Unit 2: Physical and Chemical Properties, Math Foundations
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
Atoms
submicroscopic particles that are the fundamental building blocks of matter
Molecules
Atoms bonded together in specific geometrical arrangement
3 things properties of a molecule depend on:
1.) The type of atoms bonded (elements combining)
2.) The number of each type of atom
3.) Types of bonds (ionic, covalent, angles, lengths)
2 ways matter can be classified:
1.) Physical state (solid, liquid, gas)
2.) Composition
What are the three states of matter?
1.) Solids
2.) Liquids
3.) Gases
Describe the properties of a solid and its particles
Definite Volume
Definite Shape
Particles are tightly packed in fixed locations
Particles vibrate but cannot move past each other
Crystalline
Atoms or molecules are in patterns with long-range, repeating order
Ex: table salt and diamond (regular three-dimensional pattern)
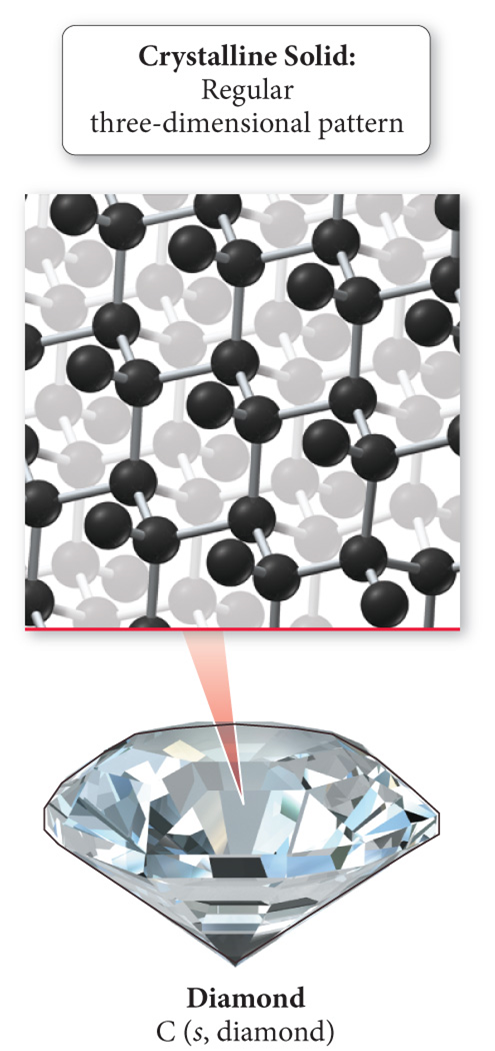
Amorphous
Atoms or molecules do not have any long-range order
Ex: glass and plastic
Describe the properties of liquid and its particles
Indefinite Shape (takes shape of container)
Definite Volume
Particles are in close contact, allowing them to move relative to each-other (reason why shape is indefinite)
Describe the properties of gas and its particles
Indefinite Shape (takes shape of container)
Indefinite Volume (takes volume of container)
Particles are far apart, meaning they do not touch each other and can move freely
Gas particles are compressible: can squeeze particles close together
Pure Substances
Made up of one component
Composition does not vary from one sample to another
ex: (water from other planet and water from earth remain the same)
Components can either be:
Individual atoms (ex: helium)
Groups of atoms (ex: water, sodium chloride)
What are the 2 types of pure substances and define them
Elements —> CANNOT be broken down into simpler substances
Basic building blocks of matter
Composed of a single type of atom (ex: helium)
chemically reactive and combine with other elements to form compounds
Compounds —> composed of 2 or more elements
ex: water (H2O) = hydrogen + oxygen
more common than pure elements
Define mixture
Matter that depends on how uniformly the components that make up the substance mix (Heterogenous and Homogenous)
Heterogenous Mixture
composition varies from one part of the mixture to another
atoms and molecules separate
portions of a sample have different composition and properties
ex: salad, vegetable soup, sand and water — each sample will be different
Homogenous Mixture
maintains same composition throughout
atoms and molecules mix uniformly
all portions of a sample have the same composition and properties
ex: salt water, stainless steel (salt diffuses into water)
Why do certain mixtures have to be separated differently?
Since every mixture has different components and properties that require a different method
Decanting
Mixture of sand and water can be separated by carefully pouring off water into another container
Some water still present in the sand, less effective than filtration
Define Distillation and its process
used to separate a homogenous mixture of liquids
mixture is heated to boil off the more volatile (easily vaporizable = lower boiling point) liquid
the volatile liquid evaporated is then re-condensed in the condenser which is later collected
Define Filtration and its process
used to separate a mixture of an insoluble solid (cannot dissolve) and liquid
uses grates / filter paper to trap solid and allow for the liquid to be collected
ex: pouring pasta with water into grate to let hot water out and keep the pasta in
What is a physical change?
Alters only physical state or appearance of matter (no change in identity / composition)
no change in composition
atoms or molecules do not change their identity
ex: water boiling —> water changed from liquid to gaseous state (gas remained composed of water molecules, H2O)
as the water heats, molecules at a very fast pace, however the molecular formula does not change
What is a chemical change?
alters the composition of matter (changes appearance and identity)
atoms rearrange, transforming the original substances into different substances (change in composition)
ex: rusting of iron—iron atoms combine with oxygen molecules in air forming iron oxide (process called oxidation)
Examples of Physical Change:
1.) Dry Ice subliming (turning into gas)
sublimation = solid turning into a gas
Chemical composition unaltered, therefore Physical Change
2.) Sugar Dissolving
dissolve = solid submerging and diffusing into mixture
Chemical Composition Unaltered, therefore Physical Change
Examples of Chemical Changes:
1.) Propane Gas Burning
Propane’s identity changes as it burns (with the help of oxygen)
Chemical Composition altered, therefore chemical change
Define physical property and give examples
Property that a substance displays without changing its composition
ex: color, taste, melting / boiling point, density, etc
Define Chemical Property and give examples
Property that a substance displays only by changing its composition via a chemical change
often indicated by temperature, color change, or production of gas (not sublimation since change in composition occurs)
ex: flammability, corrosiveness, acidity, etc.
What are S.I. Units and its advantages?
International System of Units
2 advantages over common units (feet-inches, pounds, ounces)
Universal: used by scientists all over the world
Based on multiples of 10 (metric system, easy to manipulate/use when moving decimals and adding / subtracting zeroes)