Lecture 6 - OCD
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are obsessions and compulsions?
Obsessions
* Intrusive and distressing thoughts, images or impulses
* Efforts to suppress or neutralize thoughts, images, impulses
* Insight in ‘internal origin’
Compulsions
* Behavior as response to obsessions (covert or overt)
* Behavior often rigid, repetitive and according to strict rules
* Aimed to reduce distress or prevent catastrophe
People that don’t have OCD can also have obsessions and compulsions. What is the difference between clinical and non-clinical?
•Interpretation
•Distress
•Resistance
•Effort to suppress
•Frequency
Give an example of how compulsions maintain obsessions?
Obsession about whether the oven has been turned off → Anxiety, compulsion to act → Acts on the compulsion → Feels relief, strengthening the obsession
What are common themes of intrusions?
Sexual, religious, harm, contamination
What cognitive domains exist in OCD?
Thought-action-fusion (TAF): - Your thoughts have negative consequences
- Your negative moral thoughts are equal to a
negative moral action
Exaggerated responsibility: Exaggerated conviction that the patient is able to
prevent or cause a negative event.
Controllability of thoughts: Control wishes and thoughts
Perfectionism: Conviction that there is ONE right way to do things.
Overestimate danger: The risk of serious negative incidents is overestimated
Intolerance of uncertainty: The idea that the patient cannot bear a situation
without a 100% certainty
What is the prevalence of OCD?
