LAB PP (1-7)
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
The image shows the result of a certain differential staining method that detects the presence of mycolic acid in a bacterial cell wall. Match the statement to the correct answer located in the drop down menu.
name of the staining technique
what color are positive bacteria stained
what color are negative bacteria stained
name the primary stain
name the counterstain
name of the staining technique
acid-fast stain
what color are positive bacteria stained
pinkish purple
what color are negative bacteria stained
blue
name the primary stain
carbolfuchsin
name the counterstain
methylene blue
What is the total magnification of a specimen if you are using a compound light microscope with the 40x objective lens?
400x
The image shows the result of a certain differential staining method that detects the presence of mycolic acid in a bacterial cell wall. What information can be concluded concerning the circled (blue) cells? [Be prepared to know information concerning the pinkish cells]
they are non acid-fast organisms that don't have mycolic acid in the cell wall
____________________ oil prevents the scattering of light when viewing a sample using the 100x objective lens.
immersion
A thick, detectable, discrete polysaccharide layer located outside of the cell wall that protects bacteria from the host's immune system and allow pathogens to invade the body is called a/an __________.
capsule
You are viewing a specimen using the 100x objective, but the image is fuzzy. Assuming that the microscope is clean and functioning properly, what is the likely reason why the image isn't clear?
forgot to use immersion oil
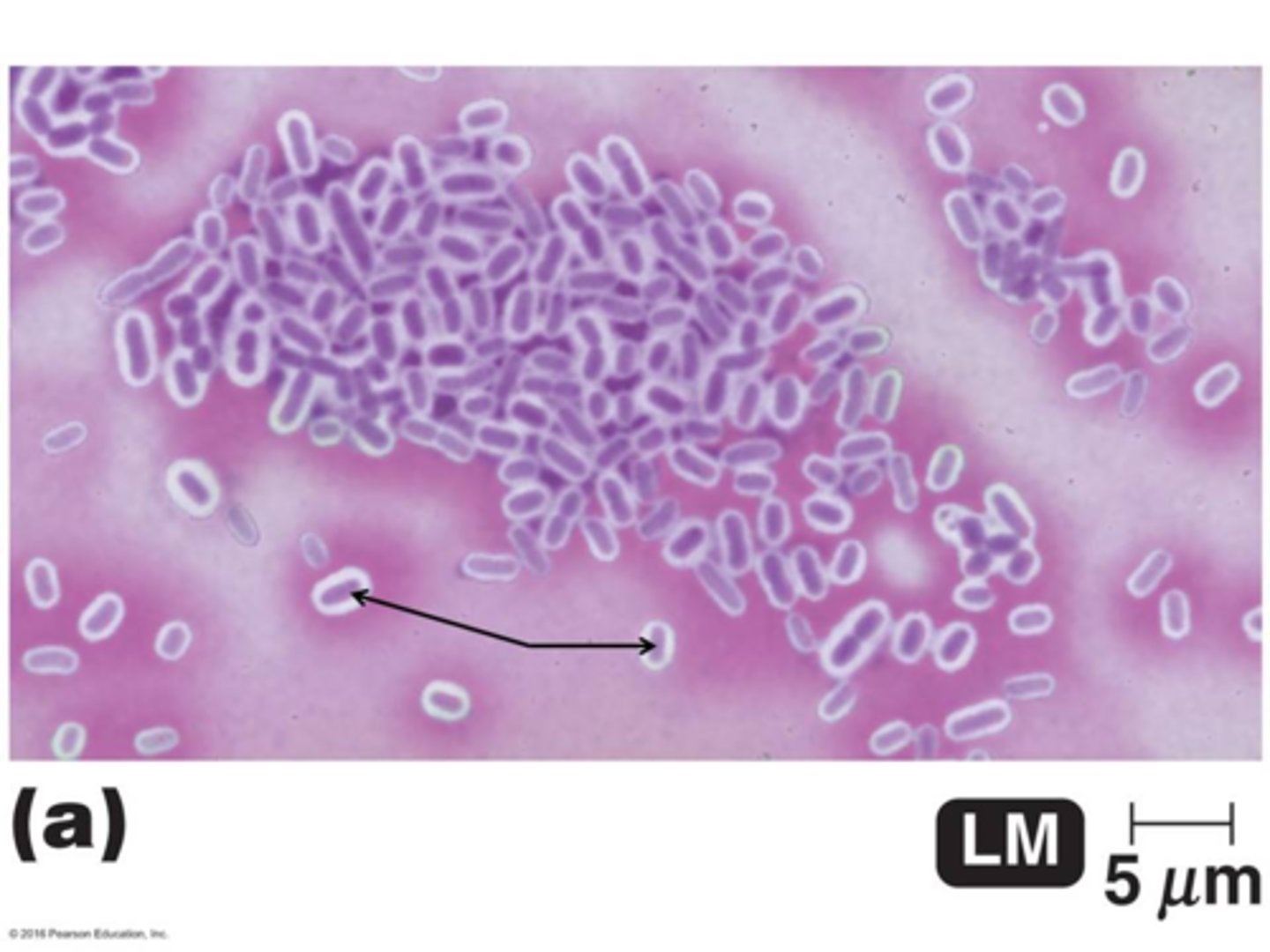
The image shows the results of a type of structural staining method called a negative stain that uses the dye, crystal violet. What are the purple colored structures depicted by the arrows? [Be prepared to identify the clear area surrounding the purple structures]
bacterial cells
When preparing a slide for bacterial staining, the _________________ step attaches the bacteria to the slide and kills the microorganisms.
heat fixing
Metabolically inactive (dormant) forms of bacteria that can survive harsh environmental conditions such as heat and UV radiation are called ____________.
endospores
The image shows the results of a staining method that differentiates between bacteria that have thick or thin layers of peptidoglycan in their cell walls. Match the statement to the correct answer located in the drop down menu.
name of the staining technique
what color are positive bacteria stained?
what color are negative bacteria stained?
name the primary stain
name the counterstain
name of the staining technique
Gram stain
what color are positive bacteria stained?
purple
what color are negative bacteria stained?
pinkish red
name the primary stain
crystal violet
name the counterstain
safranin
Lethal _____________-forming bacteria, such as Bacillus anthracis, can be used for bioterrorism.
endospore
The image shows the result of a differential staining method called the Gram stain. What information can be concluded concerning the circled (blue) cells? [Be prepared to know information concerning the pinkish cells]
the cells are gram positive and have a thick layer of peptidoglycan
The image shows the results of a structural staining method that can used to detect certain structures that can be found in bacterial species such as Bacillus anthracis and Clostridium tetani. Match the statement to the correct answer located in the drop down menu.
name of the staining technique
what are the pink structures
what are the green structures
name the primary stain
name the counterstain
name of the staining technique
endospore stain
what are the pink structures
vegetative cells
what are the green structures
endospores
name the primary stain
malachite green
name the counterstain
safranin
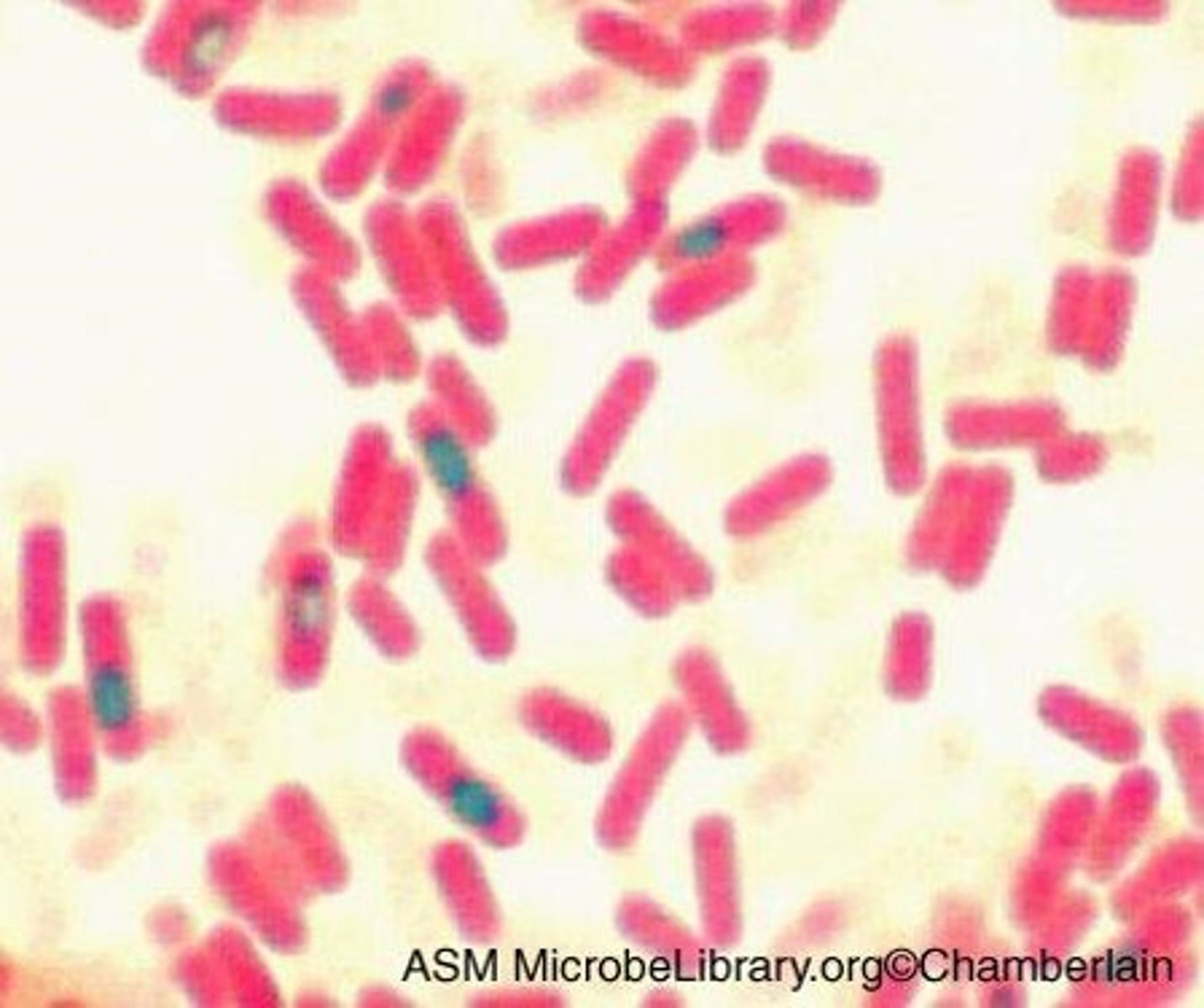
You have a mixture of gram positive and gram negative cells in culture. You prepare a slide from the culture and gram stain it, but when observing the sample using oil immersion, all cells appear purple. What is the likely technical reason why only purple-colored cells are observed?
