CMS III Final: Nephro
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
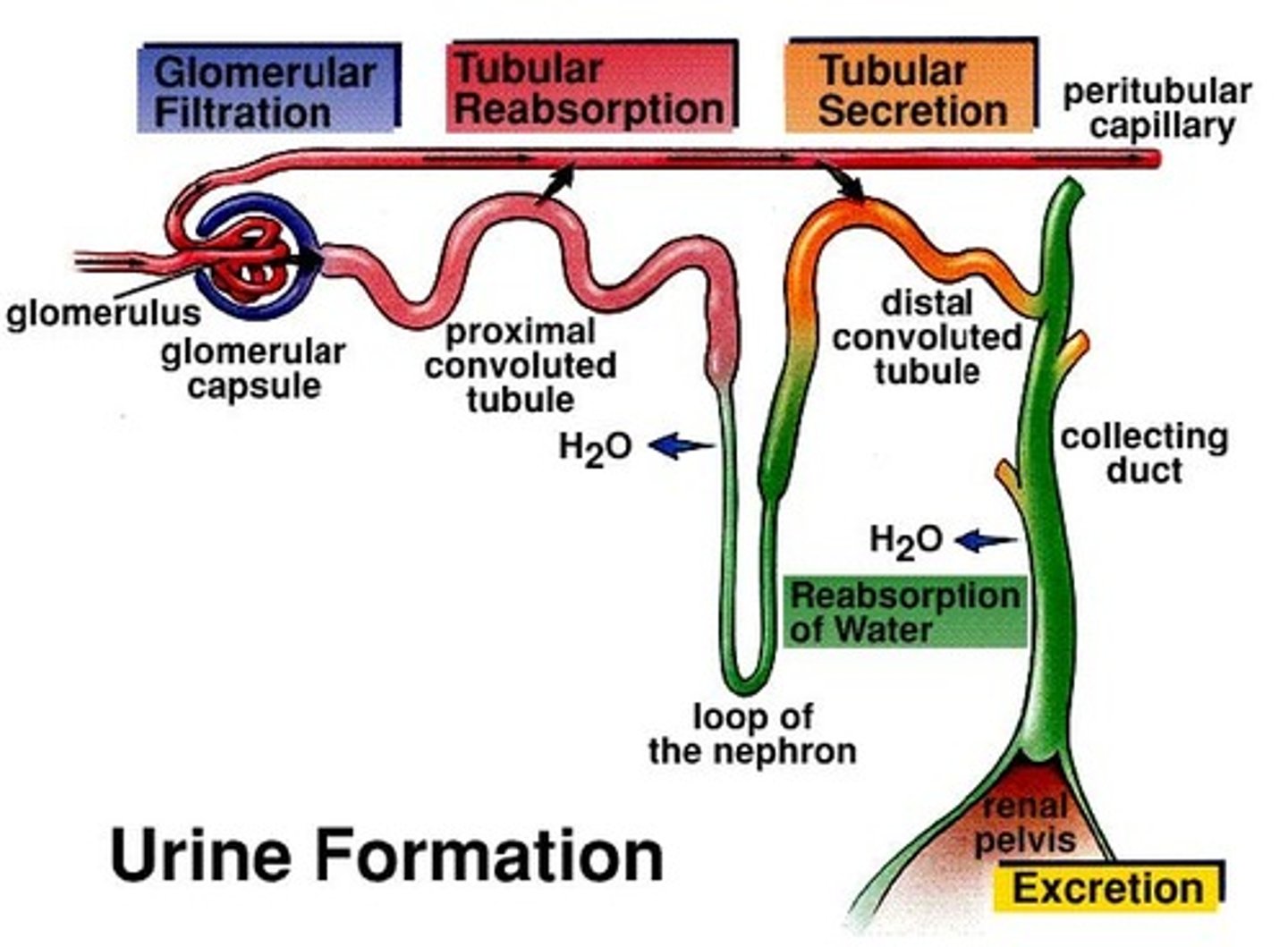
what is the difference between reabsorption, secretion, and excretion?
reabsorption = absorbed back into the blood
secretion = released into filtrate
excretion = urine outside body
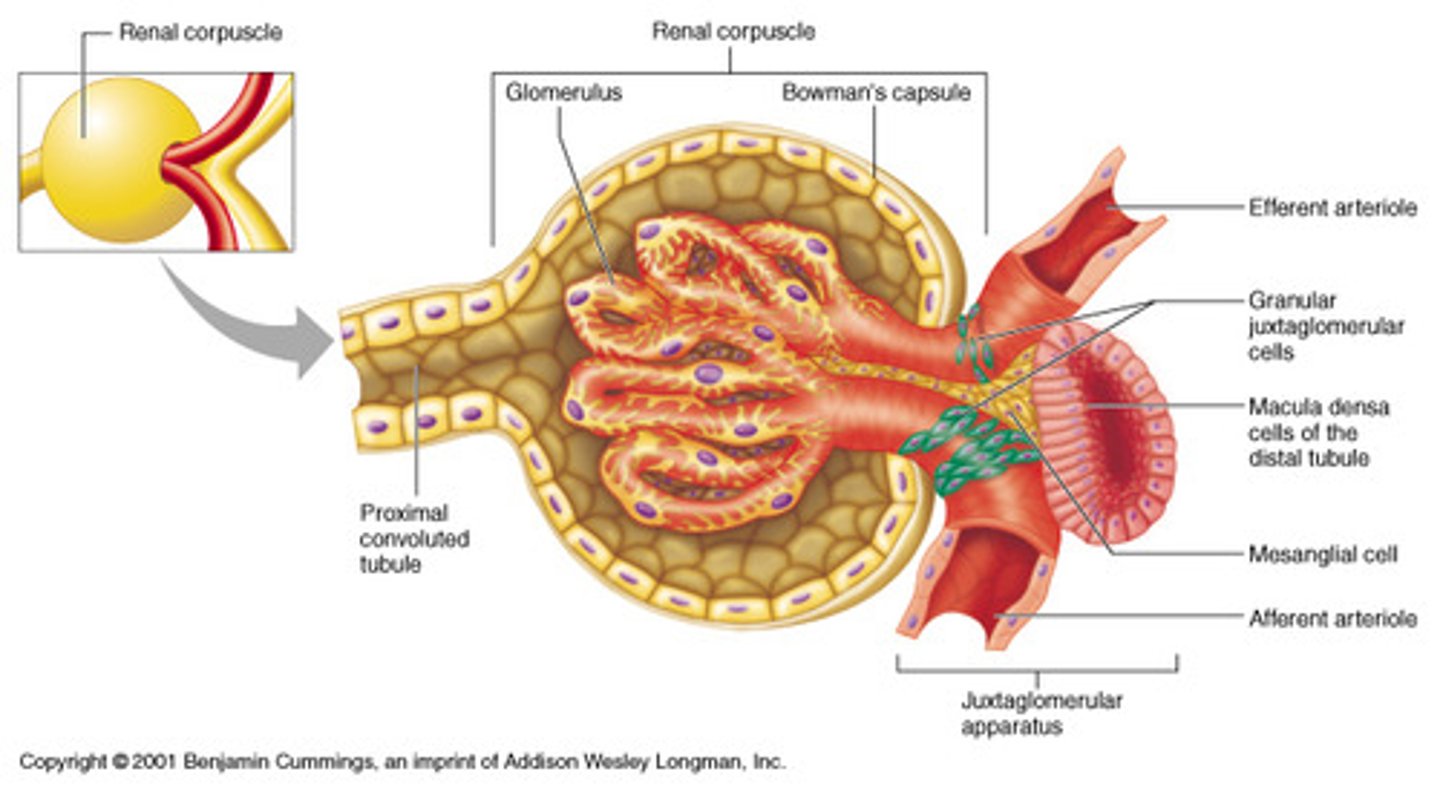
which structure in the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) senses solute load?
