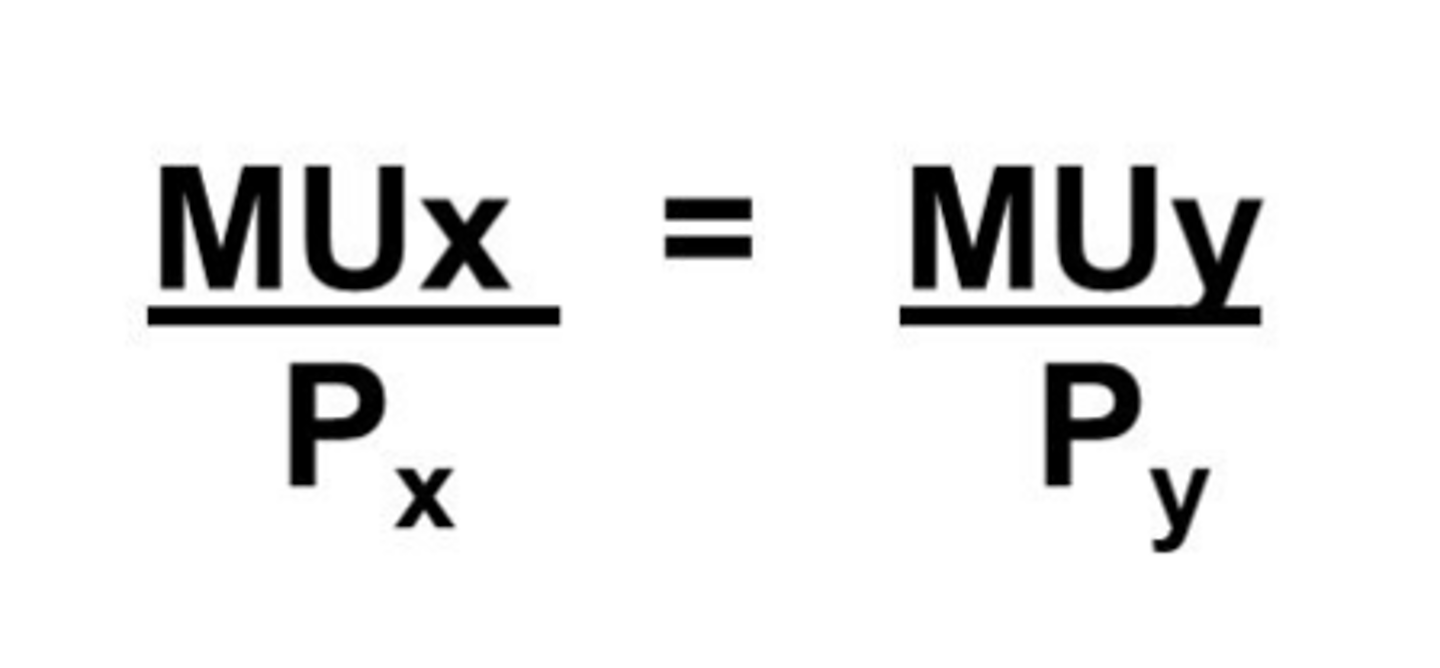AP Microeconomics Unit 1: Basic Economic Concepts
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Scarcity
Limited quantities of resources to meet unlimited wants
factors of production
Land, labor, and capital; the three groups of resources that are used to make all goods and services
capital goods
Buildings, machines, technology, and tools needed to produce goods and services.
What are the three economic questions every society must answer?
Because ALL economic resources are scarce, every society must answer three questions:
What goods and services should be produced?
How should these goods and services be produced?
Who consumes these goods and services?
What is a command economy?
an economy in which production, investment, prices, and incomes are determined centrally by a government.
What is a market economy?
A system were decisions are made by interactions between buyers and sellers. It is not controlled by the government and is used by most countries today.
