Kinesiology Notes and Vocab. - Unit 2 p.1
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Exoskeleton
The skeletal structure is outside the body
Endoskeleton
Skeletal structure is on the inside of the body
Bone is living tissue that is able to regenerate when broken.
What is bone?
Begin as cartilage
Calcification that allows for the hardening of bones
Ossification; officially a bone
How are bones formed?
There are 206 bones in the body!
~300 at birth, later fused together
How many bones do we have in the body?
Cartilage
Flexible, connective tissue that is found at the ends of bones or joints
protect and help with movement
the central core of the human body—vertical axis
Axial (80 bones)
Support/structure
Protect (vital organs/structures)
Storage (calcium, minerals, fat)
RBC/WBC production
Movement (skeletal muscles support)
what are the five functions of the skeletal system?
Calcium carbonate (26%)
Calcium phosphate (26%)
collagen (20%)
water (40%)
fat (4%)
What is bone composed of?
Compact tissue (cortical)
hard outer tissue of a bone
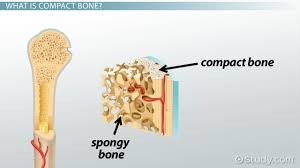
Cancellous tissue (spongy)
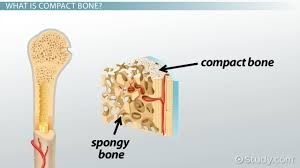
Spongy, holey tissue inside of a bone
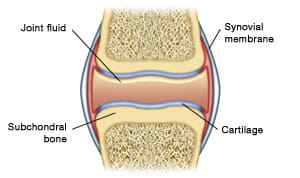
Subchondral Tissue
Smooth tissue at the ends of bones, covered by cartilage
Osteoblast Bone Cell
Cells that make and repair bone(s).
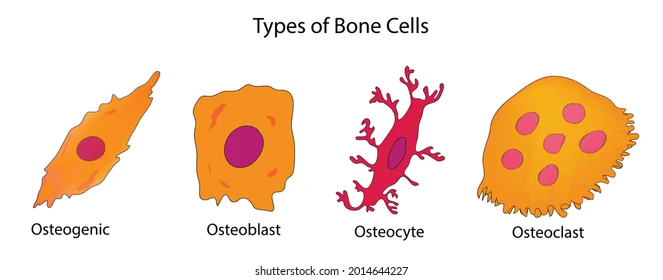
Osteocyte Bone Cell
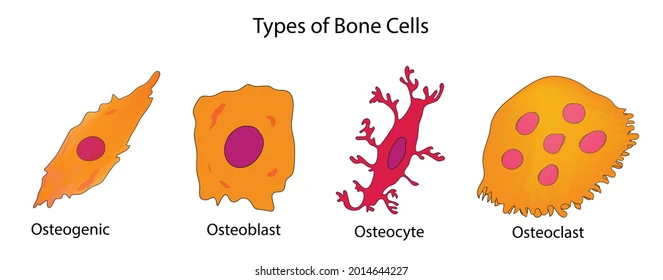
Cells that maintain bone structure, mass, and regulate bone remodeling.
Osteoclast Bone Cell
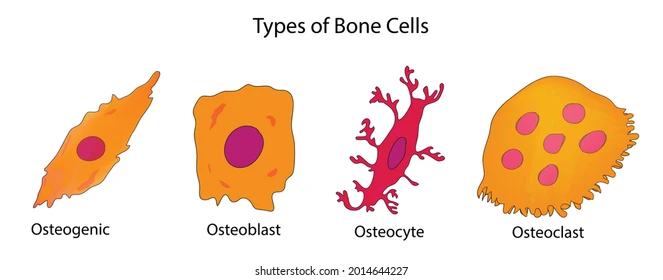
A cell that breaks down bone/bone tissue
Important for maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones
Osteogenic Bone Cell
Stem cells that create bone tissue
Used for bone growth and repair
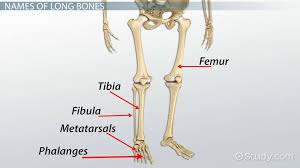
Long
A cylinder shape, longer than wide
90 bones in the body
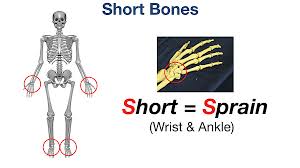
Short
A cube-like shape where its length and width are closer than they are in long bones.
