Anatomy and physiology 2 Exam 1
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
What are the components of Blood?
-Plasma (55%)
-Formed elements (45%)
-Erythrocytes
-Leukocytes
-Thrombocytes
Draw and label a test tube of spun down blood.
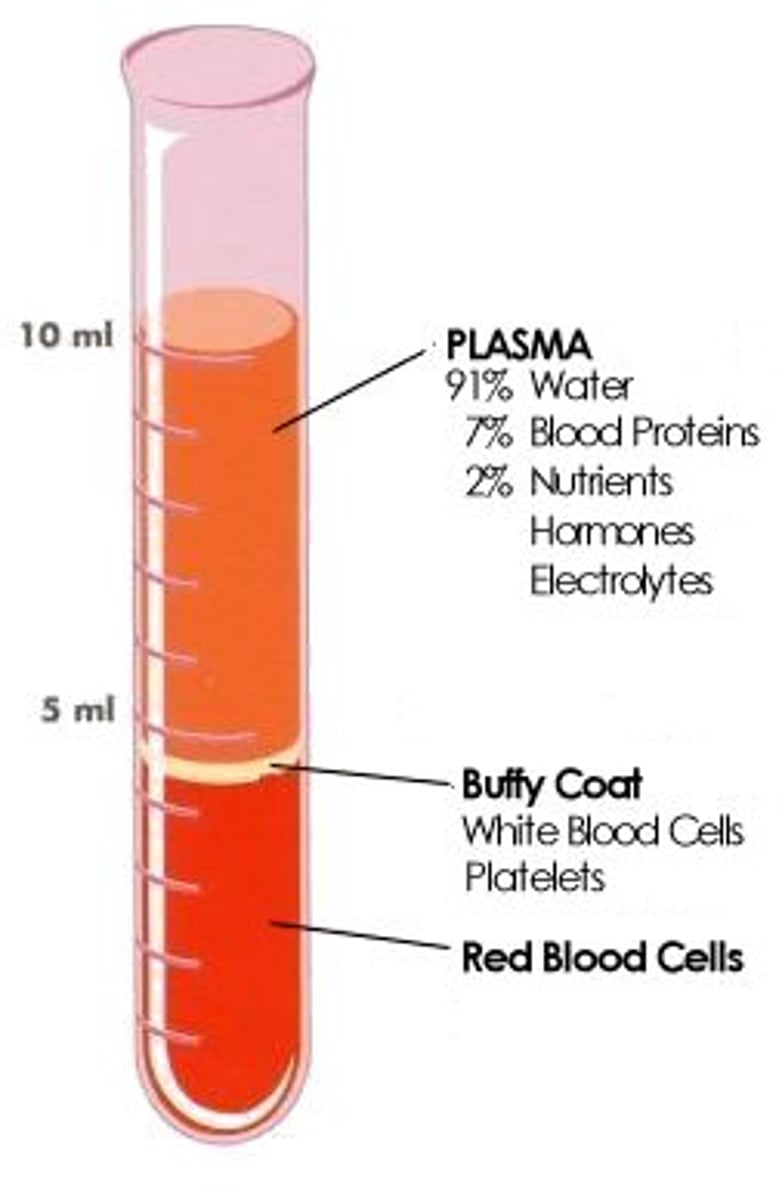
What is the function of hemoglobin?
-The main functional unit of the red blood cell.
-Carries oxygen.
Hematopoiesis
the formation of blood cells
Blood cells start off as ___ in cell development.
Hemocytoblast
Hemocytoblast split into two main groups; What are they?
Myeloid stem cells and Lymphoid stem cells.
Erythropoiesis
occurs on red bone marrow
low blood O2 causes kidneys and liver to release EPO (erythroprotein), which stimulates RBC productions
negative feedback
Newly formed red blood cells that still contain remnants of the Endoplasmic Recticulum are known as ___.
Reticulocytes.
Monocytes differentiate into ___.
Macrophages.
What does the body make in low oxygen environment, such as high altitudes?
