State of Matter
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Melting point means
Temperature at which something melts
Which of the following has the most least amount of energy
Solid
Based on the phase diagram, if you increase the pressure of a gas it will
Became a liquid
If a substance is below the freezing point, it is a
Solid
The phase of matter that has a fixed shape and fixed volume is a
Solid
What causes something to change state(solid,liquid,or gas)?
Pressure and temperature
the differences between how solids, liquids,and gases behave
The solid is a compressed and fixed shape. The Liquid has particles that can move around and no fixed shape. The gas are spread apart and particles can move at a higher speed than liquid.
How does the behavior of molecules change in different states of matter?
The behavior of the molecules change by decompressing. Going from solid, liquid, to gas the molecules begin to spread gradually each change.
What does the state of matter have to do with heat?
When rising the heat of all 3 states, it causes them to decompress faster. All 3 states’ molecules separated at a faster rate than without heat.
List the phases of matter in order from the least amount of energy to the most.
Solid, Liquid, Gas
What is common between evaporation and boiling?
The both results are vapor.
What is the difference between evaporation and boiling?
Evaporation is not a boiling liquid, while boiling is a boiling liquid.
What does “melting point” mean?
Temperature were a solid becomes a liquid.
What is the melting point of water?
100c
What phase is it if substance is in between its melting point and boiling point?
Liquid
What phase is it if something is below its freezing point?
Solid
The triple point is
the temperature and pressure at which a substance's three phases (solid, liquid, and gas) are in equilibrium.
THe critical tempertaure
Why does dry ice go from solid to gas phase in normal pressure(1atm)?
Because the diagram shows, when you increase the temperature it does not go into the liquid section.
At what temperature does water boil in normal pressure(1atm)?
Water boils at 100C in normal pressure.
What is plasma
Plasma is a state of matter. It is a mixture of freely roaming negative and positive charges is plasma.
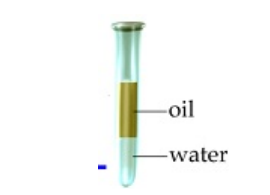
Mechanical Sorting is
- Used to separate the parts of a mixture based on properties such as particle size, colour, shape..etc. Examples: Magnetism :Can be used to separate a magnetic substance from a non-magnetic substance
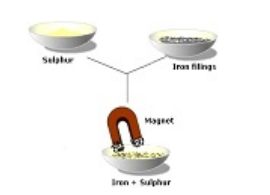
Mechanical Sorting is also
Floatation: used to separate substances by whether they float or sink
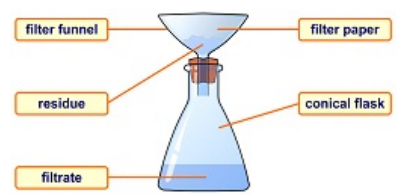
Flitration is
-Used when separating a solid substance from a fluid (a liquid or a gas) by passing a mixture through a porous material such as a type of filter. -Works by letting the fluid pass through but not the solid. -Examples of filters: coffee filter, cloth, oil filter, even sand! -The substance that is trapped by the filter paper is called the residue. The substance that passes through the filter paper is called the filtrate.
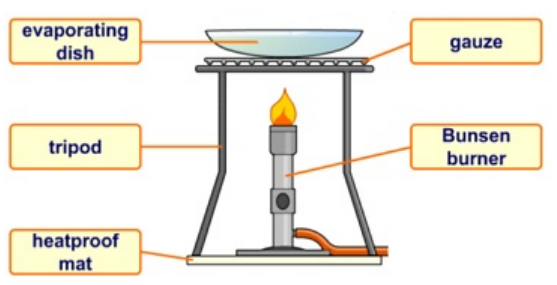
Evaporation -
Change of state from a liquid to a gas -Used to recover a solid solute from a solution.
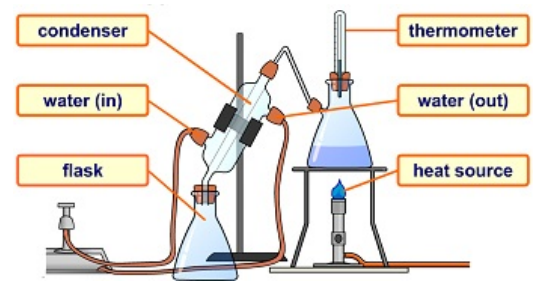
Distillation
-Is a method that you can use to separate and recover a single solute and a single solvent from a solution. -Uses the property of the boiling point to separate two components of a solution (solvent and solute) -Three key stages to distillation: 1) Evaporation 2) Condensation 3) Collection
Paper Chromatography
-Separates components of a mixture based on ability of each component to be drawn across the surface of another material -Mixture is usually liquid and is usually drawn across chromatography paper -Separation occurs because various components travel at different rates -Components with strongest attraction for paper travel the slowest -Different substances or different components move at different speeds through a strip of wet paper a gel or a gas.
Separating heterogeneous mixtures
-Mechanical sorting -Magnetism -Floatation -Filtration
Separating homogeneous mixtures
-Evaporation -Distillation -Separating a solution by paper chromatography
Which one of the following is NOT an example of a separation technique?
Boiling an egg
How could a mixture of iron filings and copper filings be separated?
Magnetism