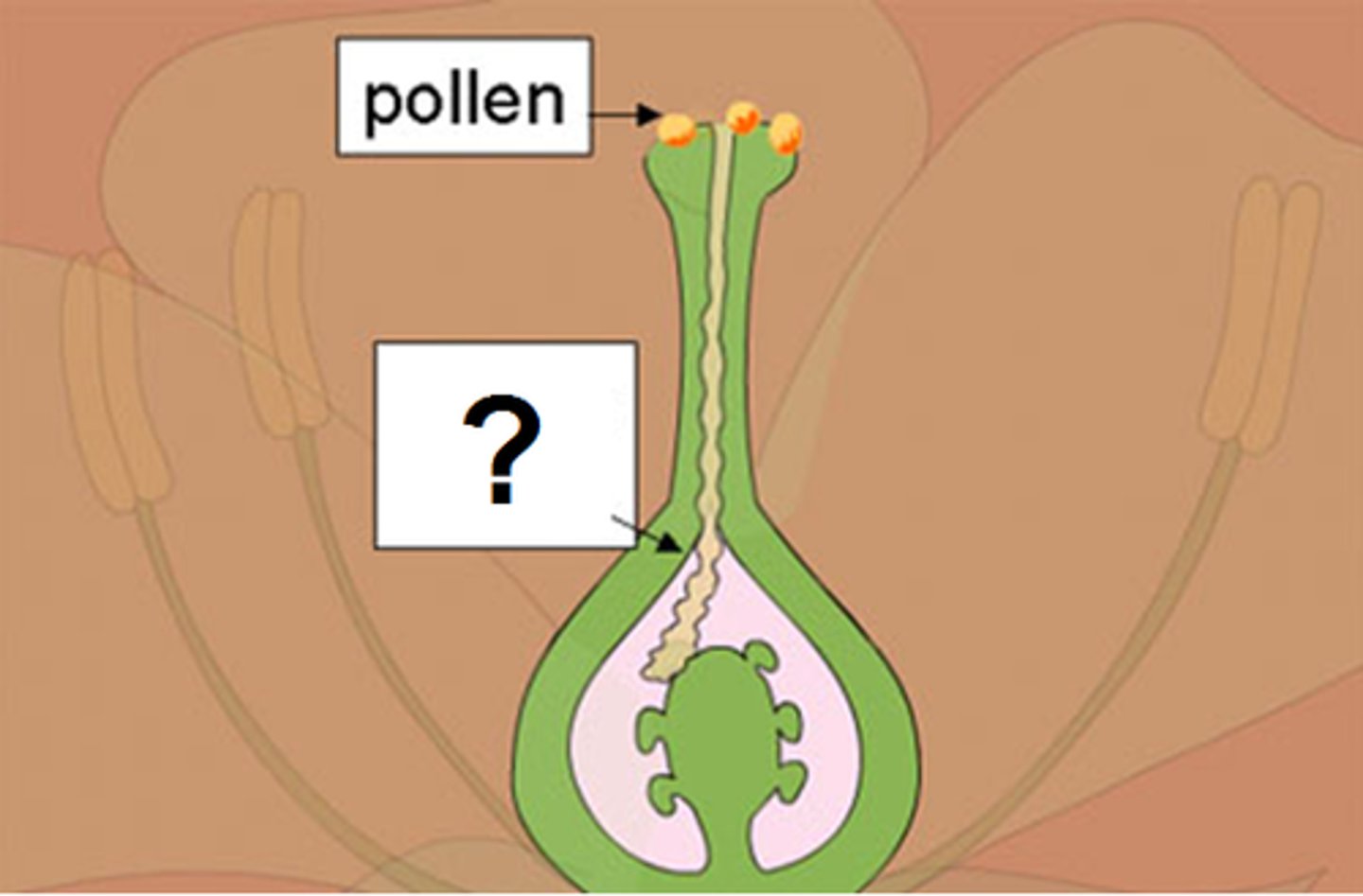
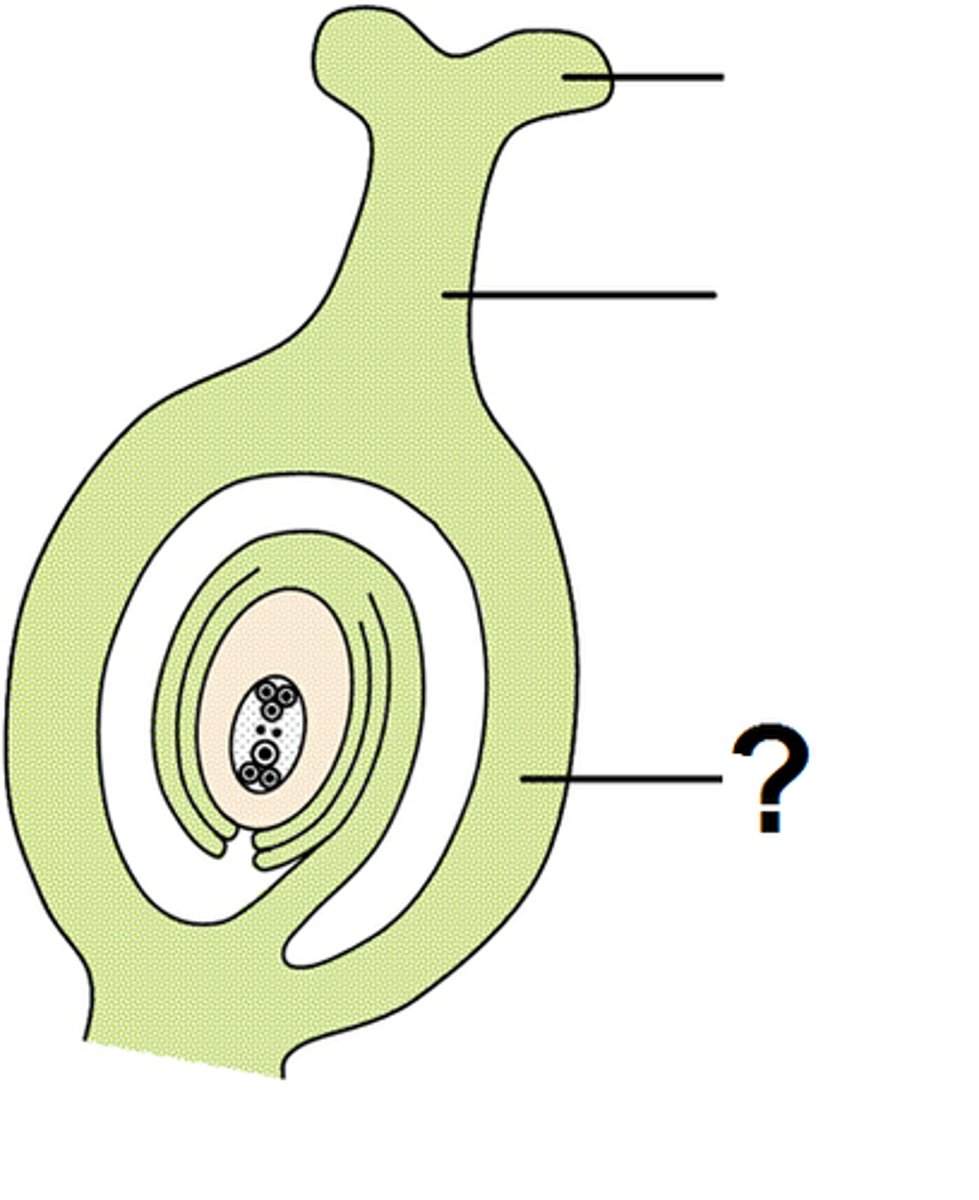
Ovules
A structure that develops within the ovary of a seed plant and contains the female gametophyte.