28 short bones
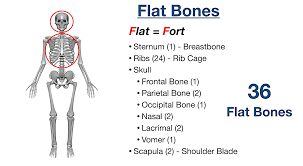
Flat
Covered and thin flat surfaces for muscles to attach to
36 flat bones
Irregular
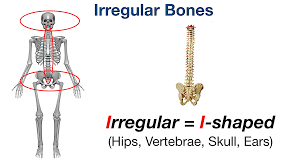
Oddly shaped bones (I-shaped)
48 irregular bones
Sesamoid

Roundish, sesame-shaped bone typically around a joint or tendon.
4 sesamoid bones
Epiphysis
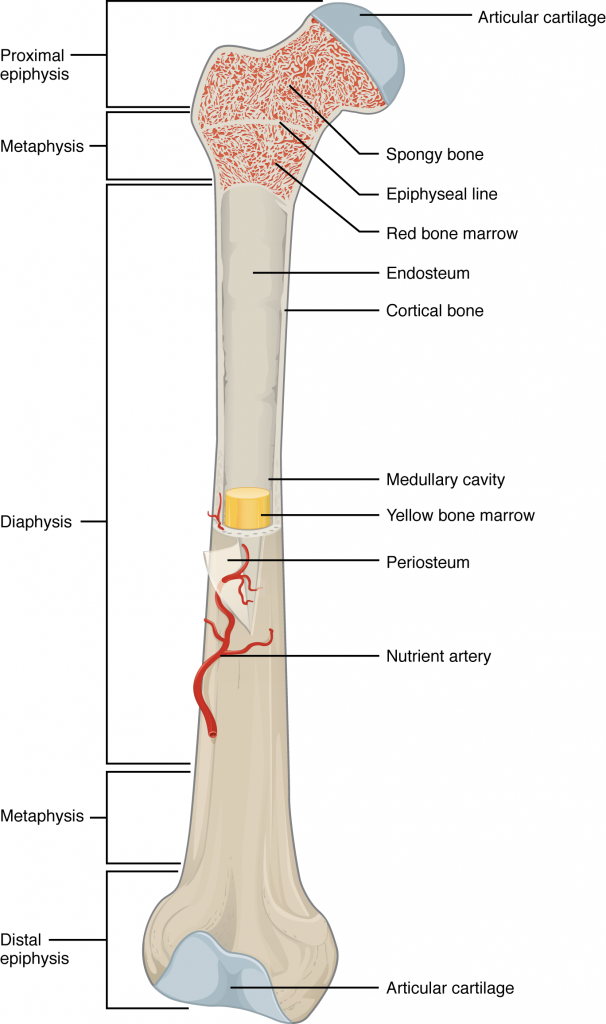
The proximal/distal of a bone
Diaphysis
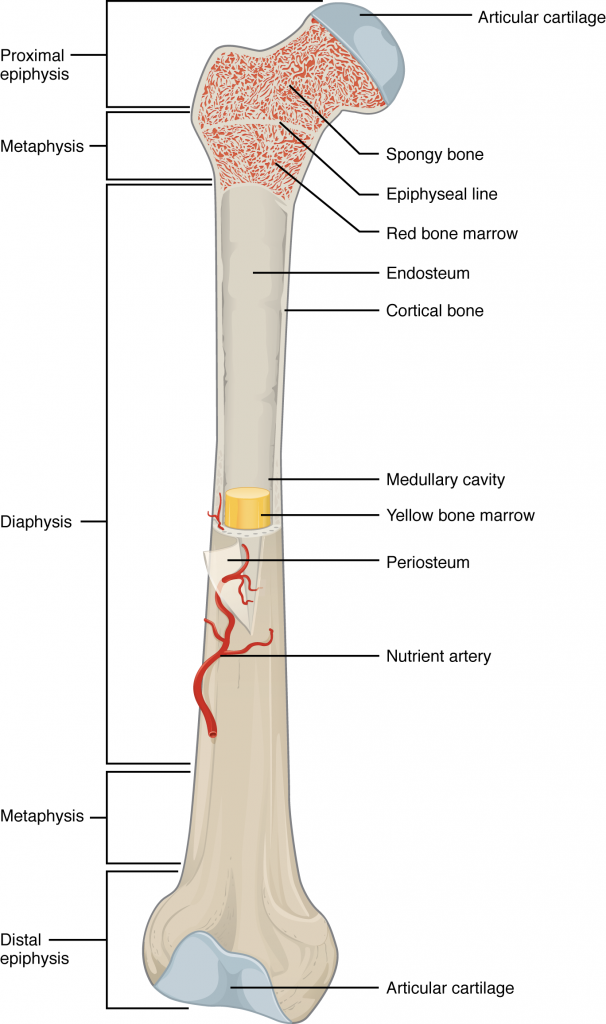
