P6 Waves
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is a transverse wave? (2)
a wave that oscillates at right angles (perpendicular) to the direction it is travelling.
they can travel through a vacuum
What is a longitudinal wave? (2)
a wave that oscillates in the same direction (parallel) as the direction it is travelling
they can only travel through a medium
What is an example of a transverse wave?
Water waves (ripples)
Light
What is an example of a longitudinal wave?
Sound waves
What is the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves?
Longitudinal waves osciallate parallel to the direction of energy transfer. Transverse waves oscillate perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer.
Are water ripples examples of a transverse or a longitudinal wave?
Transverse
Is sound an example of a transverse or a longitudinal wave?
Longitudinal
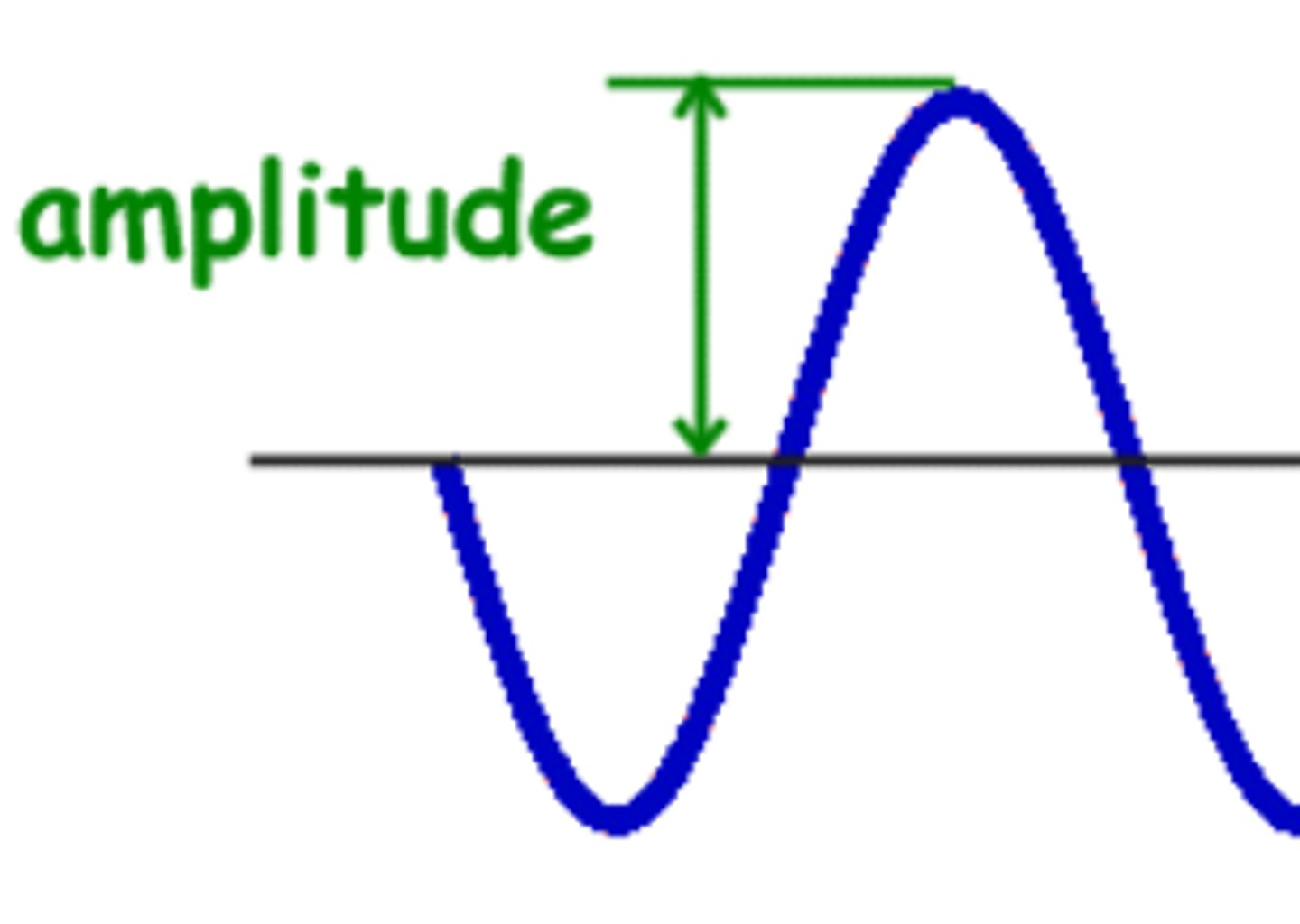
What is the definition for the amplitude of a wave?