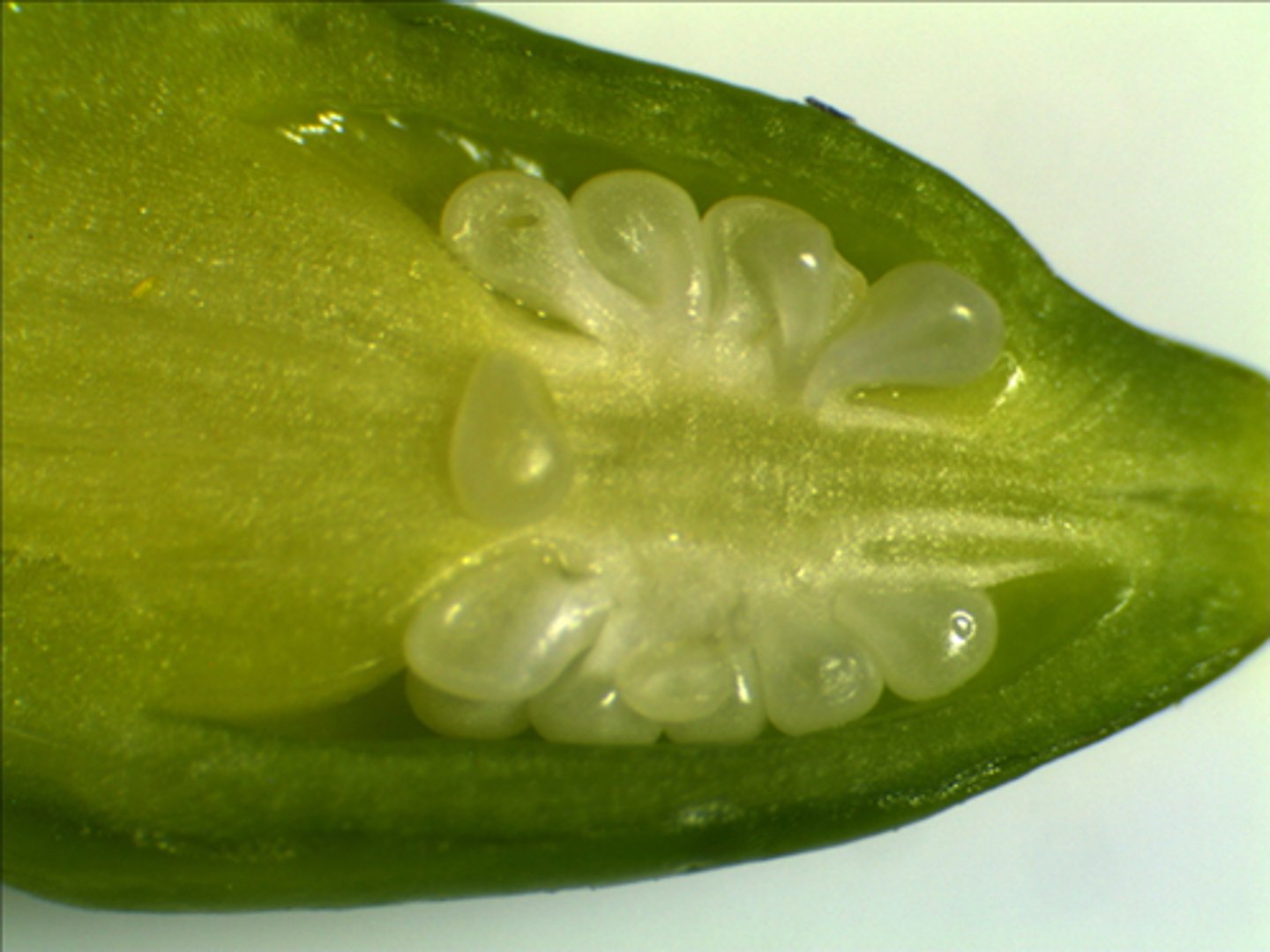

Ovary
In flowers, the portion of a carpel in which the egg-containing ovules develop.
Monocots
Flowering plant whose embryos have one cotyledon
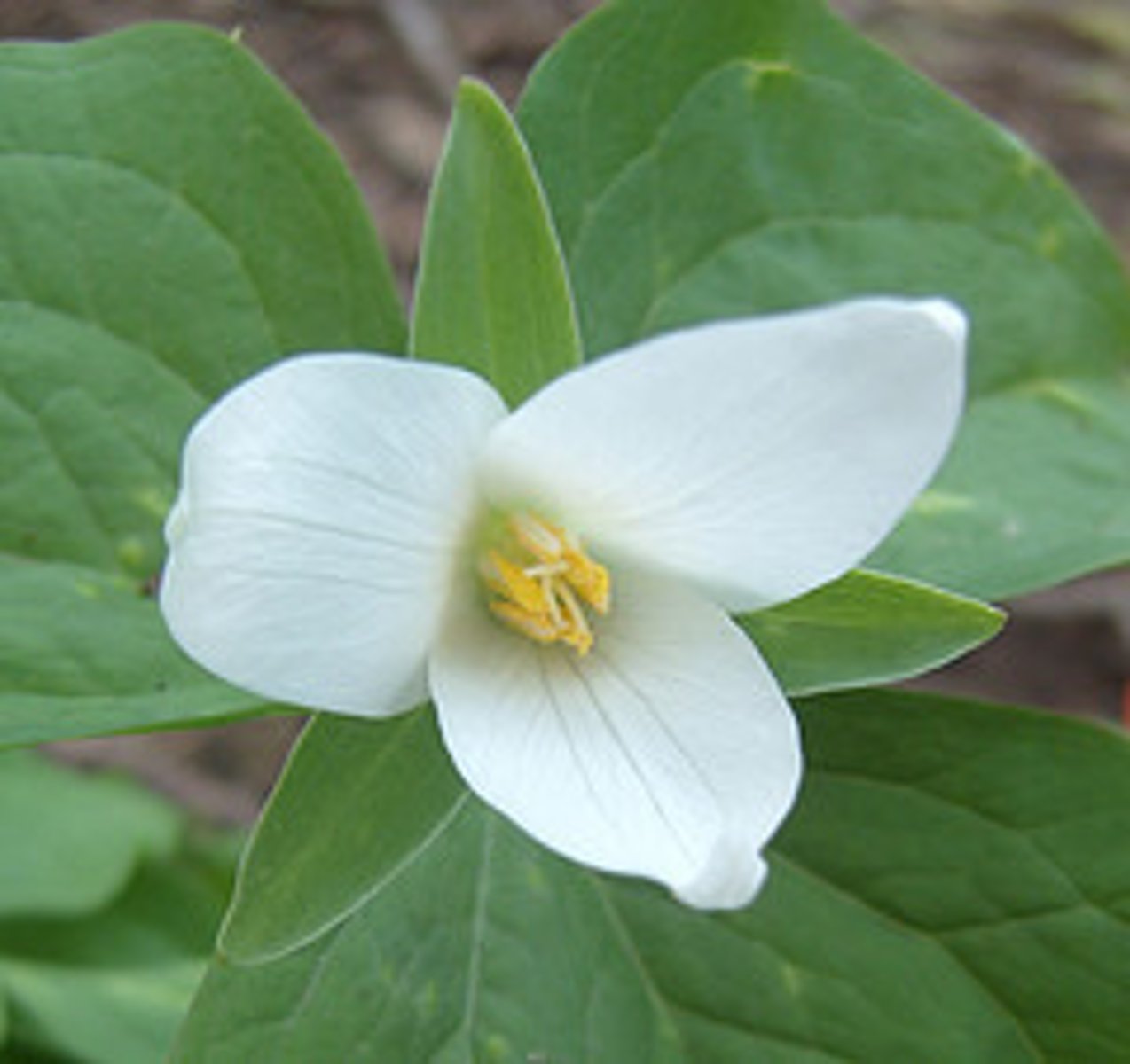

Eudicot
Flowering plant whose embryos have 2 cotyledons.
