neuro 2610 exam two
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
dystonia
disorder where muscles contract unwillingly - repeated/twisted motions. from a lack of dopamine
cajal neurons theory
neurons are the functional units of the nervous system
dendritic spines
increase dendrite surface area
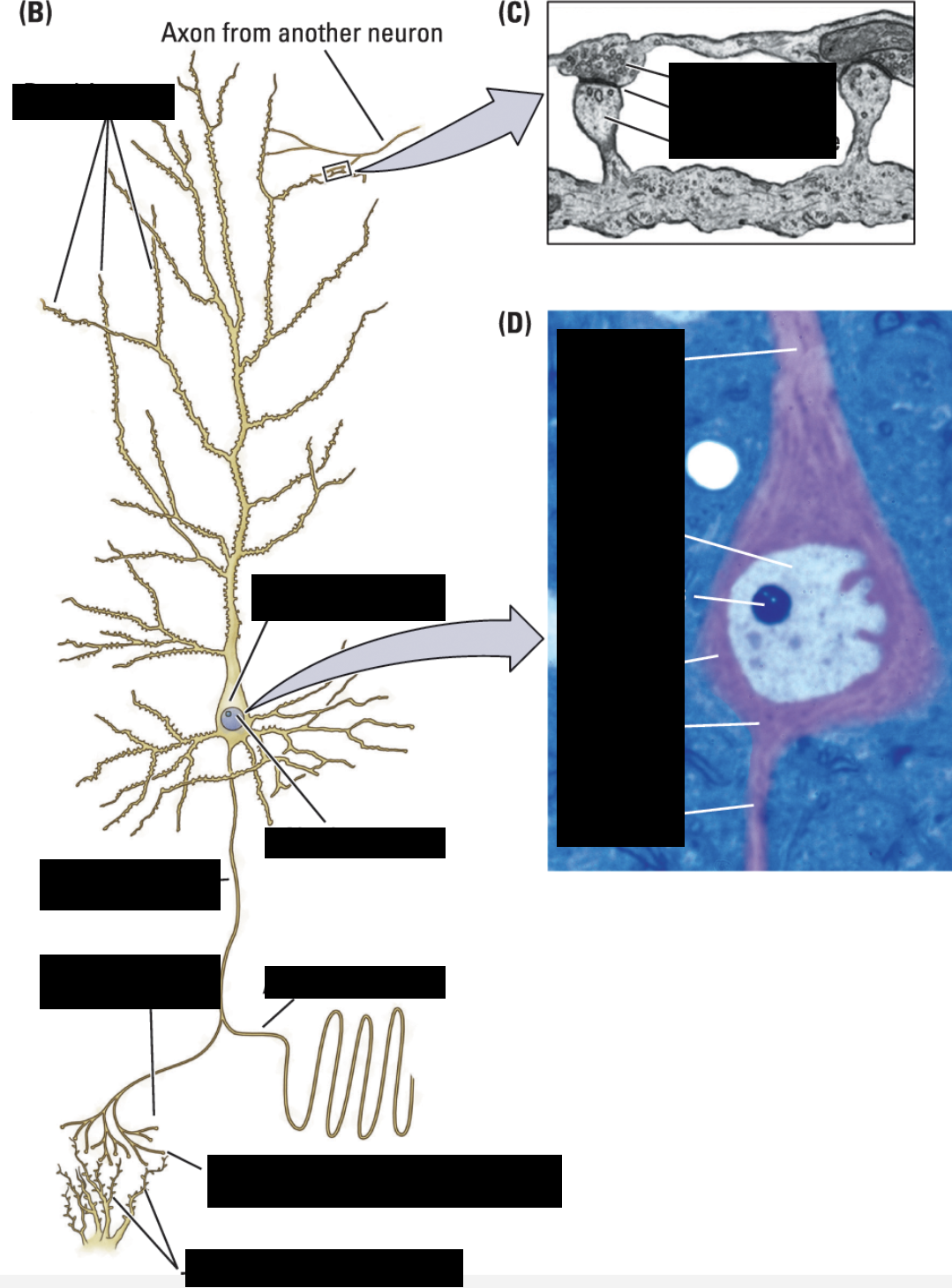
end foot
synapse
dendritic spine
dendrite
nucleus
nucleolus
cell body
axon hilock
axon
terminal button
axon collateral
nucleus
soma
teleodendria
axon
axon hillock
juncture of axon and soma
axon collateral
branches of axons
telodendria
axon callarerals divided into smaller branches
terminal button
knob at end of telodendria
information flow of a neuron
dendrites collect info, soma integrates info, axon sends info to terminals, terminals pass info to another dendrite