you forgot the decolorization step
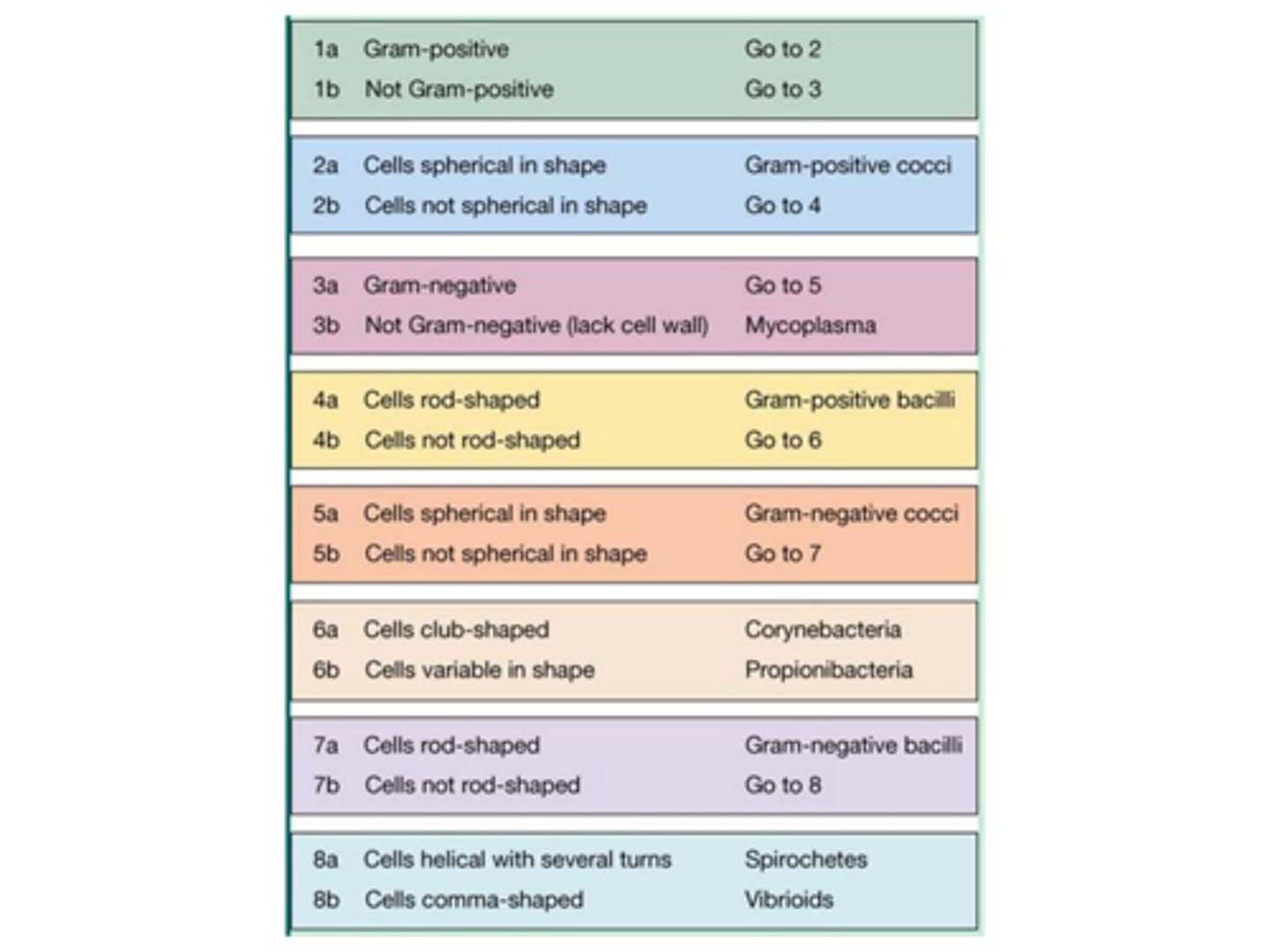
You observe gram-negative cells that aren't spherical in shape, but instead are rod-shaped. Use the information and the dichotomous key to identify the microoorganism.
gram-negative bacilli
The two organelles that are theorized to have evolved from prokaryotic cells are ______________ and _________________.
mitchondria and chloroplasts
Organisms in domain _____________ are more closely genetically related to organisms in domain ___________ than domain _____________.
archaea; eukarya; bacteria
Organisms in the domain archaea have cell walls that possess _______________.
pseudopeptidoglycan
Many extremophiles such as halophiles, thermophiles, and acidophiles belong to domain _______________.
archaea
What category of bacteria have cell walls that possess a thin peptidoglycan layer and lipopolysaccharide?
gram-negative
What category of bacteria have cell walls that possess a thick peptidoglycan layer?
gram-positive
Penicillin interferes with _____________ synthesis, so it is effective in killing gram-positive bacteria.
peptidoglycan
What category of bacteria is resistant to physical disruption and drying, but are highly susceptible to penicillin and anionic detergents?
gram-positive
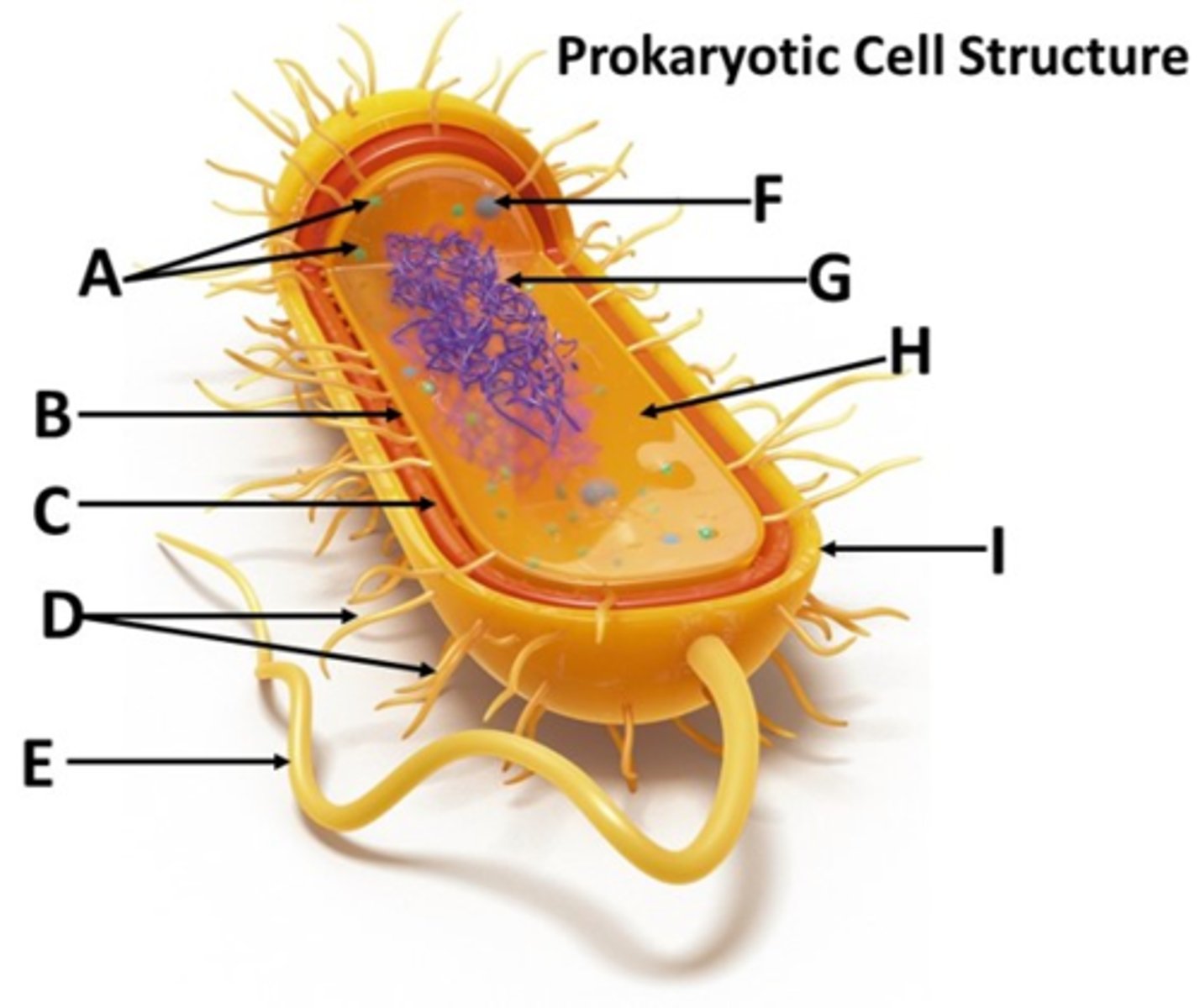
Match the prokaryotic cell structure to the letter designation in the drop down menu.
nucleoid
plasma membrane
cell wall
fimbriae
nucleoid
G
plasma membrane
B
cell wall
C
fimbriae
D
What step of binary fission is occurring in step 1? [Know all steps in binary fission for upcoming exams]
DNA replication
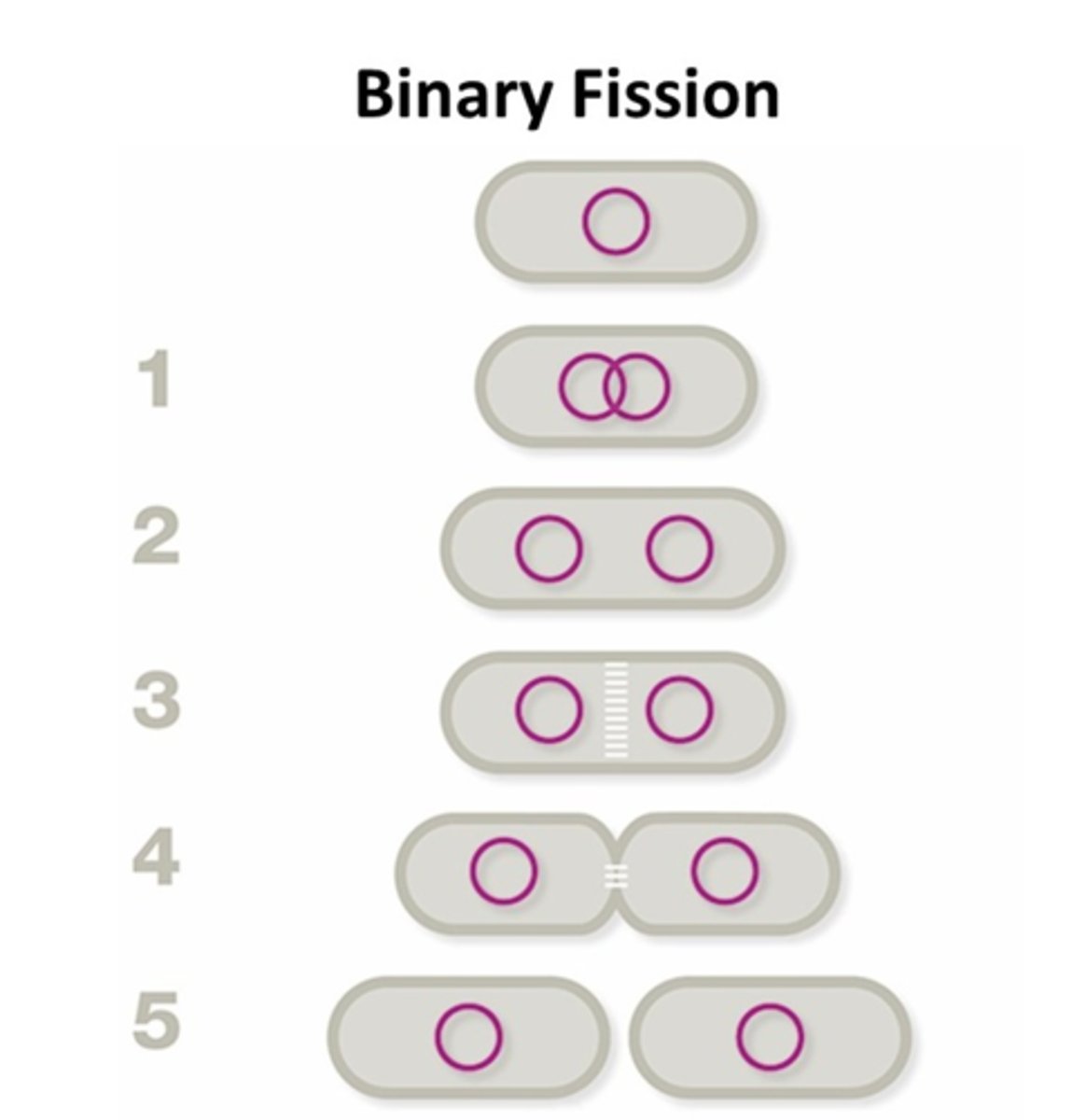
Prokaryotes reproduce asexually mainly by a process called ____________.
