Geography mock flashcards
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Where is Medmerry (managed retreat) ?
Near Chichester, West Sussex
What is the coastline like and mainly used for at Medmerry ?
low-lying coast mainly used for farming and caravan parks
What coastal defences did Medmerry used to have?
A low sea wall that needed repair
Why was managed retreat decided at Medmeery?
A new sea wall would have been very expensive
As the land was relatively low value they allowed the sea to breach the sea defences and flood some farmland
How much did the Medmerry managed retreat scheme cost and when did it take place?
£28 million and controlled breach of the defences took place in November 2013
What will the Medmerry Managed Retreat achieve?
Create a large natural saltmarsh to form a natural buffer to the sea
Help to protect surrounding farmland and caravan parks from flooding
Establish a valuable wildlife habitat and encourage visitors to the area
Why were embankments constructed at Medmerry managed retreat?
Top give protection to farmland, roads and settlements. This alteration of the coastline is called coastal realignment
Where is the Holderness coast?
In the North East of England in East Yorkshire
On the North sea and North of the Lancashire coast
Expands from Flamborough Head in the N and Spurn Head in the S
What is the Holderness Coast like?
Very weak coastline
Very weak boulder clay which is rapidly eroding away
Fastest eroding coastline in Europe (10m/yr)
Longshore drift travels from N to S
Winter storms + prevailing wind form the NE
What are key features of settlements and places along the Holderness Coast (excluding Mappelton)?
Flamborough Head
Made out of chalk (headland)
Caves, arches and stacks
Bridlington
Popular for tourism
Town protected by 4m high sea wall
Groynes protect beach
Skipsea
10 miles S of Bridlington
Village - Post offices, shops etc.
Sea defences at Bridlington making things worse
Easington
Very expensive major gas terminal
terminal built on cliff top
rock armour to protect terminal
Spurn Head
Spit with salt marsh behind and lifeboat station on tip
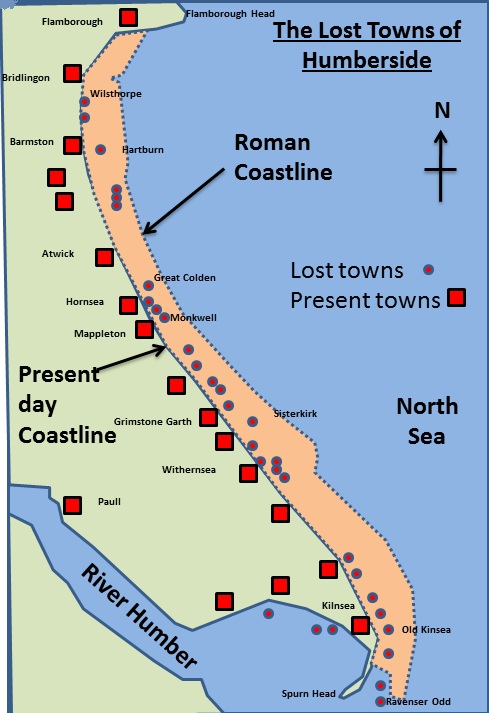
Key facts about Mappelton (Holderness coast)
342 people
50 homes
B142 road goes through village
How much was spent and what coastal defences were put in place at Mappelton?
£2 million in 1991
2 Rock groynes and rock armour
Granite for Norway create rock groynes
Cliff has been stabilised through landscaping and vegetation cover
How was Mappelton coastal protection successful?
Groynes have reduced erosion and a beach has built up, preventing more erosion
How was Mappelton coastal protection unsuccessful?
Further south the rate of erosion has significantly increased as no sediment is being replaced as it is all trapped by groynes in Mappelton
This means there is no beach to protect the cliff→increased erosion and slumping
Significant loss of land
Why do people say Mappelton should have used managed retreat?
Much cheaper
Does not harm places further down the coast
Allows salt marsh to form
Road could be moved which would prevent the need for sea defences in Mappelton in the future
What is the population of Rio?
6.5 Miliion (city) & 12.5 Million (surrounding areas too)
What is the main language of Rio?
Portuguese
Rio is the ... city in Brazil
2nd Largest
Rio is a ... capital
Cultural
Why is there urban growth in RIo?
Migrants coming from Amazon Basin, Argentina, Bolivia, South korea, China, Portugal, USA and UK 65% of growth in last 150 years
Natural increase
What major sporting events did Rio host and when?
2014 World Cup. 2016 Olympic Games
What % of GDP does Rio produce?
5% of Brazil's GDP
What are Rio's main exports?
Coffee, sugar, iron ore
What are Rio's main service industries?
Banking, finanace, insurance
What are Rio's main manufacturing industries?
