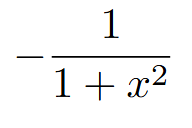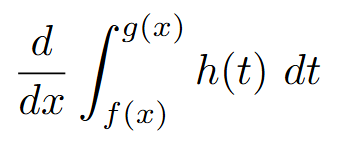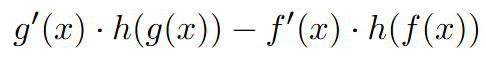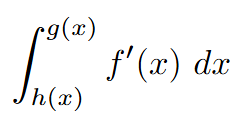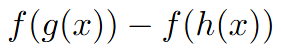AP Calc AB
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
THINGS TO KNOW BY HEART
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
MVT - Mean Value Theorem (formula)
Pre calc slope = calc slope
\frac{f\left(b\right)-f\left(a\right)}{b-a}=f^{\prime}\left(c\right)
MVT - Mean Value Theorem (description)
Diff (a,b) and continuous [a,b]
There exists at least one point c in the interval (a, b) such that the derivative at that point equals the average rate of change of the function over the interval.
Rolle’s theorem (description)
Diff (a,b) and continuous [a,b]
There exists at least one point c in the interval (a,b) where the derivative of the function is zero.
Rolle’s theorem (formula)
f\left(b\right)=f\left(a\right)
f^{\prime}\left(b\right)=0
IVT - Intermediate Value Theroem
Continuous [a,b]
Implies that for any value between f(a) and f(b), there exists at least one point c in the interval (a, b) such that f(c) equals that value.
EVT - Extreme Value Theorem
Continuous [a,b]
There’s an asbolute max and absolute min.
Average of f on a to b
\frac{\int_{a}^{b}\!f\left(x\right)\,dx}{b-a}
Rate of change of f
f^{\prime}
Average rate of change of f on a to b (formula)
\frac{f\left(b\right)-f\left(a\right)}{b-a}
Average rate of change of f on a to b (in words)
Pre calc slope
Average rate of change of f on a to b (complicated ahh formula)
\frac{\int_{a}^{b}\!f^{\prime}\left(x\right)\,dx}{b-a}
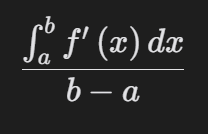
Average rate of change of f on a to b
if f is increasing? f ‘ =
positive
if f is increasing? graph of f ‘ is
above the x axis
if f is decreasing? f ‘ =
negative
if f is decreasing? graph of f ‘ is
below the x axis
f has a max or min, graph of f’ ?
crosses the x axis
f has a max or min, f’ ?
equals zero or undefined
f has a max, f’ ?
goes from positive to negative
f has a min, f’ ?
goes from negative to positive
f is concave up, f’’ ?
is positive
f is concave down, f’’ ?
is negative
f has a point of inflection (formula)
f’’ = 0 , undefined
f has a point of inflection (graphically)
f’’ crosses the x axis
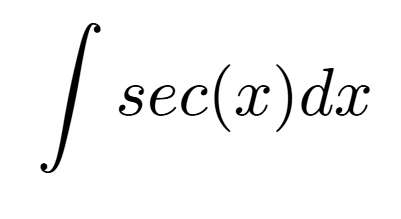
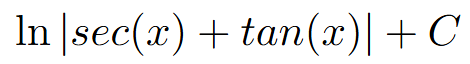
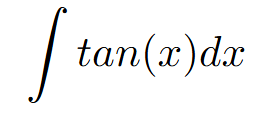
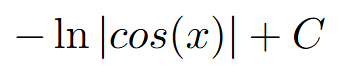
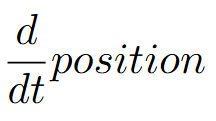
velocity
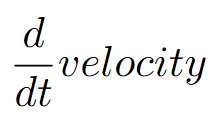
acceleration
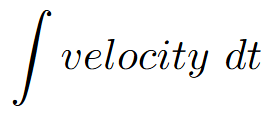
position + C
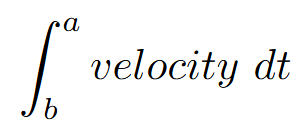
pos(b) - pos(a)
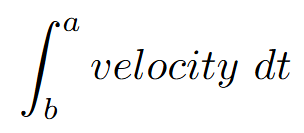
change in position
distance
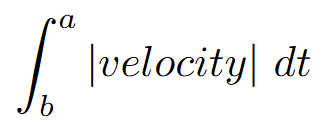
distance
integral of the absolute value of velocity
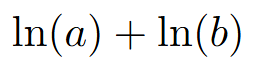
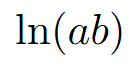
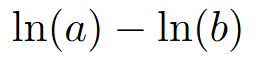
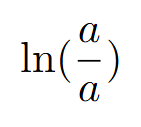
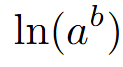
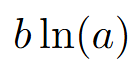
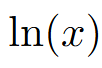
graph
crosses at x = 1
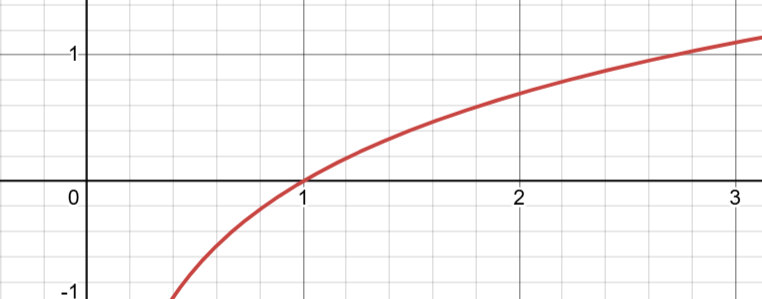
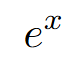
graph
crosses at y = 1