Binary fission
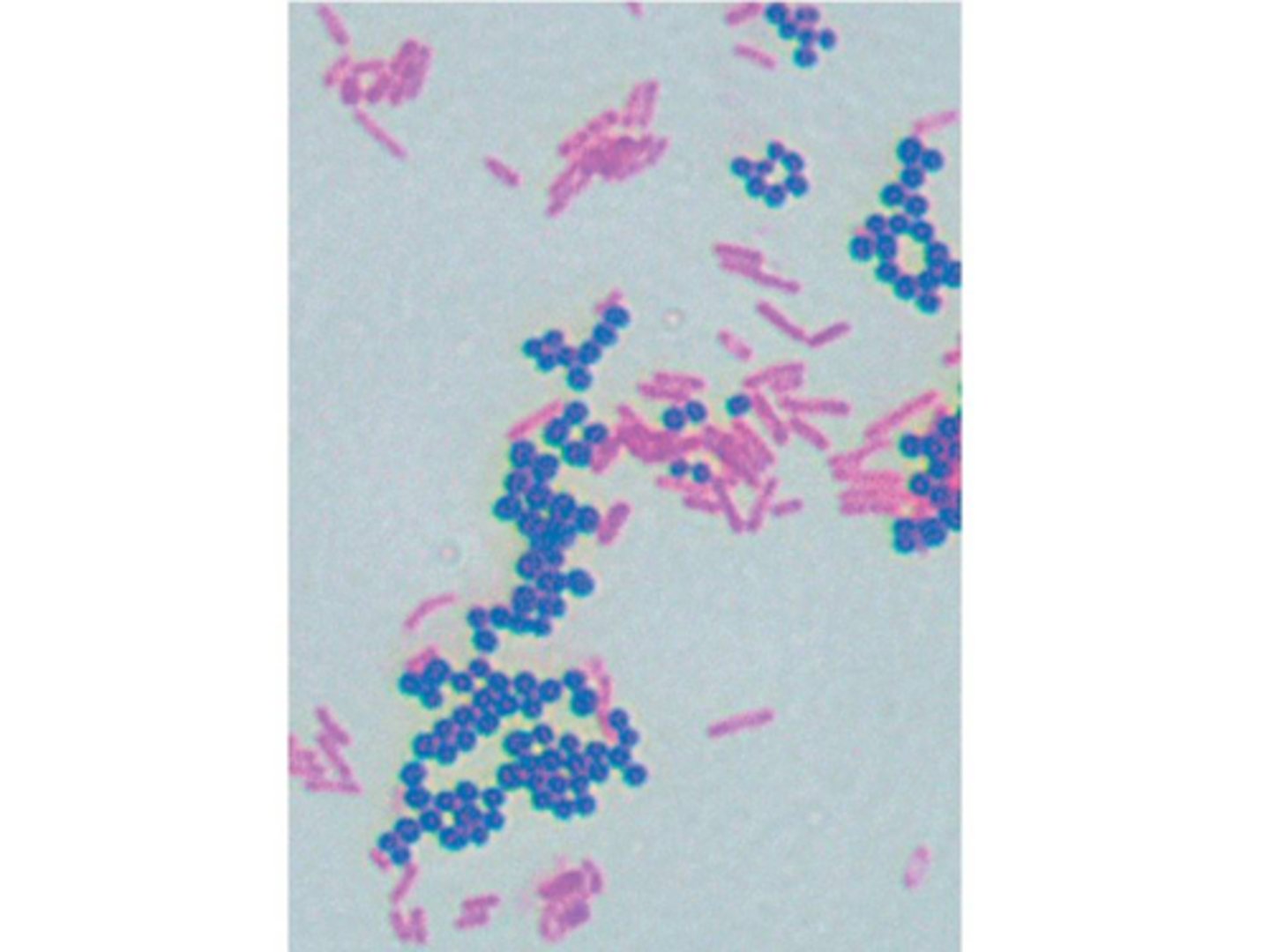
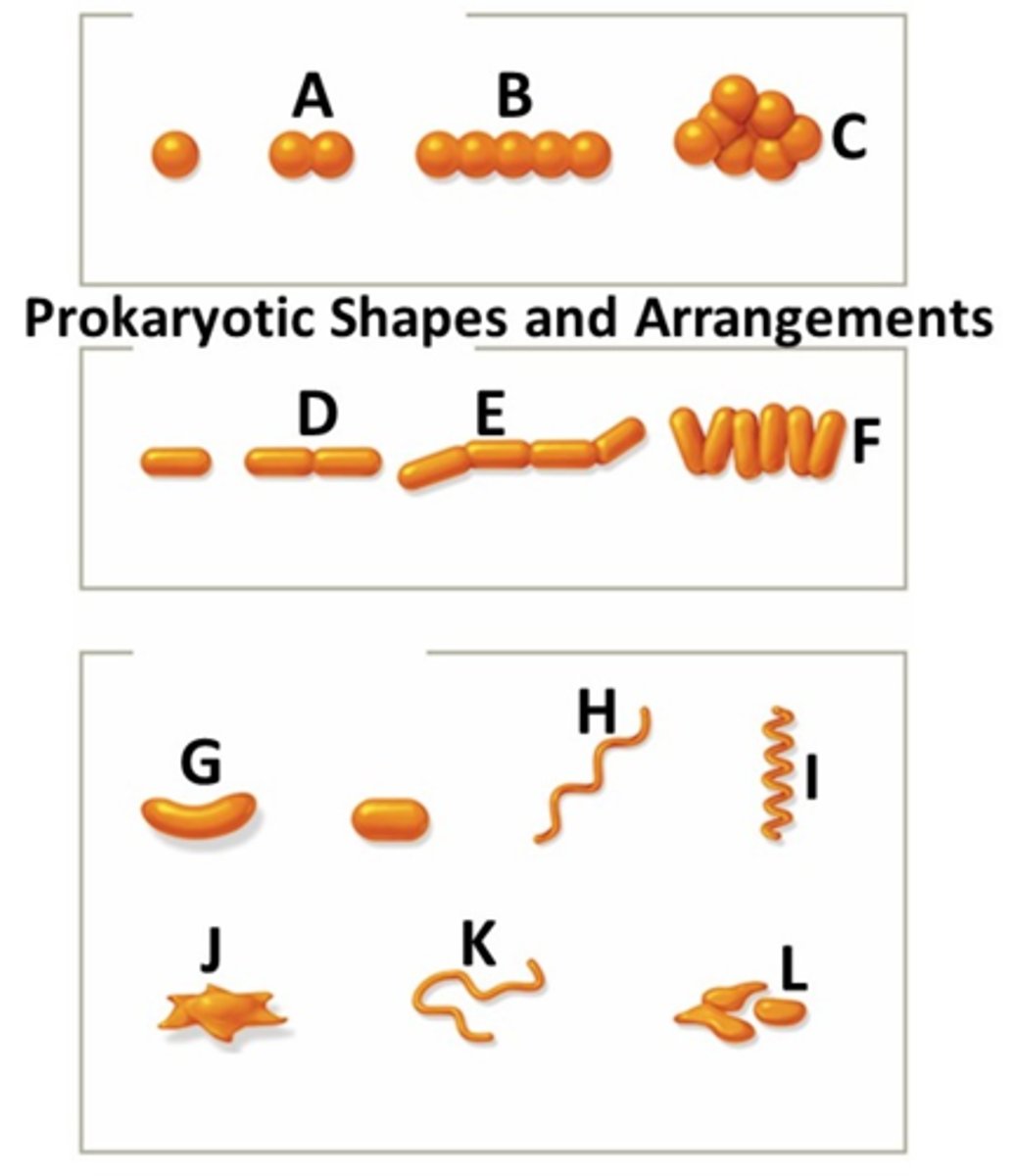
Which letter-designated bacterial shape/arrangement is considered palisade? What is the shape of the bacteria labeled "G"?
F; vibrio
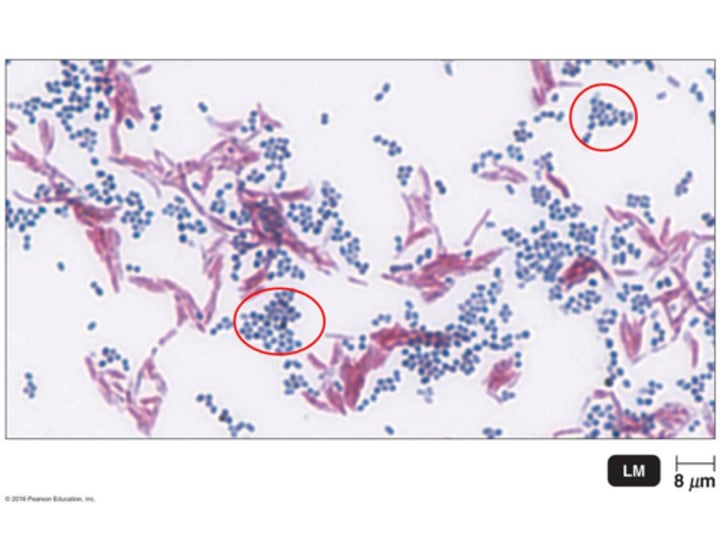
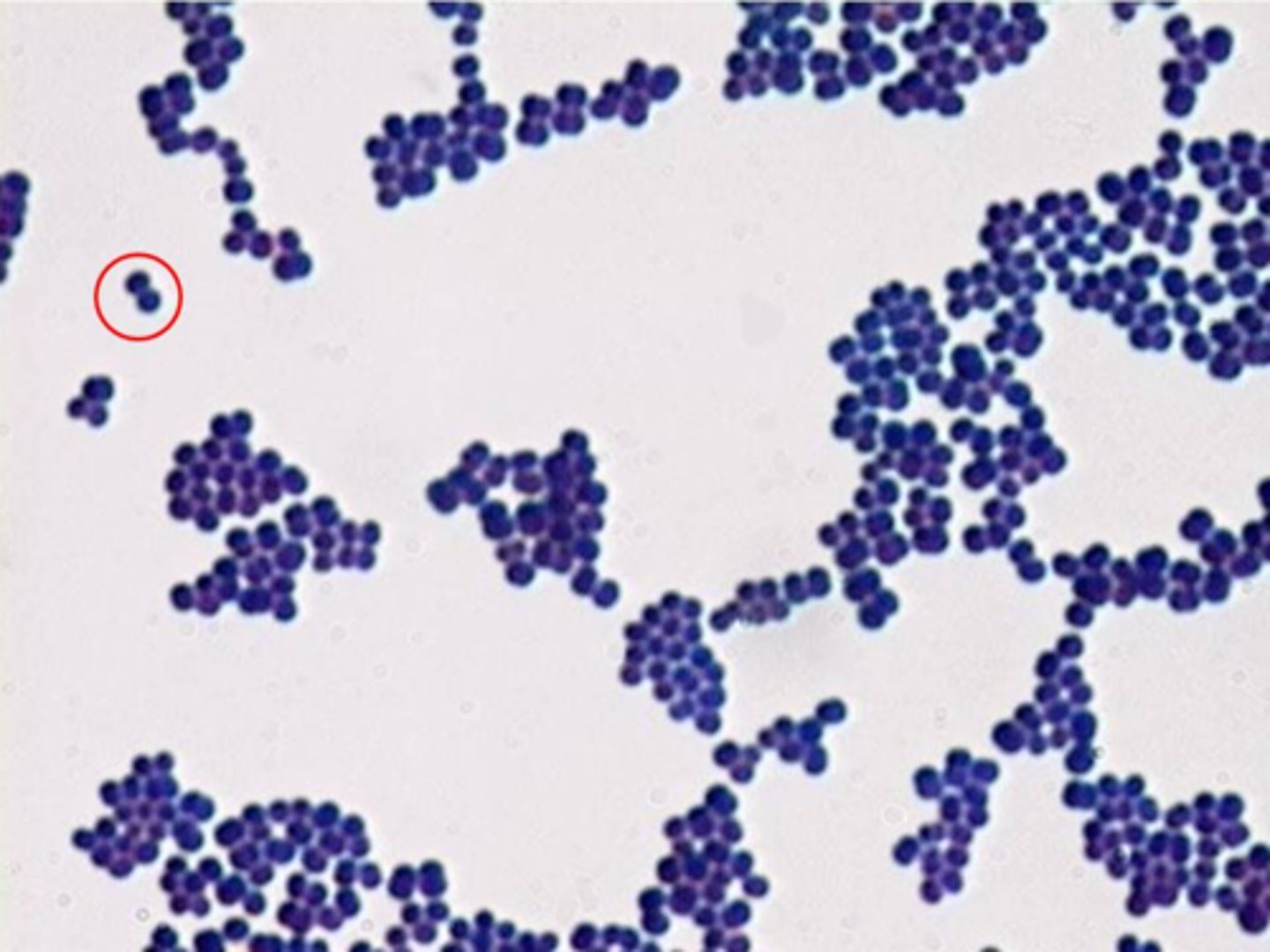
What is the shape and arrangement of the circled bacterial cells.