sensory neuron
brings information to CNS
interneurons
associate sensor and motor info in CNS
motor neurons
send signals from the brain to muscles
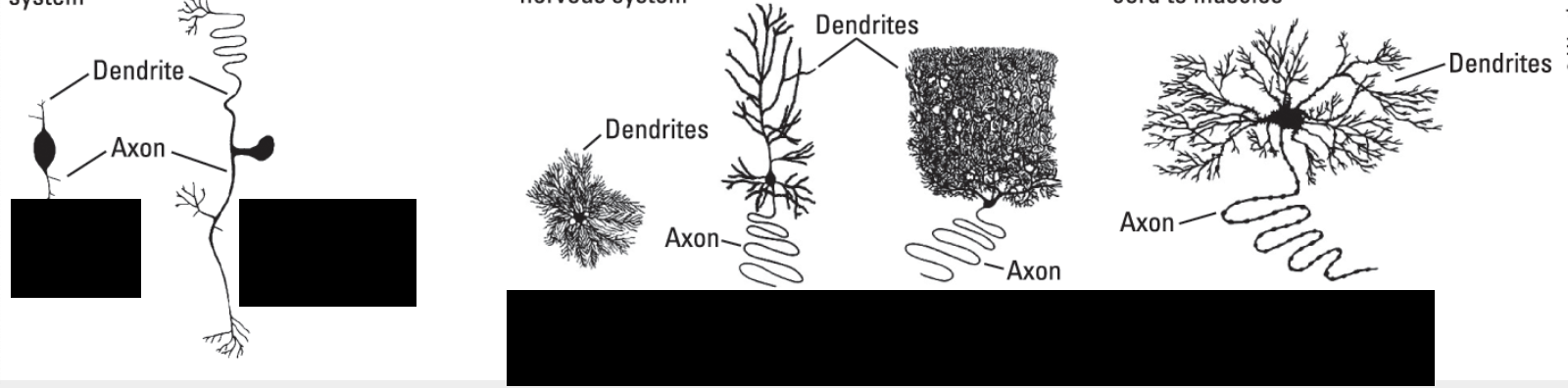
sensory neuron- bipolar
sensory neuron- somatosensory
interneuron- stellate cell
interneuron- pyramidal cell
interneuron- pukinje cell
motor neuron
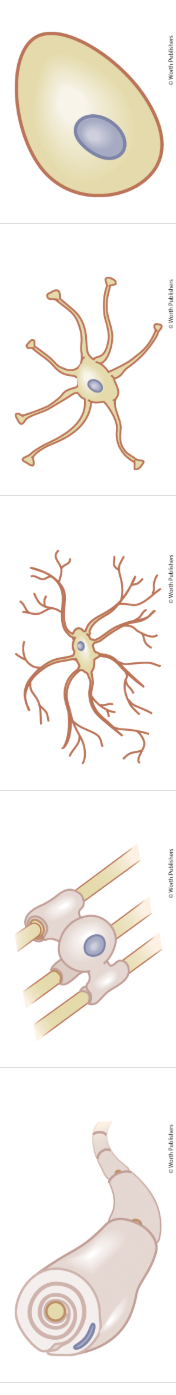
types of glial cells
ependymal cell
astrocyte
microglial
oligodendroglial
schwann
ependymal cell
glial cell- creates CSF
astrocyte
glial- support, repair, blood brain barrier, info transfer
microglial cell
glial- removes dead tissue
oligodendroglial
glial- mylein in CNS
schwann
glial- myelin in PNS
gliomas
most common brain tumor. arise from glial cells
meningiomas
tumor on the meninges
metastatic
tumor that happens when cells from one part of the body move to another