The shaft of the bone—made of cortical bone and contains bone marrow and fat
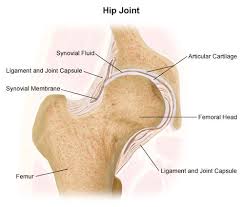
Articular Cartilage
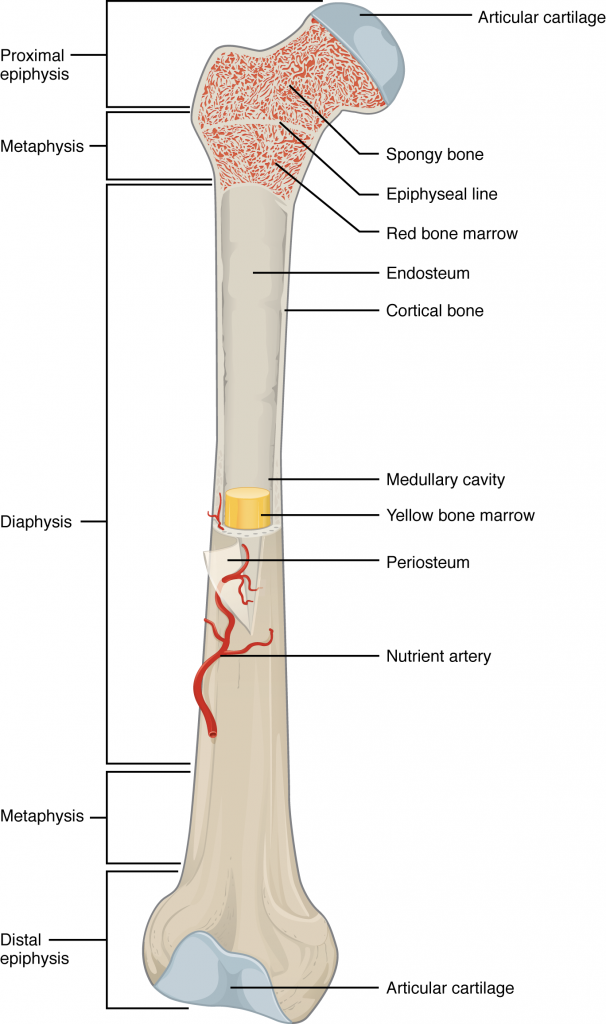
Provides a lubricated surface for articulation and movement
Spongy Bone Red Marrow
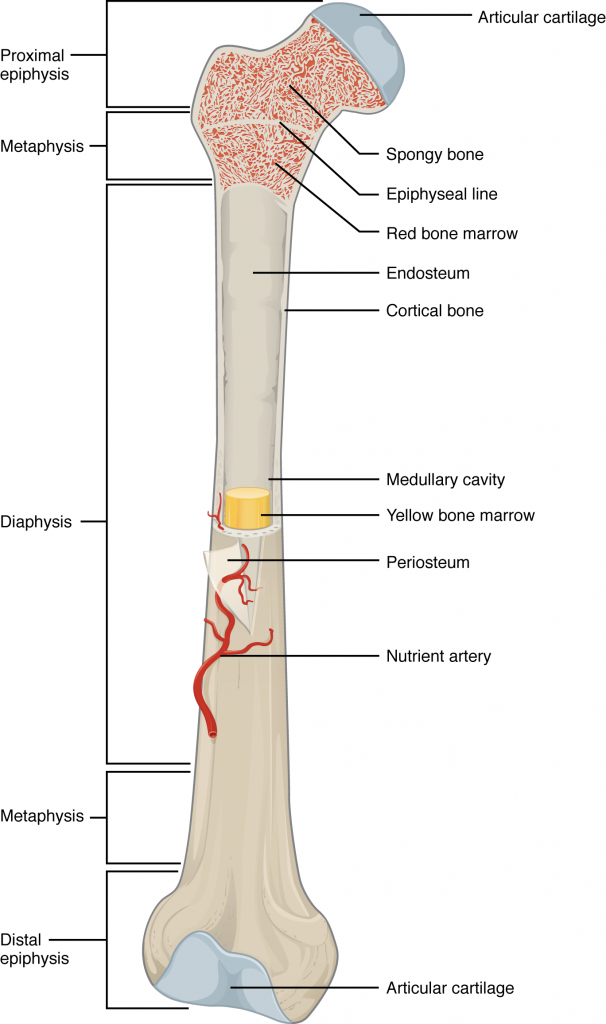
Consists of plates and bars and contains red bone marrow. (RBC/WBC)
Epipthyseal growth plate
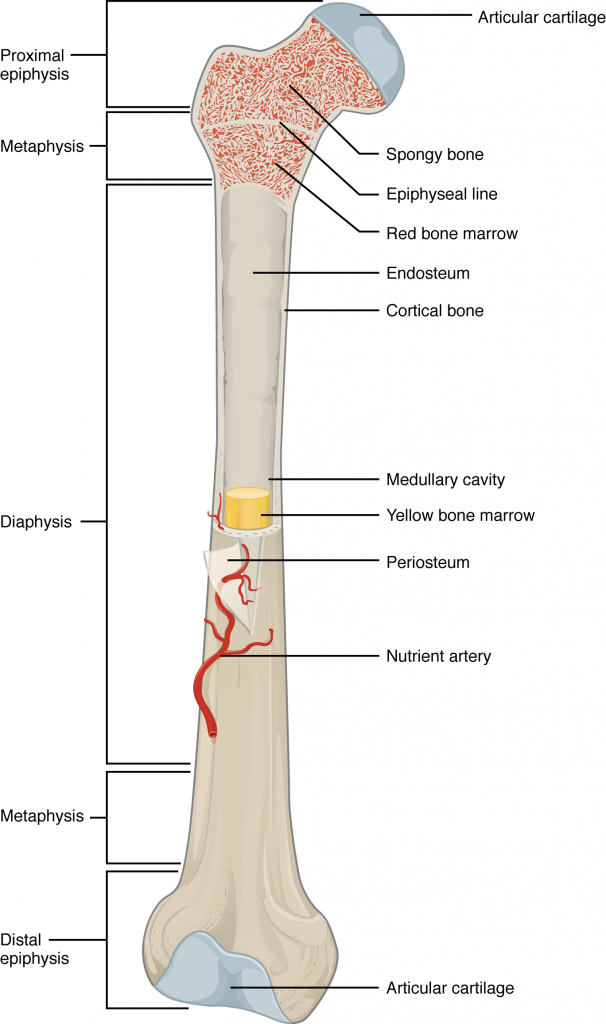
An area near the ends of long bones made up of cartilage that allows bone growth
