U.S. Legal System and Social Welfare Programs Overview
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Criminal law
The branch of law that regulates the conduct of individuals, defines crimes, and specifies punishments for criminal acts.
Civil law
The branch of law that deals with disputes that do not involve criminal penalties.
Precedent
A prior case whose principles are used by judges as the basis for their decision in the present case.
Stare decisis
The doctrine under which precedent is applied.
Trial Court
The first court to hear a case.
Appellate Court
Courts of appeals.
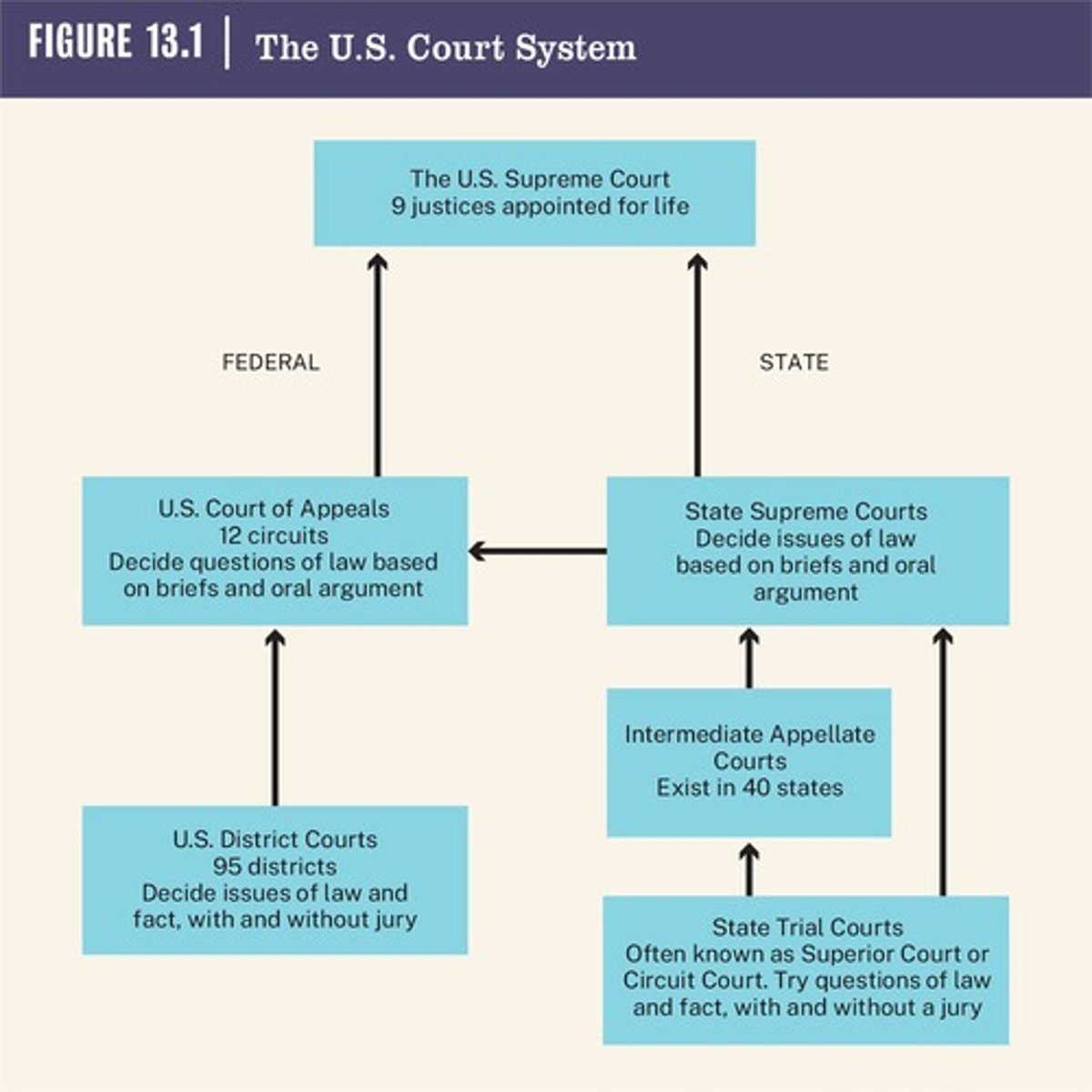
Supreme Court
Final courts of appeals.