5 types of neurons
sensory neurons
motor neurons
interneurons (stellate, pyramidal, purkinje)
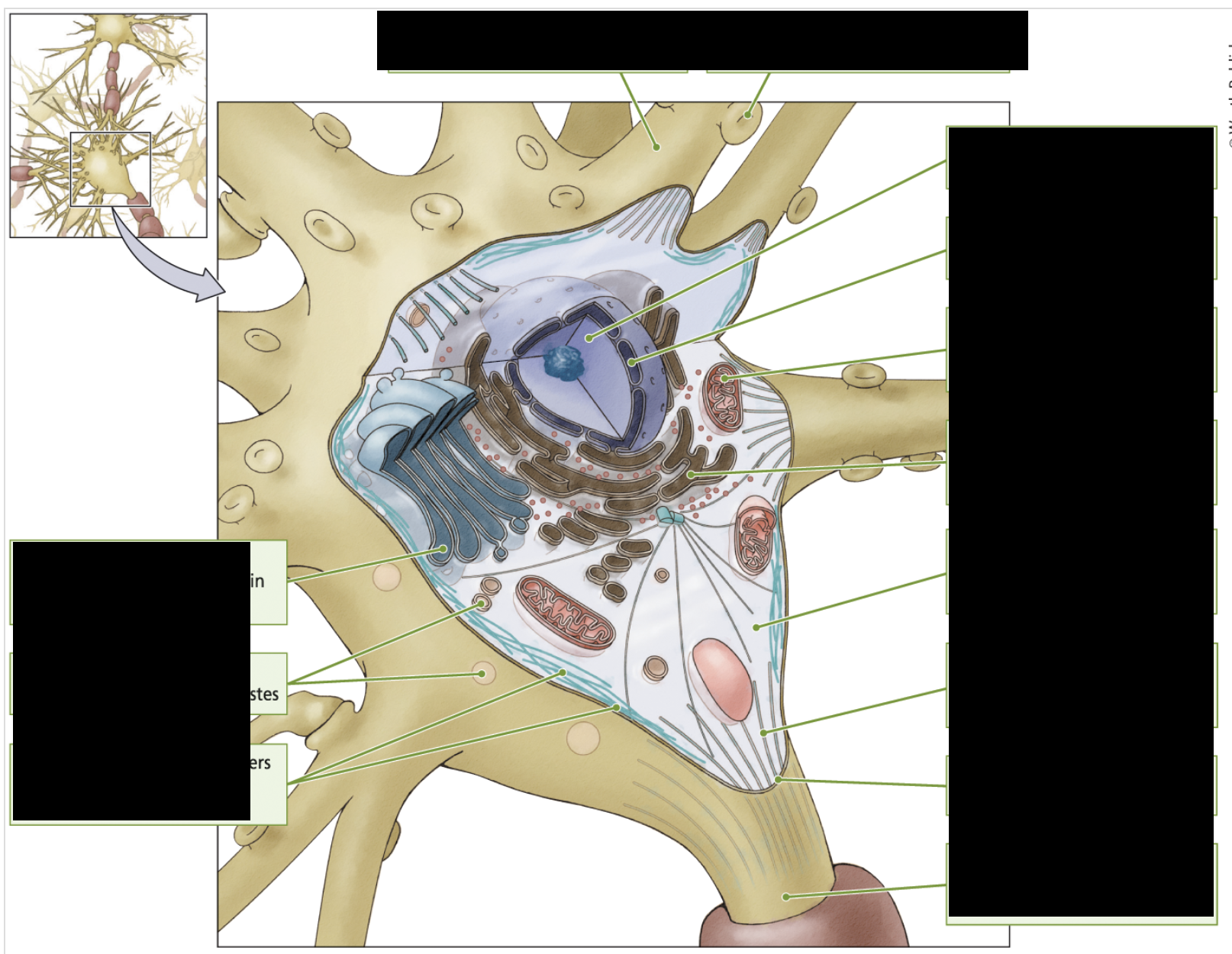
structure and function
dendrite: collects info
dendritic spine: increases surface area
nucleus: stores genes/chromosomes
nuclear membrane: protective
mitochondria: gathers/stores energy
endoplasmic reticulum: proteins
intracellular fluid: holds organelles
tubule: keep cell shape
cell membrane: protects cell
axon: transmits info to other cells
microfilaments: make up skeleton
lysosomes: break down waste
golgi body: packs proteins
phospholipid bilayer
hydrophilic head-polar
hydrophobic tail-non polar
tay-sachs disease
dysfunction of production of HexA, which breaks down lipids, resulting in cell damage. caused by the recessive allele on chromosome 15.
