Biochem 285 Week 9
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Prokaryotic transcription and lac operon: Eukaryotic transcription and mRNA splicing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
sense
coding strand
antisense
template strand
DNA and RNA are structurally similar but differ in the ___ and in the ___ used.
Ribose sugar; bases. DNA uses deoxyribose and thymine, while RNA uses ribose and uracil.
What does RNAP need to work and what helps it find it?
RNAP need to find a promoter sequence and general transcription factors (eukaryotes) or sigma factors (prokaryotes) help it find it.
RNAP + sigma factor
holoenzyme
Terminator Sequence
Part of DNA that tells RNAP when to stop transcribing.
Rho (protein) dependent termination
A method for ending transcription in prokaryotes. GC rich sequences are bound by Rho and as RNA continues to wrap around Rho, it gets closer to RNAP. Contact between Rho and RNAP is a signal for RNAP to stop transcription.
Rho independent termination
A method for ending transcription in prokaryotes. GC rich sequences form a terminator hairpin loop structure in the 3’ UTR which is followed by a string of uracils. This destabilizes the interaction between mRNA and the DNA template.
Sigma factors in prokaryotic transcription
Sigma factor and RNAP form a complex (holoenzyme), then sigma factor binds the promoter sequence (-35 and -10bp from transcription start site). Sigma factors can bind to a set of promoter sequences as there is variability in the nucleotides and this allows for differing promoter strengths that can affect gene expression. After RNAP unwinds a section of DNA it begins to add bases at the +1 site, sigma factors dissociate at this stage.
Likely to be found on prokaryotic mRNA transcript
Ribosome binding site (each gene needs its own RBS), open reading frames, stop codons, start codons
Transcriptional Regulators
DNA binding proteins that can affect gene expression by interacting with DNA through non-covalent interactions. There are often multimers as having more subunits allows them to make more connections to the DNA sequence. Most have alpha helixes for secondary structure, less have beta sheets.
Why do most DNA binding proteins bind in the major groove of a DNA molecule?
Opposed to the minor groove, the major groove exposes more nucleotides which allows proteins to bind with specificity.
Operons
A way in which bacteria organize their genes. They hold multiple related genes and have one promoter.
Activators
DNA binding proteins that activate expression of downstream genes. They stabilize RNAP interaction with promoter.
Repressors
DNA binding proteins that inhibit gene transcription. They typically bind by overlapping the promoter, blocking RNA access.
Lacl
A protein that is constitutively expressed from its promoter making it always available to the bind to the operator. This blocks RNAP from transcribing and is negative regulation of the lac operon when no lactose is present. Sometimes it falls off the operator which allows for leaky expression of the operon. When lactose is present, allolactose causes it to unbind from the operator so RNAP can work.
Positive regulation on lac operon when lactose is present
RNAP holoenzyme is not very strong on its own attached to the promoter. It gets the help of another protein bound to the CAP site which stabilizes the interaction between RNAP and the promoter. This only happens when the preferred energy source (glucose) is low.
cAMP
Only made when glucose levels are low. It binds to CAP (allosteric control) which then binds to the CAP site on DNA to turn on the lac operon.
What happens when Lacl cannot bind the operator?
Expression of the lac operon with always occur but it will enhanced in the absence of glucose.
What happens if CAP protein cannot bind to cAMP?
It will not be able to bind to DNA. RNAP won’t be stabilized and expression of lac operon will not be regulated.
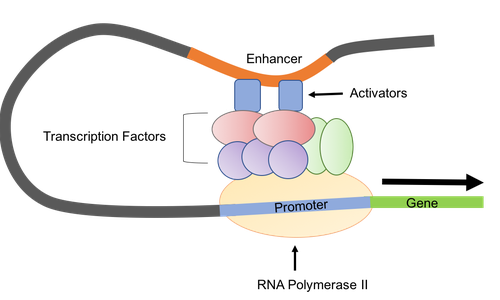
Enhancer
The binding site for the activator protein in eukaryotes. General transcription factors, mediators, and RNAP bind on the other side which creates a loop structure to initiate transcription.
mRNA processing
A process which matures the mRNA transcript to be ready for exportation out of the nucleus (then to be translated). Enzymes will first add a 50 methyl-guanosine to make a cap, then they will splice the pre-mRNA, and lastly add a poly-A tail to the 3’ end.
What is the importance of the 5’ cap in mRNA processing?
Splicing, nuclear export, stability, and translation
What is the importance of the 3’ poly-A tail?
Eukaryotic transcription termination, nuclear export, stability, translation
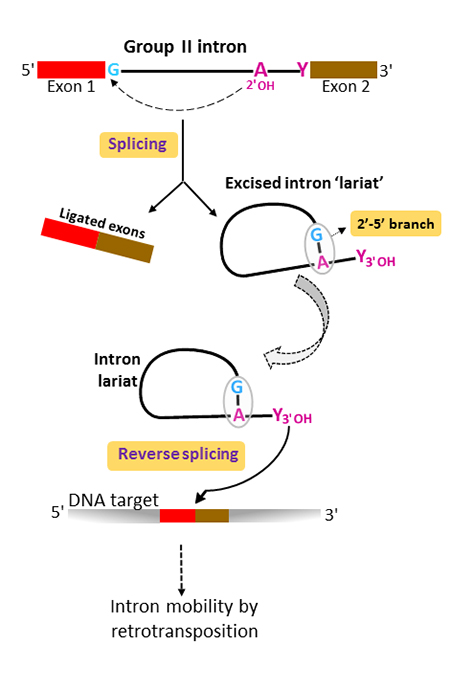
mRNA splicing
removal of introns; the spliceosome recognizes and processes specific sequences at exon/intron interfaces; snRNAs, U1, and U2 base-pair with the pre-mRNA at specific sequences and guide the formation of a lariat structure (loop) which is then removed as two exons are joined
Isoforms
different versions of the same protein arising from the same gene but with distinct amino acid sequences and biological roles due to alternative splicing; different enzymatic properties
Alternative Splicing
different patterns of exons are removed or kept to produce isoforms from the same mRNA transcript; enhancers or silencers can dictate splicing patterns; SR proteins regulate by influencing the selection of certain splice sites through binding to exonic or intronic splicing enhancers; hnRNPs can also regulate by binding to the intronic and exonic splicing silencers which interfere with the spliceosome assembly