Background radiation and radiation dose: Atomic structure: Physics: GCSE (9:1)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Background radiation
Radiation that is around us all of the time
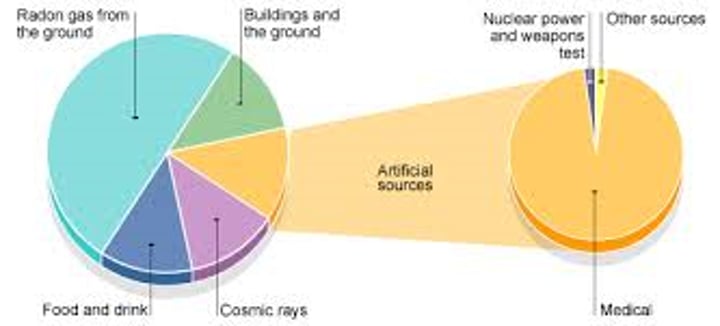
Sources of background radiation
Natural sources such as rocks and cosmic rays from space and man-made sources such as the fallout from nuclear weapons testing and nuclear accidents
Factors affecting exposure to background radiation
Location and occupation among other things
Activity
The number of decays per second from an unstable nucleus
Becquerel (Bq)
The SI unit for activity
Why activity is unsuitable to measure radiation exposure
The activity of two sources could be the same, but one could emit alpha whereas the other emits beta (so they would each have a different effect on a person)
When alpha radiation is more dangerous to a person than beta
When the radioactive source is inside the body
Why alpha radiation is more dangerous to a person than beta when inside the body
An alpha particle is more ionising and it cannot penetrate the skin so will not be able to escape from the body
When beta radiation is more dangerous to a person than alpha
When the radioactive source is outside the body
Why beta radiation is more dangerous to a person than alpha when outside the body
A beta particle is less ionising but it can penetrate the skin so will be able to pass into the body
Radiation dose
A measure of the amount of damage that would be caused by the absorption of 1 joule of energy per kilogram of body mass
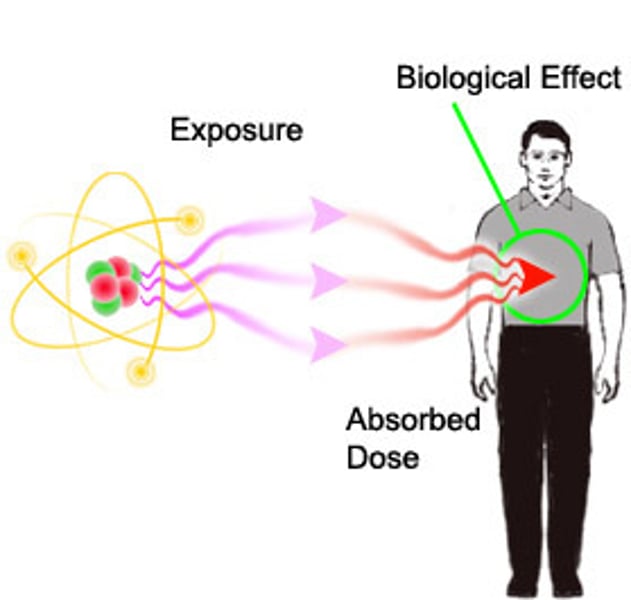
Sievert (Sv)
The SI unit for radiation dose
Millisievert (mSv)
A more commonly used unit for radiation dose, as absorption is usually less than 1 Sv
1 sievert (Sv) is equal to _____ millisieverts (mSv)
1,000 millisieverts (mSv)
Radiation dose from eating a banana
Approx. 0.00001 mSv (if it contains radioactive potassium)
Radiation dose from 3 months on the ISS (International Space Station)
40 mSv
Typical radiation dose that can lead to death
10 Sv (10,000 mSv)