macula densa → releases renin
what converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin 1?
renin
ACE converts angiotensin 1 to 2
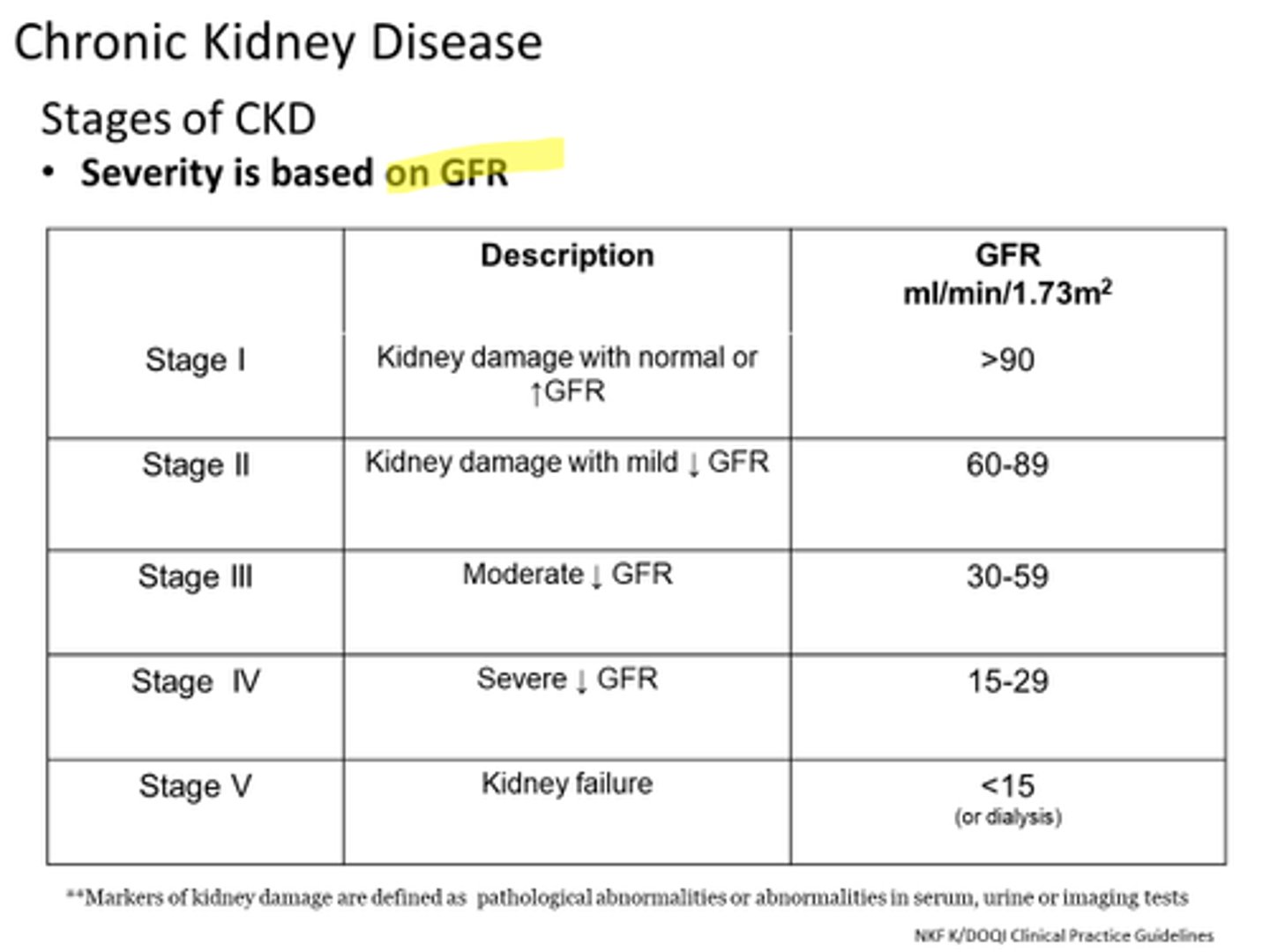
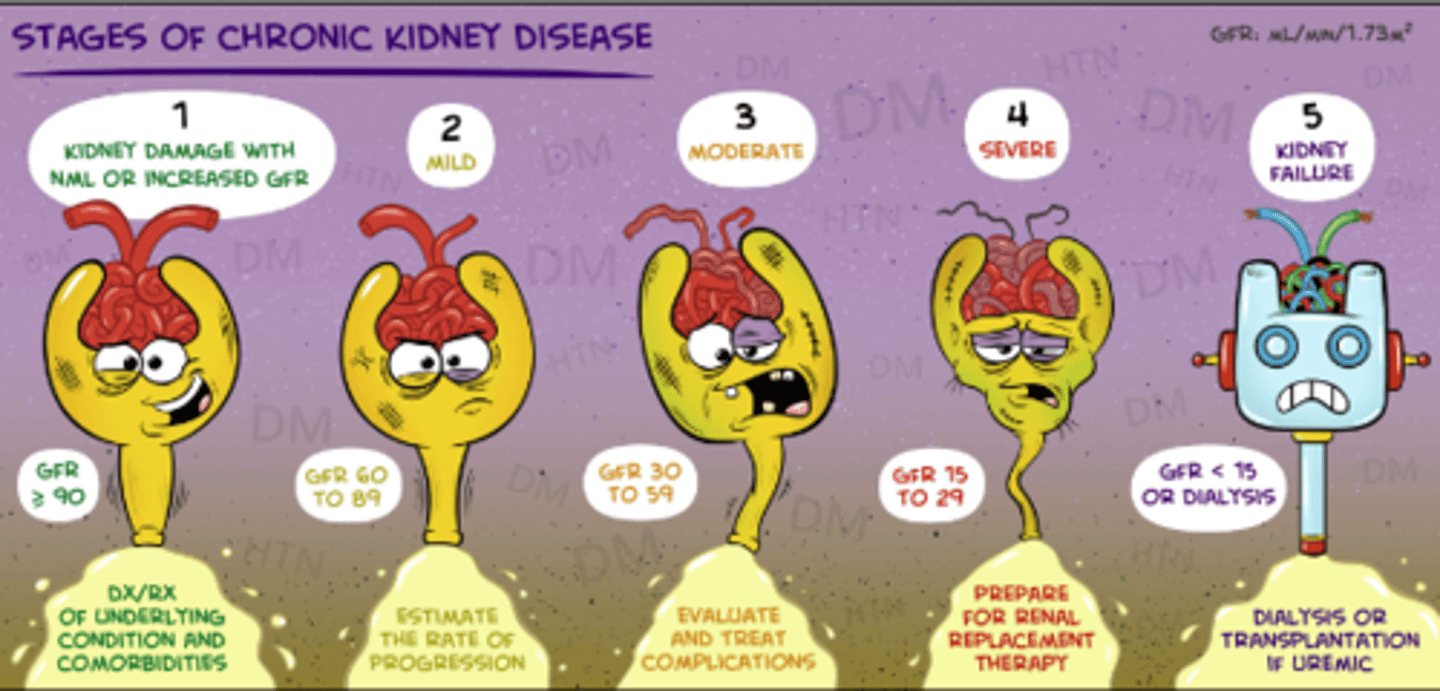
what is the best index for kidney function?
GFR
> 90 = stage 1
60-89 = stage 2
30-59 = stage 3
15-29 = stage 4
< 15 = stage 5
which imaging modality is best for evaluation of solid/cystic lesions in the kidney or peritoneal space?
renal CT → definitive role in staging renal cancer and imaging following trauma
use renal US first
what may cause BUN to increase?
- acute/chronic RF
- urinary obstruction
- dehydration
- reduced perfusion (CHF, hypovolemia)
- increased protein
- accelerated catabolism
- steroids
- tetracyclines
what may cause BUN to decrease?
- overhydration
- increased perfusion (preg, SIADH)
- restriction of protein/malnutrition
- liver dz
an osmolality gap over ____ suggests hyperosomolar state
10***
2 x serum Na + BUN/2.8 + glucose/18 ***

which hormone retains sodium and water but causes K+ loss?
aldosterone
which dipstick finding is useful for determining hydrating status and concentrating ability of the kidneys?
specific gravity →correlates with osmolality
what is often the 1st indication of renal dz?
proteinuria → dipstick is most sensitive to albumin
when may there be a false positive urine ketone?
fasting
postexercise
pregnancy
which UA finding is assoc. with intraparenchymal bleeding?
RBC casts → HALLMARK of glomerulonephritis
which UA finding is assoc. with pyelonephritis?
WBC casts*** → upper UTI
what is an infection of the renal parenchyma and renal pelvis that ascends from the lower urinary tract?
pyelonephritis → E. coli
what is the outpatient tx for pyelonephritis?
FQs
what are the causes of hypovolemic hyponatremia?
- fluid loss (GI, burns)