Erythropoietin (EPO)
What do Erythropoietin (EPO) do?
Triggers the production of erythrocytes in the red bone marrow.
What nutrient is needed to prevent pernicious anemia?
Vitamin b12
folic acid also are required for DNA synthesis; necessary for the growth and divisions of all cells.
Hemoglobin is broken down into two parts, Heme and Globin. What happens to Globin after the break down?
Globin is further broken into amino acids and then metabolized by macrophages or released to the blood stream.
What are the two main groups of white blood cells?
-Granulocytes
-Agranulocytes
What are the three types of Granulocytes and there functions?
-Neutrophils: Phagocytic, first to arrive at site of infection.
-Eosinophils: Defends against parasites.
-Basophiles: Releases histamine and heparin, appear in
allergic tissues.
What are the two types of Agranulocytes and there functions?
-Monocytes: Releases chemokins to attract neutrophils, leaves blood to become macrophages.
-Lymphocytes: Composed of T, B, and NK cells, T cells are important for immunity, B cells produce antibodies.
What are the 4 major plasma proteins and there functions.
-Albumins: Osmotic Pressure
-Alpha/Beta Globulins: Transport of lipids and fats
-Fibrinogen: Blood Coagulation
-Gamma Globulins: Constitute Antibodies
What are 4, non-protein, nitrogenous substances?
-Urea
-Uric acid
-Amino Acids
-Creatine
What does the Spleen do?
Processes old red blood cells.
Which ion is critical for blood clotting?
Vitamin K
What is the primary insoluble protein in a clot?
Fibrin
What are the corresponding antigens per blood type? Antibody?
Type A: Surface antigen A, Anti-B
Type B: Surface antigen B, Anti-A
Type AB: Both surface antigen A&B, No Antibody
Type O: No surface antigen, Anti-A and B
What is the universal blood donor? repentant?
Donor: O
repentant: AB
Cause of Aplastic anemia
• Bone marrow damaged
• Toxic chemicals
• Radiation
Cause of Hemolytic anemia
• RBCs destroyed
• Toxic chemicals
Cause of Sickle cell anemia
• Abnormal shape of RBCs
• Defective gene
Cause of Iron Deficiency anemia
• Hemoglobin deficient
• Lack of iron
Cause of Pernicious anemia
• Excess of immature RBCs
• Inability to absorb B12
Cause of Thalassemia
• Hemoglobin deficient
• RBCs short-lived
• Defective gene
What are the 3 pericardial layers?
• Fibrous pericardium
• Visceral pericardium
• Parietal pericardium
What heart has 3 distinct layers, what are they?
-Epicardium (outer)
-Myocardium (mid)
-endocardium (inner)
What part of the heart is responsible for the pumping action?
myocardium
Coronary blood vessels are supplied from what vessel?
aorta
Which chamber of the heart is responsible for systemic systolic pressure?
LV - I am pretty sure its this one pg 559
LA
Which chamber of the heart is responsible for pulmonary systolic pressure?
RV
Know the sequence of conduction system component in the firing heart?
What are S1 heart sounds caused by?
S1 is caused by
• Occurs during ventricular contraction
• AV valves closing
What are S2 heart sounds caused by?
• Occurs during ventricular relaxation
• Semilunar valves closing
What is a murmur?
abnormal heart sound
Know the ECG?
• Recording of electrical changes in the myocardium
• Used to assess heart's ability to conduct impulses
• Most important features
• P wave, represent the depolarization (contraction) of the atria
• QRS complex represents the depolarization (contraction) of the
ventricles
• T wave, represents the re-polarization (relaxation) of the ventricles
after a contraction
• Re-polarization of the atria cannot be seen because
it happens at the same time the ventricles contract
(DRAW IT)
What do the waves in a normal ECG mean?
That the heart beat is normal?
Draw it
Know how diagnosed abnormal ECG?