Chemicals, pharmacueticals, clothing, furniture, processed foods
Name some famous landmarks in Rio
Statue of Christ the Redeemer, Sugar Loaf Mountain, Guanabara Bay, Copacabana, Ipanema Beach
What are the zones of Rio?
North zone, Centro, South zone, West zone
Describe the North Zone
Port area, Maracana soccer stadium, favelas
Describe Centro
Historic buildings, CBD and main shops
Describe the South Zone
Tourist hotels and beaches. Richest area, luxury flats (Vidigal) . Overlooked by Rocinha favela - largest favela in the continent
Describe the West Zone
Olympic stadiums. Campo Grande industrial area (steel works) - low quality housing. Barra da Tijuca - Was poor,turned posh
What are the main social challenges facing Rio?
Healthcare
Education
Water Supply
Energy
How is Healthcare a challenge in Rio?
2013-only 55% of city had a local family health clinic
West Zone, only 60% of women received medical care
Life expectancy in west zone - 45 years vs 80 in the south
Average infant mortality is 19/1000
Poor sanitation + Crowded living conditions = easy for water born disease to spread quickly
What are the opportunities/solutions for healthcare in Rio?
3 public hospitals + 6 private - much easier access than in rural areas
(Mobile health clinics) Santa Marta 13km to nearest hospital… Medical kits taken to help detect + treat disease
How is Education a challenge in Rio?
Only 50% of all children continue education after 14
Many children drop out of school +get involved in drug trafficking
Teachers have poor pay + training + there are constant shortages
Compulsory education for 6-14- low enrolment - about 25% of poorest children do not go to school
what are the opportunities/solutions for education in Rio?
90% of children <10 can read + write
Encouraging local people to volunteer to help in school
Giving school grants to poor families to help meet the cost of keeping their children in school
Making money available to pay for free lessons in volleyball, football, swimming + squash in Rocinha favela
Opening a private university in Rocinha favela
How is Water Supply a challenge in Rio?
12% of of RIo’s population did not have access to running water
37% of water is lost through leaky pipes, fraud and illegal access
in 2015 SE Brazil experience worst drought in 80 years » Parabuina + Santa Branca reservoirs declared empty
What are the opportunities/solutions for water supply in Rio?
City has largest water treatment works in the world
Work to improve quality + quantity of water
7 new treatment plants built between 1998+2014 + 300+km of pipe laid
by 2014 95% of population had a mains water supply
How is Energy a challenge in Rio?
Rio frequently suffers blackouts due to electricity shortages
Many people in favelas illegally tap into main electricity supplies →dangerous + can cause fire
Rio is expected to grow by 1 mil in next 10 year + demands of Olympics = more demand
what are the opportunities /solution for energy in Rio?
Government concentrates increasing energy supplies to cities like Rio with high population density
99% of city residents have direct access to electricity
3x more people have access to electricity than in countryside
installing 60km of new power lines
2 new nuclear reactors, third due to start in 2023
Simplício hydro electric complex will increase supply of electricity by 30% - took 6 years to build, us$2 billion
Favela community energy projects: Babilonia favela, NGO Revusolar installed solar panels to provide sustainable energy to 35 families,2 shops+ 1 school
What are Rio’s economic opportunities?
one of highest income per head in country - many jobs and service sector
second most important industrial centre in Brazil after Sao Paulo
Growing pop. of skilled migrants
Existing industries stimulate development of new industries (Multiplier effect)
Oil discovered offshore - oil related industry
Popular for tourism
How have industrial areas stimulated economic development (Give an example rio)?
Large employment and attracts investment
Terenium steelworks, Sepeiitba Bay
Rich iron ore deposits
Built in area of natural beauty - controversial
Multiplier effects -construction, industry, income etc.
Brazilian + local government have benefited from tax revenue + investment into the city
Local people have secure employment, healthcare, education
Local communities benefited form investment + self-help projects
How is Rio challenged by unemployment?
2017-2020 unemployment rate was 15%
Women unemployment rate in 2019 was 18%
High unemployment in favelas
Large informal economy - 3.5 million workers do not have a formal employment contract - no taxes
2015 recession
High corruption
2016 Olympics had few long term employment
2018- government had an economic crisis
How is Rio challenged by crime?
Robbery + violent crime is common
Powerful gangs control drug trafficking in the favelas e.g Red Command
2017, murder rate increase by 20%
Many people distrust police - corrupt
What are the solutions to Crime in Rio?
2013 - Pacifying Police Units (UPPs) set up to reclaim favelas from drug dealers
Police taken control of crime dominated Complexo de Alemano + 30 other small favelas
2020, 25 people killed after armed police stormed Jacarezinho in pursuit of drug traffickers
What are the main environmental challenges in Rio?
Air pollution
Water pollution
Waste disposal
How is Air pollution a problem in Rio?