huntingtons disease
abnormal HTT is dominant. build up of abnormal protein kills cells of basal ganglia and cortex
down syndrome
extra chromosome, typically two 21 (smallest chromosome
histone modification
a methyl group binds to the tails of histones, blocking or allowing to open
DNA methylation
methyl groups bind to CG base pairs, stopping transcription
mRNA modification
ncRNA binds to mRNA to stop translation
CRISPR/CAS9
for gene modification. a spacer identifies the DNA to be cut and RNA does the cutting
primary, secondary, tertiary, quanternary protein structure
amino acids
helix or sheet
protein
complex protein
protein synthesis steps
DNA uncoils exposing a gene
gene serves as a template=transcription
mRNA leaves nucleus to endoplasmic reticulum
ribosomes move along mRNA=translation
wild type allele
most common nucleotide sequence
transgenic techniques
introduction of genes to embryos
transcription/translation
DNA-mRNA-polypetide chain-protein
transcription- template strand, copies into mRNA
translation- translates mRNA to an amino acid
which ions are more concentrated inside the axon? outside?
A- and K+
Na+ and Cl-
hyperpolarization vs depolarization
voltage increases- inhibitory (down)
voltage decreases- excitatory (up)
action potential
resting potential. inside is more negative
depolarization. sodium floods in=more positve
peak. stop letting in sodium
repolarization. potassium channels open, letting potassium out
hyperpolarization. potassium channels begin to close, but are slower than sodium channels so too much has left
return. transports sodium out and potassium in to restart
absolute vs relative refractory