- hypotonic fluid replacement
- thiazide diuretics (inc. Na, dec. K+)
- K+ depletion in cells (Na+ moves into cells)
- aldosterone deficiency (Inc. Na+ excretion and water loss)
what are the causes of euvolemic hyponatremia?
edema is NOT present!
- SIADH
- polydipsia
- diuretics
- hypothyroidism (low CO triggers ADH secretion)
- severe HYPERglycemia (polyuria)
what are the causes of hypervolemic hyponatremia?
edema is present!
- CHF
- cirrhosis
- overhydration
- nephrOtic syndrome
- renal failure (can't get rid of water)
what are the causes of redistributive hyponatremia?
TBW and sodium is unchanged
hyperglycemia or admin of mannitol
what is the MCC of hypernatremia? what are the causes of it?
hypOvolemic hypernatremia:
- dehydration
- vomiting or diarrhea
what are the causes of euvolemic hypernatremia?
- insensible losses (skin/stool/lung loss)
- polyuria
- DI
what are the causes of hypervolemic hypernatremia?
- hypertonic saline/bicarb tx
- hyperaldosteronism
- cushing's
when is pseudohyponatremia seen?
hypertriglyceridemia**
multiple myeloma
what is the sweet 16 rule for pseudohyponatremia?***
correcting sodium for hyperglycemia → add 1.6 to sodium for ever 100 mg of glucose over 100
ex: Na 126 and glucose 600 → (600 - 100 = 500) 500/100 = 5, 5x1.6 = 8 + 126 → 134 is true sodium
what are causes for hypokalemia?
- decreased dietary intake
- diuretics → MC!!
- insulin
- alkalosis
- hypomagnesemia
- hyperaldosteronism
what are causes of hyperkalemia?
- excess intake
- metabolic acidosis ***!!!!!
- insulin deficiency
- drugs
- ACEIs
- K+ sparing diuretics
- decreased excretion (RF, hypoaldosteronism)
hypo or hyper kalemia causes cardiac arrhythmias/arrest and peaked T waves?
hyperkalemia
which dx is characterized by increased thirst, hypernatremia, and loss of large volumes of urine?