Rio is most congested city in South America- increases air pollution
Rio’s mountainous coast restricts options for road building » congestion on main routes
Car ownership increased by 40%
Air pollution causes 5000 deaths per year
Brown smog hangs over city - exhaust fumes + industrial pollution
What are the solutions to air pollution in Rio?
Expansion of metro systems under Guanabara Bay, to South zone + Barra de Tijuca
Toll roads in city centre to reduce congestion
Making coasts one way roads during rush hours to improve traffic flow
How is Water pollution a problem in Rio?
Guanabara Bay is highly polluted- major threat to wildlife
Commercial fishing declined by 90% in last 20 years
Pollution could impact tourism
Rivers heavily polluted with sewage + waste
Over 50 tonnes of industrial waste discharged daily
Oil spills + other ship discharges contaminate the bay
What are the solutions to water pollution in Rio?
12 new sewage works built since 2014 - US$68 mil
Ships fined for discharging fuel into the bay illegally
5km of new sewage pipes installed around badly polluted areas
How is Waste disposal a problem in Rio?
3.5 million tonnes of waste produced annually - only 2% recycled
Most waste ends up in recently opened Seropedica landfill site - 70km from city » Landfill gas produced used to generate electricity / converted into fuel for waste collection vechiles
Waste collection infrequent in favelas due to narrow steep streets
Waste litters the streets + enters rivers → algal blooms, floating debris
How many favelas are in Rio and where are they found?
1000 - housing about 24% of Rio’s population
85% is suburbs /outer areas
Many favelas developed on steep slopes
Some located near industrial areas for employment
Recently favelas near city centre have been cleared to make are more attractive for businesses and tourists - controversial
What are the main challenges of living in favelas?
Construction
Unemployment
Crime
Health
Services
How is construction a challenge in the favelas?
Houses initially poorly built - now most built from concrete + brick
Heavy rain can cause landslides- 2010, 214 people killed + 13000 lost homes as they were swept away
Limited road access due to steep slopes
How is unemployment a challenge in the favelas?
Unemployment rates as high as 20%
Most employment is poorly paid with irregular jobs in the informal sector
Average incomes may be less than £75 a month
How is Crime a challenge in the favelas?
20 per 1000 murder rate in favelas
Drug gangs dominate the favelas
Many inhabitants distrust police due to violence + corruption
How is health a challenge in the favelas?
Population densities of 37000 per km2
Infant mortality rate as hi9gh as 50/1000
Waste builds up in street- danger of disease
Occasional fires produce harmful smoke
How are services a challenge in the favelas?
In non- improved favelas - 12% of homes do not have running water, >30% have no electricity, 50% have no sewage connections
Many homes use illegal connections to electricity pylons
Sewers are often open drains
Drinking water often comes from city water mains - located at bottom of steep slopes
When did authorities in Rio acknowledge the existence of favelas?
1980 - before areas not shown on maps
How are favelas being improved?
mind 1980s city planners decided to upgrade them and provide essential services
After being awarded Olympics, move to destroy favelas near Olympics
What is the Favela Bairro Project?
1995-2009 , US$1 billion ‘slum to neighbourhood’ project
Aimed to integrate favelas into city - addressing issues of land ownership, infrastructure + service provision
Involved over 25000 residents in 73 communities
How were Social Problems addressed by the Favela Bairro Project?
Day care + after school care, enabling adults to get jobs
Improving adult literacy
Medical services for drug addiction, alcoholism, victims of domestic violence
Building of new health, leisure + education facilities
Pacifying Police Unit set up with police patrolling the community to reduce crime
Access to water supply + drainage system
Cable car system across the Complexo de Alemao hillsides
How were Environmental Problems addressed by the Favela Bairro Project?
Replacement of wooden buildings with brick - more permanent, stronger
Removal of house from dangerous steep slopes
Widening + paving of streets to allow access for waste collection + emergency services
Paved + formally named roads
Hillsides secured to prevent landslides
How were the Economic Problems addressed by the Favela Bairro Project?
Access to credit allows inhabitants to buy materials to improve homes
100% mortgages available for people to buy homes
What are the successes of the Favela Bairro Project?
Improved Quality of Life, Employment, mobility
Model for UN and other Brazilian cities
What are the issues of the Favela Bairro Project?
More needed to improve literacy + employment
Rents risen in improved favelas
New elevated pavements have cause rainwater to flood homes
Some new infrastructure costly and not maintained
Credit schemes not widely available
Residents may lack skills + resources to make repairs
What has happened since the Favela Bairro Project?