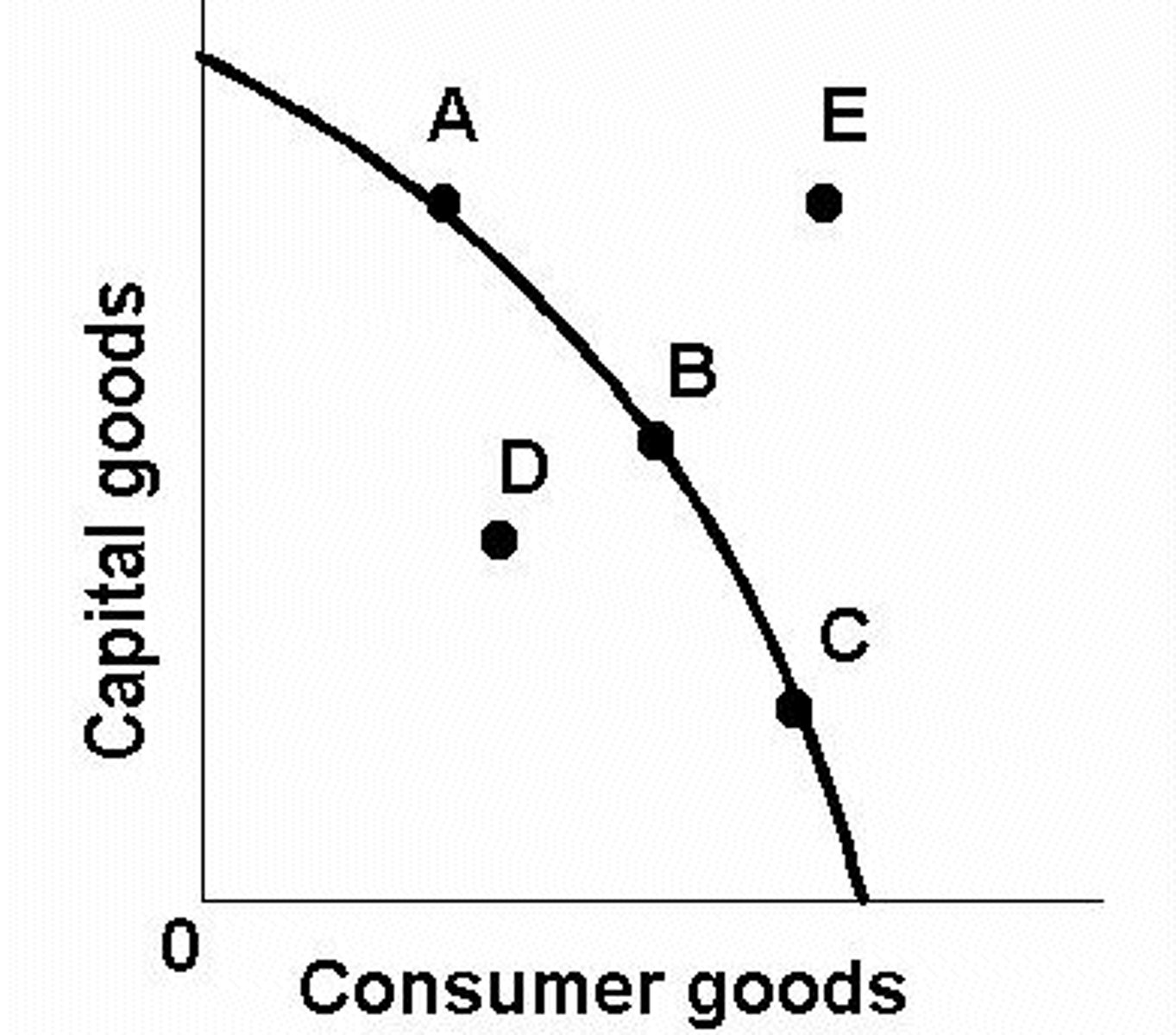
production possibilities curve
A curve showing the different combinations of two goods or services that can be produced in a full-employment, full-production economy where the available supplies of resources and technology are fixed.