DI → loss of ADH production/function
which drugs can cause SIADH?
lithium
SSRIs
ecstasy
cytoxan
narcotics
which drug can cause nephrogenic DI?
lithium***
which renal dz can be caused by secretion of small cell lung cancer (AKA oat cell)?
SIADH***
which dx is characterized by pathologic water retention and hyponatremia with concentrated urine?
SIADH
what is a serious complication of rapid correction of hyponatremia using hypertonic saline?
central pontine myelinolysis
when is hypertonic saline indicated for hyponatremia?
seizures
coma
focal findings
neuro symptoms***
what are the indications for normal saline?***
- ECF volume depletion
- post op fluid management
- shock
- hemorrhage
- burns
- blood transfusion
what are the indications for hypotonic saline?
- hypertonic pt
- hyperosmolar state d/t hyperglycemia
- hypernatremia w ECF volume depletion
why can't pure water be given IV?
causes hemolysis → use D5W for pts with normal BP***
what are the causes of respiratory acidosis?
hypoventilation
PNA
HF (shunting)
coma
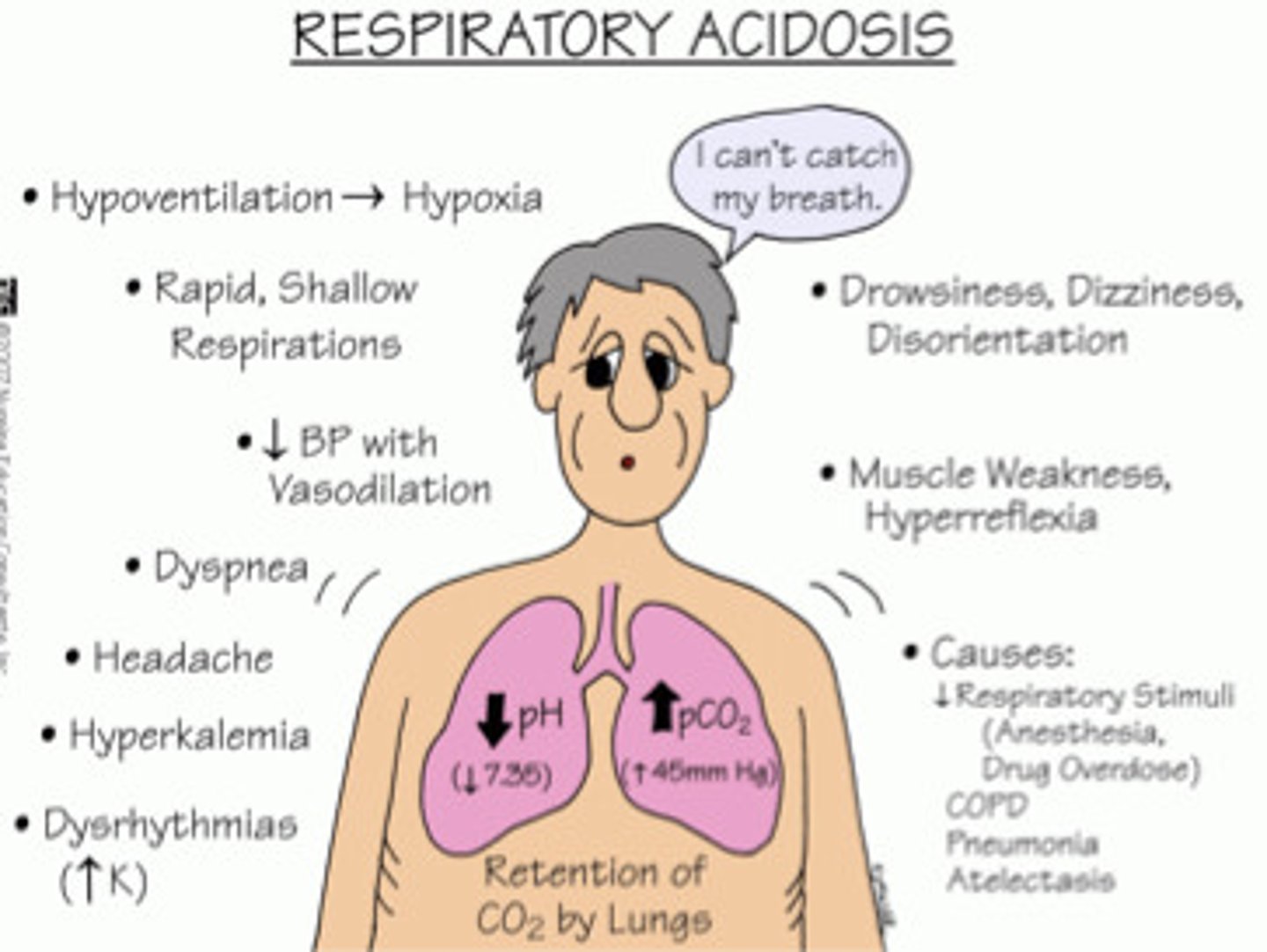
what is the compensation for respiratory acidosis?
kidney retain bicarb (slow process)
what are the causes of respiratory alkalosis?
hyperventilation → panic attacks, anxiety → blowing off too much CO2
what is the compensation of respiratory alkalosis?
kidney excretes excess bicarb, retains H+
what are causes of HAGMA?
MUDPILES***
Methanol
Uremia
DKA
Paraldehyde
Isoniazid, iron
Lactic acidosis
Ethylene glycol
Salicylates
what are causes of NAGMA?
HARDUP (loss of HCO3 and/or gain of Cl)***
Renal tubular acidosis
Diarrhea
what is the compensation for metabolic acidosis?
lung hyperventilate →get rid of CO2 and raise bicarb
what are the causes of metabolic alkalosis?
vomiting
gastric suction (NG tube)
antacids, diuretics
what is the compensation for metabolic alkalosis?
lung hypoventilation → retain CO2 to increase PaCO2
how do you determine if there is compensation for metabolic acidosis?
Winter's formula***
PCO2 = (1.5 x HCO3) + 8 +/- 2
if value falls in range → compensatory
what is the MC form of acute glomerulonephritis (GN)?
