Arson, Ballistics, & Tools— Forensics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Arson evidence can be difficult to investigate because evidence may be…
burned
charred
wet (water damage)
fire investigators detect & identify:
chemical materials
igniters
Fire & Investigation
fire is a product of oxygen combining heat & light (a flame)
Investigators look for a V-pattern of char/soot that leads them to the fire’s origin
Accelerants are detected by…
portable hydrocarbon detectors
accelerants sniffing dogs
identifiable pour patterns
Fire evidence should be…
packaged immediately in airtight containers to avoid evaporation
Reasons for arson crime:
insurance fraud (#1 reason)
crime concealment
pyromania
revenge
classification of arson
1st degree: burning an occupied building
2nd degree: burning an unoccupied building
3rd degree: burning an abandoned building/ area
firearm
weapon capable of firing a projectile using a confined explosive
ballistics can tell investigators…
firearm type
caliber of bullet
# of bullets fired
angle of impact from shooter to victim
if firearm was used in previous crime
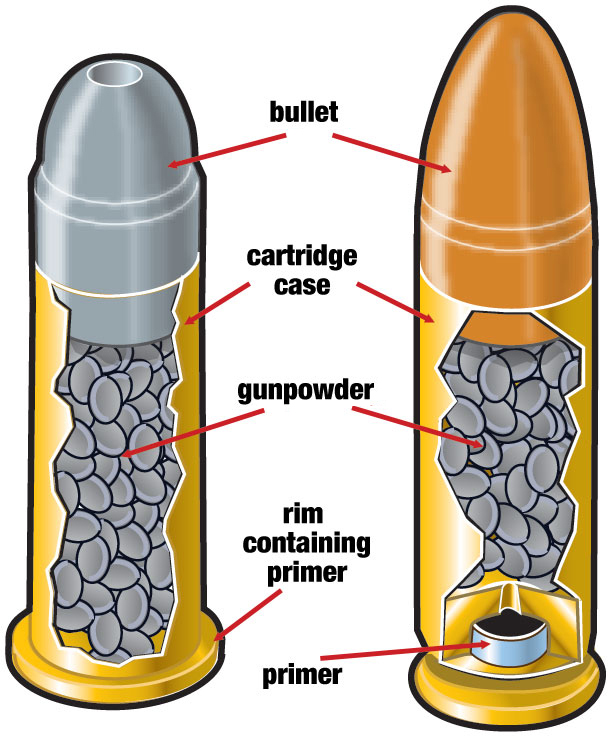
Cartridge
Bullet
Casing
Gunpowder
Rim
Primer
Handgun (firearm classification)
pistols & revolvers
fire with 1 hand
can be semi-automatic (1 bullet per trigger) or fully automatic
Long gun (firearm classification)
rifles & shotguns
require 2 hands
rifles fire bullets
shotguns fire pellets (multiple projectiles) or a slug (single projectile)
How a firearm works
trigger pulled
firing pin hits base of cartridge
ignites powder inside bullet
pressure pushes bullet from casing into barrel of firearm
bullet follows land & groove patterns of barrel & spirals out of barrel
Identification
Every weapon leaves its own unique, reproducible marking on a bullet & cartridge (regardless of gun type, style, manufacturer, etc.)
useful in convicting criminals to crimes involving guns
Striations
stratch marks on bullet from rifiling lines inside the barrel
lands & grooves
lands & grooves in barrel produce bullets with specific patterns that make the bullet spin upon firing
Breech markings
marks left on spent cartridge casings
explosive force pushes bullet forward
Newton’s 3rd law sends casing backward against breechblock
Fire pin markings
leave unique stamping on cartridge primer/rim
Gunshot Residue (GSR)
traces of smoke & unburned powder are released as the bullet is fired
GSR contains nitrates that can stick to the person holding the firearm or anyone nearby
that amount of GSR decreases as the distance between firearm & victim increases
can be removed by washing, but chemical tests can detect residual residue
Bullet Trajectory
can be calculated to find the location of a shooter
you need 2 reference points along the flight path of the projectile
ex) bullet holes, wounds, spent cartridge casings