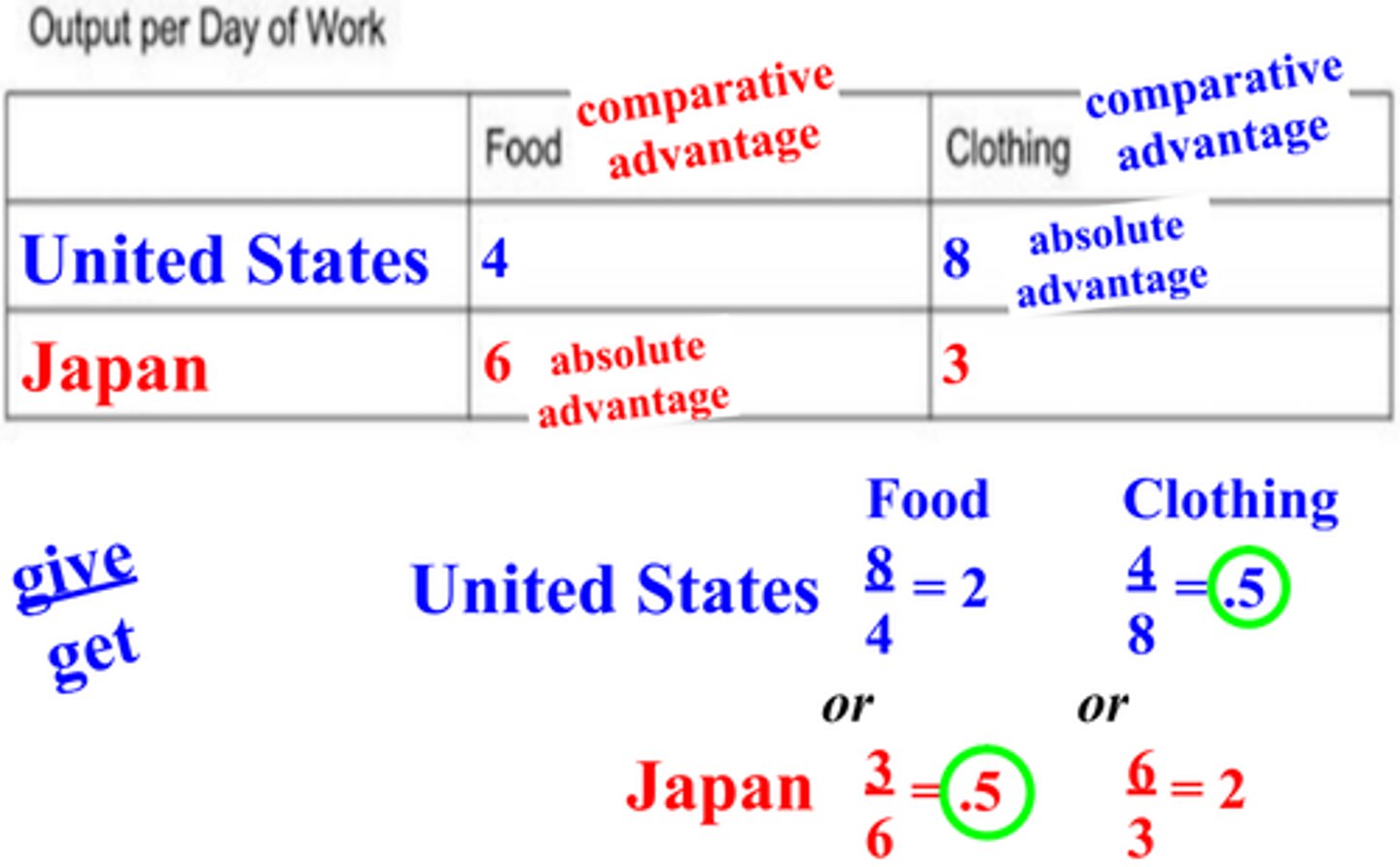
calculating opportunity cost
what you give up/what you get
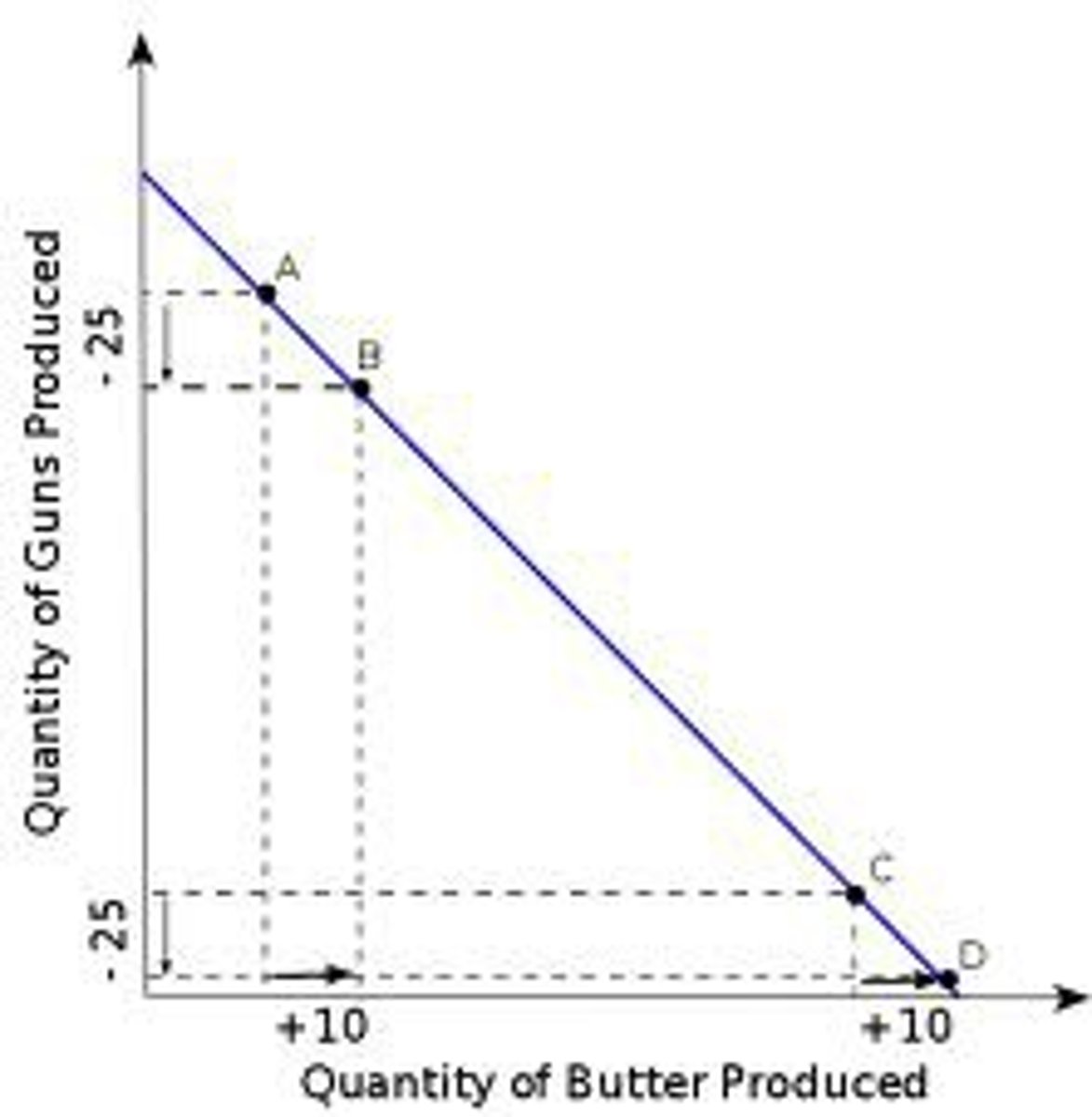
Why might producing two different products result in a constant opportunity cost?
Resources are easily adaptable between both products.
Why might producing two different products result in an increasing opportunity cost?
Resources are not easily adaptable.