IgA nephropathy AKA Berger's dz → assoc. with URI/flu-like illness
pt presents with dark cola colored urine, decreased urine volume, and periorbital edema. what is the tx?
nephritic syndrome → steroids for inflam, reduce BP with water/Na+ restriciton/diuretics/diaysis
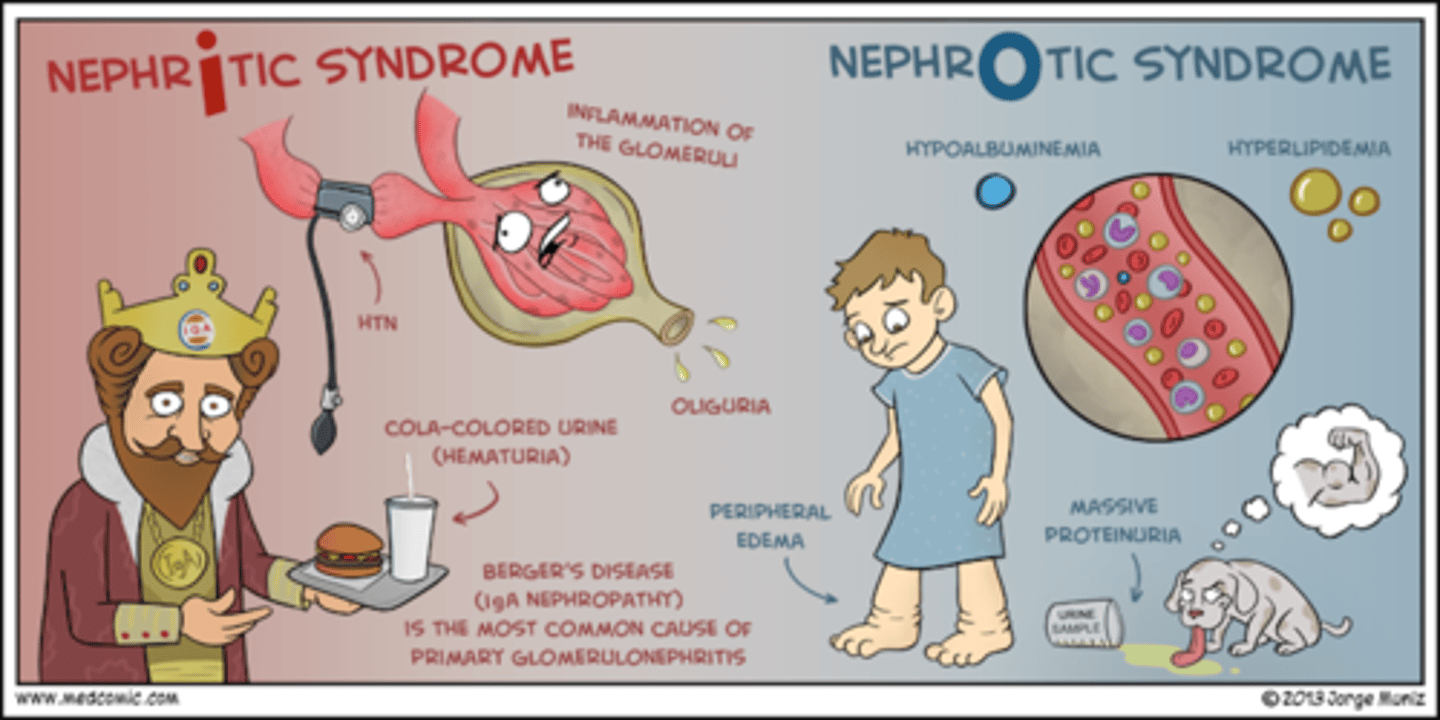
what are the s/sx of nephritic syndrome?
triggered by immune response (think infection)
- dark cola urine
- decrease urine volume
- edema (scrotal/periorbital)
- HTN d/t fluid overload
- Dec. GFR, RBC casts
what is the standard for dx of IgA nephropathy?
renal Bx → diffuse mesangial IgA deposits and proliferation
what are the sx of IgA nephropathy?
- painless hematuria***
- inc. serum IgA
which dx is likely when > 50% of glomeruli contain cresents?
rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) → crescents are in response to glomerular rupture d/t severe injury
which dx involves GN plus pulm hemorrhage that is mediated by anti-GBM antibodies?***
goodpasture's syndrome
what are the s/sx of Goodpasture's syndrome?
