Kinesiology Notes (Test 3)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
1
New cards
Cognitive Neuroscience
Responsible for cognitive processes such as learning, memory, and motivational states
2
New cards
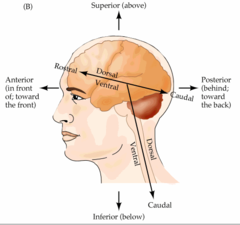
Anterior
Front
3
New cards
Posterior
Back
4
New cards
Superior
Above
5
New cards
Inferior
Below
6
New cards
Rostral
- Toward the face/anterior part of the brain
- Front/top of axis
- Front/top of axis
7
New cards
Caudal
- Toward the back/posterior part of the brain
- Back/bottom of axis
- Back/bottom of axis
8
New cards
Dorsal
Top or upper side
9
New cards
Ventral
Bottom or lower side
10
New cards
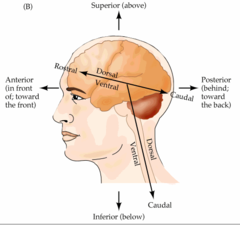
Frontal/Coronal
Separates front and back
11
New cards
Sagittal
Separates left and right
12
New cards
Transverse
Separates top and bottom
13
New cards
CNS
- Differentiated from the PNS
- Consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS includes all other nervous system tissue
- Consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS includes all other nervous system tissue
14
New cards
Cerebral Hemispheres (Brain Lobes)
- Frontal: Planning and movement
- Temporal: Emotion and language (audition)
- Parietal: Somatosensory processing; attention
- Occipital: Vision
- Temporal: Emotion and language (audition)
- Parietal: Somatosensory processing; attention
- Occipital: Vision
15
New cards
Cerebral Cortex
- Location of processing
- More surface area = more processing
- More surface area = more processing
16
New cards
Gyrus (ridges) and Sulus (fissures)
Increase the surface area of the cortex and form brain regions
17
New cards
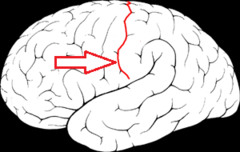
Brain sulcus
- Grooves on the surface of the brain
- Shallow, surrounds gyrus
- Shallow, surrounds gyrus
18
New cards
Gyrus (picture)
19
New cards
Brain fissure
Deep groove that divides the brain into lobes
20
New cards
Lateral/sylvian fissure (Central sulcus)
- Separates frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe
- Able to separate easily
- Able to separate easily
21
New cards
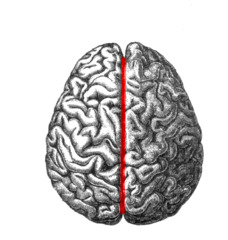
Longitudinal fissure
- Separates cerebral hemispheres
- Largest fissure
- Able to separate easily
- Largest fissure
- Able to separate easily
22
New cards
Corpus callosum
Connects hemispheres allowing them to communicate
23
New cards
Hypothalamus
Connects to the pituitary gland and controls the endocrine system
24
New cards
Brainstem
Midbrain, Pons, Medulla
25
New cards
Cranial nerves
Supply muscles of the face, neck, and head and takes the sensory input from them
26
New cards
Gray matter
- Cell bodies, dendrites, and axon terminals of neurons
- Location of processing along with the location of all synapses
- Location of processing along with the location of all synapses
27
New cards
White matter
Bundles of axons which connect to different parts of gray matter
28
New cards
Basal ganglia
Cells bodies in the CNS located in the base of the brain
29
New cards
Optic Nerve II
Sight from retina into brain
30
New cards
Oculomotor III
Moves eyelid & eyeball and adjusts the pupil & lens of the eye
31
New cards
Trochlear IV / Abducens VI
Moves eyeballs
32
New cards
Vestibulocochlear VIII
Sensory, hearing and balance (auditory)
33
New cards
Spinal cord
- Part of nervous system that innervates your whole body
- Nerves connect with glands or motor functions
- Cervical: Neck
- Thoracis: Trunk
- Lumber: Back
- Sacral: Bottom of lumber
- Nerves connect with glands or motor functions
- Cervical: Neck
- Thoracis: Trunk
- Lumber: Back
- Sacral: Bottom of lumber
34
New cards
Dorsal horn
Sensory part of the spinal cord that receives information
35
New cards
Ventral horn
Motor part of the spinal cord that sends information
36
New cards
What is a Stroke?