State Trial Courts
The first court to hear a state case, handling most criminal cases like felonies and misdemeanors, probate cases, and civil cases.
Double jeopardy
The constitutional principle that prohibits trying a person for the same crime after an acquittal.
Appellant
The party filing an appeal.
State Supreme Court
Only hears cases that are related to the Constitution and will not hear cases from the court of appeals.
Federal District Courts
Courts that engage, hear, and preside over cases involving federal laws, treaties, or the U.S. Constitution.
Federal jurisdiction
The official sphere of power and authority of the federal courts, including cases involving the U.S. government or civil suits over $75,000 between citizens of different states.
Federal circuit courts
Serve as the first level of appeal in the federal system, typically reviewed by a panel of three judges.
Circuit court rulings
Can be appealed to the U.S. Supreme Court, which hears only a small percentage of cases.
Brown v. Board of Education
A case that advanced to the U.S. Supreme Court questioning the constitutionality of segregated schools.
Becoming a federal judge
Generally involves selection from state court judges or state/local prosecutors, with no formal qualifications required.
Federal judges' appointment
Nominated by the president and confirmed by the U.S. Senate, often aligning with the president's partisan views.
Lifetime appointment
Protects federal judges from political pressure, allowing them to interpret the law from an unbiased position.
U.S. Supreme Court
The highest court in the nation, having the final say on legal matters, especially within the U.S. Constitution.
Article III of the Constitution
Vests 'the judicial power of the United States' in the Supreme Court.
Original jurisdiction
The Supreme Court's authority to hear cases first, in a limited variety of classes, including disputes between the United States and one of the 50 states, between two or more states, involving foreign ambassadors or other ministers, and brought by one state against citizens of another state or against a foreign nation.
Judicial review
The power of courts to review and, if necessary, declare laws or executive actions invalid or unconstitutional.
Marbury v. Madison (1803)
The landmark case where Chief Justice John Marshall declared that the courts had the authority to interpret the Constitution and strike down laws that violate it.
Acts of Congress declared unconstitutional
In more than two centuries, the Court has declared fewer than 160 acts of Congress to be unconstitutional.
Separation of powers
The principle that the Supreme Court respects, generally assuming that Congress and the president are acting within their authority.
Justices' Ideology
The impact of political ideology on the interpretation of law, which has intensified with growing political polarization in the United States.
Institutional interests
The desire of justices to protect the Court's power, legitimacy, and reputation for integrity.
Public trust in the Supreme Court
The Court's power depends entirely on public trust and the belief that its rulings are fair, impartial, and rooted in law—not politics.
Judicial philosophy
The differing approaches justices may have regarding how to interpret the law.
Judicial restraint
The philosophy that courts should be cautious about overturning laws or second-guessing elected branches of government.
Judicial activism
Occurs when judges are seen as going beyond simply applying the law as written to instead make or change policy through their rulings.
Brown v. Board of Education (1954)
A liberal example of judicial activism that struck down racial segregation in public schools.
Roe v. Wade (1973)
A landmark case that established a constitutional right to abortion.
Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization (2022)
A conservative example of judicial activism that overturned Roe v. Wade.
Citizens United v. FEC (2010)
A conservative example of judicial activism that expanded corporate free speech rights.
Originalism
A judicial philosophy that interprets the Constitution based on its original meaning.
Living Constitutionalism
A judicial philosophy that allows the Constitution to adapt to new issues and modern values.
Pros of Originalism
Includes predictability and stability, and democratic accountability.
Cons of Originalism
Includes historical rigidity, selective history, and an exclusionary past.
Pros of Living Constitutionalism
Includes flexibility, inclusion, and practical governance.
Cons of Living Constitutionalism
Includes unpredictability, weaker democratic control, and textual drift.
Supreme Court Procedures: Saying 'No'
The Supreme Court chooses to hear only important cases, rejecting most petitions.
Petitions for a Writ of Certiorari
Formal requests submitted to the Supreme Court, with 7,000-8,000 received annually.
Supreme Court Case Hearing
The Court hears about 60 to 80 cases a year, which is less than 1% of petitions.