hemoptysis
tachypnea
malaise
anorexia
HA
may have preceding URI
HTN and edema (components of nephritis syndrome)
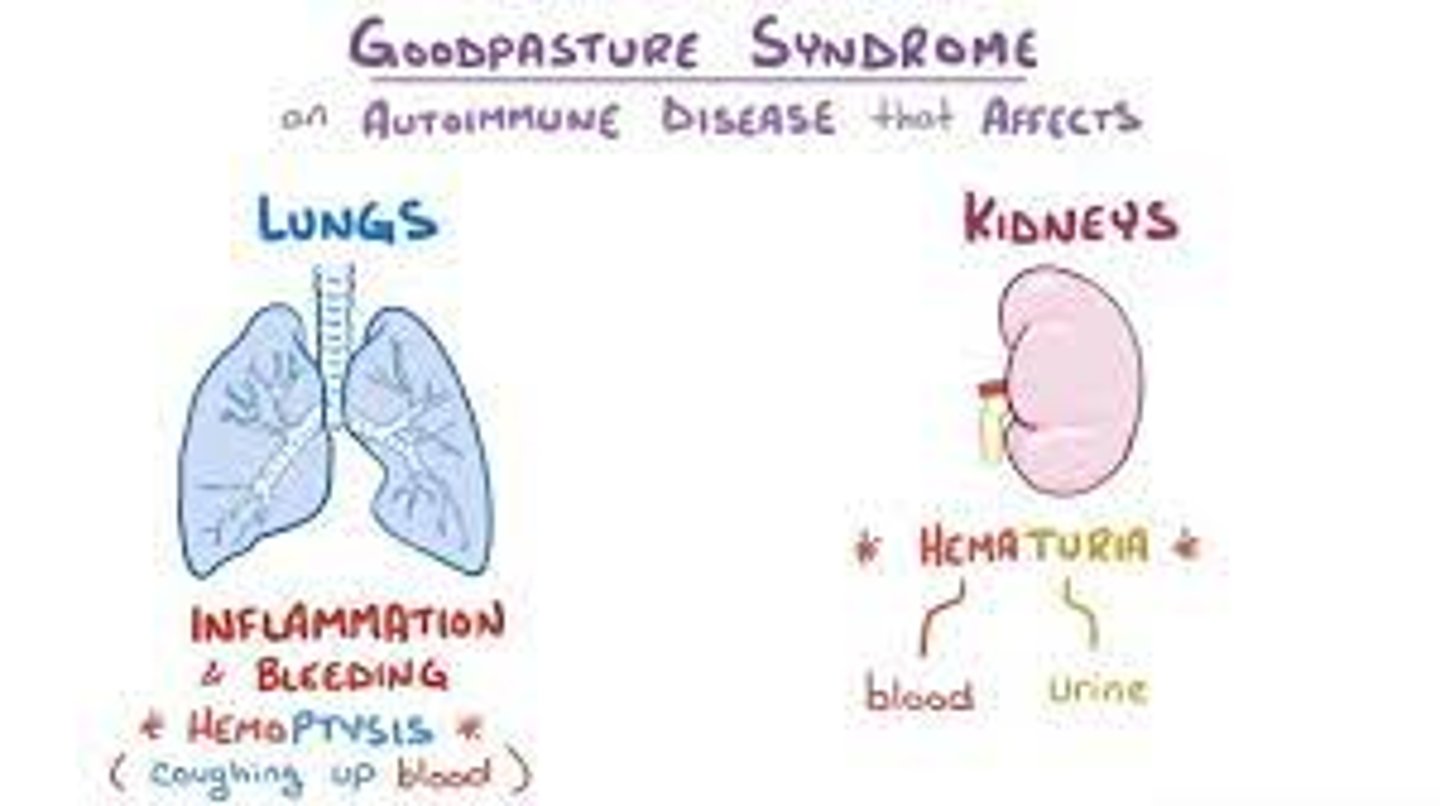
what is the tx for Goodpasture's?
high dose steroids and immunosuppressive tx
what is the confirmatory finding for Goodpasture's?
circulating anti-GBM abs**
other findings:
bx shows crescents/adhesions, inflam infiltration
CXR shows pulm infiltrates d/t pulm hemorrhage
what is the hallmark sign of nephrotic syndrome?
peripheral edema
what are the 4 MCC of nephrotic syndrome?***
1. minimal change dz
2. membranous nephropathy
3. focal glomerular sclerosis
4. membranoproliferative GN
common in kids and adults
what are the s/sx of nephrotic syndrome?
-Edema: periorbital, peripheral, generalized, anasarca; worse in morning
- HEAVY proteinuria >3.5/day
- dyspnea (d/t pulm edema, pleural effusion)
- hypoalbuminemia (causes edema)
- VTE (severe cases)
- hyperlipidemia
NO HTN OR HEMATURIA
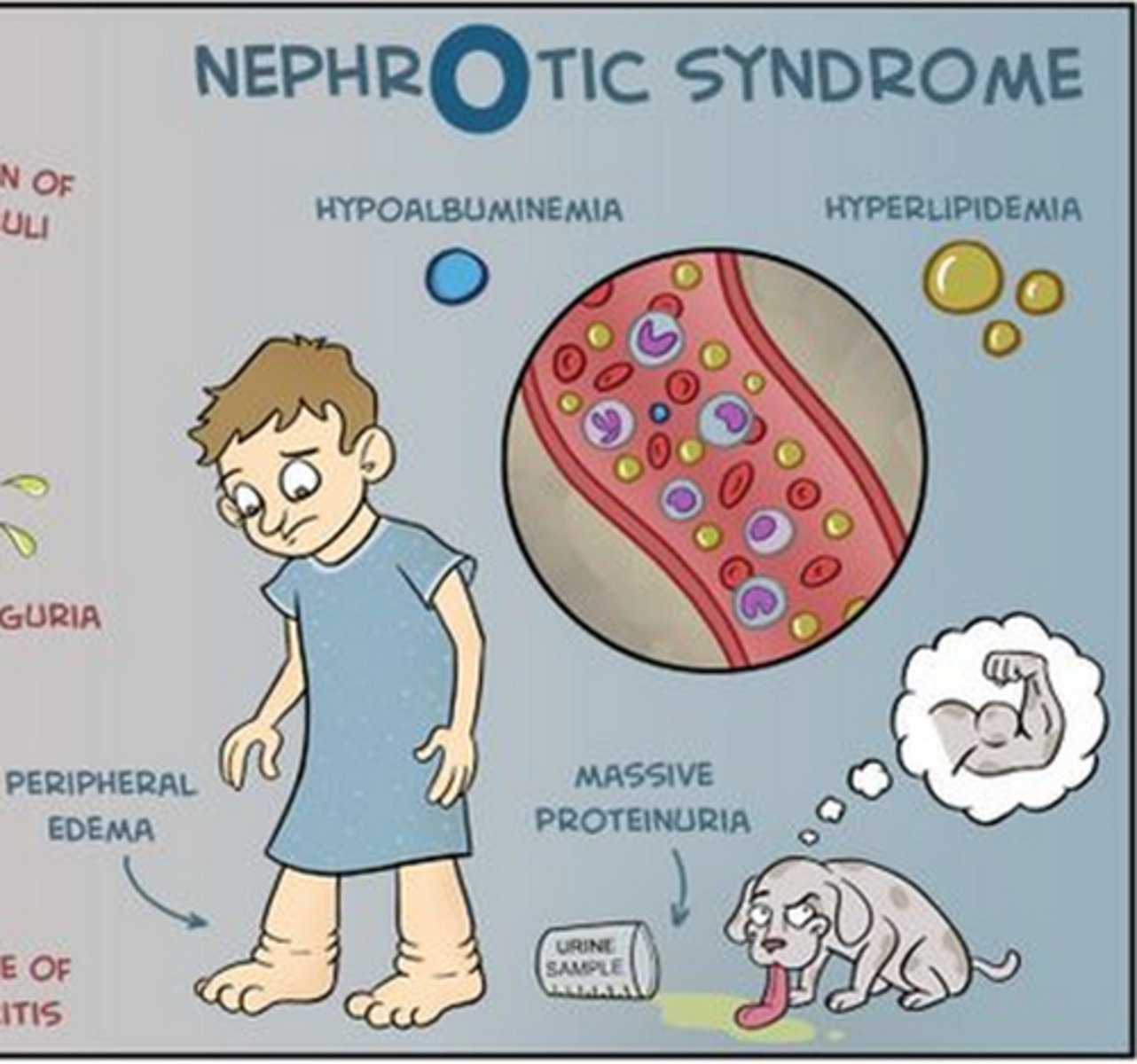
what is the most specific lab finding in nephrotic syndrome?
lipiduria → d/t hypercholesterolemia
maltese cross!