medullary cavity
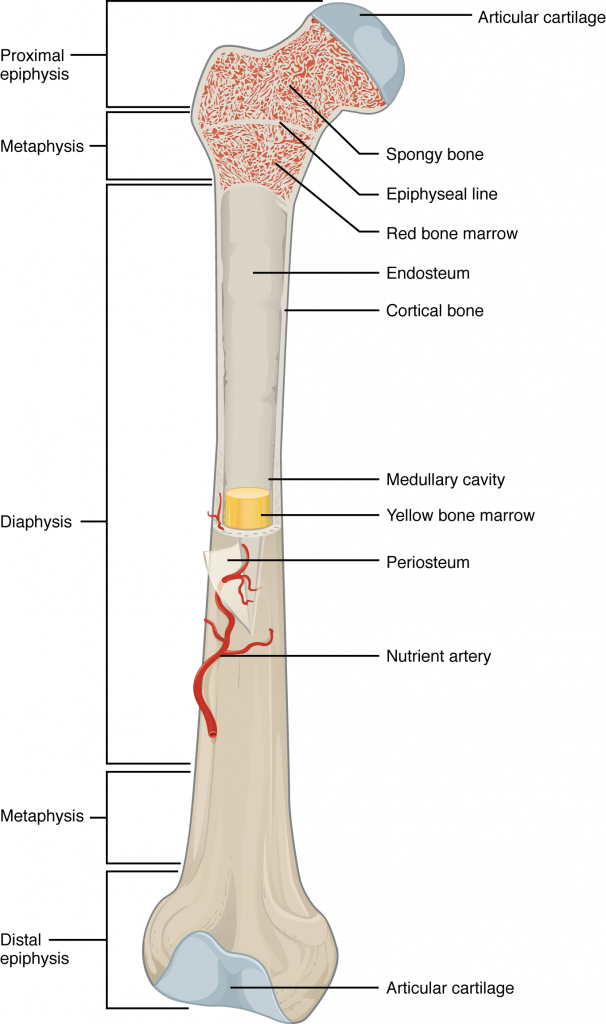
Hollow part of bone that contains yellow bone marrow and stores fat.
Periosteum
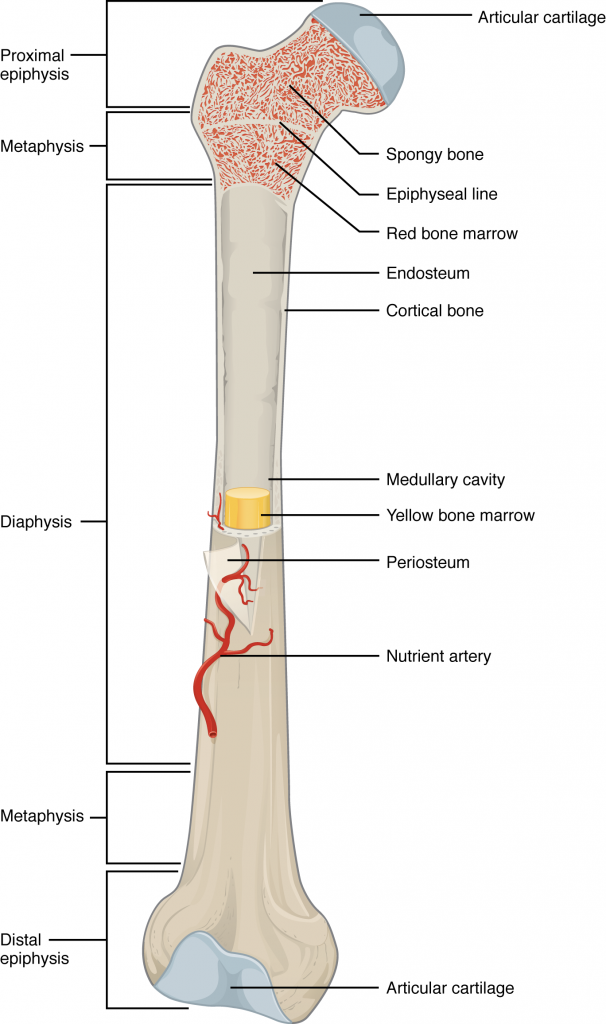
A thin layer of connective tissue lining the outer surface of a bone except at the joints
-has nociceptive nerve endigs
Endosteum
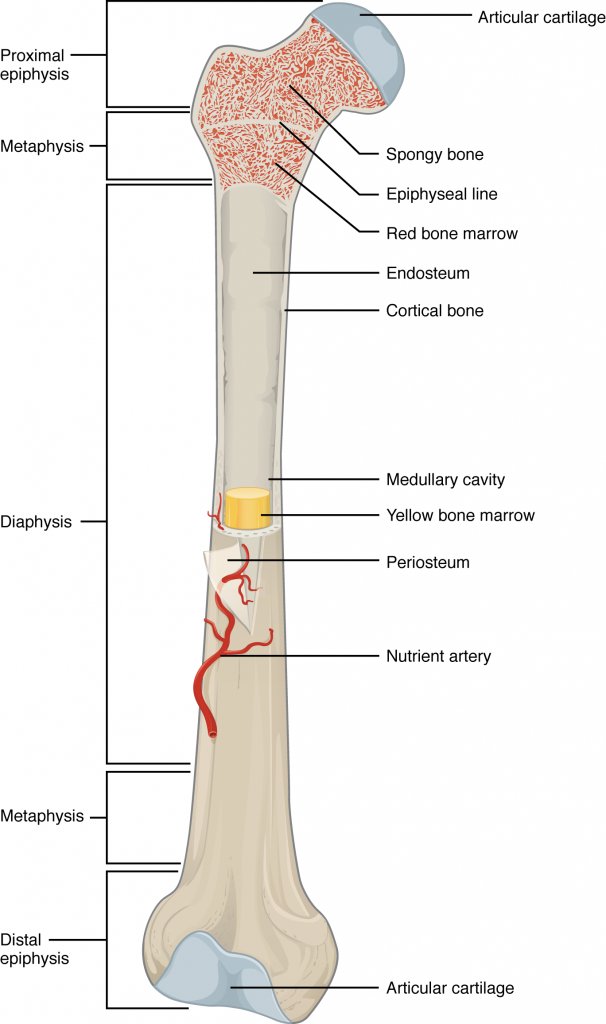
The membrane lining the inner surface of the bony wall
Joint
A point of connection between two or more bones.
Ligaments
Connective tissues that connect bone-to-bones
