genomics - functional assays I technology
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
why not just measure naturally occurring molecular species?
many important natural genetic variants are rare - it may be hard to find individuals w them. 60% of variants are unique among 1 million people
making perturbations is a powerful way to test hypotheses
depp learning: we often need bigger, more informative training sets to model cellular systems
how do we leverage the power of cheap sequencing/synthesis to perform functional assays at scale?
synthesize a library of variants/cCREs, gRNAs
turn your measurement of function into a sequencing assay
barcoding system
cis regulatory element (cre) or whats being tested for functionality
minimal promoter
reporter gene
unique dna barcode
sort-seq
reporter gene = gfp
flow cytometry - sort into bins of fluorescence level, sequence barcodes to ID calls in each bin
landing pads
single copy genome integrated construct for recombination-mediated integration of dna libraries
has recombinase sites so it can be integrated into a defined locus w crispr
requires prior cell line engineering
library recombination efficiency into landing pad can be low
one library member per cell at a defined location
can be used to test same cre in diff chromosomal locations
plamids
easy to clone libraries
requires transfectable cell type
multiple library members per cell
lentivirus/adeno-assoicated virus
genome integrated
genomic positioin can affect expression of construct
about one library member per cell when applied at low multiplicity of infection (moi)
construct size may be limited by what can be packaged in virus
key tricks for functional assays
you need an assay to directly test the function of non-coding sequences & variants at scale:
turn your functional assay into a sequencing assay
leverage cheap dna synthesis to build libraries of designed sequences
use sequence barcodes to id library elements in readout
massively parallel reporter assay (mpra)
pooled library of lots of distinct barcoded reporter genes
libraries can be made by custom array oligo synthesis
can be used to test cres, enhancers, splicing, utrs, etc
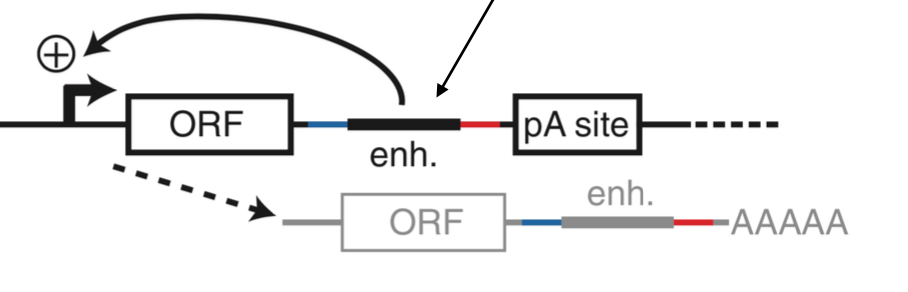
self-transcribing active regulatory region sequencing (starr-seq)
sheared genomic dna creates genomic fragments that can be cloned downstream of reporter gene, it itself acts as an enhancer & barcode
mpra limitations
lack of native genomic context
multiple dna copy number
mainly done in transfectable cell lines which may not recapitulate enhancer biology
potential assay toxicity: plasmids, high reporter gene levels
compatibility w reporter/minimal promoter: minimal promoter used may lead to false positives or negatives
VUS
variants of unknown significance
solving their effects very impactful for cancer research
deep mutational scans
create a library of all possible protein aa variants
pick an assayable function
pick a cell type
integrate one variant per cell
read out assay by sequencing dna of variants
variant abundance by massively parallel sequencing (vamp-seq)
create variants by site-saturation mutagenesis
variants fused to gfp, sequence barcodes cloned in
integrate library at single locus in cells
sort seq
what you need for pooled crispr screen
a library of designed guide rnas
a common readout of function (maybe reporter)
method to get cas9 and 1 grna per cell
a way to link grna identity w phenotypic readout of the cell
perturb-seq
combine pooled crispr library w single cell rna-seq