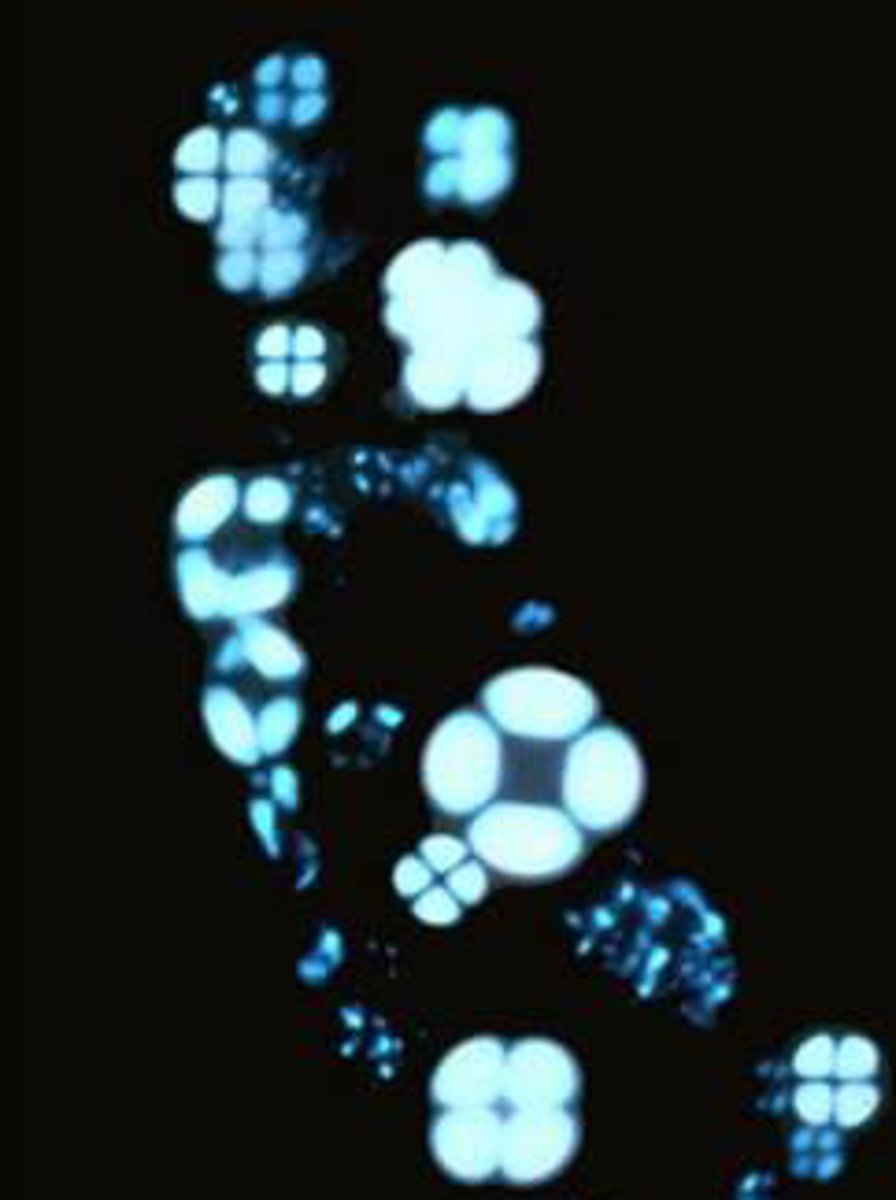
why is VTE a risk in severe nephrotic syndrome?
albumin <2 = hypercoagulable
what is the tx for nephrotic syndrome?
1. proteinuria = ACE/ARB
2. edema = salt restriction/diuretic
3. hyperlipidemia = diet/exercise, statin
what is the MCC of primary nephrotic syndrome in children?
minimal change disease AKA lipoid nephrosis
disappearance of proteinuria with prednisone is considered diagnostic for which dx?
minimal change disease → same sx as nephrotic syndrome
tx with prednisone!!
what is the MCC of primary nephrotic syndrome in adults?
membranous nephropathy → assoc. with occult carcinoma and thromboembolism***
in which nephrotic syndrome is there a high incidence of renal vein thrombosis and occult neoplasms?***
membranous nephropathy
which conditions does focal glomerular sclerosis occur secondarily to?
heroin abuse
morbid obesity
HIV infection
NSAIDs
Folks (focal sclerosis) with HIV do Heroin
what do most pts with focal glomerular sclerosis present with?
microscopic hematuria
many also have HTN
what is the tx for focal glomerular sclerosis?
long term oral steroids
which dx is seen in lupus nephritis patients?
membranoproliferative GN → most pts are <30 yrs old
tx with steroids and antiplatelets
which lab test can be used for muscular/obese people to estimate their creatinine?***
cystatin C
which endocrine dx can cause CKI?
hyperparathyroidism**
which acid base disorder is seen in aspirin overdose?***
met acidosis PLUS resp alkalosis
where are glucose and bicarb reabsorbed?
PCT
what is the definitive test for dx of interstitial nephritis?
biopsy***
what is seen in postinfectious GN?***
- oliguria
- edema
- cola colored urine
- RBC casts, proteinuria <3.5
- 10-14 days after strep
what is the MC UTI organism in sexually active female adolescents?
staph saprophyticus ***
E. coli is MC in general → ascending route of infection
how are Tamm-Horsfall glycoproteins preventative of UTIs?***
inhibit bacterial adherence
excreted with excessive exercise!!!!***
which dx shows dysmorphic RBCs on UA?
