Chapter 11 (2) & Chapter 12
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Trends in workforce diversity
age, gender, race/ethnicity, sexual orientation, disabilities, & educational levels
Barriers to diversity
stereotypes and prejudices, fear of discrimination, resistance, negative climate, lack of support, hostile environment
Stress
tension people feel when they are facing or enduring extraordinary demands, constraints, or opportunities and are uncertain about their ability to handle them effectively
Burnout
state of emotional, mental, and even physical exhaustion, expressed as listlessness, indifference, or frustration.
Sources of job related stress
demands created by individual differences, individual task demands, individual role demands, work-family conflict, group demands, organizational demands, demands created by schedules
Reducing stressors
building resilience, employee assistance, holistic wellness, supportive environment, interesting jobs, career counseling
Holistic wellness program
focuses on self-responsibility, nutritional awareness, relaxation techniques, physical fitness, and environmental awareness
Employee assistance programs
a host of programs aimed at helping employees to cope with stress, burnout, substance abuse, physical and mental health-related problems, family and marital issues, and any general problem that negatively influences job performance.
Motivation
psychological processes that arouse and direct goal-directed behavior
Extrinsic rewards
payoff, such as money, recognition, or encouragement, a person receives from others for performing a particular task
Intrinsic rewards
the satisfaction, such as a feeling of accomplishment, a person receives from performing the particular task itself
Motivation is important so that people
join, stay, work, are engaged, and put forth effort in your organization
Four major perspectives on motivation
content (needs), process, job design, & reinforcement theories
Content perspectives
need-based perspectives, are theories that emphasize the needs that motivate people
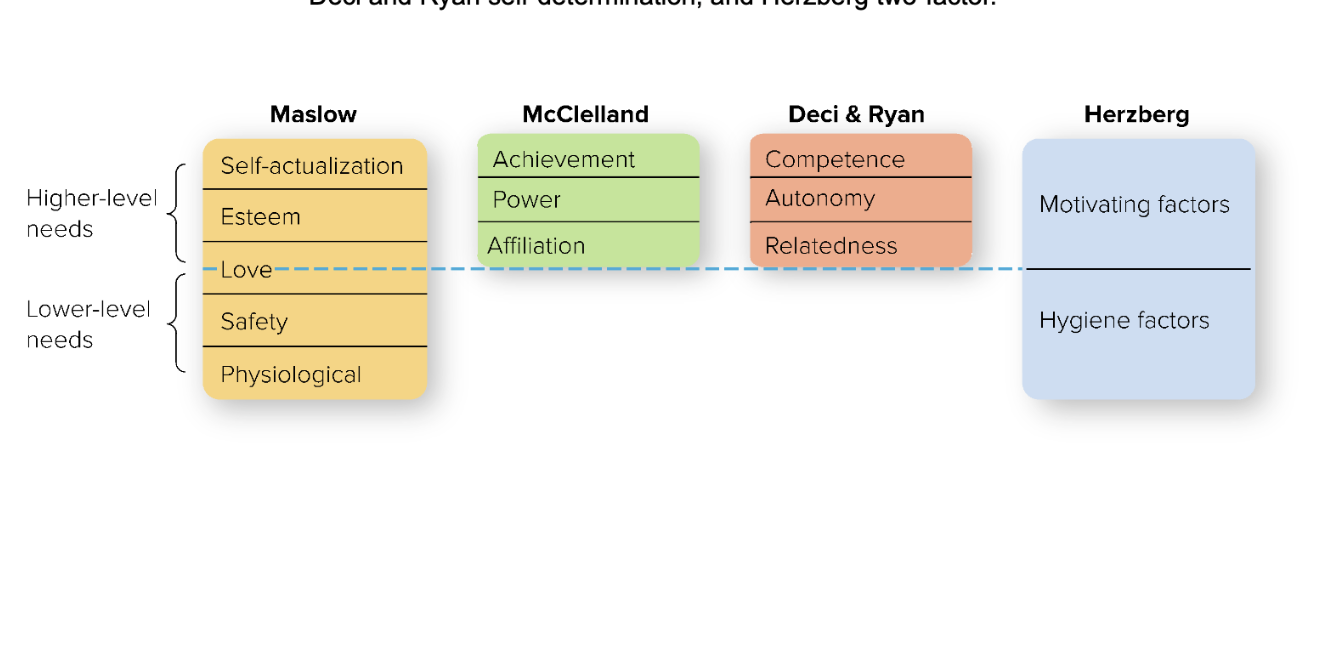
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
physiological, safety, love, esteem, & self-actualization
McClelland’s acquired needs theory
three needs—achievement, affiliation, and power—are major motives determining people’s behavior in the workplace
Important assumptions for McClelland
needs are learned & one need often dominates
Deci & Ryan’s self-determination theory
assumes that people are driven to try to grow and attain fulfillment, with their behavior and well-being influenced by three universal needs: competence, autonomy, and relatedness
Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
proposed that work satisfaction and dissatisfaction arise from two different factors—work satisfaction from motivating factors and work dissatisfaction from hygiene factors
Comparison of the content theories
Process perspectives
concerned with the thought processes by which people decide how to act—how employees choose behavior to meet their needs.
Equity/justice theory
Adams; model of motivation that explains how people strive for fairness and justice in social exchanges or give-and-take relationships.
Expectancy Theory
Vroom; deciding how much effort to exert in a specific task situation
Goal-setting theory
Locke & Latham; employees can be motivated by goals that are specific and challenging but achievable
Job design
division of an organization’s work among its employees and the application of motivational theories to jobs to increase satisfaction and performance.