4.4 Manufacturing Processes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:50 AM on 5/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
1
New cards
Examples of Additive techniques
**Paper-based rapid prototyping**
**Laminated object manufacture (LOM)**
**Stereolithography**
**Laminated object manufacture (LOM)**
**Stereolithography**
2
New cards
Paper-based rapid prototyping
Layers of paper cut and glued together to create a 3D shape. Low-fidelity.
3
New cards
Laminated object manufacture (LOM)
3D printing technique that involves the layer-by-layer construction of objects using sheets of material, typically paper, plastic film, or metal foil
4
New cards
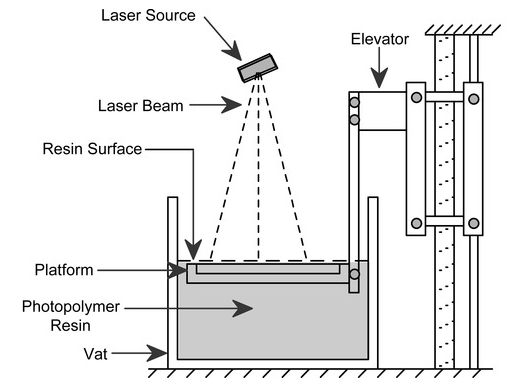
Stereolithography
Solidification of powder using 3D printing
5
New cards
Examples of subtractive techniques
**Cutting** (Laser, Saws, Chiseling, Drilling)
**Machining** (Router or Milling machine)
**Turning** (Metal or Wood Lathe)
**Abrading** (Sanding, Filing, Grinding)
**Machining** (Router or Milling machine)
**Turning** (Metal or Wood Lathe)
**Abrading** (Sanding, Filing, Grinding)
6
New cards
Examples of shaping techniques
**Moulding**
**Thermoforming**
**Laminating**
**Knitting**
**Weaving**
**Thermoforming**
**Laminating**
**Knitting**
**Weaving**
7
New cards
Moulding
Injection moulding, extrusion
8
New cards
Thermoforming
Heating plastics and vacuum forming, or using a strip heater to heat and bend acrylic
9
New cards
Laminating
Flexi-plywood by gluing layers together over a former/shaped mould
10
New cards
**Casting**
Sand casting, Die casting- usually solid to liquid then cooled
11
New cards
Examples of Joining techniques
**Permanent**
**Temporary**
**Adhering- Gluing**
**Fusing (welding)**
**Temporary**
**Adhering- Gluing**
**Fusing (welding)**
12
New cards
Permanent
\
Methods used to permanently bond or join materials together, creating a strong and lasting connection.
e.g. Welding, Brazing, Soldering (joining metals by melting a filler metal), Pop riveting
Methods used to permanently bond or join materials together, creating a strong and lasting connection.
e.g. Welding, Brazing, Soldering (joining metals by melting a filler metal), Pop riveting
13
New cards
**Adhering- Gluing**
once formed, cannot easily be separated
14
New cards
**Fusing (welding)**
Permanent process involving the heating of the surfaces such as metals and plastics. This process isn’t recommended when considering design for disassembly
15
New cards
Temporary
(non-permanent fastening)
Fastening or joining materials mechanically through the use of screws, rivets, bolts, pins, clips, nails, press studs and snaps.
Fastening or joining materials mechanically through the use of screws, rivets, bolts, pins, clips, nails, press studs and snaps.
16
New cards
Adv and Disadvantages of permanent vs temporary
Temporary:
ease for disassembly at the expense of permanent damage to the materials used eg. installing screws
Adjustability: Temporary joining methods offer flexibility in terms of adjustment and alignment of the joined parts.
\
Permanent:
Strength and durability: Permanent joining techniques, such as welding or adhesive bonding, can create strong and durable connections between materials.
Seamless appearance
Load distribution: Permanent joining techniques distribute the load across the entire joint, minimizing stress concentration.
ease for disassembly at the expense of permanent damage to the materials used eg. installing screws
Adjustability: Temporary joining methods offer flexibility in terms of adjustment and alignment of the joined parts.
\
Permanent:
Strength and durability: Permanent joining techniques, such as welding or adhesive bonding, can create strong and durable connections between materials.
Seamless appearance
Load distribution: Permanent joining techniques distribute the load across the entire joint, minimizing stress concentration.
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
CRISC - Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control term definition - Part 53
20Updated 1207d ago0.0(0)
CRISC - Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control term definition - Part 53
20Updated 1207d ago0.0(0)