I-V graphs
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What does Ohm’s Law state?
The current through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across it
What is a ohmic conductors?
Electrical conductors that obey Ohm's Law
Examples of ohmic conductors?
Fixed resistors, wires, heating elements.
Equation for Ohm’s Law?
V = I × R
When is the Ohm’s law irrelevant?
When not at constant temperature
What does an I–V graph for an ohmic conductor look like?
Straight line through the origin.
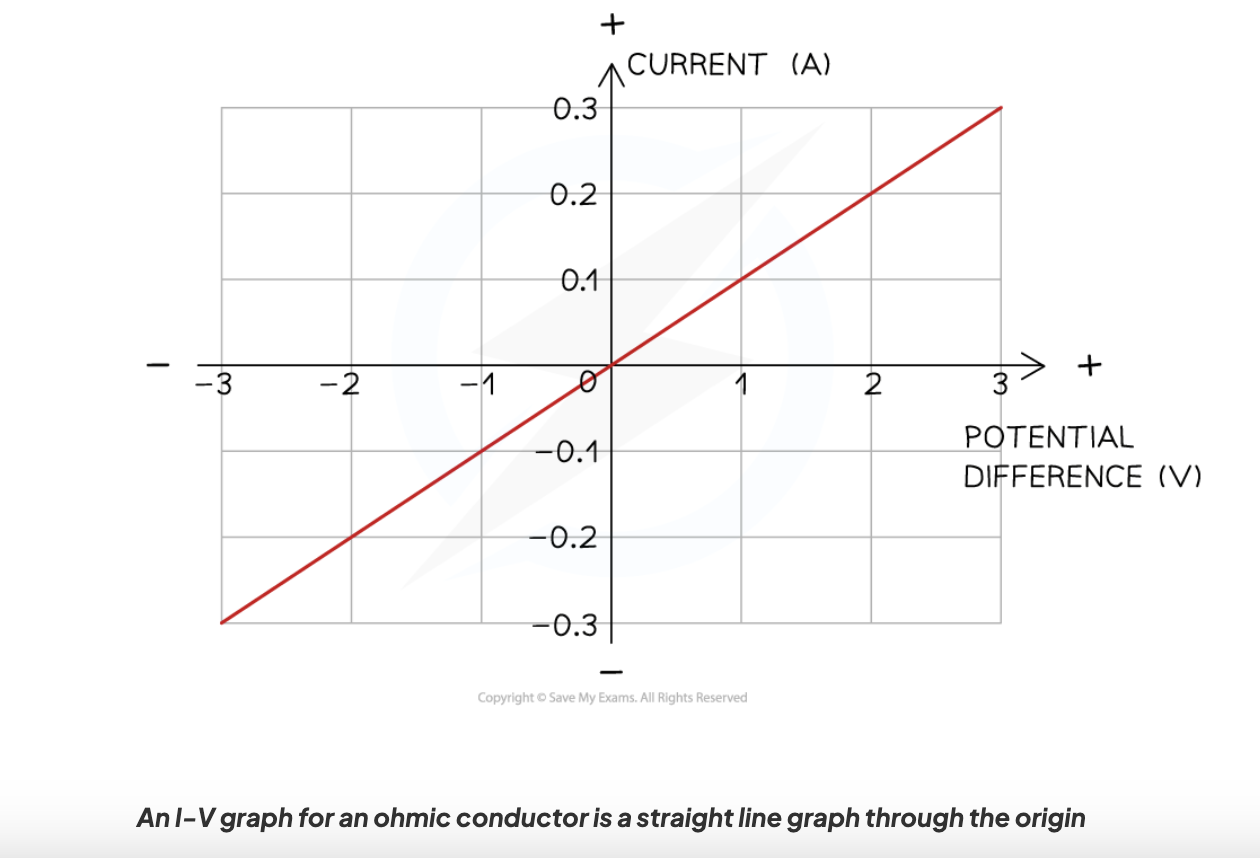
What happens to the I-V graph of an ohmic conductor when reversing the potential difference (and direction of the current)?
no difference to the shape of the line, the potential difference and current values will just be negative
What does it mean when a conductor is a non-ohmic?
the current and potential difference are not directly proportional
Why is a filament lamp non-ohmic?
Its resistance increases as temperature increases.
What does the I–V graph of a filament lamp show?
Curve → the current increasing at a proportionally slower rate than the potential difference
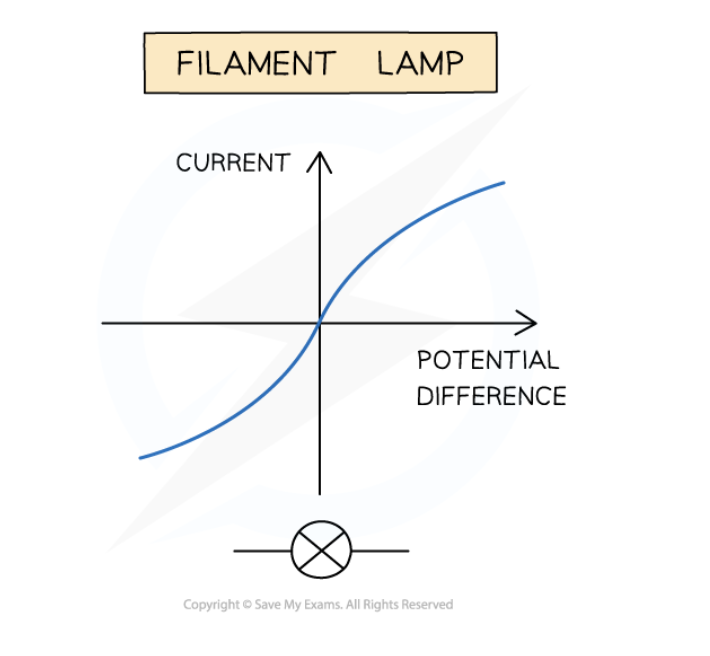
Why is a filament lamp a non-ohmic conductor?
current increases → the temperature of the filament in the lamp increases → resistance increases → opposes current → current increase at slower rate
Why does resistance increase as temperature increases?
Atoms vibrate more → electrons collide with them → impedes flow → reducing current.
What is a diode?
A non-ohmic conductor that lets current flow in one direction only.
What is forward bias in a diode?
Current flows in the same direction as the arrow symbol.
What is reverse bias in a diode?
Current is blocked (very high resistance).
What does the I–V graph of a diode look like?
Flat (no current) in reverse, sharp rise in forward bias only after significant voltage.
What is an LED?
A diode that emits light when current flows through it.
What does the I–V graph of a LED look like?
Flat (no current) in reverse, sharp rise in forward bias only after significant voltage.
What is meant by linear vs non-linear components?
Linear → straight line I–V graph (constant resistance).
Non-linear → curved I–V graph (resistance changes).
Examples of linear components?
Fixed resistors, wires, heating elements.
Examples of non-linear components?
Filament lamps, diodes, LEDs, LDRs, thermistors.
Can a component change from linear to non-linear? Give an example.
Yes — some components are linear at low current, but become non-linear at high current (because temperature increases).
Example: A fixed resistor is linear at room temperature but becomes non-linear when very hot.