action potential cant happen b/c it already is
action potential cant happen during hyperolarization unless its stronger
stretch activated vs voltage acitvated
mechanical force, in dendrite membranes
change in membrane potential, in initial segment
acetocholine
muscle stimulation
epinephrine vs norepinephrine
mobilize body during stress
speeds heart rate
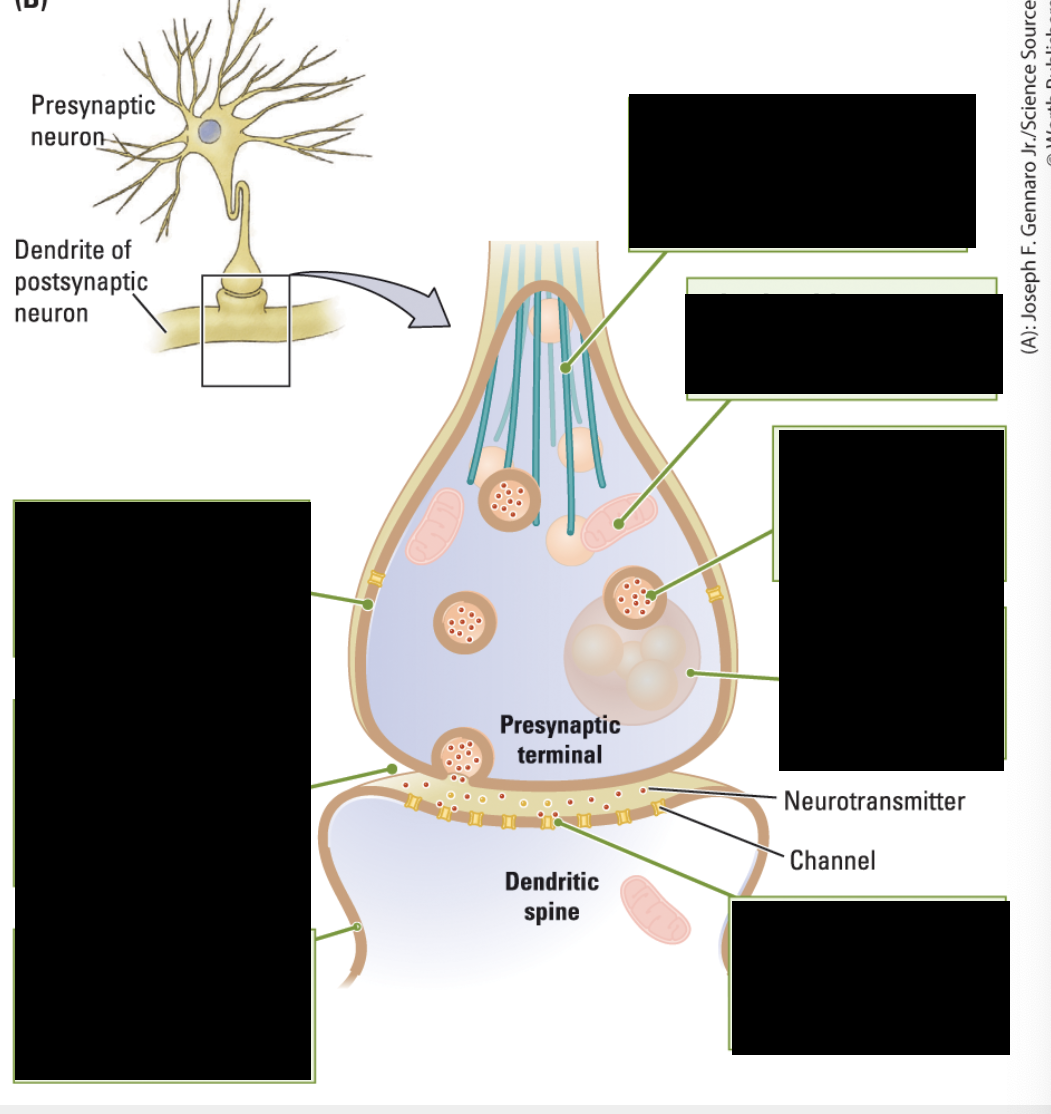
microtubule, carries substances to axon terminal
mitochondria, energy
synaptic vesicle, holds neurotransmitter
storage granule, holds synaptic vesicles
postsynaptic receptor, where NT bind
postsynaptic membrane, contains receptors
synaptic cleft, space between pre and post
presynaptic membrane, holds NT
tripartite synapse
presynaptic membrane, postsynaptic membrane and intimate association with astrocytes
anterograde synaptic transmission
5 steps of transmitting info
NT is synthesized
packed/stored in vesicles in axon terminal
moved to presynapse, released into synaptic cleft
binds to receptors
degraded/removed
cholinergic system
motor neurons- acetylcholine
attention/waking
dopaminergic system
dopamine
motor behaviour
noradrenegic system
norepinipherine
emotional tone
setotonergic system
seratonin
waking eeg
OCD, sleep apnea
cholinergic system
memory and attention
alzheimers
peptide hormones
insulin, growth hormone
made by cellular dna
amino acid hormones
melatonin
derived from amino acids
lipid hormones
thromboxanes
inhibit blood clots, blood flow
steroid hormones
testosterone, cortisol
synthesized from cholesterol
anabloic vs androgenic
muscle building
masculinizing
slow vs fast response
cortisol
epineperhine