diplococci
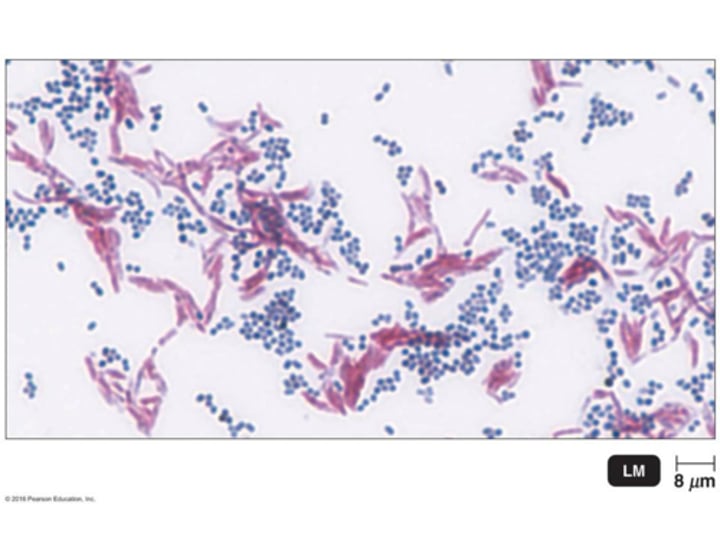
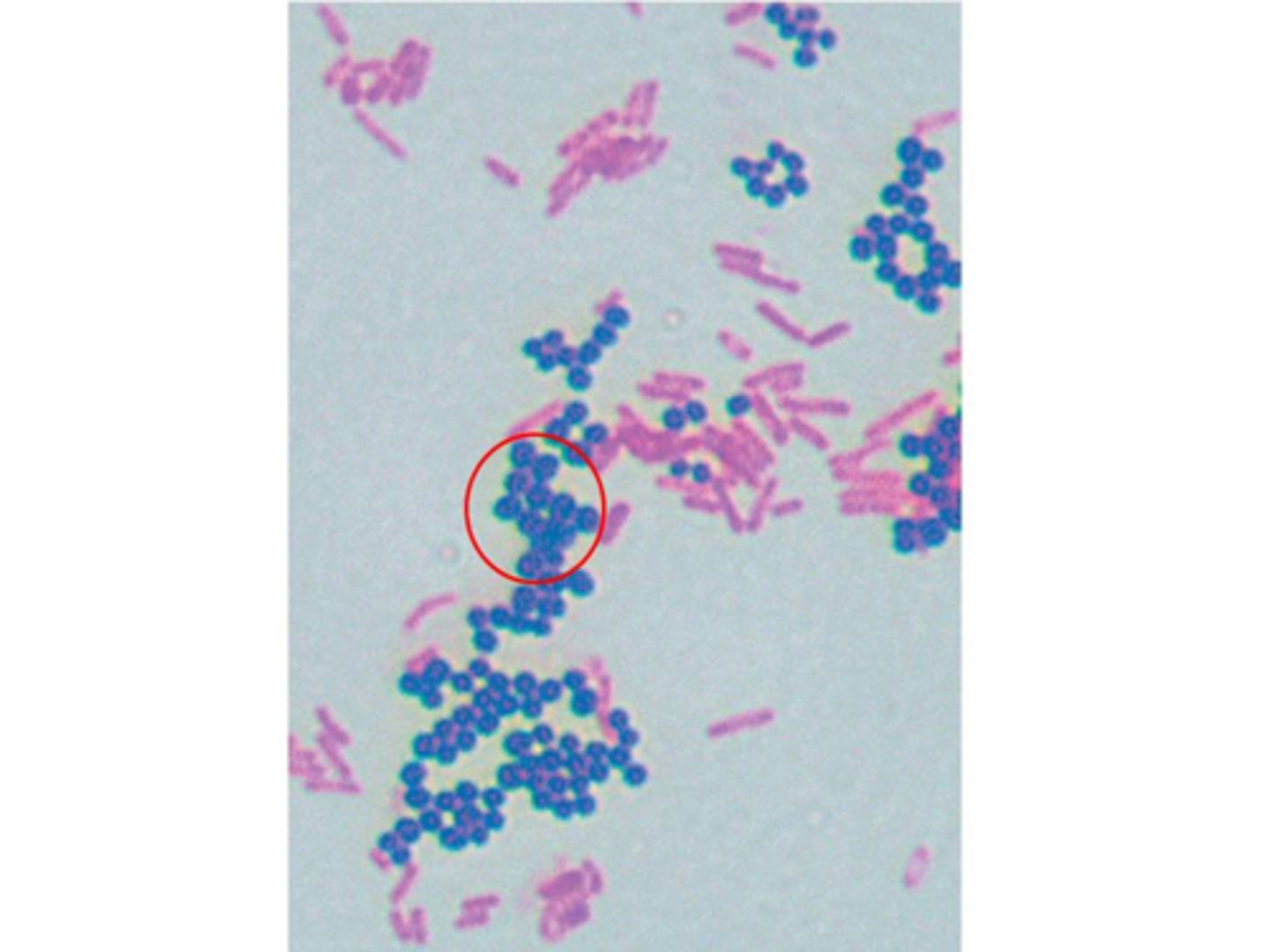
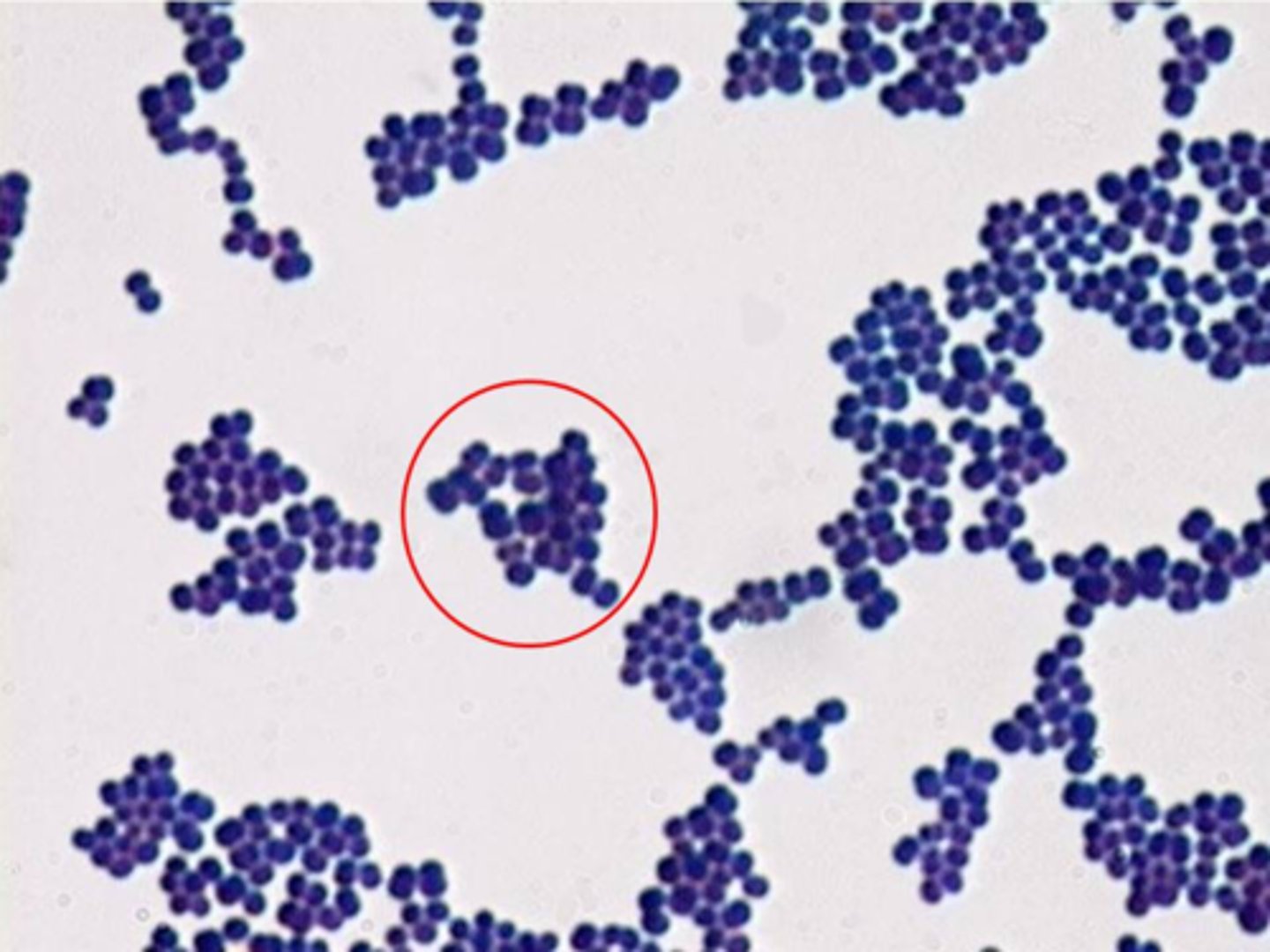
The image shows the Gram stain results of a patient sample. What characteristics can you ascertain about the circled group of bacteria?
they are Gram positive staphylocci
A patient presents with nausea and diarrhea, and informs you that he was recently in Africa and drank water from a stream. Tests for various parasitic infections were negative, so the illness is likely caused by a bacterial infection. After further testing the patient is diagnosed with chlorea caused by the bacterium, Vibrio cholerae. Using the information ascertained from the bacteria's name, what shape do you think this organism is?
comma shaped
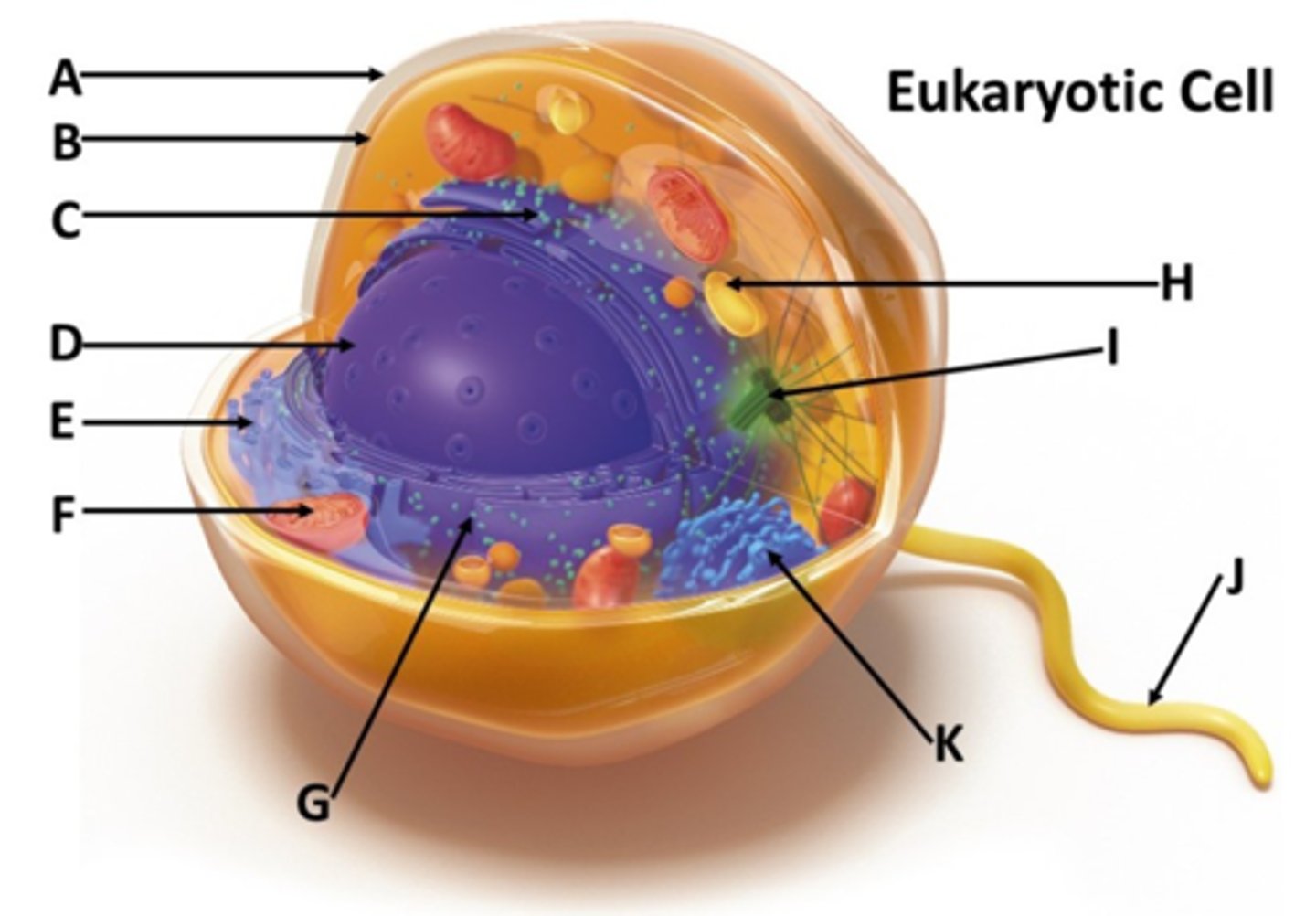
Match the eukaryotic cell structure to the letter designation in the drop down menu.
rough ER
smooth ER
centrioles
golgi appartatus
mitochondrion
rough ER
C
smooth ER
E
centrioles
I
golgi appartatus
K
mitochondrion
F
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic extrachromosomal DNA is called ______ DNA.
plasmid
Prokaryotic DNA is found in the __________ region and eukaryotic DNA is located in the ___________.
nucleoid, nucleus
Determine if the properties listed on the left-hand side column are describing DNA or RNA.
the sugar ribose
nucleotides A, U, C, G
used as a template for transcription
nucleotides A, T, C, G
translated to synthesize a polypeptide
the sugar deoxyribose
double stranded
single stranded
the sugar ribose
RNA
nucleotides A, U, C, G
RNA
used as a template for transcription
DNA
nucleotides A, T, C, G
DNA
translated to synthesize a polypeptide
RNA
the sugar deoxyribose
DNA
double stranded
DNA
single stranded
RNA
What mRNA sequence is synthesized using the DNA template strand AAT CCG AGG T?