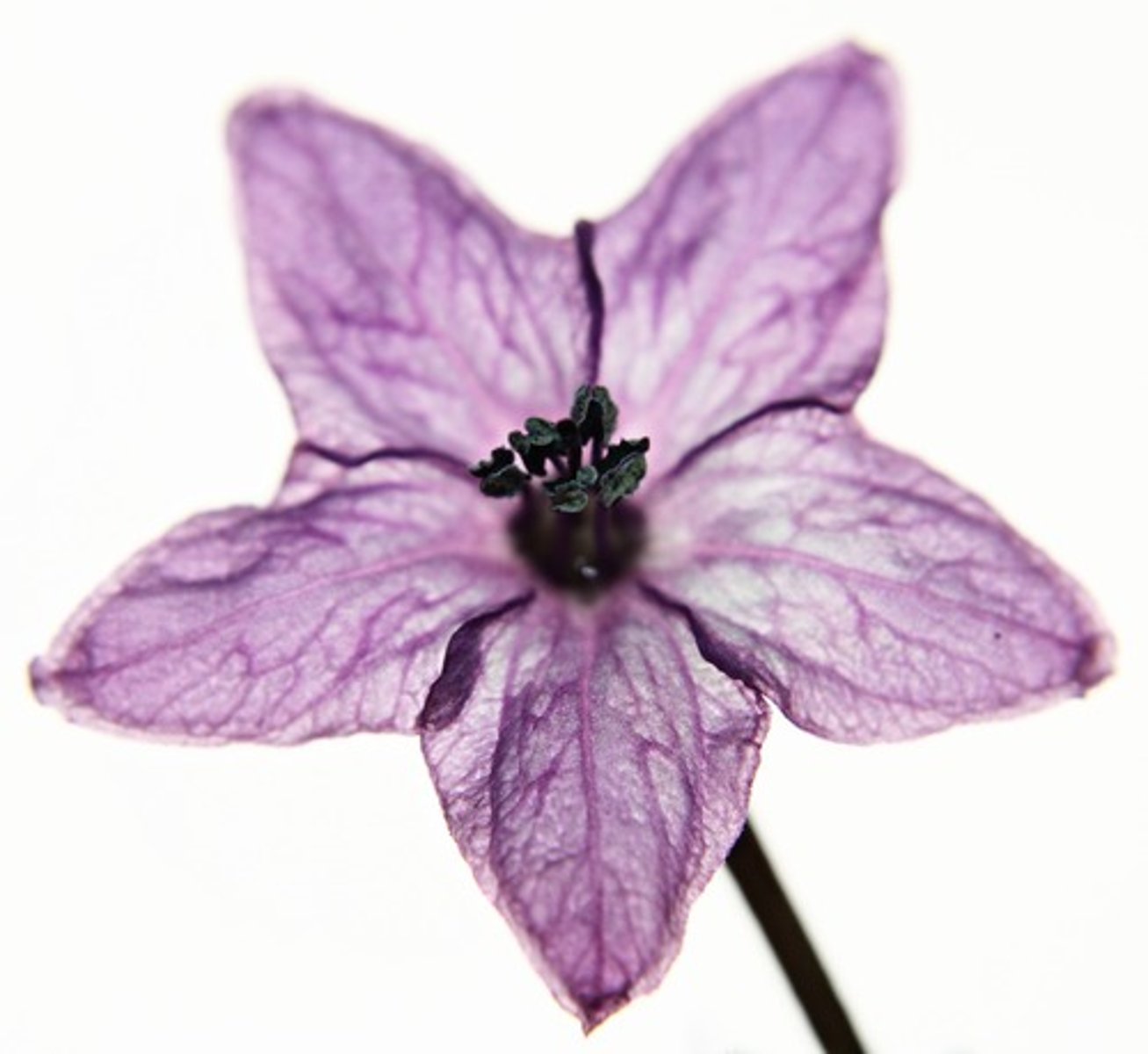

Nectar
Plant fluid that attracts insects for pollination
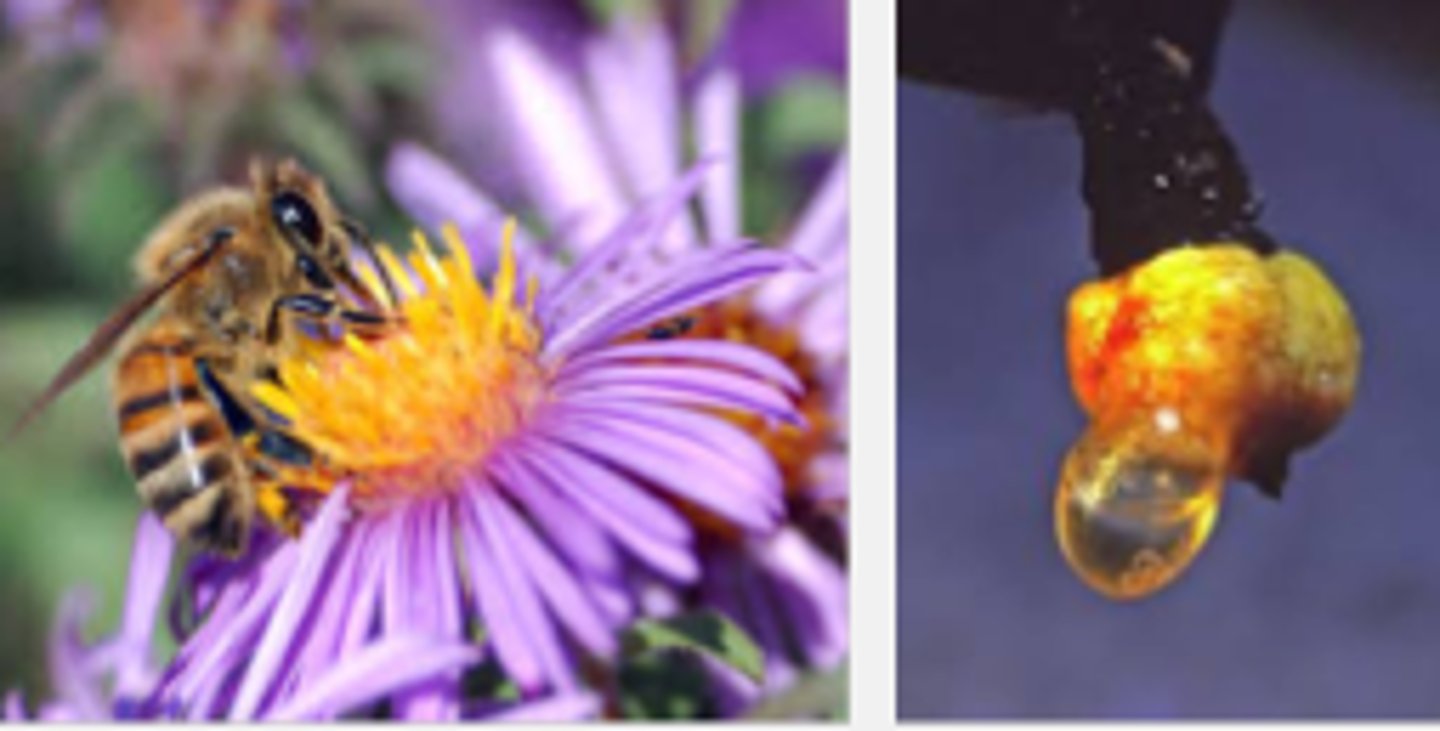

Pollination Syndrome
Suites of flower characters that are associated with certain types of pollinators and that have evolved through natural selection imposed by the interaction between flowers and pollinators.