Tendon
Fibrous tissues at the ends of muscles that connect muscle-to-bone
Fibrous Joint (Synarthoses)
No movement; skull, teeth
Cartilaginous Joint (Amphiarthroses)
Partial/limited movement; spine, frontal, ribcage
Synovial Joint (Diarthroses)
Full movement; shoulder, knee
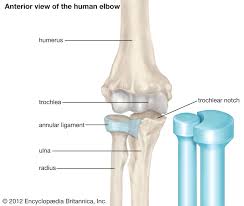
Hinge
Extension/Flexion movements—knees, fingers, elbows, toes
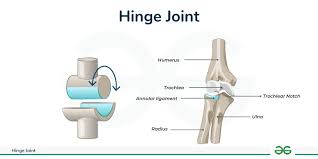
Pivot
Limited external/internal or pronation/supination rotational movements—neck joints
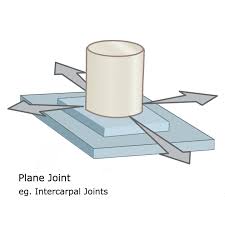
Plane
Gliding movement—wrists, ankle, vertebral
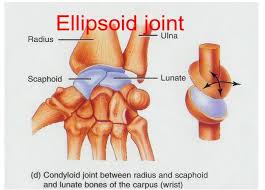
Ellipsoid/condyloid
flexion/extension, adduction/abduction, and circumduction—wrist, ankle, fingers
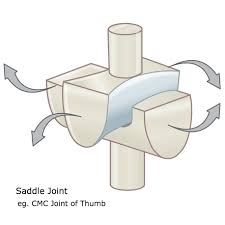
Saddle
Flexion/extension and abduction/adduction—thumb and heel
Ball + Socket
flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, and medial/lateral rotation—hip/shoulders