UUA GGC UCC A
What type of RNA codes for proteins?
mRNA
What enzyme is necessary for transcription?
RNA polymerase
Eukaryotic mRNA have non-coding sequences called _______ that are spliced out before the RNA leaves the nucleus.
introns
Transcription occurs in the _________ of prokaryotes and the __________ of eukaryotes.
cytoplasm/nucleus
What is the anticodon sequence of a tRNA molecule for the mRNA codon UCA?
AGU
What type of RNA makes up a portion of the ribosome?
rRNA
The fact that more than one codon can code for a single amino acid is referred to __________ in the genetic code.
redundancy
What type of bond joins amino acids to a growing protein chain?
peptide bond
Which of the following is NOT a stop codon?
UGA
UAG
UAA
UGG
UGG
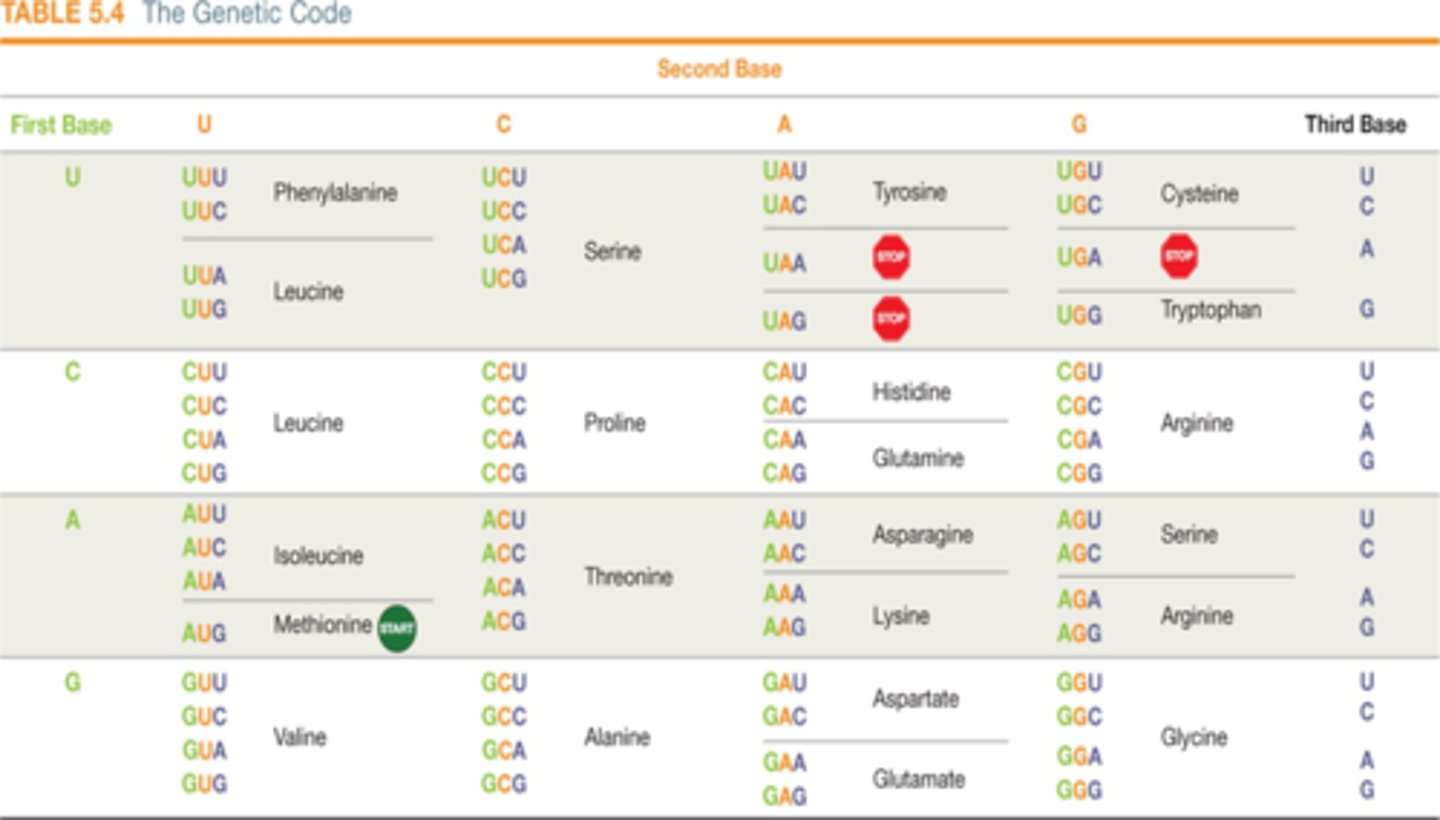
How many codon sequences code for the amino acid serine?
7
6
4
2
6
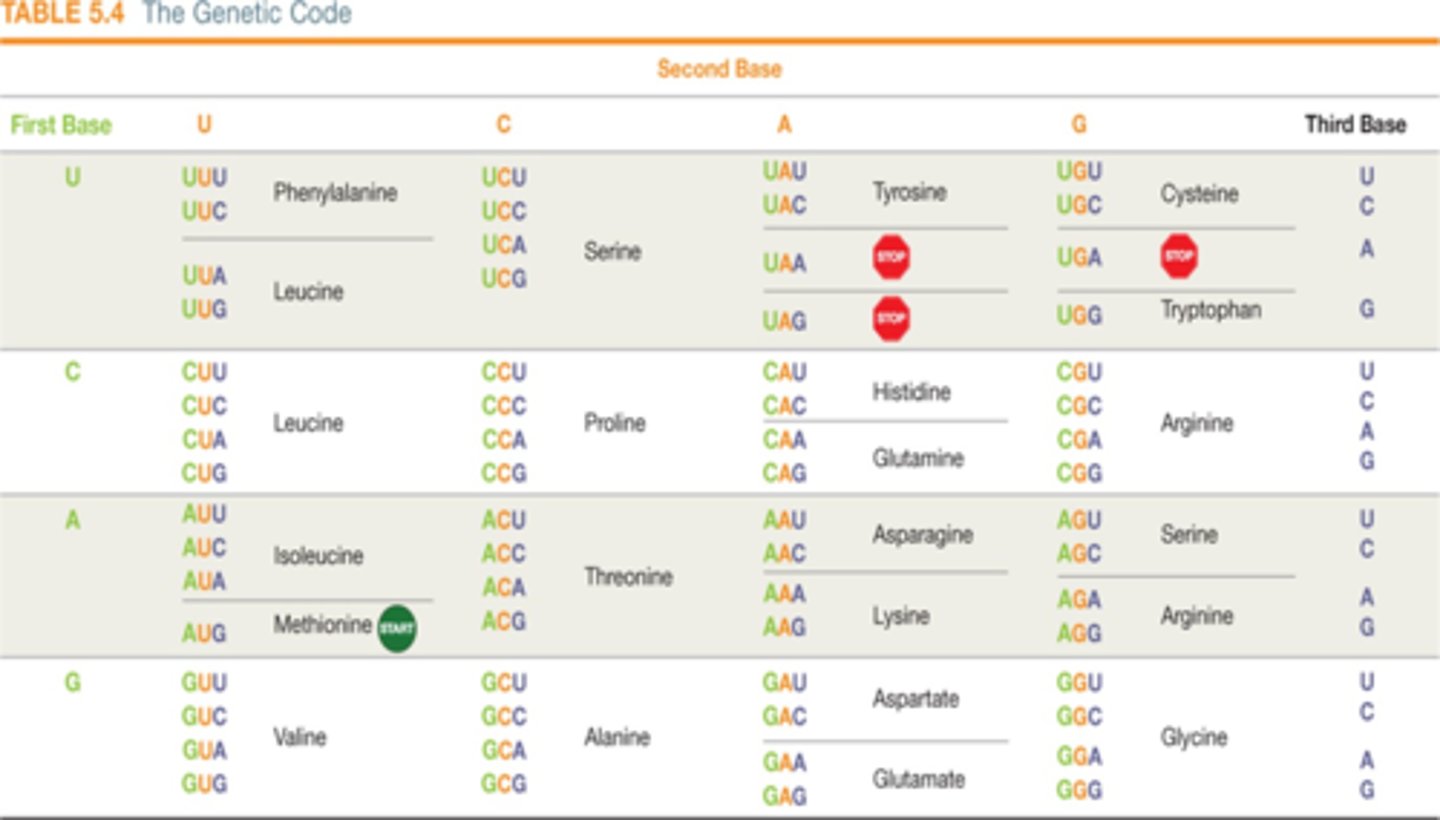
Translate the mRNA sequence ACA CAG AUG GUG CCC
threonine-glutamine-methionine-valine-proline
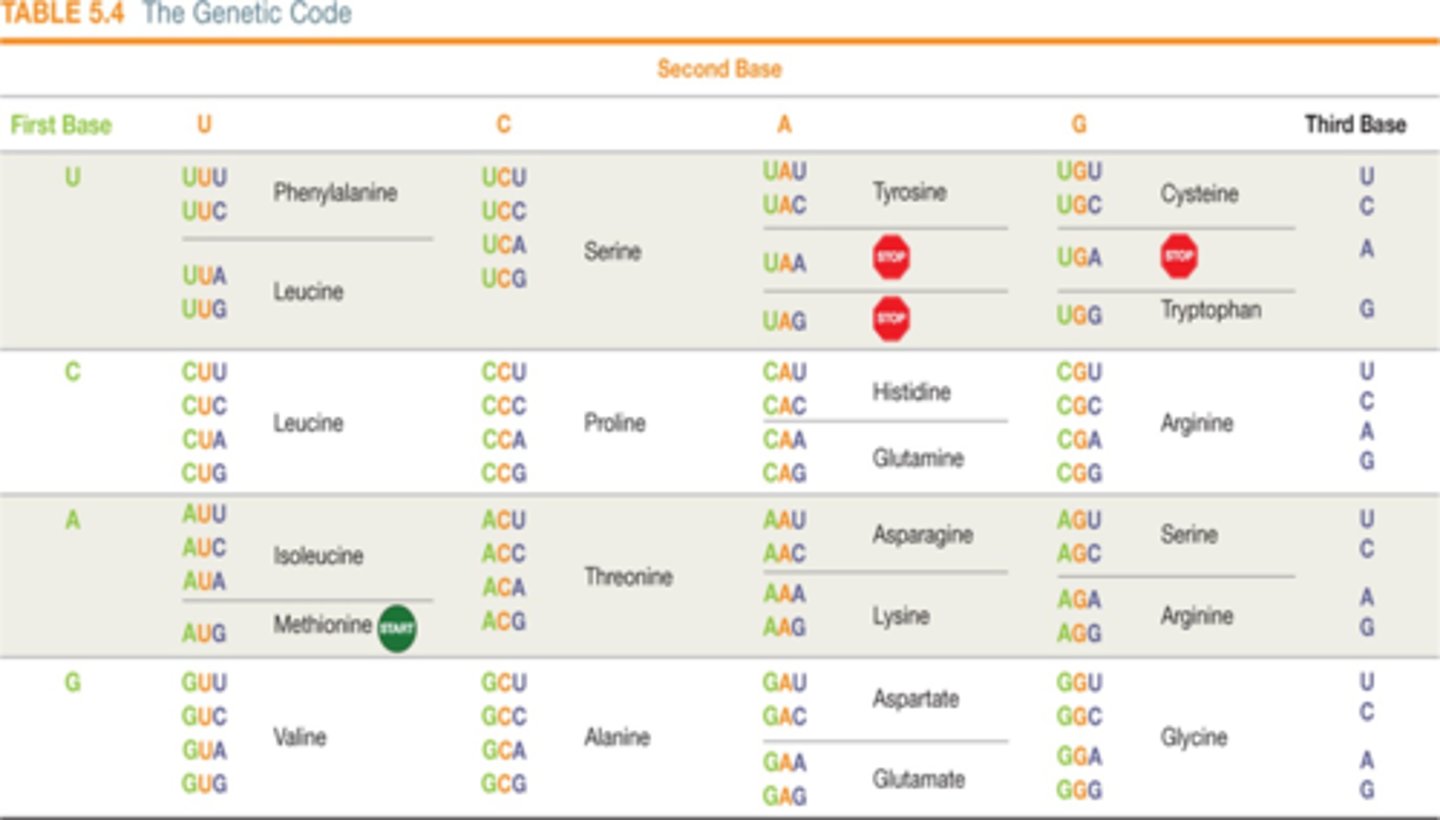
Sometimes during DNA replication a change in the DNA nucleotide sequence, which is called a mutation, can occur. There are various reasons why mutations occur. In certain instances, a chemical called _______ can increase the mutation rate.