- Issue with the vascular system carrying blood into the brain
- Blocked artery
- Blocked artery
37
New cards
Blood brain barrier
- The semipermeable barrier of endothelial cells
- Prevents solutes in the circulating blood from non-selectively crossing into the ECF of the CNS
- Prevents solutes in the circulating blood from non-selectively crossing into the ECF of the CNS
38
New cards
Ventricular System
- (Ventricles as open chambers) that help with the production & circulation of the CSF
- CSF is produced by specialized tissue containing glial cells and blood vessels called the choroid plexus
- CSF is circulated to the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord
- CSF is produced by specialized tissue containing glial cells and blood vessels called the choroid plexus
- CSF is circulated to the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord
39
New cards
The fourth ventricle:
Directly connects to the cerebral aqueduct and central canal of the spinal cord
40
New cards
Meninges
- Surface protection of the spinal cord
- Dura, arachnoid, and pia mater
- Arachnoid Villi: Allows recycling of CSF
- Dura, arachnoid, and pia mater
- Arachnoid Villi: Allows recycling of CSF
41
New cards
Subarachnoid space
Location of CSF
42
New cards
Cell body
Contains one nucleus
43
New cards
Dendrites
- Short extensions off the cell body
- Site for receiving signals from other neurons
- Site for receiving signals from other neurons
44
New cards
Axon
- Extension away from the cell body
- Some can be myelinated to improve conductivity
- Typically branched at end
- Some can be myelinated to improve conductivity
- Typically branched at end
45
New cards
Synapse
Site of communication between neurons or between a neuron and a target tissue
46
New cards
Nodes of Ranvier
- Gaps in myelin sheath, only location of action potential
- Signal "jumps" down the axon -> saltatory propagation
- Signal "jumps" down the axon -> saltatory propagation
47
New cards
Neural impulse
Action potential, electrical signal traveling down the axon
48
New cards
Myelin sheath
- Covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed up neural impulses
- Insulation formed from oligodendrocytes to allow saltatory conduction
- Insulation formed from oligodendrocytes to allow saltatory conduction
49
New cards
Saltatory conduction
The jumping of action potentials from node to node
50
New cards
Axon terminal
Release neurotransmitters into synaptic cleft
51
New cards
Glial cells
Helps regulate the ECF of the CNS through the provision of metabolic and immunological support for the nerve cells
52
New cards
Types of glial cells
Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, schwann cells, and microglia
53
New cards
Astrocytes
- Star-shaped
- Maintains chemical environment and extracellular ion balance
- Provide nutrients to surrounding tissue
- Maintains chemical environment and extracellular ion balance
- Provide nutrients to surrounding tissue
54
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
- Forms myelin sheath in CNS
- Gives structural integrity
- Gives structural integrity
55
New cards
Schwann Cells
Forms myelin sheath in PNS
56
New cards
Microglia
- Macrophages: scavenges for plaques, damaged neurons/synapses, and infectious agents
- "Garbage guys" of the CNS
- "Garbage guys" of the CNS
57
New cards
The central nervous system is an:
Electric organ
58
New cards
The brain transmits information from neuron to neuron to form:
Circuits
59
New cards
Circuits
Process information, much like computer circuits process information
60
New cards
Ions
- Atoms with net positive or negative charge
- Ex: K+, Na+, Cl-, Ca++, A- (valence)
- Ex: K+, Na+, Cl-, Ca++, A- (valence)
61
New cards
Semipermeable membrane
Selectively allows some ions to pass through specific ion channels
62
New cards
Electric Signal
- Current
- To produce movement of an ion, an electrical potential must exist
- To cause movement, an electrical field created by a voltage must exist
- To produce movement of an ion, an electrical potential must exist
- To cause movement, an electrical field created by a voltage must exist
63
New cards
Battery
- An electrochemical cell
- Provides a static potential for power or a released electrical charge when needed