Pollen
A fine dust that contains the sperm of seed-producing plants
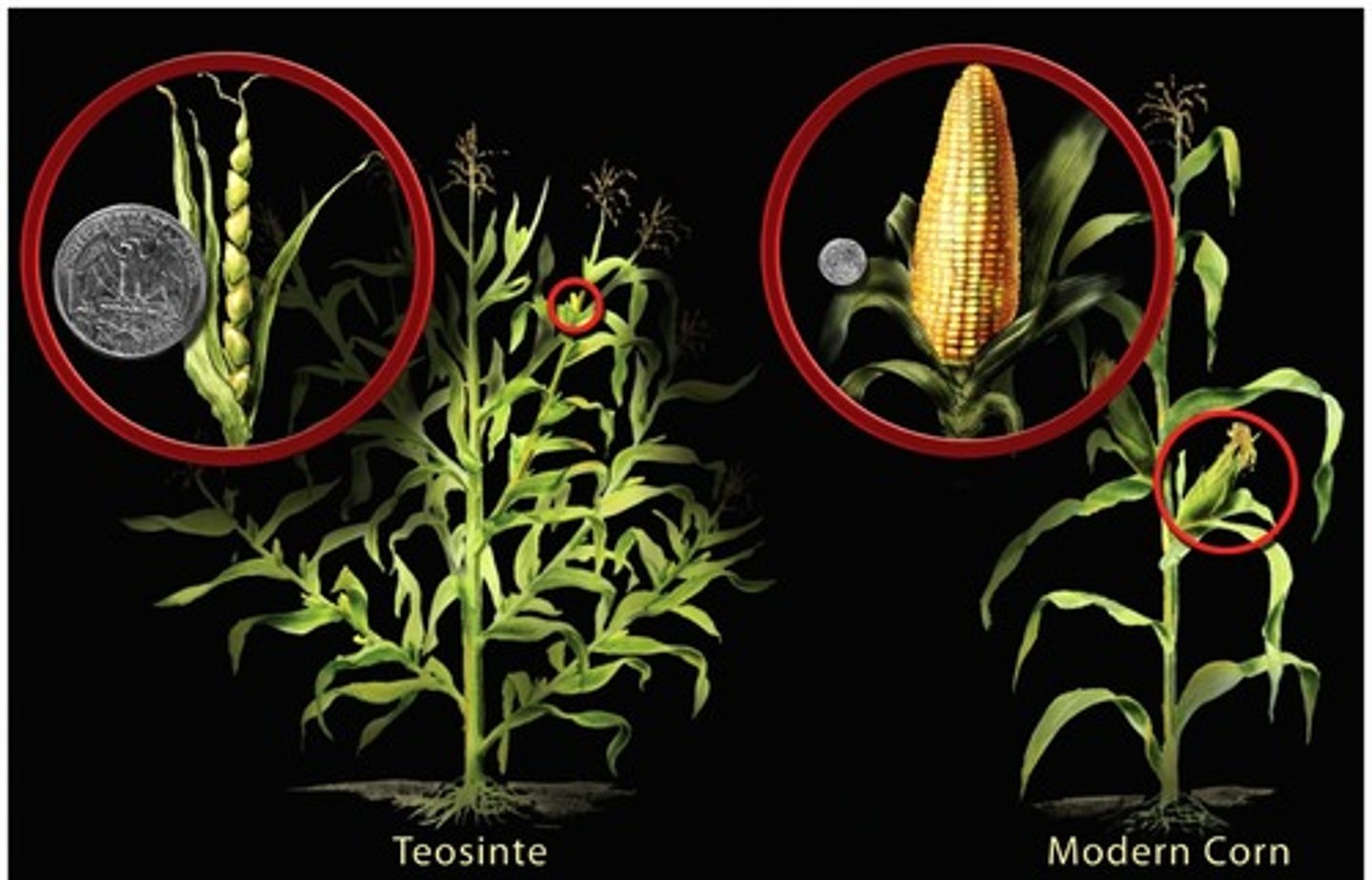
Teosinte
A wild grass found in the highlands of Mexico, is the wild ancestor of maize (corn)
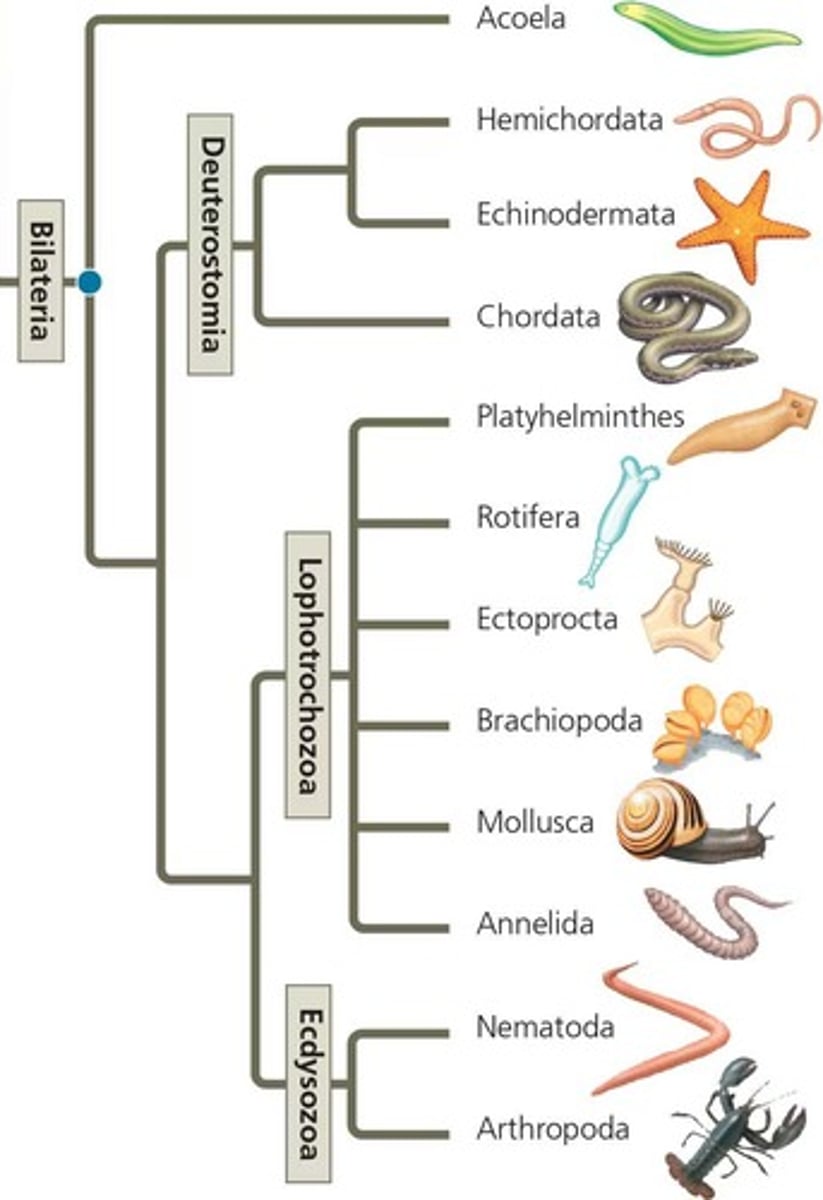
Bilateria
Members of the branch of eumetazoans possessing bilateral symmetry.