Draw the abnormal ones
• Ventricular fibrillation
-Rapid, uncoordinated depolarization
of ventricles
• Tachycardia
- Rapid heartbeat
• Atrial flutter
- Rapid rate of atrial depolarization
Know the 3 major intake vessels for the right atrium?
inferior vena cava
superior vena cava
coronary sinus
Know the major layers of a blood vessels wall.
Endothelium - The inner layer of an artery
Tunica Media - The middle layer of an artery
Tunica Adventitia - The outer layer of an artery
What happens in capillaries?
• Sites of exchange of substances between blood and body cells
How is blood pressure regulated ?
Dilating arterioles help regulate blood pressure
What is the major parasympathetic nerve to the heart?
Vagus nerve
What exactly causes blood to flow from one heart chamber to another?
pressure differential
What component of blood accounts for the largest proportion of the blood volume?
A. Platelets
B. Red blood cells
C. Plasma
D. White blood cells
C
Destruction of red blood cells; toxic chemicals are one possible cause |
hemolytic anemia
Defective gene leads to abnormally shaped RBCs in conditions of low oxygen |
sickle cell anemia
Damage to bone marrow due to toxic chemicals, radiation, and other factors |
aplastic anemia
The kidney hormone that stimulates red blood cell production is called __________.
Erythropoietin
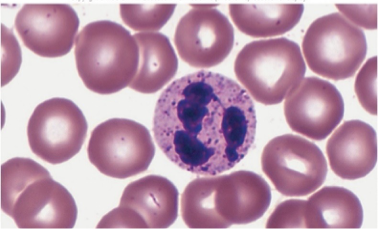
what kind of WBC is this?
Neutrophils
neutrophils
small, light purple granules in acid-base stain
lobed nucleus; 2-5 sections
called PMN’s polymorphonuclear leukocytes
first to arrive as infection site
strong phagocytes
54-62% of leukocytes
elevated in bacterial infections
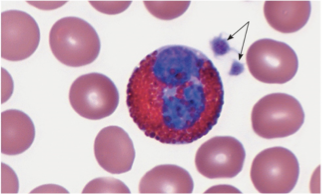
what type of WBC is this?
Eosinophils
Eosinophils
course granules; stain deep red in acid stain
Bi-lobed nucleus
moderate allergic reactions sometimes allergies and asthma
defend against parasitic worm infections
1-3% of leukocytes '
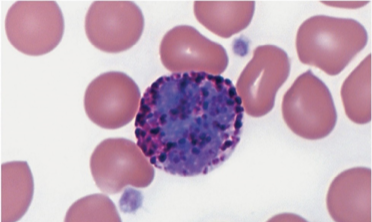
what type of WBC is this?
basophil
basophil
large granules; stain deep blue in basic stain
granules can obscure view of nucleus
release histamine to stimulate inflammation
release heprain to stop blood from clotting
< 1% of leukocytes
similar to eosinophils in size and shape of nuclei
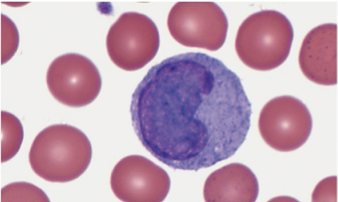
what type of WBC is this?
monocyte
monocytes
largest of the WBC’s
spherical, kidney shaped, oval or lobed nuclei
agranulocuytes
leave bloodstream to become macrophages
3-9% of leukocytes
live for week-months
phagocytize bacteria, dead cells, debris
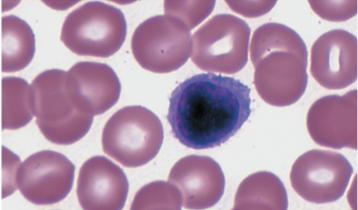
what type of WBC is this?
lymphocytes
lymphocytes
slightly larger than RBC’s, smallest WBC (often found in lymph tissue)
large spherical nucleus surrounded by thin rim of cytoplasm
agranulocytes
T cells and B cells are major types; both important in immunity
T cells directly attack pathogens, tumor cells
B cells produce antibodies
25-33% of leukocytes
may live for years
Chemicals released by damaged cells, white blood cells, and platelets act to attract white blood cells to the area. What is this attraction called?