a mutagen
There are two main types of mutations: base-substitution and frameshift mutations. Match the type of base substitution mutation located in the left-hand side column with the result of that mutation.
missense mutation
silent mutation
nonsense
missense mutation
a change in the wild type amino acid to a different amino acid
silent mutation
no change in the amino acid sequence
nonsense
premature stop codon introduced
If a nucleotide is inserted or deleted from the DNA sequence, the resulting mutation is known as a _________________ mutation.
frameshift
Thymine dimer mutations cause by ultraviolet light can be repaired using ___________.
photolyases and excision-repair enzymes
Mismatch-repair enzymes cannot repair a DNA mutation once it becomes ______________.
methylated
Which of the following characteristics doesn't describe viruses?
they don't have cells
they exhibit metabolism while outside of the host cell
they contain DNA or RNA
they are considered non-living
they exhibit metabolism while outside of the host cell
Which domain of life do viruses belong to?
viruses do not belong to any domain of life
Which of the following characteristics describe viruses?
they contain a nucleoid region
they are usually larger than bacteria
they are filterable (can pass through a filter)
they contain ribosomes
they are filterable (can pass through a filter)
Identify the icosahedral capsid. [Be prepared to to identify all labeled capsid shapes on upcoming exams]
b
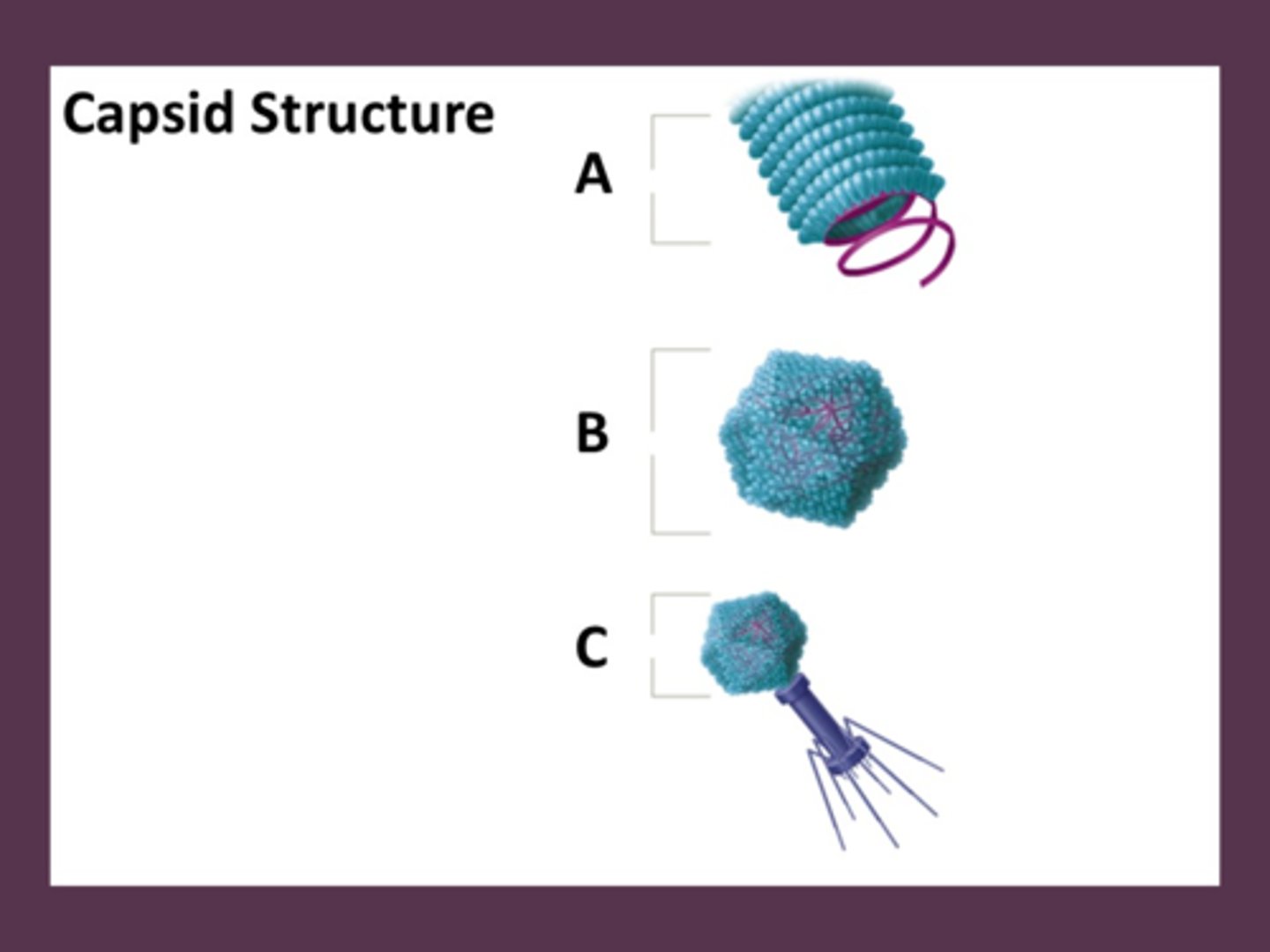
A polyhedral virus that has 20 triangular-shaped sides are called ____________ viruses.
icosahedral
"Naked" viruses lack what structural component?
envelope
Viruses are surrounded by a protein capsid composed of individual subunits called ____________.
capsomeres
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic used to classify viruses?
nucleic acid type
capsid shape
presence/absence of an envelope
cell wall composition
cell wall composition
A ________ is an infectious viral particle that has yet infected its host's cells.
virion
Why are RNA viruses that use RNA-dependent RNA polymerase for transcription more likely to have genome mutations?
the enzyme doesn't have proofreading capabilities
Antigenic _________ occurs when advantageous mutations in viral genomes result in minor changes.
drift
Antigenic _________ occurs when there is a reassortment of genetic material from coinfecting viruses that produce a new viral strain.
shift
Which of the following is not a disease caused by prions?
Lou Gehrig's disease
Prions are misfolded ___________.
proteins
Mad cow disease is transmitted to humans by _______________________.
consuming contaminated beefq
The presence of specific ___________ on viruses determine whether it can infect a particular cell or not.
receptors
The first human virus was discovered in 1901. What scientist discovered the first human virus?
walter reed
Some scientists theorize that an ancient virus infected a bacterium helping it produce the first cell ___________.
nucleus
How do prion proteins create more prion proteins?
by catalyzing a conformation change in the wild type protein by direct contact with the prion
Which of the following abbreviations represent prion proteins?
A) PrPC
B) PrPSC
C) PrPMP
D) PrPP
B
Which of the following phases of bacterial growth doesn't match its description?
lag phase- intense activity preparing for growth and moderate increase in population
What are the nutrient requirements for an organism classified as a photoautotroph?
sun and CO2
Most extremophilic organisms belong to the domain __________.
archaea
__________ are moderate temperature-loving organisms that optimally grow at 25-40oC.
mesophiles
Many food spoilage bacteria are characterized by temperature as ___________.
psychotrophs
In what type of conditions would you expect to find a halophilic acidophile?
high salt and low pH
A certain species of bacteria grows the best on 25% glucose, 5% NaCl, and 0.2% magnesium sulfate agar plates. From this description, identify this general type of growth media.
chemically defined
A certain species of bacteria grows the best on 5% peptone, 5% beef heart extract, and 8% sodium chloride. From this description, identify this general type of growth media.
complex
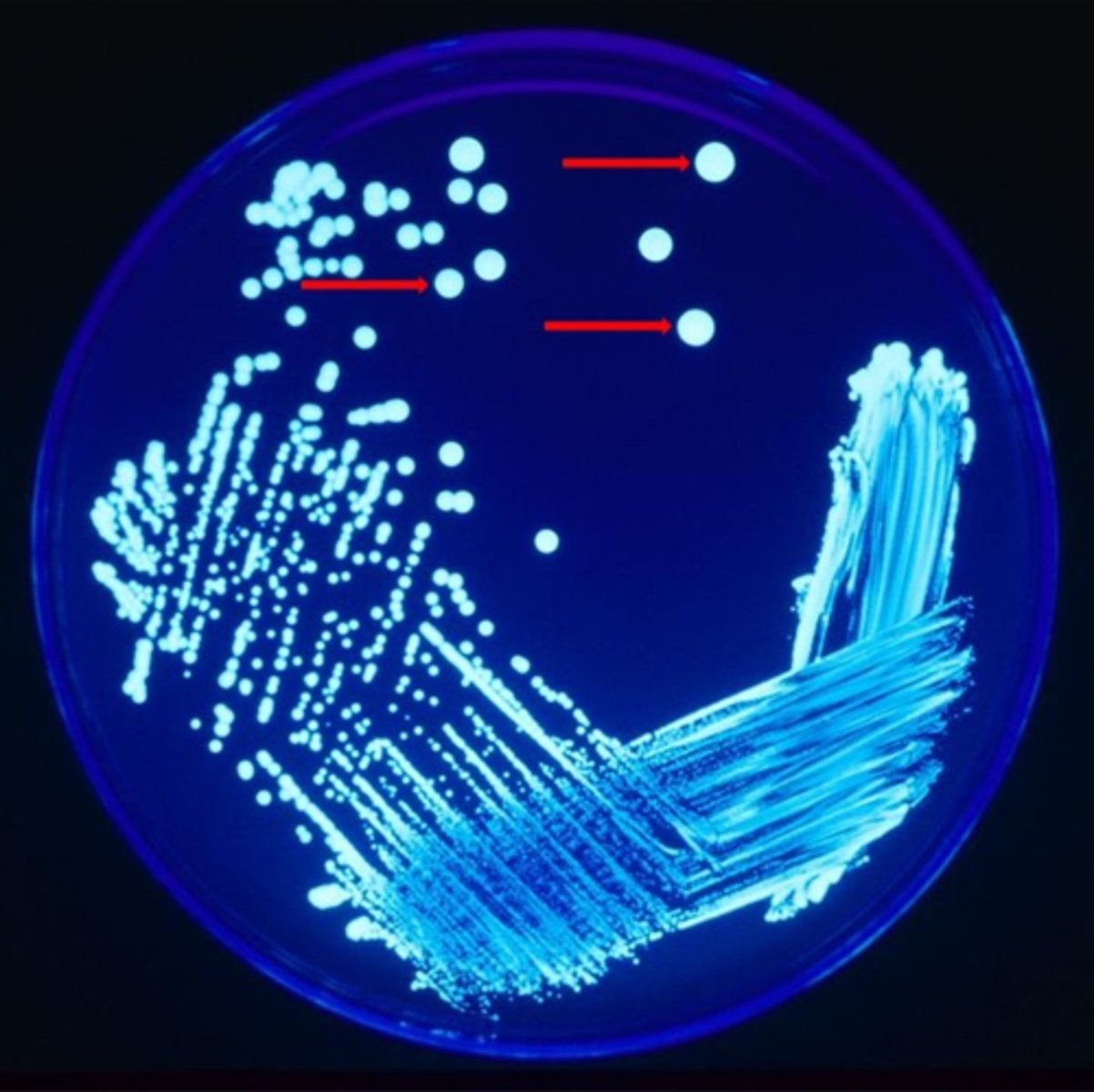
The red arrows are pointing to _________________.
