final accounts / balance sheet / depreciation
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
statement of profit / loss is also known as
Income statement
statement of financial position is also known as a
balance sheet
The Statement of Profit or Loss shows
the income and expenditure of a business over a period of time - usually a year - and calculates the amount of profit made
the statement of profit loss is divided into three parts called the….
The trading account
The profit and loss account
The appropriation account
the trading account in a statement of profit/loss is where…
the cost of sales is deducted from sales revenue to calculate the gross profit
the profit and loss account in a statement shows …
expenses
profit before interest and tax
interest
profit before tax
tax
profit for period
the appropriations account in a statement of profit/loss shows
the dividens
retained profit
why are shareholder interested in P/L acc
Interested in revenues, costs and profits earned, business growth and dividend payments
may use ratio analysis tools to identify profit margins and returns on investment
why are employees interested in P/L acc
Interested in profits earned and the potential for wage increases and job stability
__ may look at notes to the accounts that detail levels of executive pay
why are Managers and directors interested in the P/L acc
Interested in performance data such as an improvement in sales revenue and net profit
This data can aid business decision making
Financial data can provide evidence to support the payment of bonuses
why are suppliers interested in the P/L acc
Interested in the continued success of the company they are supplying and this information is also used by ______ to determine the level of trade credit offered to businesses
why is the government interested in the P/L acc
Used to determine how much tax is payable
The Statement of Profit or Loss can provide an insight into whether the business will continue to provide employment, place orders with other businesses and supply goods and services to the public sector
The Statement of Financial Position ( balance sheet) shows …
the financial structure of a business at a specific point in time , It records the business assets and liabilities and specifies the capital (equity) used to fund the business
Statement of Financial Position is also known as the Balance Sheet bc the _______ should equal ______
net assets , total equity
statement of financial position / balance sheet has ….
non current assets
current assets
total assets
current liabilities
non current liabilities
total liabilities
net assets
equity
non current assets are
items that are owned by the business in the long term such as : machinery , buildings , vehicles
current assets are
items that are converted into cash quickly usually within 12 months , the main types are cash , debtors and stock
total assets are
non current assets + current assets
current liabilities are
money owed by a business that will fall due within 12 months ex: bank overdrafts and creditors
non current liabilities is:
money owed by the business that does not need to be payed back for at least 12 months ex: bank loans mortgages
total liabilities =
current liabilities + non current liabilities
net assets =
total assets - total liabilities
equity/ capital employed shows
how the net assets of a business are funded
how do shareholders use a balance sheet
Used to identify the asset structure of the business and how their investment has been put to use
Used to calculate the working capital of the business and determine its solvency
Used to determine the rough value of a business which helps a judgement on whether their investment is growing
how do managers and directors use a balance sheet
Used to identify the financial position of the business at a given point in time
Useful to assess the working capital position of the business and determine if there are enough liquid current assets to pay its bills
Provides information on the capital structure of the business which helps guide decisions on whether to raise further funds through borrowing or via other means (e.g. share issue)
how do suppliers and creditors use a balance sheet
Used to judge the solvency of the business to determine the risk when offering firms trade credit
Businesses with low levels of working capital may find it difficult to pay short-term debts and so ____ may offer trade credit, but with stricter terms
how do employees use the balance sheet
Used to answer questions such as:
Is the business financially stable or are jobs at risk?
Has the businesses performance improved or worsened?
What is the business spending its money on?
How much are senior executives paid?
How much tax is the business paying?
intangible assets
are non-physical and cannot be held
Businesses need to account for ______ _____
in their annual reports as it adds to the value of the business
intellectual property includes
patents, trademarks, patents and copyrights which protect unique ideas, inventions, artistic works, and brand names
brand value
The reputation and recognition associated with a brand has a value
It includes the brand name, logo, slogans, and customer loyalty to the brand
customer relationship
Long-term ______ ______ including customer lists, contracts, and customer loyalty programs
These relationships can provide recurring revenue and a competitive advantage
licenses and permits
___________ and regulatory approvals that grant exclusive rights or access to certain markets or resources, often issued by governments
depreciation is
an accounting technique which recognises that the value of fixed (non-current) assets falls over time
It reflects wear and tear, the reduction in an asset's value as it ages or obsolescence
what are the two common methods of calculating depreciation
Straight line depreciation
Units of production depreciation
historic cost
original cost of purchasing an asset or item
straight line method of depreciation
reduces the value of an asset by the same value each year of its useful life
the three key variables to calculate this are
Life expectancy
The number of years it is expected to be used before it will need to be replaced
Residual value
The scrap value of the asset at the end of its useful life
Historic cost
The initial cost of purchasing the asset
formula of annual rate of depreciation
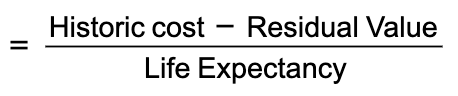
units of production depreciation
The ________ depreciates an asset based on its usage or production output during an accounting period (usually a year)
It is commonly used for assets that wear out based on the number of units produced or hours of operation rather than the passage of time
Vehicles commonly lose value as their mileage increases
Machinery wears out as it is used in production
depreciation per unit formula
step 1 = (historic cost - residual value) / expected units over an assets lifetime = depreciation per unit
step 2= depreciation per unit x number of units produced
once depreciation is calculated its recorded as:
an expense on the income statement AND The value of the asset is reduced by this amount in the balance sheet and is recorded as its book value