Diapedesis
Agglutination
Inflammation
Positive chemotaxis
Positive chemotaxis
diapedesis
W B C s can squeeze between the cells of a capillary wall and leave blood vessel; then migrate toward infection site. (help of cell adhesion molecules)
Phagocytosis
Engulfing and digestion of pathogens; neutrophils and monocytes are most mobile and active phagocytes
Inflammatory response
Reaction that restricts spread of infection; promoted by basophils, by secretion of heparin and histamine; involves swelling and increased capillary permeability.
What results when a patient with type A blood receives a transfusion of type B blood?
Agglutination of the donor red blood cells
Adherence of platelets to donor red blood cells
Agglutination of the recipient's red blood cells
Coagulation involving donor red blood cells
C
What is the name of the condition in which there is a deficiency in red blood cells or in the amount of hemoglobin
anemia
Thrombocytopenia
Low platelet count; results in decreased blood clotting and bruising.
Thalassemia
Deficiency of hemoglobin due to defective gene; short life-span for RBCs.
An excessive number of white blood cells is classified as
leukocytosis: High WBC count (>10,500/ μL)
Acute infections, vigorous exercise, great loss of body fluids
Protein that maintains osmotic pressure
albumin
Protein that functions in blood clotting
fibrinogen
Plasma nutrients
Vitamins, lipids, sugars, and amino acids used in metabolic processes
thrombin
Name the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction that converts fibrinogen to fibrin.
Describe the role of plasmin.
Breaks down fibrin, dissolving the clot
What results when a type A patient receives a transfusion of type B blood?
Agglutination of the donor red blood cells
Percentage of RBCs is called the:
hematocrit or packed red cells
White blood cells (Leukocytes, WBCs):
-Protect against disease
-WBCs are produced in red bone marrow, under control of hormones: interleukins and colony-stimulating factors
Platelets (thrombocytes)
-pieces of cytoplasm
-Produced by hemocytoblasts because of hormone, thrombopoietin
-Release serotonin
Hemostasis
stop bleeding
Platelet plug formation
Triggered by exposure of platelets to collagen
Platelets adhere to rough surface to form a plug
Extrinsic clotting mechanism:
Triggered by blood coming in contact with tissues outside of blood vessels.
-Damaged tissues release tissue thromboplastin (factor III),
-Thrombin converts fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin threads
Fibrin threads stick to damaged blood vessel surfaces, and trap blood cells and platelets
Intrinsic clotting mechanism:
Activated when blood comes in contact with foreign surface.
-formation of a fibrin mesh and a blood clot
thrombus
abnormal blood clot that forms in a blood vessel
embolus
blood clot moving through the blood vessels
Thrombosis
Blood clot in a vessel supplying a vital organ (brain, heart)
Infarction
Death of tissues which have blocked blood vessels due to blood clot formation
Embolism
Blood clot that travels, and then blocks a blood vessel in an organ (such as pulmonary embolism in lungs
Antigen
Any molecule that evokes an immune response
Antibodies
Proteins that react against a specific antigen
Rh positive:
Presence of antigen D or other Rh antigens
Agglutination
Clumping of RBCs, which occurs when an antibody (in recipient's plasma) encounters its specific antigen (on donor RBCs)
Rh negative
Lack of the Rh antigens
Pulmonary Circuit
Transports oxygen-poor blood from heart to lungs, and back to heart
In lungs, blood picks up O2 and drops off CO2
Systemic Circuit
Transports oxygen-rich blood from heart to all body cells, and back to heart
Location of the heart:
-Posterior to the sternum
-The base lies beneath the 2nd rib
-The apex lies at the 5th intercostal
sits on diaphram
Ventricles
: thick-walled lower chambers; pump blood into arteries
Atria
thin-walled upper chambers; receive blood returning to heart