Some favelas demolished for Olympics
Morar Carioca program aimed to improve 800 favelas by installing water, sanitation+ drainage systems + improving roads + social services - slow progress
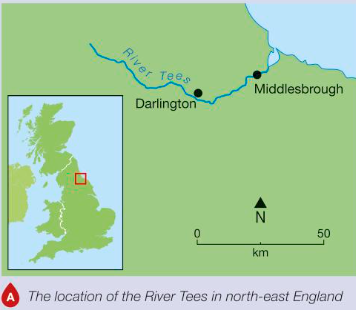
Where is the River Tees?
North East England
Source is in Pennines and flows east to mouth at North sea Middlesbrough
What are the characteristics of the River Tees’ upper course?
Hard impermeable rocks
V shaped valley
interlocking spurs
Many small tributaries
High Force- Uk’s largest waterfall- 21 metres high
12000 mm annual rainfall
600m altitiude
Cumbrian moorlands
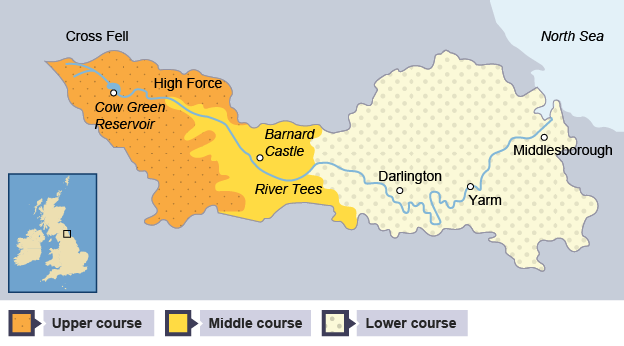
How did High Force on the river Tees form?
area of hard rock, called Whin Sill (or Whinstone), is located above a layer of soft rocks (sandstone and shale)
leaves a gorge
20m3 /s flow rate
What are the characteristics of the River Tees’ middle and lower course?
Middle
Meanders - near Barnard castle
Lower
Near Yarm - large meanders → oxbow lakes. Yarm is enclosed in meander bend
levees
large estuary with mudflats - one of largest container ports in UK. Industrial land works
Stockton - river straightening
95% agricultural land use
Where are the Sommerset levels and what are they like?
Area of low lying coastal plains + wetlands in the SW of UK in Sommerset
Several rivers flow through and drain into the Bristol Channel
Low lying - prone to flooding
Why was prolonged heavy rainfall a cause of the Somerset floods?
series of Atlantic storms brought persistent rainfall + gale force winds
Record rainfall - 183.3mm - 200% higher than average for month
Caused ground to be saturated
Why was high tides + storm surges a cause of the Somerset floods?
High tides in Bristol channel created tidal surges that blocked floodwater from escaping
Why was reduced river dredging a cause of the Somerset floods?
Sediment build up in rivers due to reduced dredging reduced carrying capacity of rivers
Why was land use changes a cause of the Somerset floods?
Conversion of grassland to maize field reduced the land’s ability to retain water
What were some social effects of the 2014 Somerset floods?
Over 600 homes flooded
16 farms evacuated
Residents evacuated into temporary accommodation, for months in some cases
power supplies disrupted
Villages (Moorland + Muchelney) completely cut off
Lives severely disrupted - shopping, school, work
Contaminated floodwater posed health risks
What were some economic effects of the 2014 Somerset floods?
Estimated damage over £10 million
Agricultural land flooded -14,000 hectares underwater 3-4 weeks, 1,000 livestock evacuated
Road closures
Trains cancelled
People unable to go to work
Businesses forced to close due to flooding and infrastructure damage
What were some environmental effects of the 2014 Somerset floods?
Sewage, chemicals like pesticides and oil contaminated floodwater which spread
Ecosystems and habitats destroyed
Lots of debris deposited
Prolonged flooding
Soli erosion + degradation
Stagnant water deoxygenated - had to be reoxygenated before pumped back into rivers
What were some immediate responses of the 2014 Somerset floods?
Warnings - weather + flood warnings issued + monitors
Flood defences- barriers ,sand bags, pumps, valuables moved upstairs
Emergency evacuation and rescue
Army, 40 royal marines sent in do deliver food, equipment etc.
65 pumps used to drain 65 million m3 of floodwater
What was done for dredging as a long term response for the Somerset floods?
River Tone + Parrett dredged to increase capacity
8km dredged
What long term flood defences were put in place after the Somerset floods?
500m of road in Muchelney raised to prevent village being cut off
river banks raised + strengthened
Bridgewater tidal barrier plans - protect against tidal surges from the Bristol channel
How were drainage systems enhanced as a long term response to the Somerset floods?
Pumping stations installed to manage water levels
New river channels under the a372 at Beer Wall
What is the Flood action plan (Somerset)
20 year flood action plan- improve resilience and flood management - £80 million cost
Somerset Rivers Authority (SRA) established to oversea and coordinate flood risk management
How has land management been affected as a long term response to the Somerset floods?
Aim to improve water retention and reduce runoof