GN!!**
what is the MC type of renal cancer?
renal cell carcinoma (RCC) → arise from PCT/small tubules of nephron
what should you do if your pt with RCC has metastatic disease?
refer for dialysis ***
what are the risk factors of RCC?
- SMOKING!!!
- obesity
- analegics
- FHx
where are H+ ions secreted in the nephron?
cortical collecting duct***
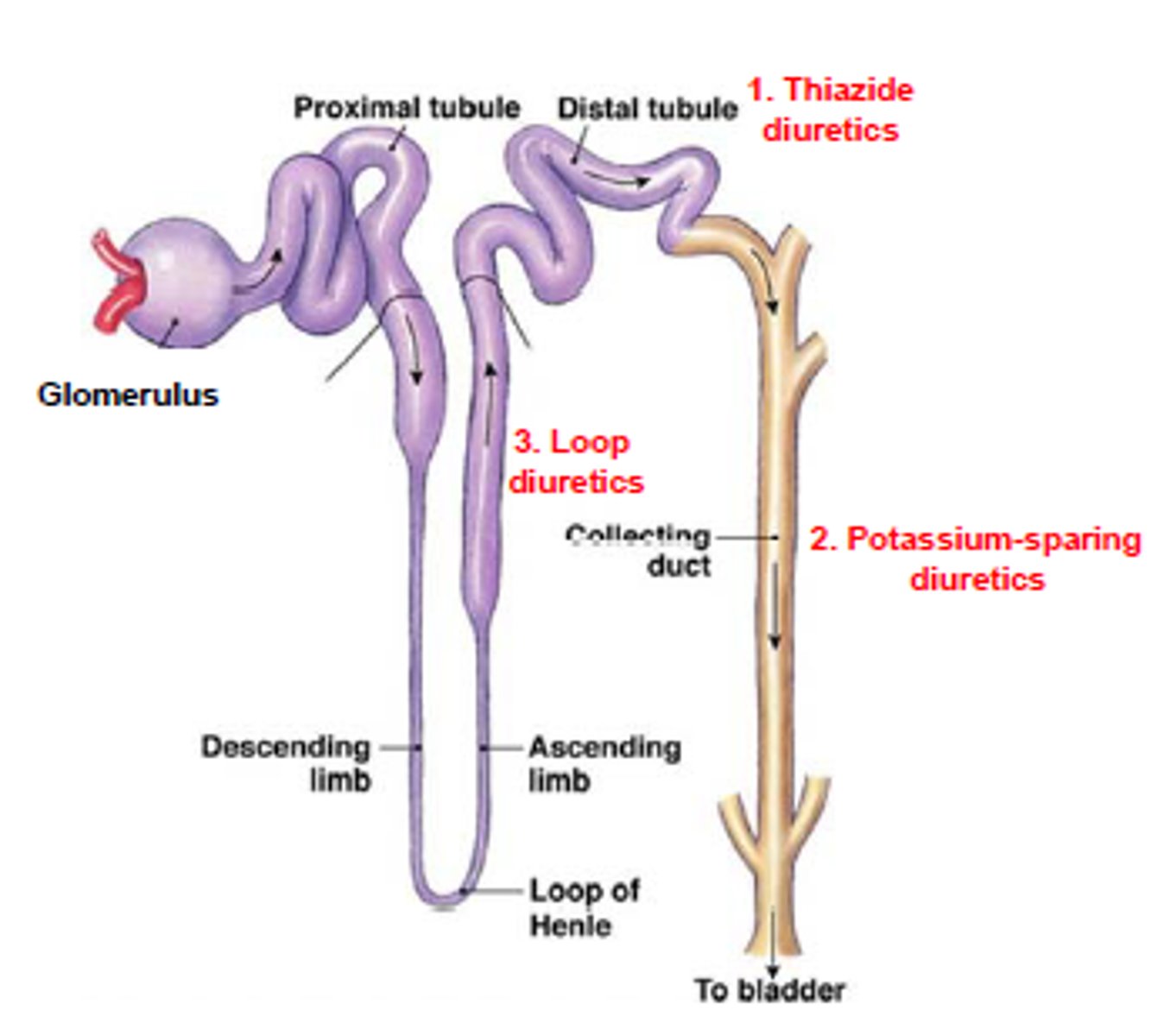
where do thiazide diuretics work?
distal convoluted tubule***
what are the causes of pre-renal azotemia?
- intravascular volume loss (ECF)
- change in vascular resistance
- low CO
hemorrhage, GI loss, dehydration, excessive diuresis, pancreatitis, burns, trauma, peritonitis
what do labs show in pre-renal azotemia?
BUN:Cr > 20:1
urine Na+ < 20 (low)
FEna <1 (low)
hyaline casts
what is the MCC of renal (intrinsic) AKI?**
ATN → 2 major causes = ischemia and nephrotoxin exposure
what are the exogenous nephrotoxins that cause intrinsic azotemia?
- aminoglycosides !!
- vanco, cephalosporins
- contrast media
- cyclosporin
- antineoplastics (cisplatin)
- heavy metals
what are the endogenous nephrotoxins that cause intrinsic azotemia?
- heme products (Myoglobin, Hgb)
- uric acid
- paraproteins (Bence jones)
EXogenous MC than ENdogenous
what are the s/sx of ATN intrinsic azotemia?
- generalized swelling
- n/v
- oliguria
- decreased LOC
- anorexia
- muscle weakness
- pulm edema
what are the causes of postrenal azotemia?
obstruction → BPH, cancer, neurogenic bladder, clots, stones
what do labs show in postrenal azotemia?
- BUN:Cr > 20:1
- urine Na+ > 20 (high!!)
- FE na >1 (high)
tx by relieving obstruction!!
taking anticholinergic drugs is a risk of developing which type of azotemia?
post renal → risk for urinary retention
what is the MC indicator for CKI? When should you refer to nephro?
BUN and SCr (best is GFR)
refer to nephro at stage 3 (GFR <30)
which acid base disorder is MC in CKI?
metabolic acidosis
which type of renal stone is radiolucent?***
uric acid
which type of kidney stone is assoc. with proteus mirabilis UTI?
struvite
which stones are radioopaque?
Calcium Oxalate (MC), Calcium Phosphate, and Struvite