Briefs
Written documents where attorneys explain why a court should find in favor of their client.
Amicus Curiae Briefs
Supportive briefs submitted by interested parties to assist the court.
Oral Argument
The stage where attorneys present their positions and answer justices' questions.
Supreme Court Conference
A private meeting where justices hold an initial vote on a case.
Majority Vote
The basis on which a decision is reached in the Supreme Court.
Majority Opinion
The written explanation of the Supreme Court's decision drafted by one justice.
Concurring Opinion
An opinion written by a justice who agrees with the decision but not the reasoning.
Dissenting Opinion
An opinion written by justices who disagree with the majority decision.
Social Programs
Government initiatives designed to support individuals and families, addressing issues like poverty and healthcare.
Safety Net
A system designed to provide support to individuals and families in need.
Mobility Ladder
Programs that aim to help individuals improve their economic status.
Economic Security
Benefits provided to citizens to ensure their financial stability.
Benefits to Society
Social programs promote stability and cohesion within society.
Veil of Ignorance
A thought experiment where individuals design the rules of society without knowing their own class, race, gender, talents, or life circumstances.
Rational Actors
Individuals who would choose principles that protect the most vulnerable when behind the veil of ignorance.
Great Depression
A period during which approximately 15 million Americans were unemployed, about 25% of the labor force.
Unemployment Rate in 1929
About 3% before the Great Depression crash.
Unemployment Rate in 1933
Nearly 25%, with one in four workers out of a job.
New Deal Programs
Federal government initiatives that expanded its role in providing economic relief and social support during the Great Depression.
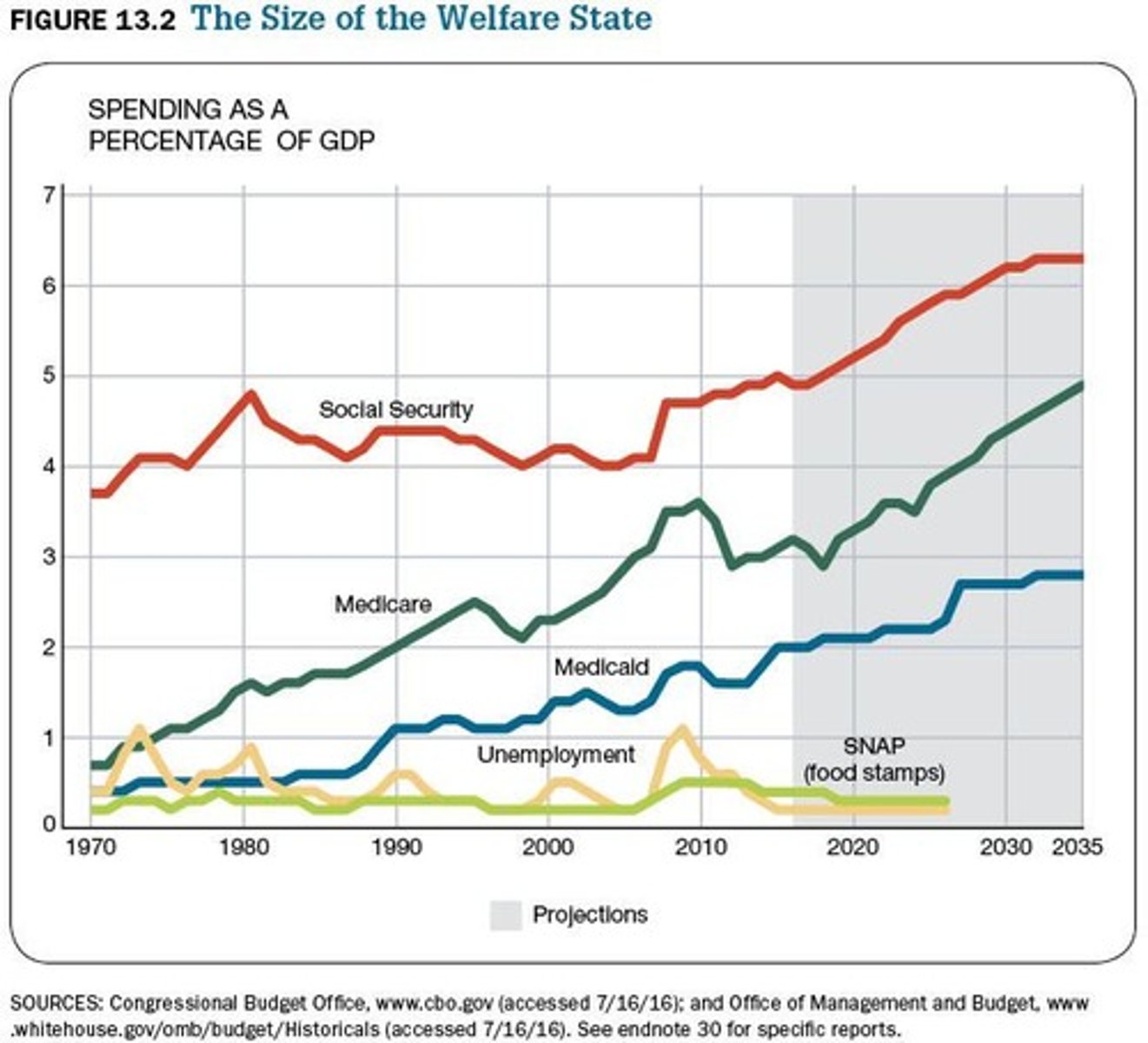
Contributory Programs
Social programs financed by taxation or other mandatory contributions.
Social Security
A contributory program into which workers contribute a portion of their wages for benefits after retirement.
Medicare
A form of national health insurance for the elderly and disabled, funded through payroll taxes.
Unemployment Insurance
A program funded by federal and state taxes that provides temporary financial assistance to workers who lose their jobs through no fault of their own.
Non-Contributory Programs
Benefits based on demonstrated need rather than contributions made, funded through taxpayer dollars.
Medicaid
Health insurance for the poor.
Supplemental Security Income (SSI)
A non-contributory program providing financial assistance to individuals with low income.
Temporary Aid to Needy Families (TANF)
A non-contributory program that provides financial assistance to families in need.
Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)