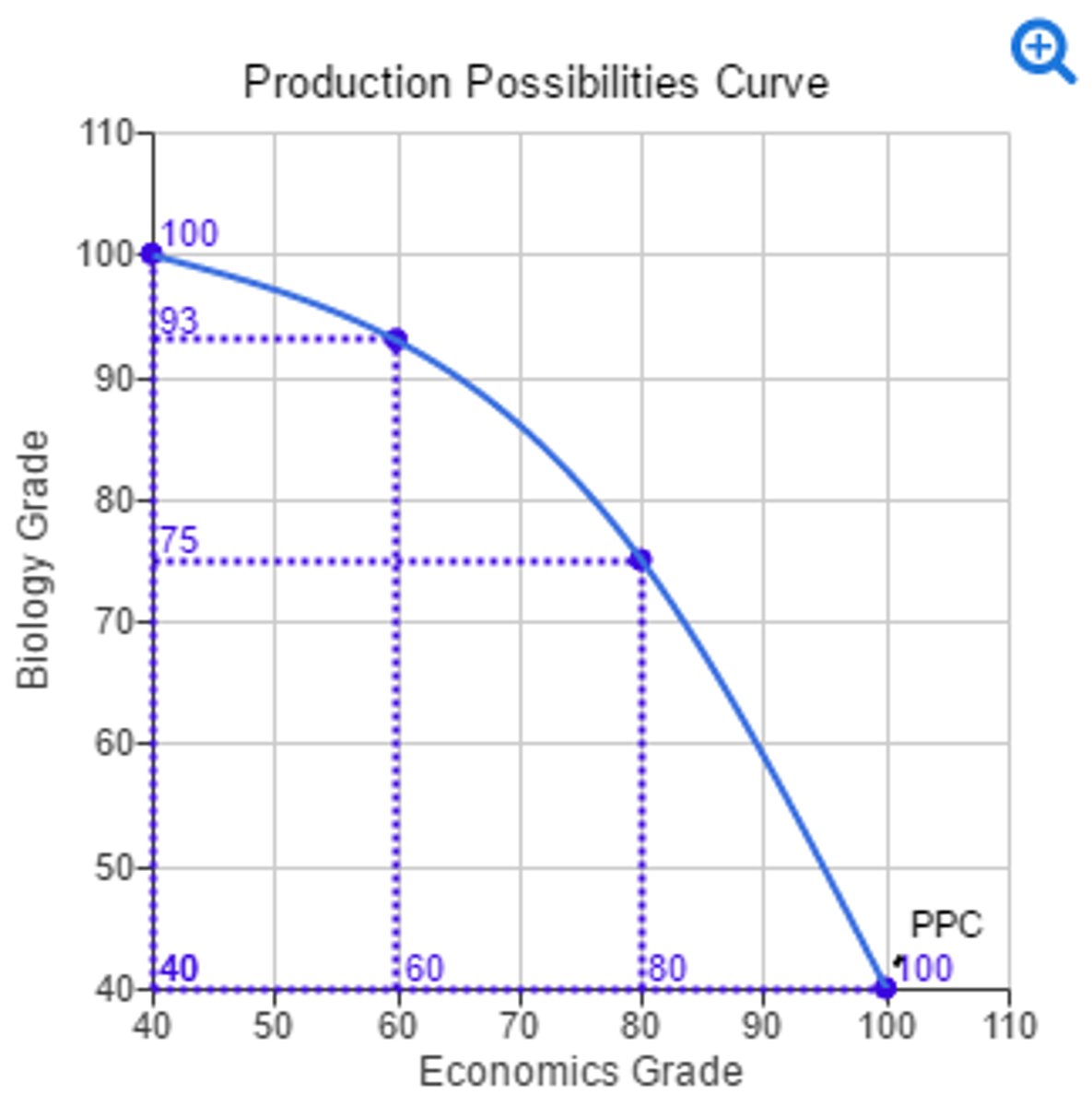
Identify three things that shift the production possibilities curve.