Cephalization
Concentration of sense organs and nerve cells at the anterior end of an animal
Endoderm
the inner germ layer that develops into the lining of the digestive and respiratory systems
Mesoderm
middle germ layer; develops into muscles, and much of the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory systems
Ectoderm
outermost germ layer; produces sense organs, nerves, and outer layer of skin
Triploblastic
Organisms with three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm.
Coelomates
An animal that possesses a true coelom (a body cavity lined by tissue completely derived from mesoderm).
blastopore
The opening of the archenteron in the gastrula that develops into the mouth in protostomes and the anus in deuterostomes
Protostome
an animal whose mouth is formed from the blastopore
Deuterostome
animal whose anus is formed from the blastopore of a blastula
Ecdysozoa
Supergroup of protostomes; characterized by periodic molting of their exoskeleton. Include the roundworms and arthropods.
radial symmetry
The quality of having many lines of symmetry that all pass through a central point.
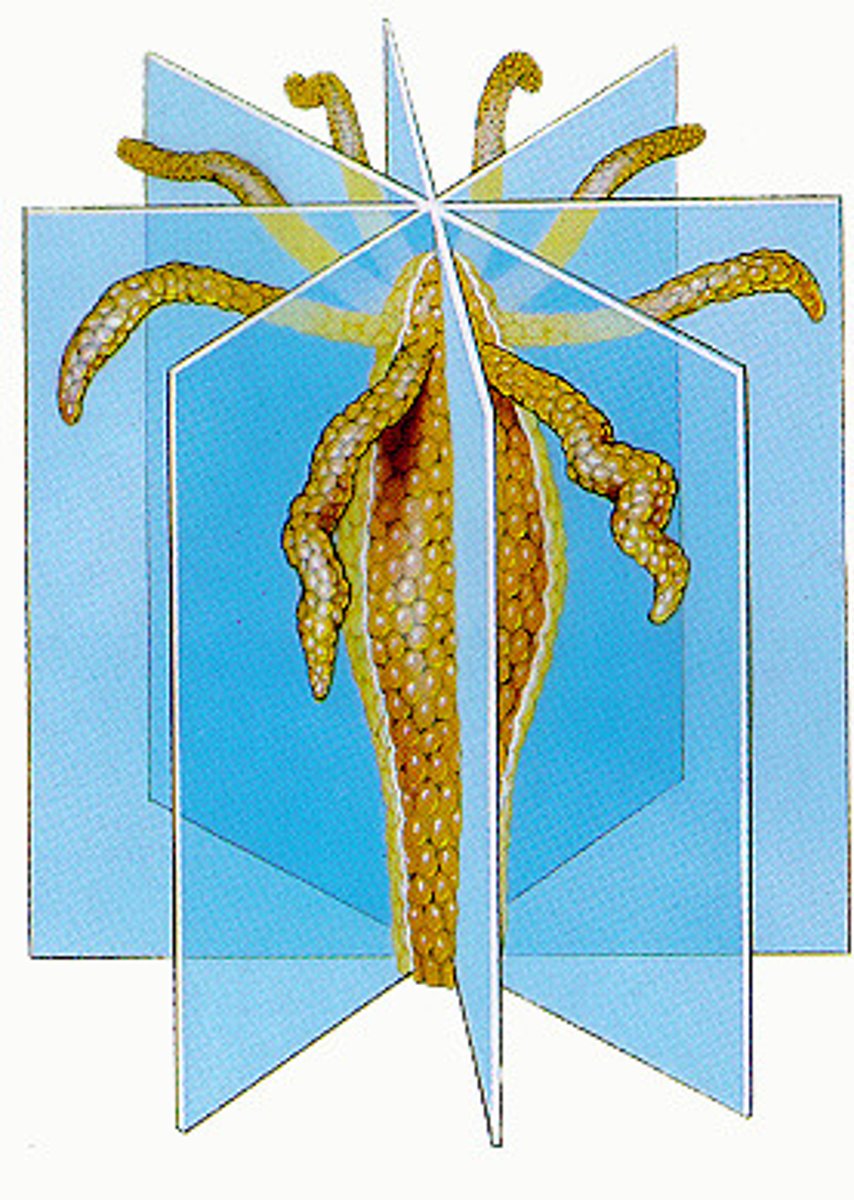
acoelomate
an animal that lacks a coelom, or body cavity
Trochophore
a free-swimming, ciliated larva of many worms and some mollusks
Sessile
Describes an organism that remains attached to a surface for its entire life and does not move
Motile
Capable of movement
Invertebrates
Animals without backbones
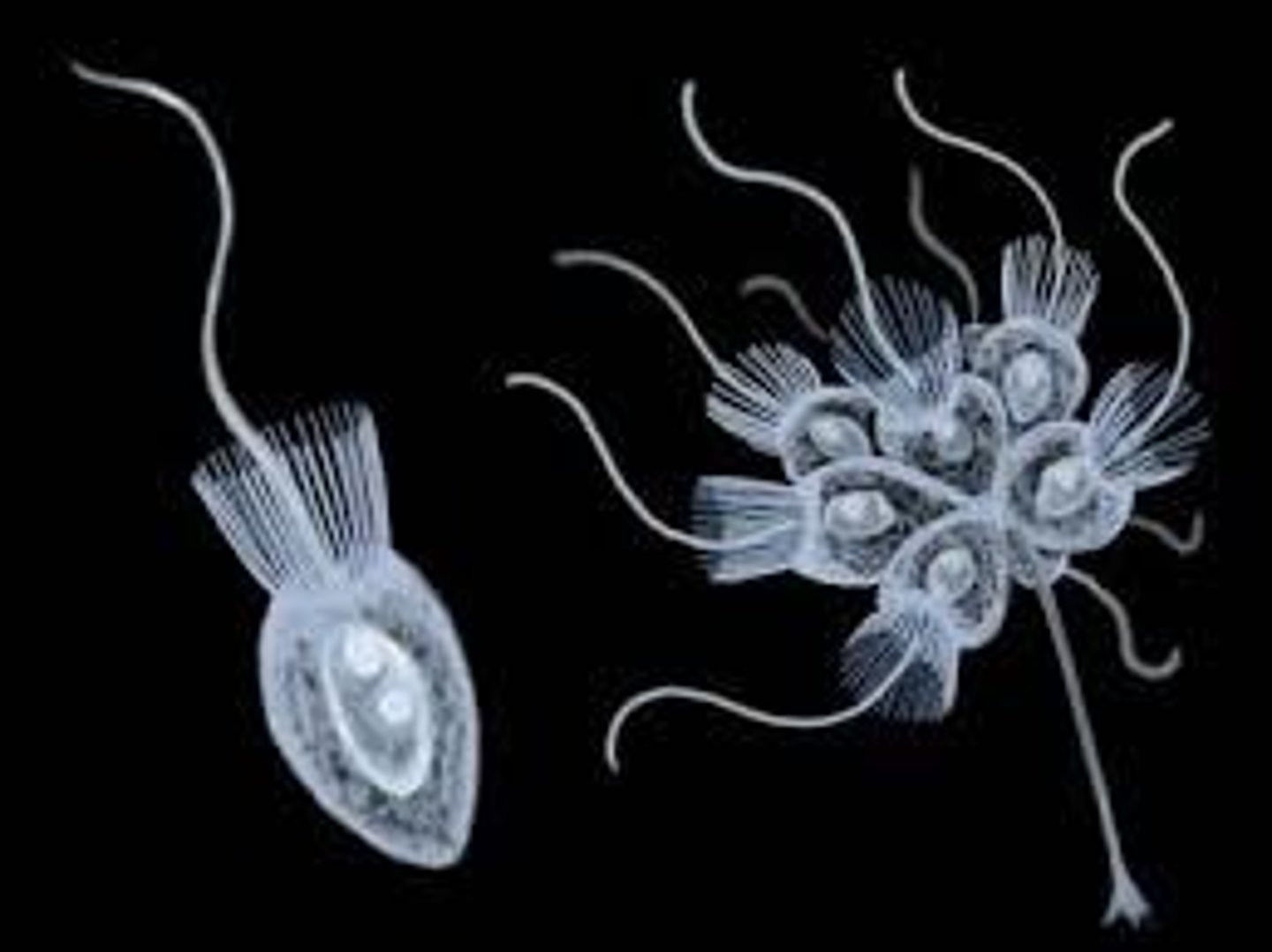
Choanoflagellates