the maximum displacement of a point on a wave away from its undisturbed position
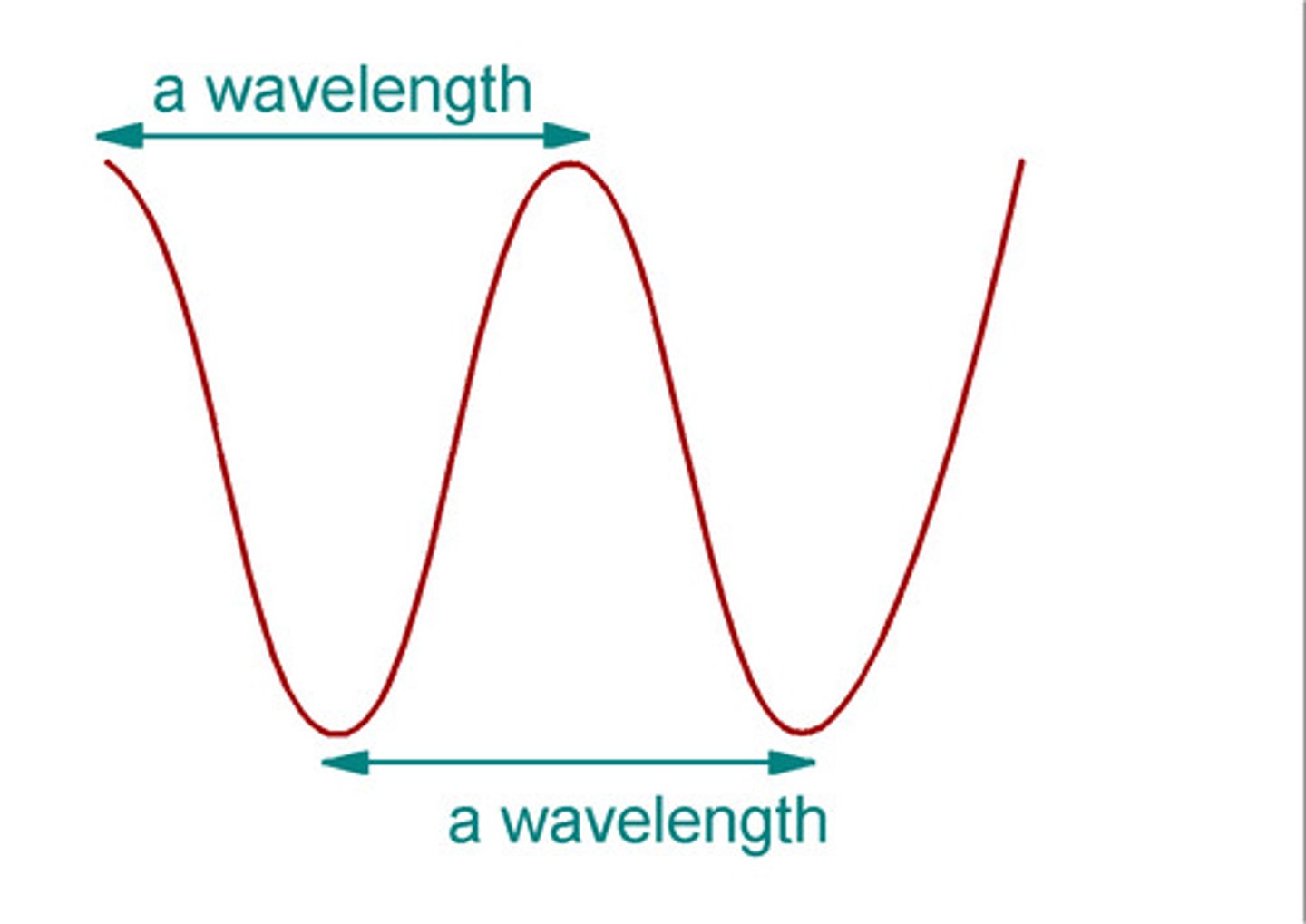
What is the definition for the wavelength of a wave?
the distance from a point on one wave to the same point on the next wave
What is the definition for the frequency of a wave?
the number of waves passing a point each second
What is the definition for the time period of a wave?
the time taken for a wave to complete one full oscillation
What is the equation that links time period and frequency of a wave?
Period = 1 / frequency
What is the unit for time period?
seconds, s
What is the unit for frequency?
Hertz, Hz
What is the equation that links wave speed, wavelength, and frequency of a wave?
wave speed = frequency x wavelength
What is the unit for wave speed?
metres per second, m/s
What is the unit for wavelength?
metres, m
Describe a method to measure the speed of sound waves in air (4)
Make a loud noise on a field near a wall
Use a measuring tape to measure the distance to and from the wall
Use a stopwatch to measure the time for the echo of the noise to be heard
Use the equation: speed = distance / time to calculate the speed of the sound waves
Describe a method to measure the speed of ripples on water (4)
Set up a ripple tank
Use a ruler to measure wavelength
Use a stopwatch to measure frequency
Use the equation wave speed = frequency x wavelength to calculate the speed
What are electromagnetic waves?
transverse waves that transfer energy from the source of the waves to an absorber
What are the waves on the electromagnetic spectrum, in order from longest to shortest wavelength? (7)
Radio
Microwaves
Infrared
Visible light
Ultraviolet
X-rays
Gamma rays
Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum transfers the most energy?
Gamma rays
Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum has the shortest wavelength?
Gamma rays
Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum has the highest frequency?
Gamma rays
Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum has the longest wavelength?
Radio waves
Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum has the smallest frequency?