change in resource quality and quantity, change in technology, and change in trade
workers lose their jobs due to a recession
DOES NOT shift
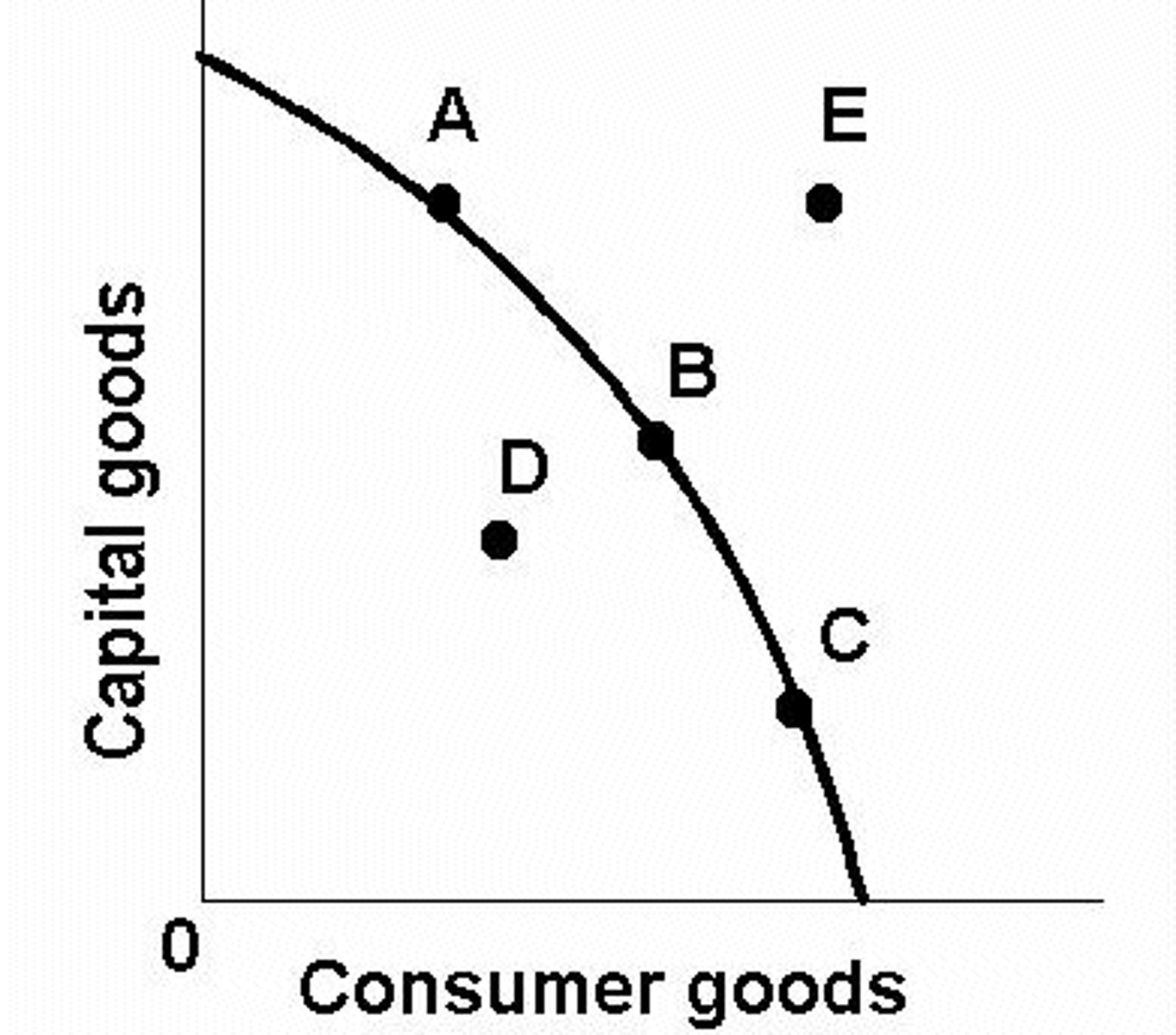