A non-contributory program that provides food assistance to low-income individuals and families.
TANF Support Variation
Support varies widely by state due to federal block grants and state administration.
Political Values and TANF
States' approaches to TANF often reflect their dominant political values, affecting benefit levels and eligibility rules.
Conservative-leaning States
States like Texas and Mississippi that emphasize individual responsibility and limited government, resulting in lower benefits.
Liberal-leaning States
States like California and New York that view TANF as a tool for promoting economic equity and invest more in benefits.
Cost of Living and TANF
States with a higher cost of living generally offer higher TANF benefits to match local needs.
TANF
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families, a program meant to reduce poverty but often leaves families well below the poverty line.
Federal Poverty Line
The income threshold set by the federal government, which TANF benefits do not meet or exceed in any state.
SNAP
Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, a smaller share of GDP (around 0.5-0.6%) that spikes during economic downturns.
Shadow Welfare State
A system of social benefits delivered through the tax code, including tax breaks, deductions, and credits that subsidize private welfare provisions.
Tax-deferred retirement savings
Savings accounts like 401(k) and IRA contributions that are excluded from taxable income.
Mortgage interest deductions
Tax deductions available to homeowners that reduce taxable income based on mortgage interest paid.
Child and dependent care tax credits
Tax credits that help offset the costs of child care for working parents.
Economic output
Measured as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), representing the total economic activity in the U.S.
Political priorities
The influence of political decisions on the structure and funding of welfare programs.
Economic realities
The actual financial conditions that affect the availability and distribution of welfare benefits.
Social values
The societal beliefs and norms that shape welfare policies and programs.
Eligibility thresholds
Income limits set by states that determine who qualifies for TANF and other welfare programs.
Aging population
A demographic trend contributing to increased spending on programs like Social Security and Medicare.
Rising health care costs
An economic factor driving the growth of Medicare spending.
Economic downturns
Periods of economic decline that lead to increased demand for welfare programs like SNAP and Unemployment Insurance.
Part-time or low-wage jobs
Employment types that often do not provide benefits like employer-sponsored insurance or retirement plans.
Stable, full-time employment
Jobs that typically offer benefits and allow individuals to take advantage of tax-deferred accounts.
Welfare spending
Government expenditure on social programs aimed at supporting low-income individuals and families.