- Provides a static potential for power or a released electrical charge when needed
64
New cards
Resting Potential
- The neuron is inactive, just waiting for a nerve impulse to come along
- The inside of the cell membrane has a negative electrical charge (some K+ channels are open at rest)
- The resting potential is created by a transport protein called the sodium-potassium pump
- This protein moves large numbers of sodium ions (Na+) outside the cell, creating the positive charge
- At the same time, the protein moves some potassium (K+) ions into the cell's cytoplasm
- This pump also contributes to the negative charge of the inside of the membrane
- The inside of the cell membrane has a negative electrical charge (some K+ channels are open at rest)
- The resting potential is created by a transport protein called the sodium-potassium pump
- This protein moves large numbers of sodium ions (Na+) outside the cell, creating the positive charge
- At the same time, the protein moves some potassium (K+) ions into the cell's cytoplasm
- This pump also contributes to the negative charge of the inside of the membrane
65
New cards
Synaptic Potentials
- EPSP: Excitatory synapse, Depolarization
- IPSP: Inhibitory synapse, Repolarization
- IPSP: Inhibitory synapse, Repolarization
66
New cards
Synaptic Summation
- EPSP & IPSP Cancellation: Excitatory and inhibitory graded potentials cancel each other out
- Spatial Summation: Excitatory potentials from many neurons trigger threshold point
- Temporal Summation: Many excitatory potentials from one neuron triggers threshold point
- Spatial Summation: Excitatory potentials from many neurons trigger threshold point
- Temporal Summation: Many excitatory potentials from one neuron triggers threshold point
67
New cards
Action Potential
- All or none response
- Summation of EPSPs and IPSPs causes a large enough voltage at the axon hillock
- Na+ channels open into the neuron and potential becomes more positive
- Na+ channels start to close just before the peak of action potential when K+ channels open, causing repolarization
- When the K+ channels close, the neuron has more K+ channels outside than Na+ channels inside causing the cell potential to drop lower than resting
- Neuron enters a refractory period just before peak action potential when Na+ channels are still closed and K+ are still open
- Summation of EPSPs and IPSPs causes a large enough voltage at the axon hillock
- Na+ channels open into the neuron and potential becomes more positive
- Na+ channels start to close just before the peak of action potential when K+ channels open, causing repolarization
- When the K+ channels close, the neuron has more K+ channels outside than Na+ channels inside causing the cell potential to drop lower than resting
- Neuron enters a refractory period just before peak action potential when Na+ channels are still closed and K+ are still open
68
New cards
"Battery" setup by storing ions on different sides of the membrane:
Produces signals caused by ions moving through membrane channels
69
New cards
Action potentials travel down:
The axon at rapid speeds (100m/s) but require insulation to do so
70
New cards
Two types of synapses
Electrical and chemical
71
New cards
Chemical transmission
- Occurs at synapse
- Specific post synaptic receptors determine effects of neurotransmitters
- Specific post synaptic receptors determine effects of neurotransmitters
72
New cards
Neurotransmitters
Released from the synaptic cleft
73
New cards
Important Neurotransmitters
- Acetylcholine
- Glutamate
- GABA
- Catecholamines
- Serotonin
- Glycine
- Glutamate
- GABA
- Catecholamines
- Serotonin
- Glycine
74
New cards
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Transmitter at the neuromuscular junction that is important for memory; blocked by tubocurarine
75
New cards
Glutamate
Major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and spinal cord
76
New cards
GABA (Aminobutyric acid)
Major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain
77
New cards
Catecholamines
- Dopamine & Norepinephrine
- Can be excitatory or inhibitory on their targets
- Important in additional regulation, motor control, and DNA is functional in some psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia
- Can be excitatory or inhibitory on their targets
- Important in additional regulation, motor control, and DNA is functional in some psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia
78
New cards
Serotonin (5-HT)
- Made from Tryptophan
- Functional in sleep-wake cycles and depression
- SSRIs: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (Prozac)
- Monoamine Oxidase inhibitors prevent the breakdown of catecholamines and serotonin
- Functional in sleep-wake cycles and depression
- SSRIs: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (Prozac)
- Monoamine Oxidase inhibitors prevent the breakdown of catecholamines and serotonin
79
New cards
Glycine
Major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the spinal cord
80
New cards
Stroke
A neurological impairment caused by a disruption in blood supply to a region of the brain
81
New cards
Stroke facts
- Leading cause of adult disability
- Up to 80% of all strokes are preventable through risk factor management
- On average, someone suffers a stroke every 40 seconds in America
- Up to 80% of all strokes are preventable through risk factor management
- On average, someone suffers a stroke every 40 seconds in America
82
New cards
Stroke symptoms
Sudden severe headaches, dizziness, confusion, trouble walking & speaking & seeing, numbess/weakness in the face, arms, legs
83
New cards
Stroke strikes FAST
F: Face (smile)
A: Arm
S: Speech
T: Time to call 911
A: Arm
S: Speech
T: Time to call 911
84
New cards
Circle of Willis
- The joining area of several arteries at the bottom (inferior) side of the brain
- Internal carotid arteries branch into smaller arteries that supply oxygenated blood to over 80% of the cerebrum
- Internal carotid arteries branch into smaller arteries that supply oxygenated blood to over 80% of the cerebrum
85
New cards
What artery is a continuation of the internal carotid artery?
Middle cerebral
86
New cards
Which artery supplies the primary sensory and motor cortices in the posterior frontal and anterior parietal lobes?
Middle cerebral
87
New cards
What type of stroke is due to blockage of an artery?
Ischemic
88
New cards
Types of strokes
Hemorrhagic and Ischemic
89
New cards
Hemorrhagic
- 15% of strokes
- Causes by a burst blood vessel
- Leaking of blood causes blood clots to push on the brain
- Causes by a burst blood vessel
- Leaking of blood causes blood clots to push on the brain
90
New cards
Ischemic
- 85% of strokes
- Blood clots block the blood flow
- Loss of blood & oxygen
- Thrombotic & Embolic
- Small strokes
- Blood clots block the blood flow
- Loss of blood & oxygen
- Thrombotic & Embolic
- Small strokes
91
New cards
Thrombotic
Blood clot is stationary
92
New cards
Embolic
Blood clot is traveling
93
New cards
Small stroke
- Transient ischemic attacks (TIA)
- Can lead to Lacunar Lesions
- Can lead to Lacunar Lesions
94
New cards
Intracerebral
Arteriovenous malformation (aneurysm)
95
New cards
Subarachnoid
- Aneurysm
- Trauma
- Trauma
96
New cards
Voluntary Movements are controlled through 4 major processes
- Idea: Abstract motivation
- Conform to environmental constraints
- Plan the necessary body movements
- Execution: Activate muscles and correct errors
- Conform to environmental constraints
- Plan the necessary body movements
- Execution: Activate muscles and correct errors
97
New cards
Brain Regions activated
- Having an idea: Prefrontal cortex
- Conforming to environmental constraints: Posterior parietal cortex
- Making a plan: Supplementary and Premotor Cortex
- Executing the plan: Primary motor cortex
- Conforming to environmental constraints: Posterior parietal cortex
- Making a plan: Supplementary and Premotor Cortex
- Executing the plan: Primary motor cortex
98
New cards
What Cortical area is associated with visual to body centered coordinate transformations?
Posterior parietal cortex
99
New cards
What Cortical area is associated with coordinating bilateral arm movements?
Supplementary Motor Area (SMA)
100
New cards
Premotor Areas
- Planning of specific body segment motions and learning through observation of movements
- Once plans are transformed into body coordinates, planning of body segment motion occurs
- Once plans are transformed into body coordinates, planning of body segment motion occurs