increase in consumer demand for pizza
curve does not shift, but combo does
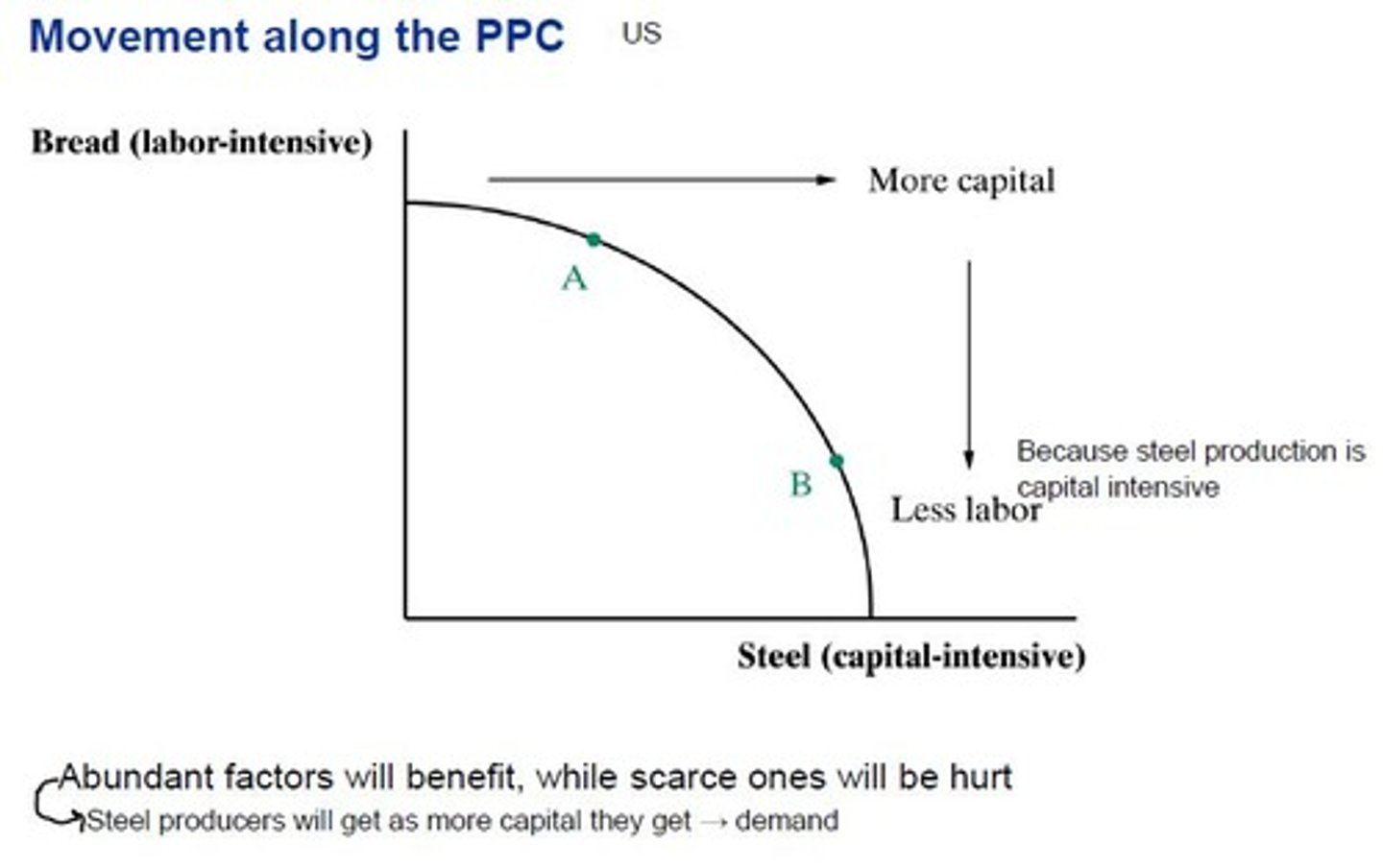
more resources to produce cars
only car production improves