Radio waves
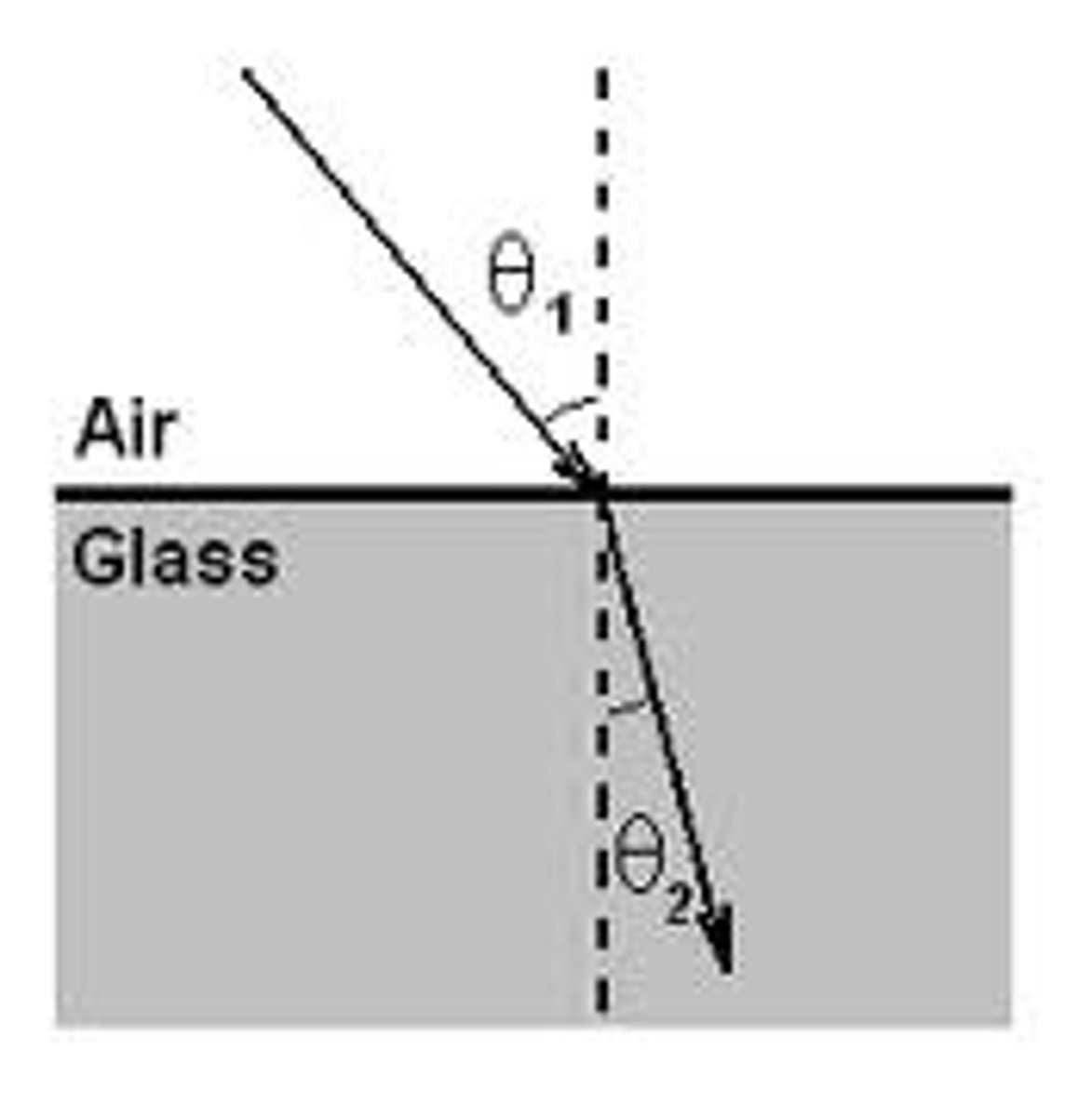
What happens when a wave refracts?
It changes direction
What type of surfaces are good at absorbing and emitting raditation?
Dark, matte (dull) coloured surfaces
What type of surfaces are good at reflecting radition?
Bright, shiny coloured surfaces
How can gamma rays be produced?
by changes in the nucleus of an atom
Which types of waves can have hazardous effects on body tissue? (3)
ultraviolet waves
X-rays
gamma rays
What is radiation dose (in Sieverts) a measure of?
the risk of harm resulting from an exposure of the body to radiation
What are the risks of ultraviolet waves on body tissue? (2)
can cause skin to age prematurely
can increase the risk of skin cancer
What are the risks of X-rays and gamma rays on body tissue?
they are ionising radiation that can cause the mutation of genes and cancer
What are uses of radio waves?
Television and radio
What are uses of microwaves? (2)
Satellite communications
cooking food
What are uses of infrared? (3)
Electrical heaters
cooking food
infrared cameras
What are uses of visible light?
Fibre optic communications
What are uses of ultraviolet?
Energy efficient lamps, sun tanning
What are uses of X-rays? (2)
medical imaging
treatments (e.g. treating cancer)
What are uses of gamma rays? (2)
medical imaging
treatments (e.g. treating cancer)