a single bacterial colony
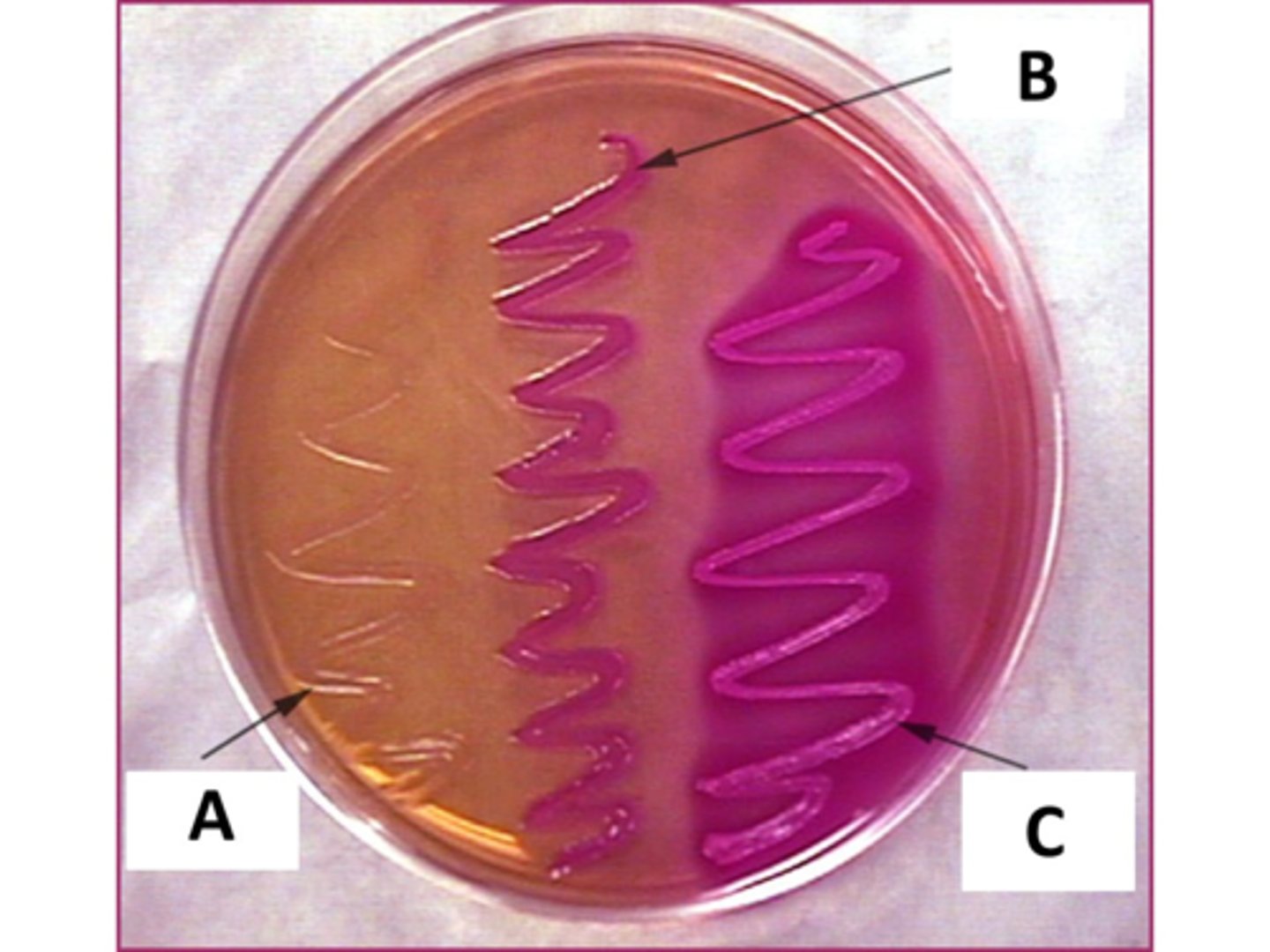
This image shows the results of three different bacterial species grown on MacConkey media. Escherichia coli is a very strong lactose fermenter. Which letter likely indicates E. coli growth?
C
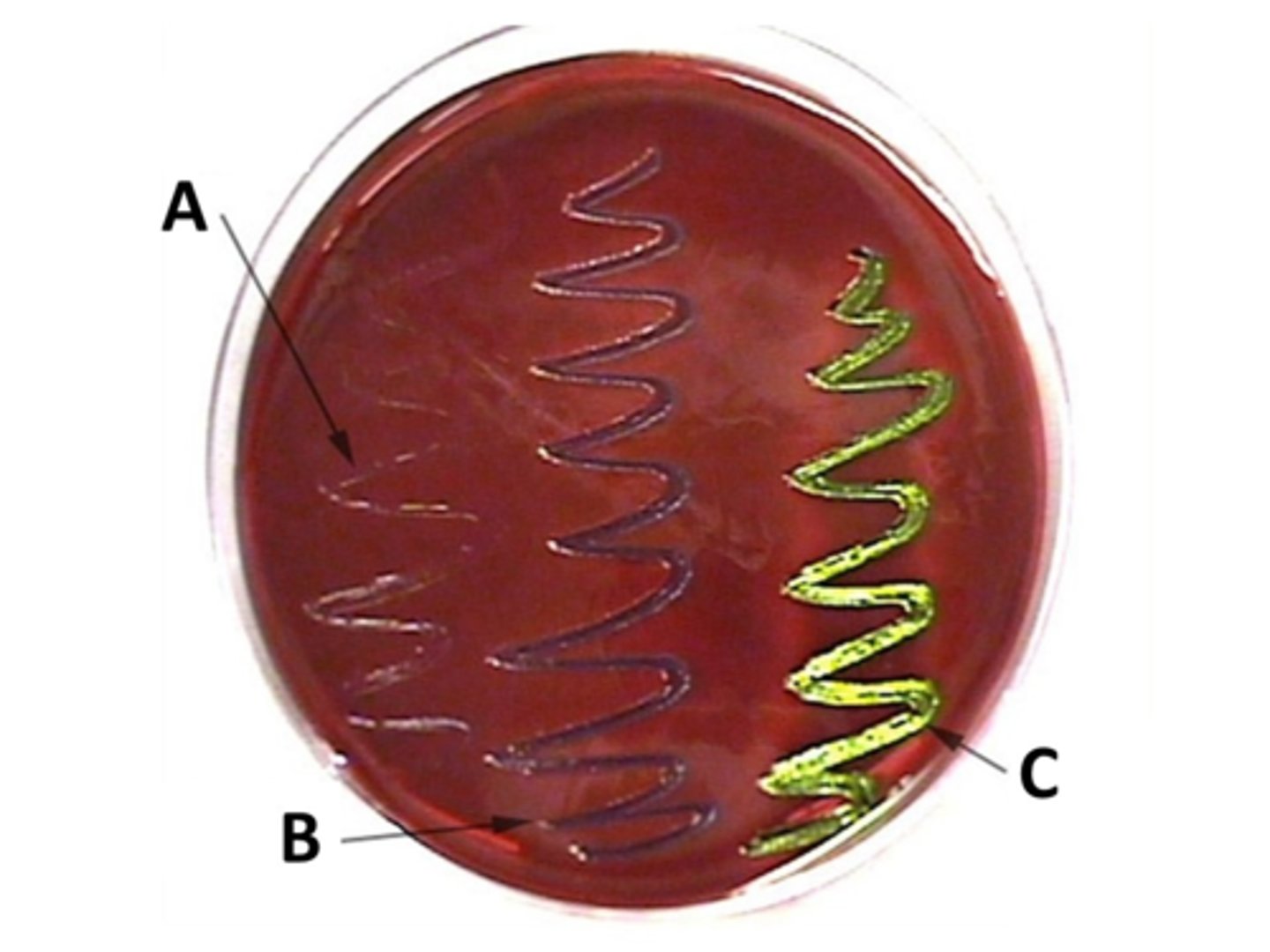
This image shows the results of three different bacterial species grown on EMB media. Escherichia coli is a very strong lactose fermenter. Which letter likely indicates E. coli growth?
C
The results in this image represent 4 different bacterial species inoculated onto an MSA plate. Which organism(s) is(are) halophilic acidophiles?
A and C
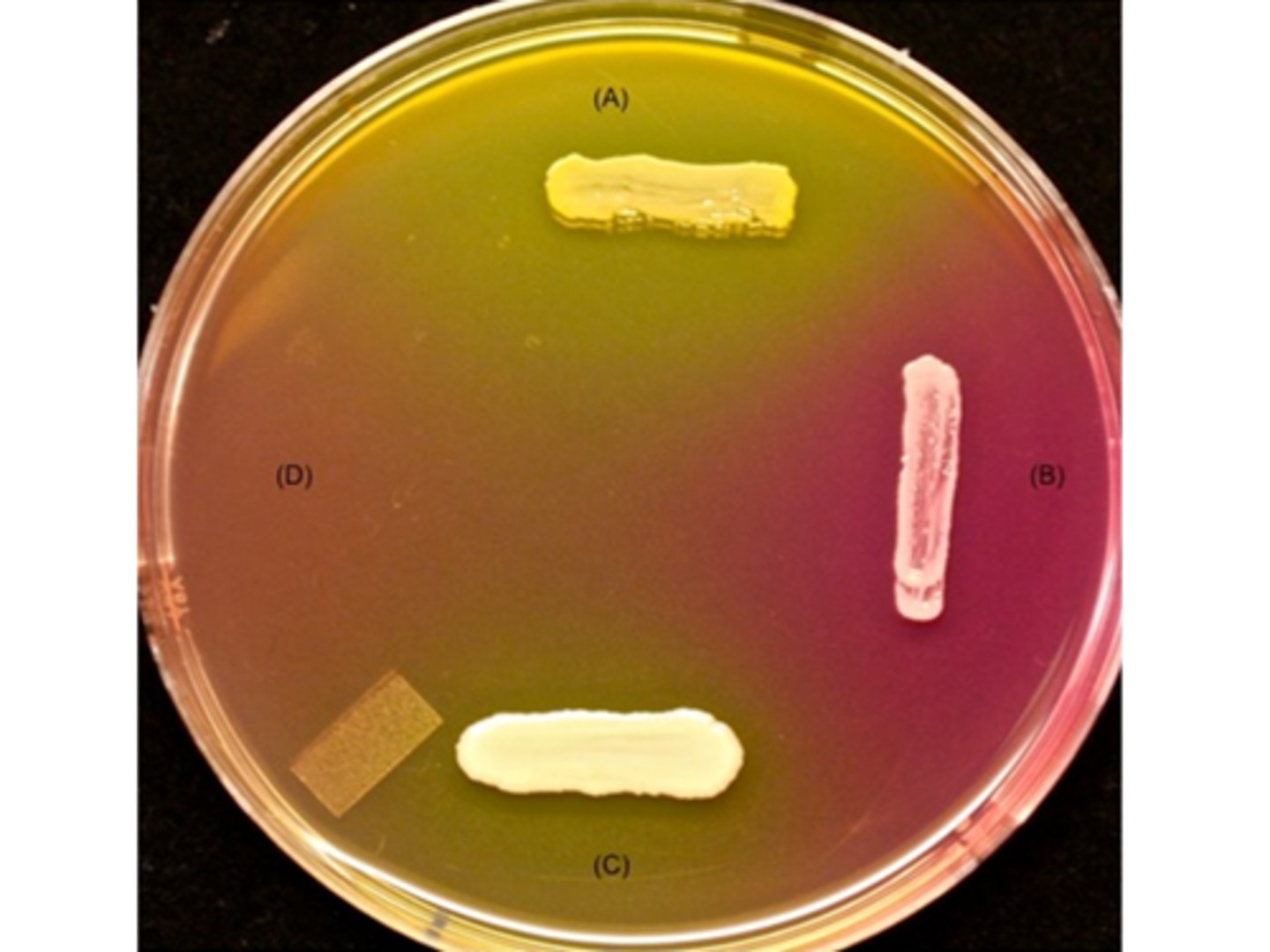
The results in this image represent 2 different bacterial species inoculated on an MSA plate. Which organism(s) ferment lactose?