Estimated prevalence is about
1-3% of adult population
1% of young people
Fourth most common mental disorder after
depression, alcohol and substance abuse,
and social phobia
What is the comorbidity for OCD?
About 30 to 55% comorbid with depression (MDD);
65% life-time history of MDD
25% concurrent with another anxiety disorder most often GAS, social phobia and PTSD
8% concurrent with an eating disorder
5% concurrent with Tourette’s syndrome
Explain the two-factor learning theory view of OCD by Mowrer?
Obsessions give rise to anxiety or distress →
Compulsions reduce obsessional anxiety →
The performance of compulsions prevents the extinction of obsessional anxiety →
Compulsions are negatively reinforced by the brief reduction of anxiety they engender
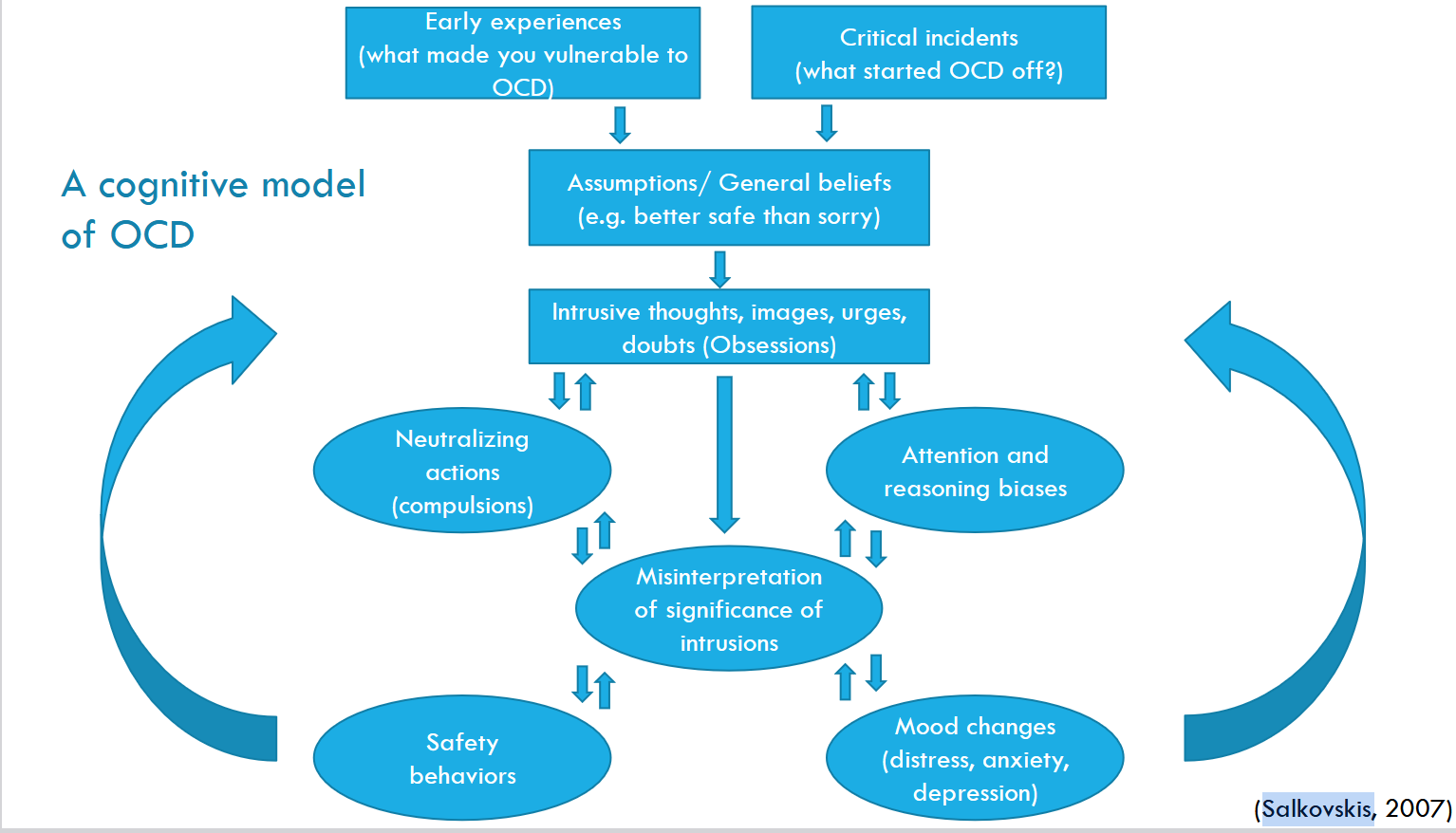
Name the elements of the cognitive model of OCD (Salkovskis, 2007)
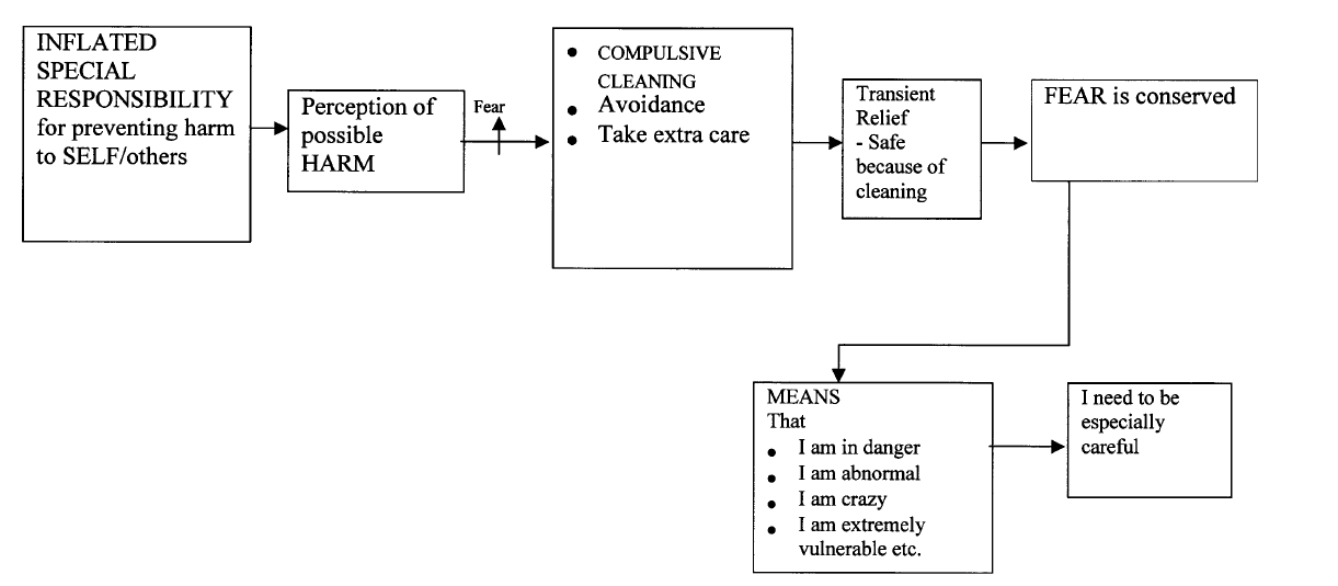
Explain the OCD model by Rachmann (2002)
What did the study by Dek et al. find?
That OCD patients check uncertain situations more, but that this also leads to memory distrust (this is why people check 5 times whether they left the stove on, for example)
Exposure with response prevention
A type of exposure therapy where the patient is put into an anxiety-inducing situation and not allowed to perform the compulsion that would relieve their anxiety
What are the steps of exposure w response prevention?
Before exposure:
Make concrete what the aim of the exposure is – make concrete what the “If I do….,
then … will happen” expectancy is.
