1.2.4 Price Elasticity Of Demand
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Price elasticity of demand
measures to the extent of the extent to which the quantity of a product demanded changes in response to change in price
Elacticity
measures the responsiveness of demand to change in a relevant variable - such as price or income
Factors that influence our sensitivity to price changes
Substitutes - The greater the choice the easier it is for consumers to switch to similar alternatives, e.g. if Coke increased their prices then people would likely switch to Pepsi.
Necessity or luxury - Necessities like petrol will be bought even if its price increased significantly; e.g. luxury items such as exotic holidays can be forsaken if they become too expensive as we can live without them!
Addictive nature - If we buy a product out of habit or, in more extreme cases, have an addiction, then we generally ignore minor price rises, e.g. cigarettes, morning Starbucks etc.
Proportion of income - If a product takes up a major chunk of our income then we are more likely to notice price changes, e.g. confectionary is quite cheap relative to our incomes, whereas cars may cost an entire year's salary!
Price Elasticity of Demand Equation (PED)
% change in Demand / % change in Price
% change = new - original / original x100
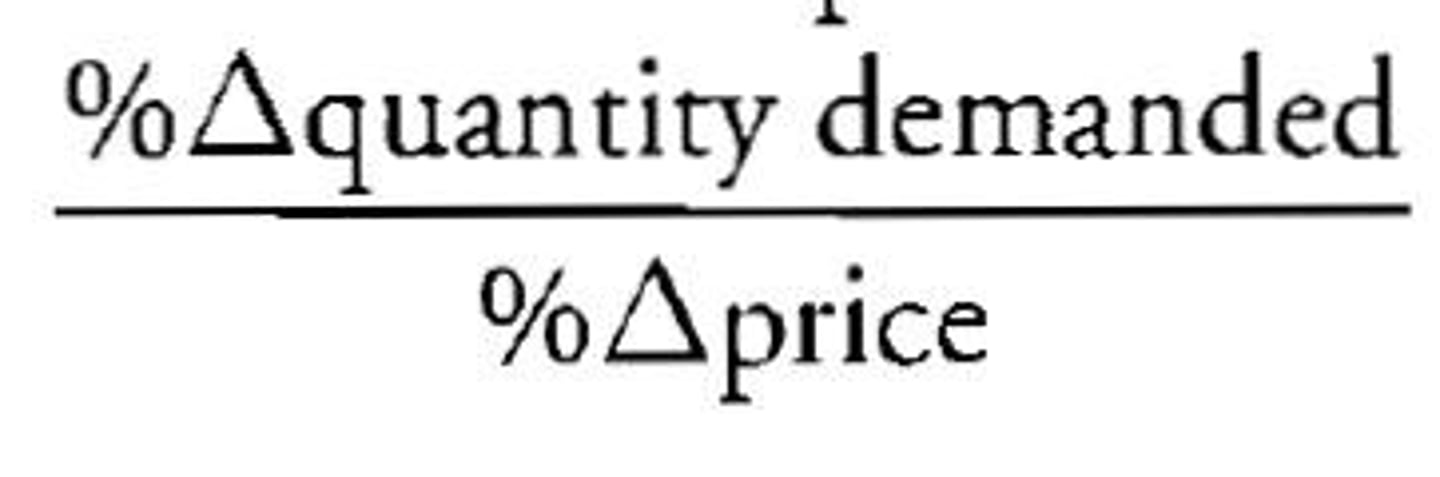
PED value 0
0 = Perfect inelastic
-Price has no effect on demand ie quantity is fixed (will be vertical)
PED value 0 to -1
0 to -1 = Inelastic
-Price has a small effect on demand
PED value -1
-1 = Unitary Elastic
-A price change results in a proportional change in demand
PED value below -1/ PED value above 1
Below -1/Above 1 = Elastic
Price has a big effect on demand
PED value - ∞
Perfectly elastic
consumers would stop buying a good completely if the price increases even slightly, but would buy an infinite amount at the going market price
Perfectly elastic demand is more likely if competition between firms in a market is what?
Highly competative
How does price elasticity of demand (PED) change along the demand curve?
-At zero demand or high price - minus infinity.
-At midpoint - elasticity is minus one.
-At zero price or high quantity - elasticity is zero.
PED of +/- one = maximised total revenue. The closer a product's price is to the midpoint, the higher the revenue.
If a product is price elastic in demand..
-Decreasing price = increases total revenue.
-Increasing price = decreases total revenue.