Chem 2- Valence bond theory (*exam 1)
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
advanced theories of covalent bonding
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
what can you use quantum mechanics to predict?
the specific regions around an atom where electrons are LIKELY to be located
how are s-orbitals shaped?
S-orbitals are spherical in shape, indicating that the probability of finding an electron is uniform in all directions around the nucleus.
how are p-orbitals shaped?
P-orbitals are dumbbell-shaped, with two lobes on opposite sides of the nucleus, indicating that the probability of finding an electron is higher in these regions.
what is Valence bond theory?
Valence Bond Theory is a model that explains how atoms bond by overlapping their atomic orbitals to form covalent bonds, emphasizing the role of electron pairs in bond formation.
how do orbitals on two different atoms overlap?
a portion of one orbital and a portion of another orbital combine, leading to the formation of a covalent bond, resulting in increased electron density between the two nuclei.
what are the two conditions that must be met in order for a covalent bond to result? (according to Valence bond theory)
1) An orbital on one atom overlaps an orbital on a second atom
2) the single electron sin each orbital combine to form an electron pair
what is a covalent bond?
A type of chemical bond formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, resulting in a stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces.
what does the strength of a covalent bond depend on
the extent of the overlap of the orbitals involved.
are bonds stronger with orbitals that overlap less or orbitals that overlap extensively?
orbitals that overlap extensively
what does the energy of the system depend on?
how much the orbitals overlap.
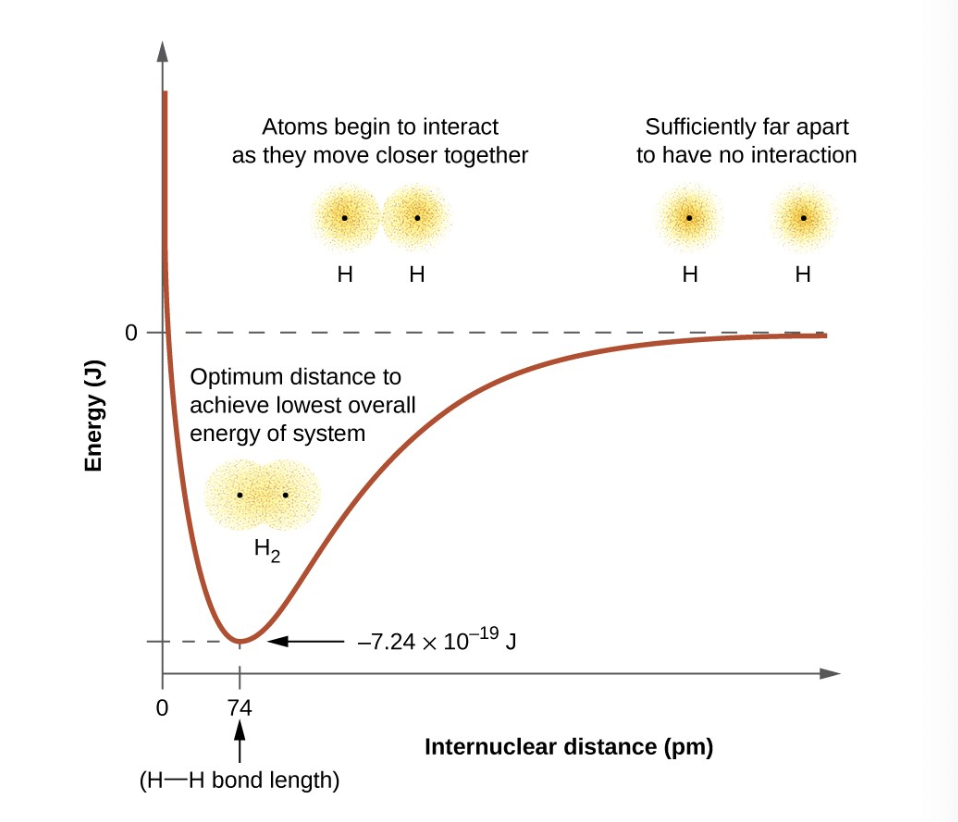
what is the bond energy?