a group of free-living unicellular and colonial flagellate eukaryotes considered to be the closest living relatives of the animals.

Medusa
body form in cnidarians where the mouth is facing down
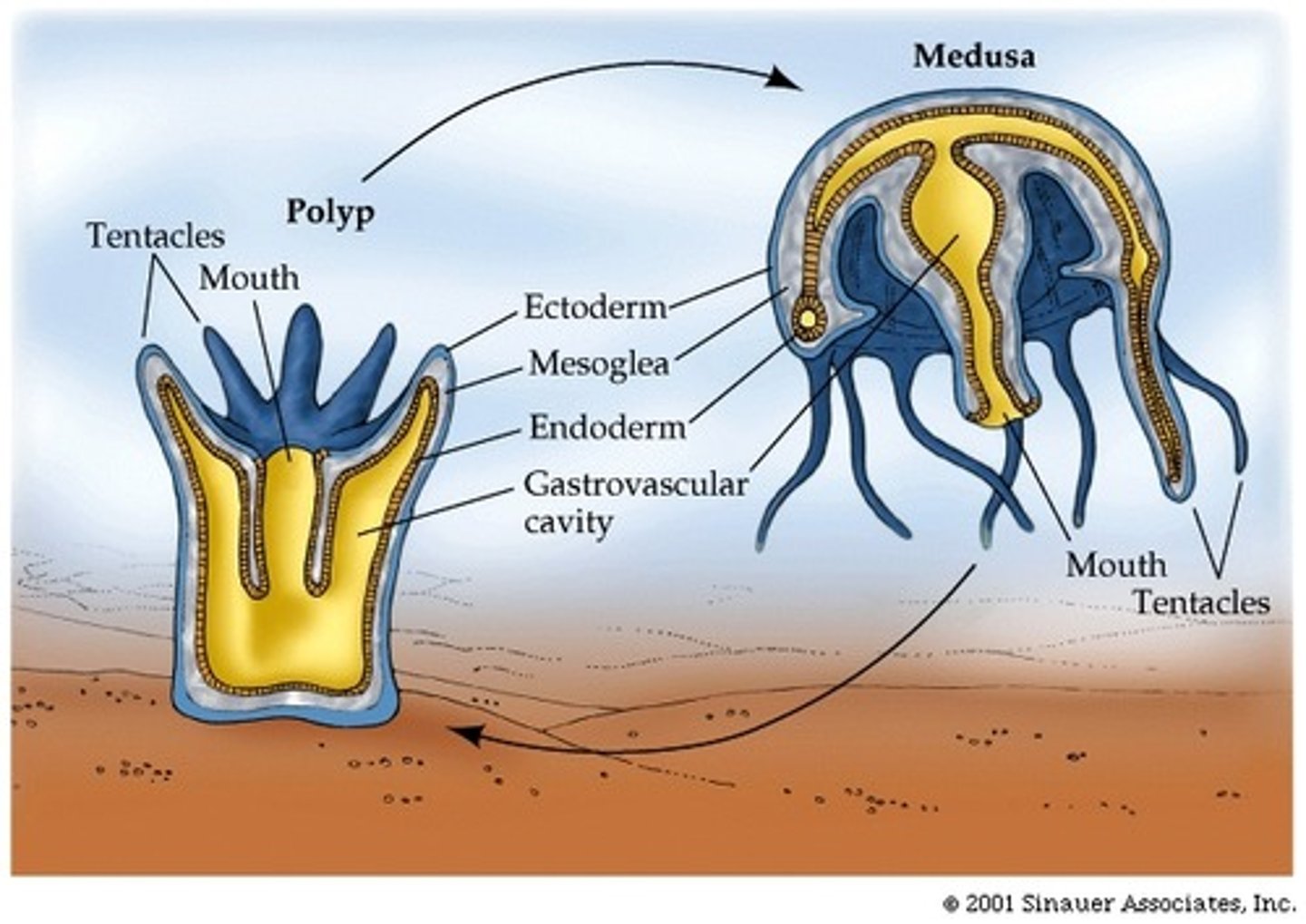
Polyp
The sessile, tubular form of a cnidarian with a mouth and tentacles at one end and a basal disk at the other

Radula
An organ covered with teeth that mollusks use to scrape food into their mouths
Annelids
A segmented worm which include earthworms, polychaetes, and leeches
Metamerism
Segmented arrangement of body parts
water vascular system
A network of hydraulic canals unique to echinoderms that branches into extensions called tube feet, which function in locomotion, feeding, and gas exchange
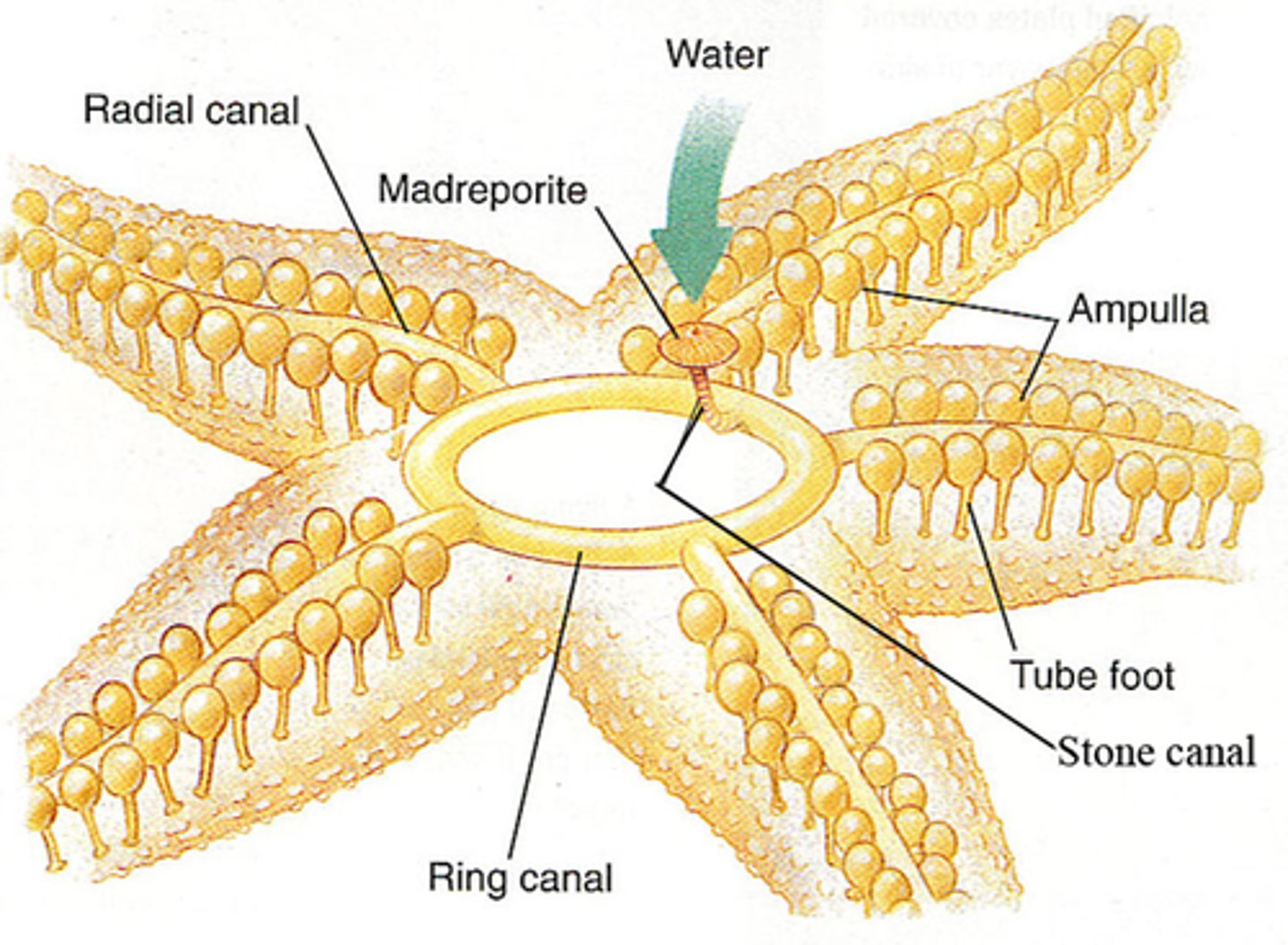
Madreporite