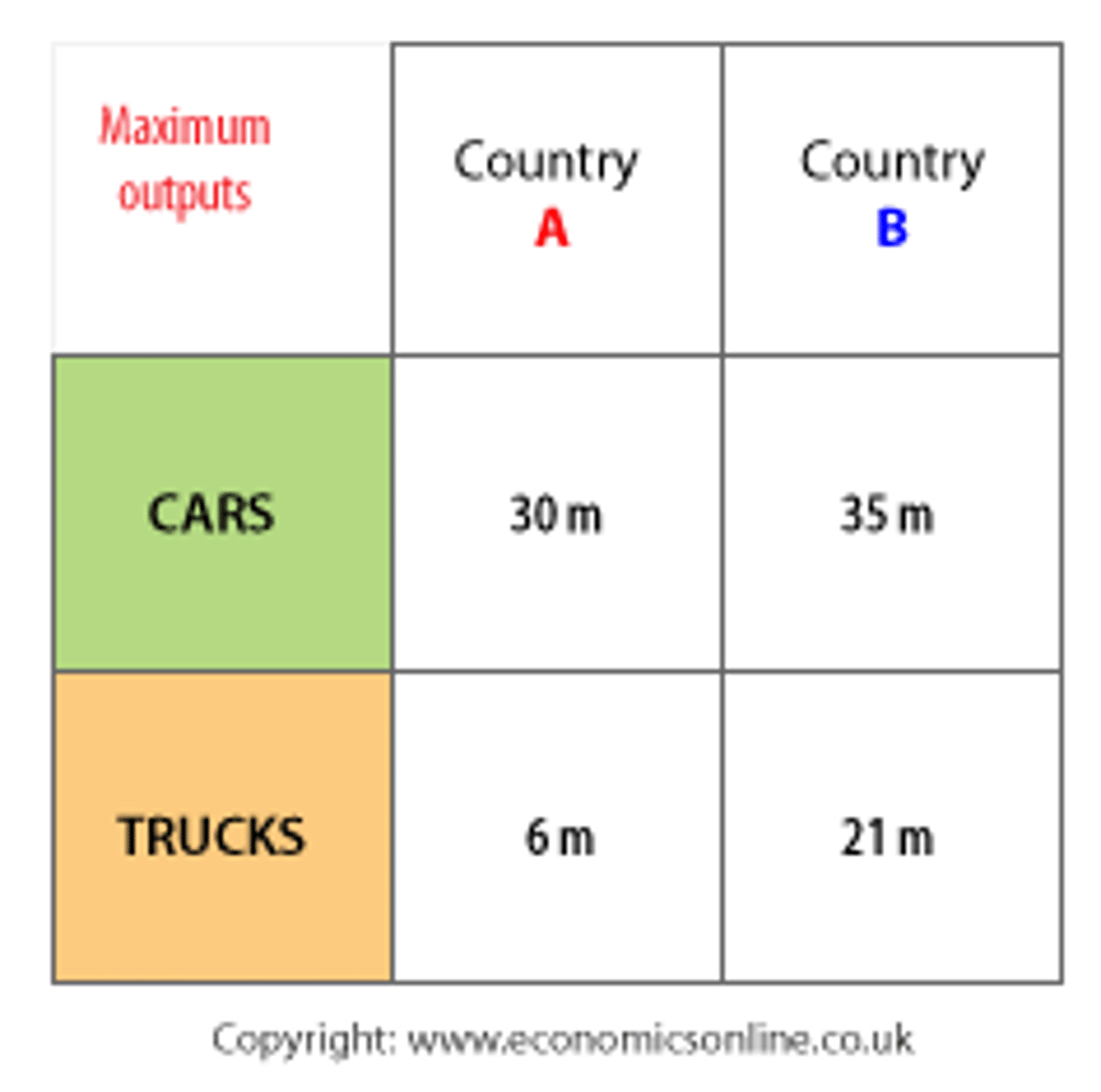
comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer
Explicit vs implicit cost
paying college tuition (explicit) vs working (implicit)
utility maximizing rule