the difference between the energy minimum and the energy of the two separated atoms. the quantity of energy released when the bond is formed (the same amount of energy is required to break the bond!)
what occurs at the bond distance
bond energy
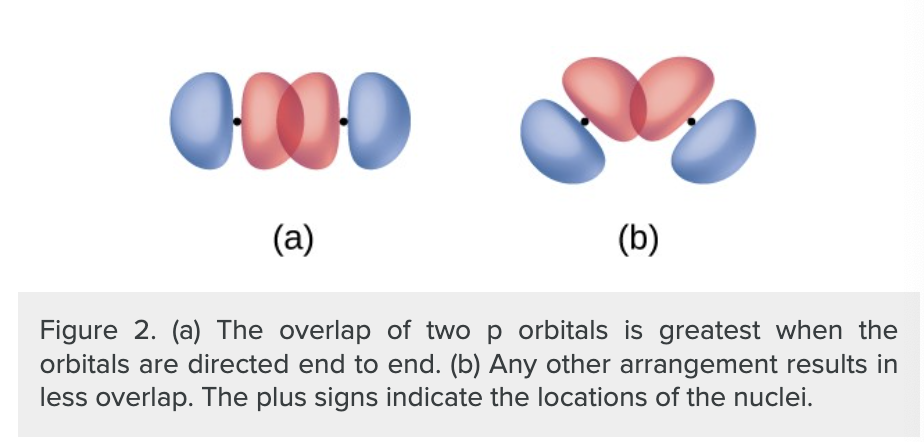
does the orientation of orbitals affect their overlap?
yes (other than for two s orbitals because theyre spherically symmetric.
what produces sigma bonds?
the overlap of two s orbitals
the overlap of an s orbital and a p orbital
the end-to-end overlap of two p orbitals
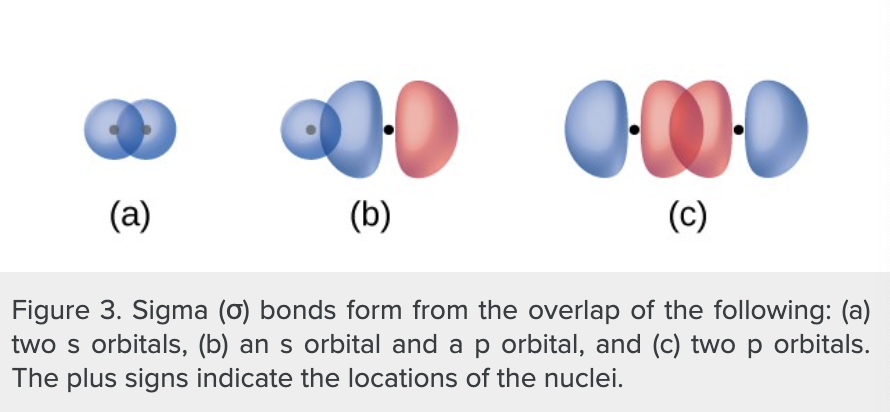
what is a sigma bond?
a covalent bond where the electron density is concentrated in the region along the internuclear axis
single bonds in lewis structures are described as sigma bonds in VBT
what is the internuclear axis
a line between the nuclei of the two atoms that participate in a bond, around which the bonded electron density is symmetrically distributed.
what is a pi bond?
type of covalent bond that results from the side-by-side overlap of two p orbitals
the regions of orbital overlap lie on opposite sides of the internuclear axis which has nodes
what is a node?
a plane with no probability of finding an electron
how many sigma/pi bonds do single bonds contain? how many sigma/pi bonds do double bonds contain? how many sigma/pi bonds do triple bonds contain?
1 sigma bond NO pi bonds
1 sigma bond ONE pi bond
1 sigma bond TWO pi bonds