opening used to filter water into the water vascular system of echinoderms
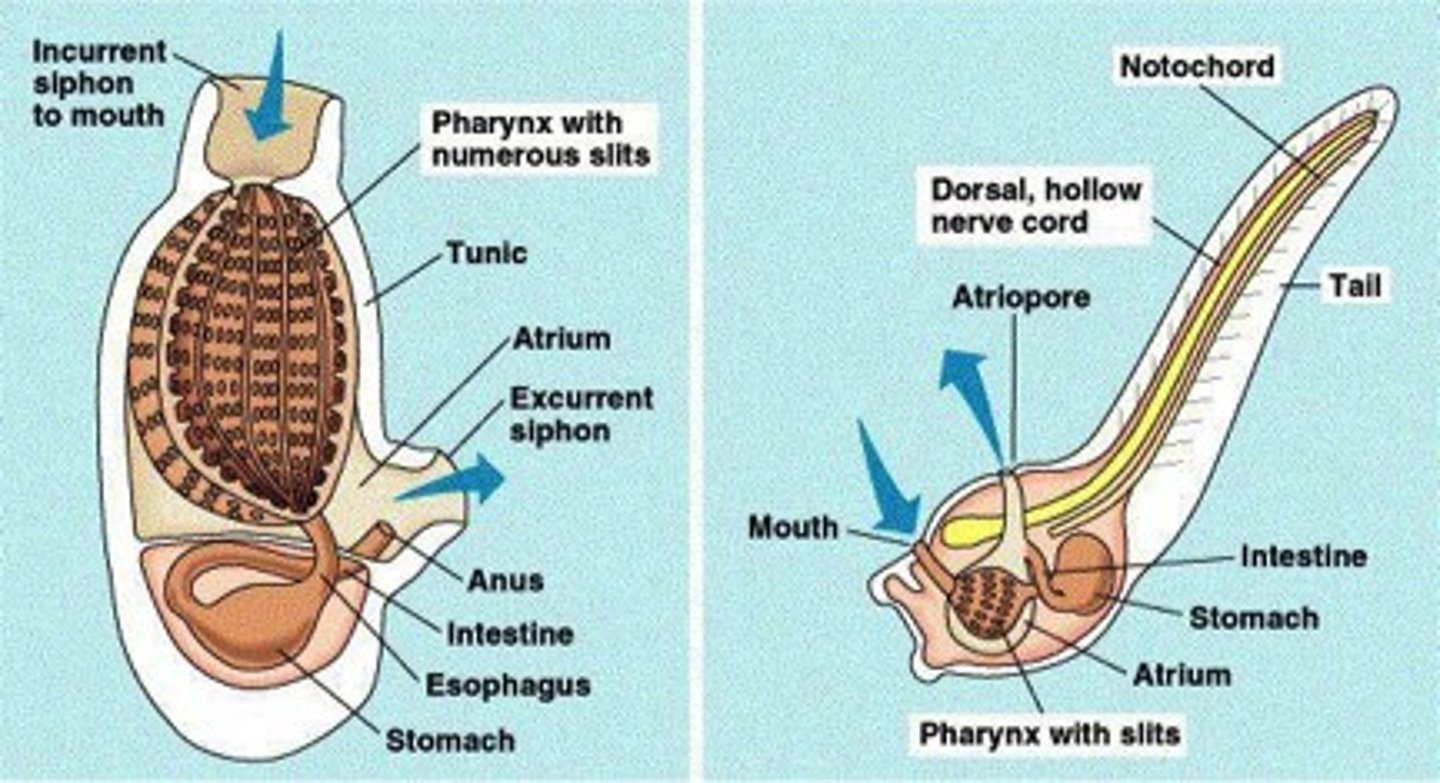
Cephalochordata
a chordate clade whose members possess a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail in the adult stage

Urochordata
tunicates, sea squirts
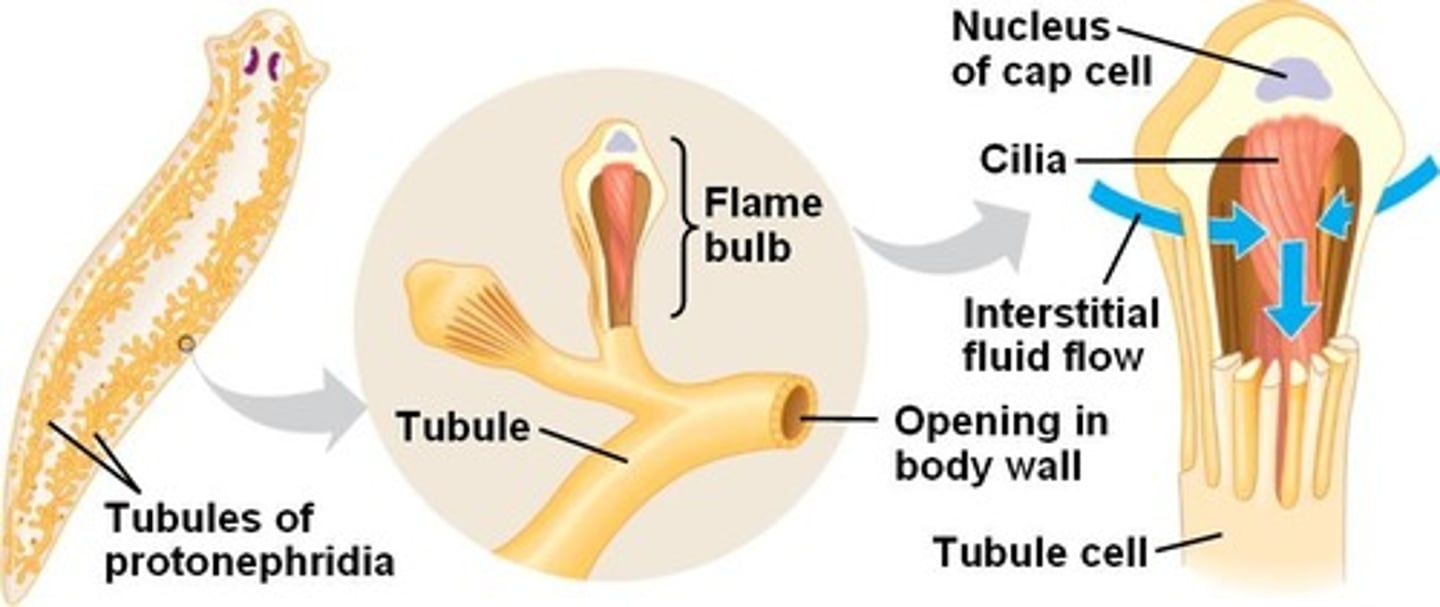
Flame cells
In flatworms (Platyhelminthes), specialized cells that remove excess water from the body.
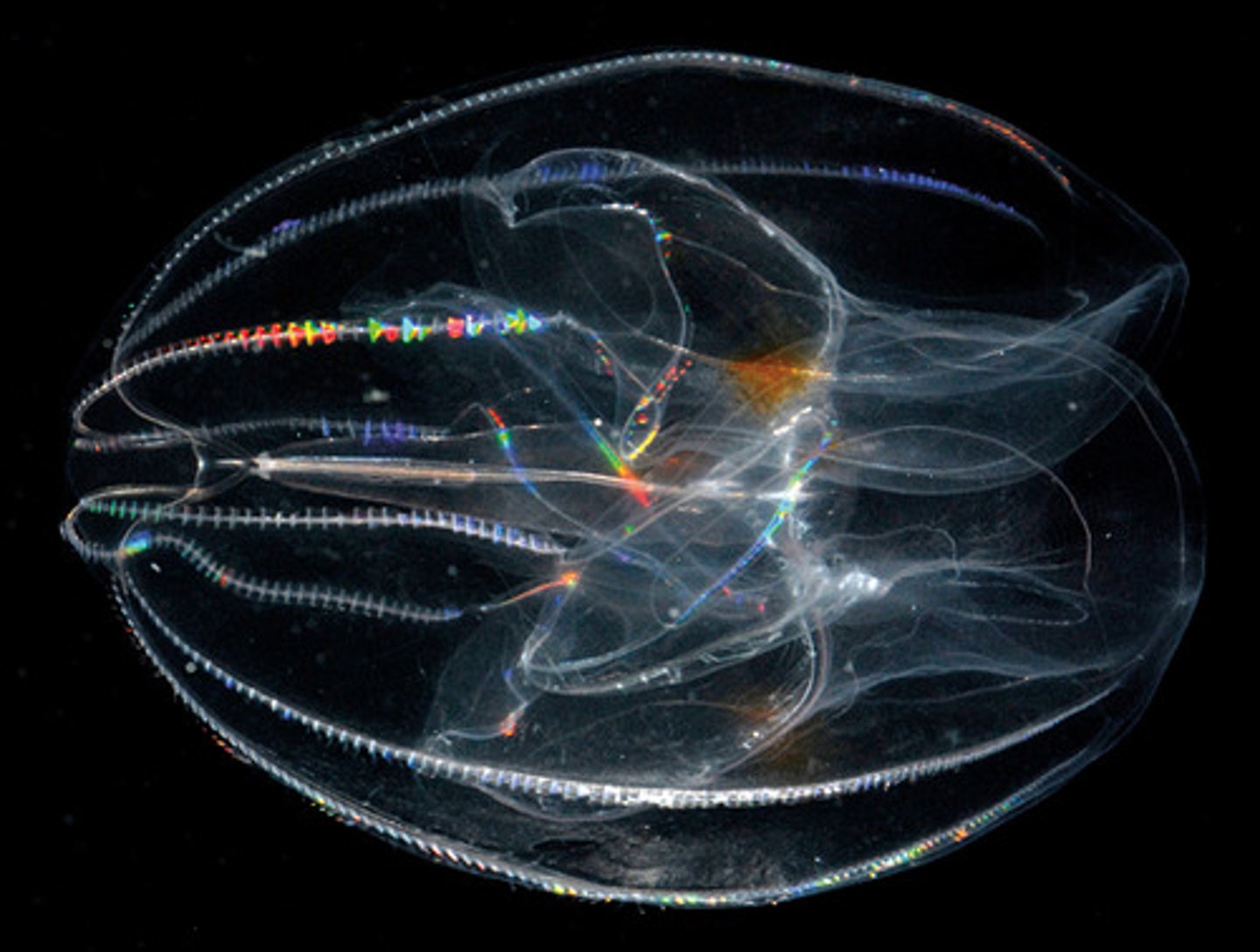
Ctenophores
radially symmetrical
diploblastic
complete gut
Metamorphosis
changing of one body form to another within a species
endothermic
Animals capable of producing their own body heat by way of metabolism and of retaining it
follicles
Structure in the dermis of the skin from which a strand of hair grows.