there isn't enough information provided to answer the question
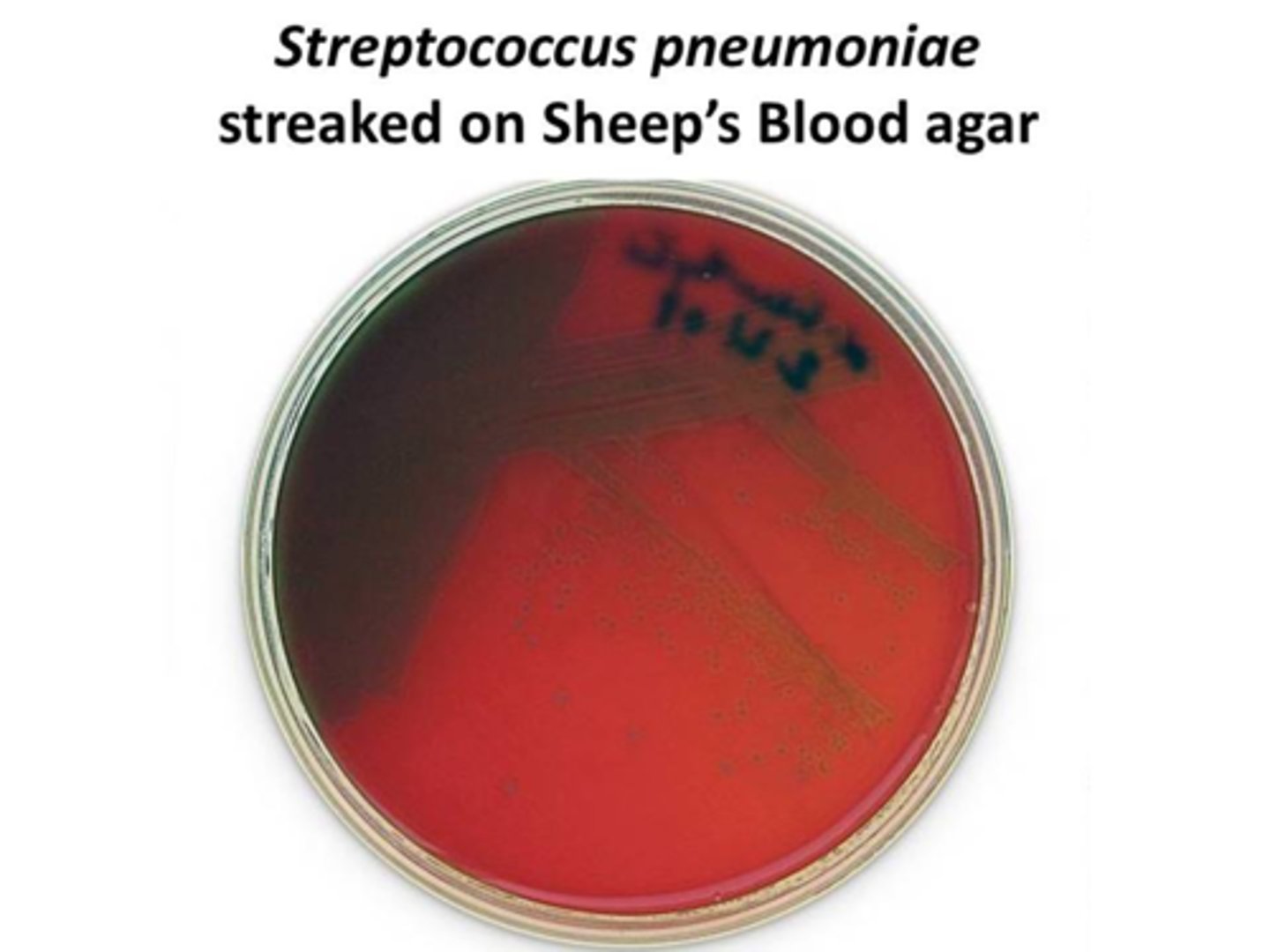
Streptococcus pneumoniae exhibits a greenish appearance when grown on sheep’s blood agar. What type of hemolytic pattern does this indicate?
alpha
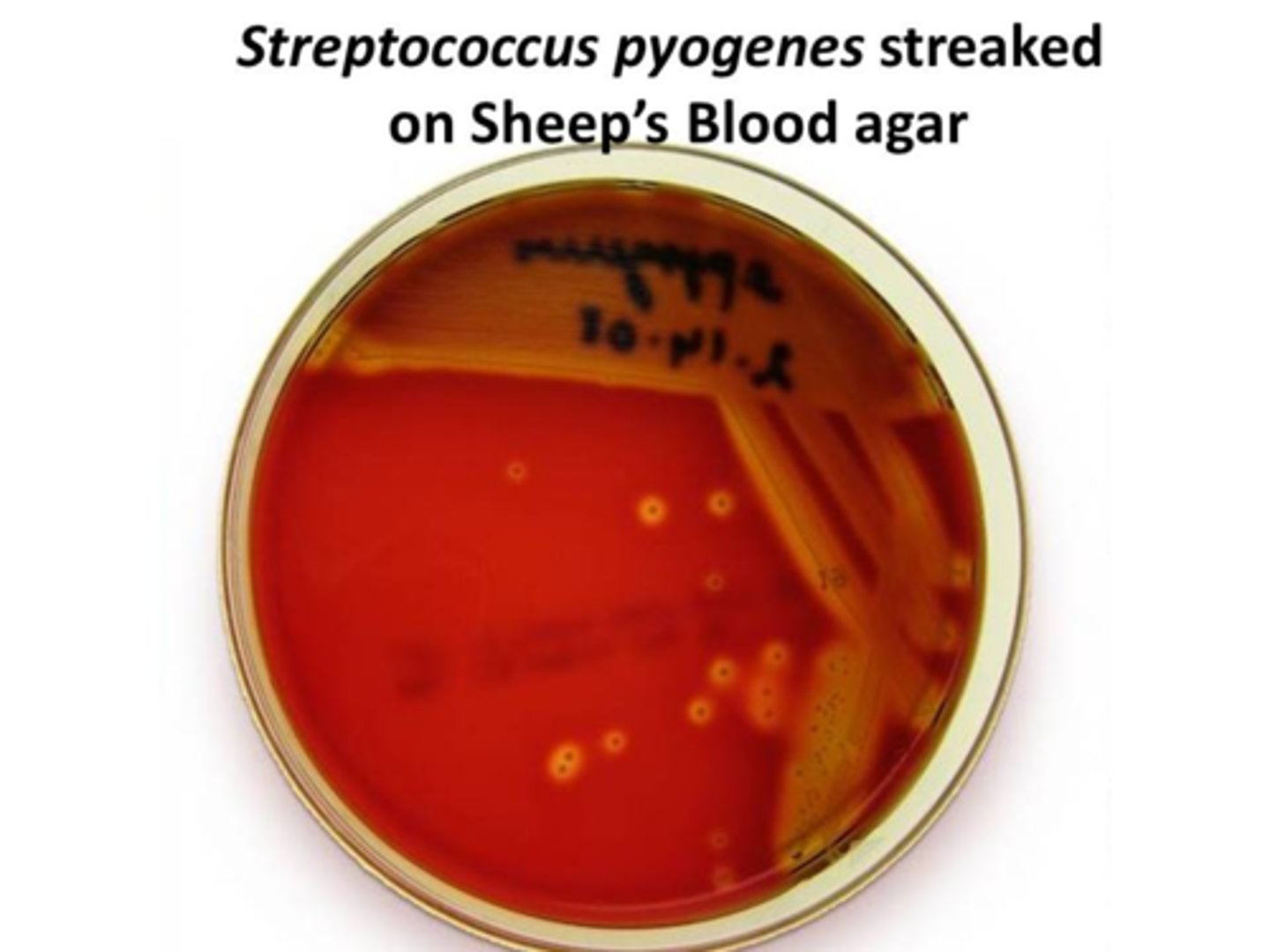
Streptococcus pyogenes, the etiological agent of strep throat, scarlet fever and rheumatic fever, exhibits complete clearing of RBCs when grown on sheep’s blood agar. What type of hemolytic pattern does this indicate?
beta
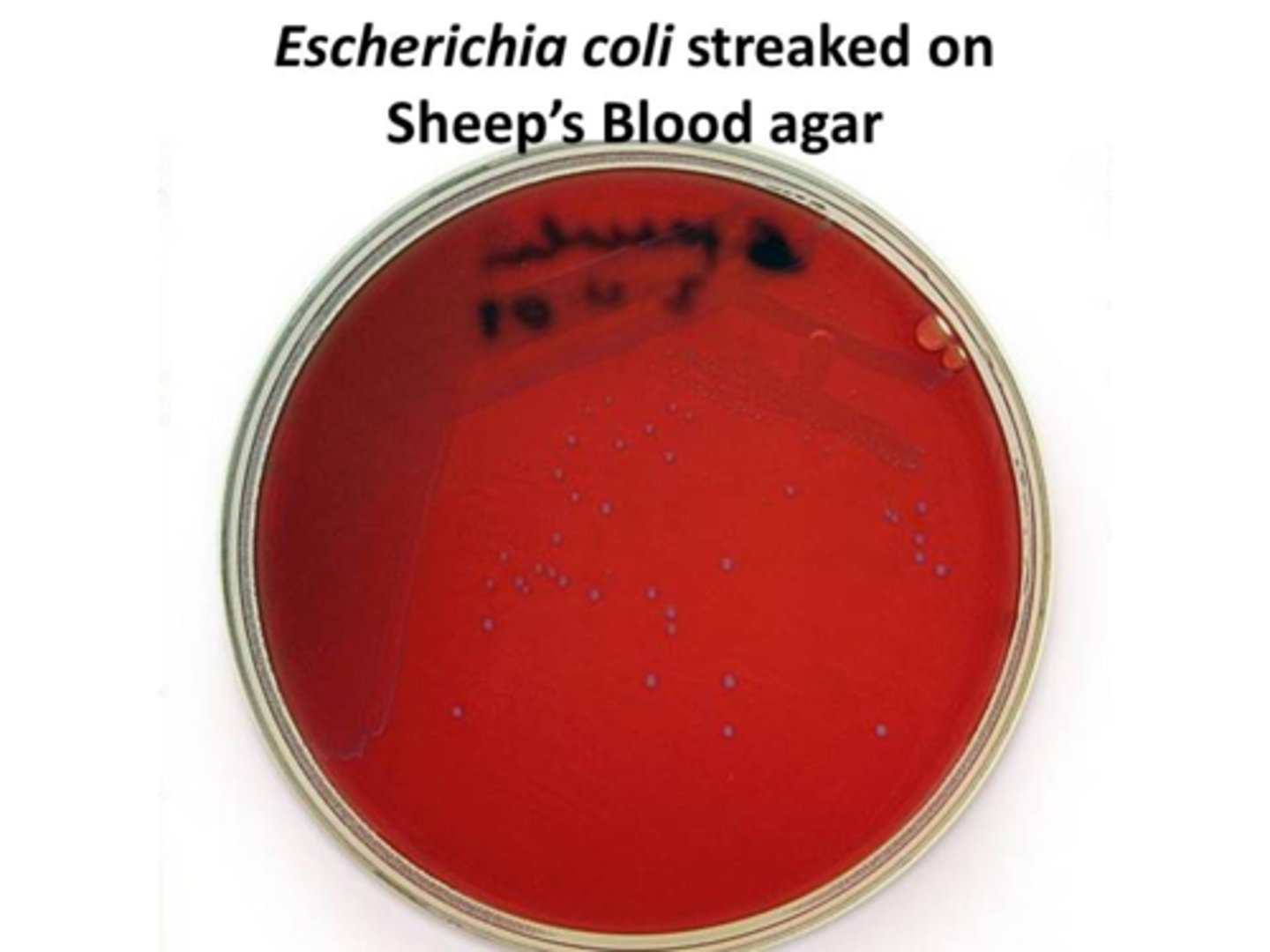
Escherichia coli yields whitish colonies when grown on sheep’s blood agar. What type of hemolytic pattern does this indicate?
gamma
What is the rational of having a high salt content in the diagnostic media, MSA?
to select for halophiles and/or facultative halophiles
The selective & differential media called MAC contains a chemical called neutral red that will detect a change in pH if the sugar in the media is metabolized by the growing organism. What is the general term for the chemical added to media that detect changes in pH?
indicator
Sheep's blood agar differentiates between bacteria that produce a toxin called __________, which is indicated by the partial or complete destruction of red blood cells contained in the media.
hemolysin
When a sheep’s blood agar plate is streaked with bacteria, such as Streptococcus pyogenes, beta hemolysis occurs. What does beta-hemolysis indicate about the pathogenicity of S. pyogenes?
it is likely to be pathogenic
What occurs when a high-energy bond in ATP is broken resulting in ADP?
energy is released that will drive chemical reactions
During a redox reaction, the molecule that loses an electron is ______________ and the molecule that gains the electron is _______________.
oxidized/reduced
NADH and FADH2 play an important role in energy production by donating electrons for redox reactions that occur in the ___________.
ETC
Which process of glucose catabolism doesn't generate ATP?
intermediate step
The majority of the high-energy coenzymes (such as NADH and FADH2) are generated during
Kreb's cycle
Where does glycolysis occur in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
cytoplasm
How many pyruvic acid molecules are produced from the glycolysis of 1 glucose molecule?
2
How many acetyl CoA molecules are produced during the intermediate step from 1 molecule of glucose?
2
What type of phosphorylation is used to produce ATP in the Krebs cycle?
substrate-level phosphorylation