Register the credibility of the “If (cs)…, then (US)” expectancy instead of the level of
anxiety
During exposure:
try to provide the patient with as much disconfirmative information in different contexts!
After exposure:
Check if the the “If (cs)…, then (US)” expectancy has become true or disconfirmed
How do you know this? Have information provided why the CS is not an adequate
predictor of the US (beware of safety behavior!).
What if a patient does not have a specific threat expectation but just performs a compulsion because something “does not feel right”
Do the ERP until it “feels right”
What, in short, did various studies find regarding OCD symptoms and the Covid-19 pandemic?
OCD symptoms especially regarding contamination got 87% worse during Covid
Intolerance of uncertainty and fear of Covid-19 relates to the use of non-essential safety behaviours
Small differences between Spain and the Netherlands and
Germany
Intolerance of Uncertainty predicts the use of non-essential safety behaviors in the
Netherlands and Germany, but fear of Covid-19 predicts the use of non-essential safety behaviors in Spain
What are the most common reasons for why people hoard?
Temperamental
• Environmental
• Genetic & physiological
=> CBT and/or anti-
depressants
What is body dysmorphic disorder?
Perceived flaws in physical appearance
• Hair line
• Nose
• Egality of skin
• Eyebrow ark
• Lips
How does body dysmorphic disorder differ between sexes?
Muscle dysmorphia occurs almost
exclusively in men
-> more likely to have comorbid
substance abuse disorders
Preoccupation with weight more
likely to occur in women
(Breasts/chests, buttocks, legs, hips
and excessive body hair)
What is the treatment for BDD?
CBT
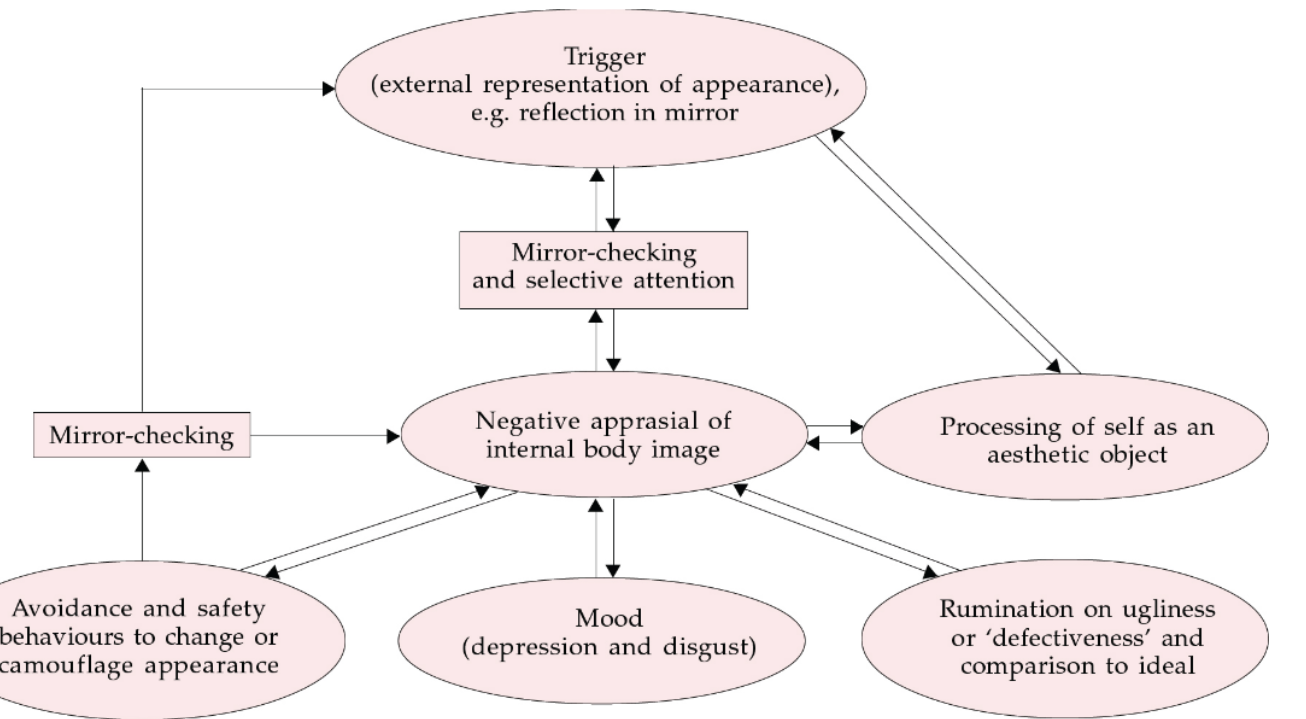
Explain the cognitive behavioural model for BDD?